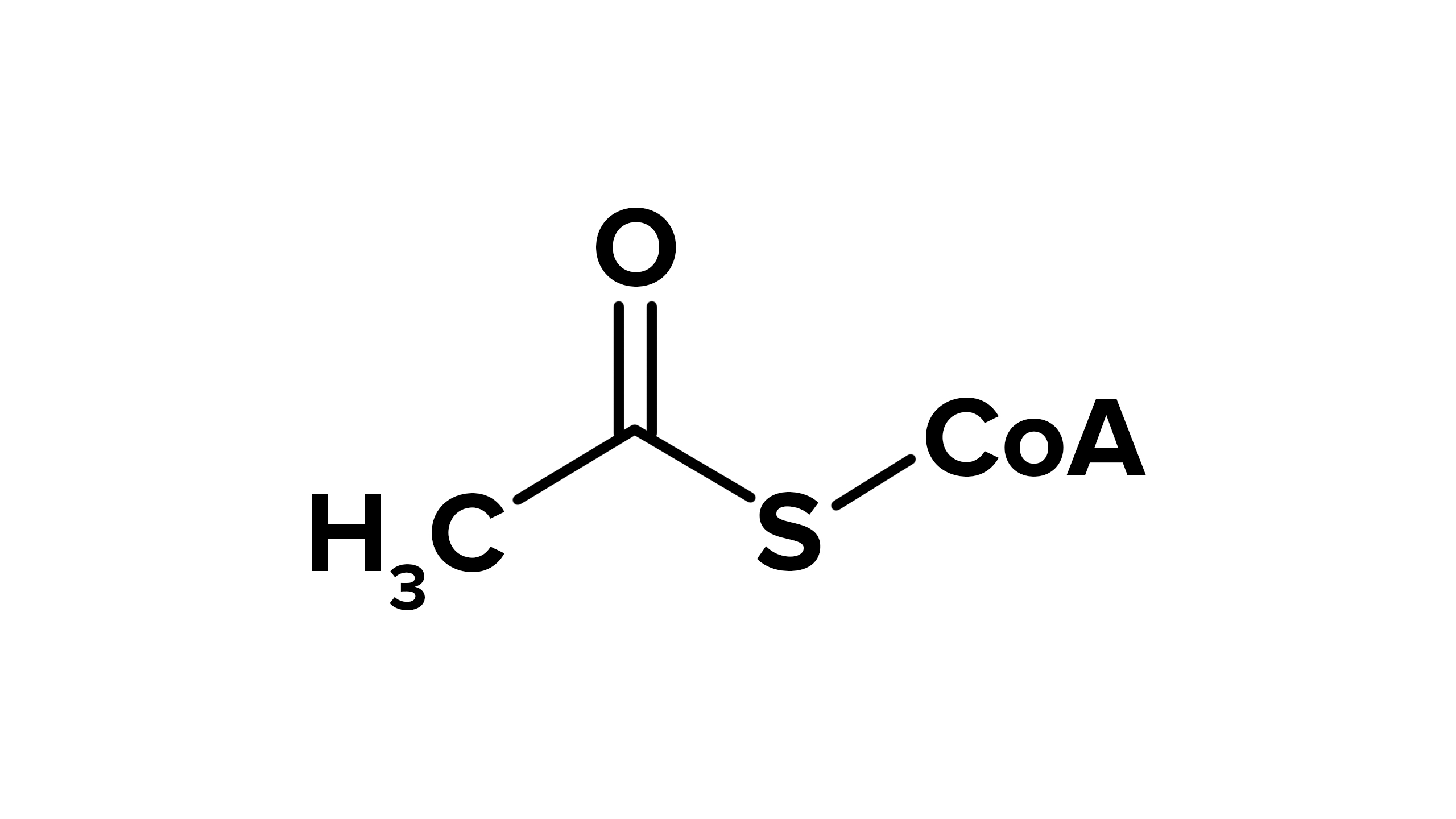
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Complex
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Pyruvate
synthesized via glycolysis and transported to mitochondrial matrix by the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC)
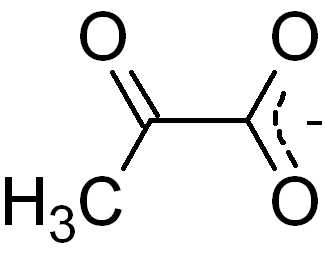
Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA
in the mitochondrial matrix, pyruvate is decarboxylated by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to form acetyl coA
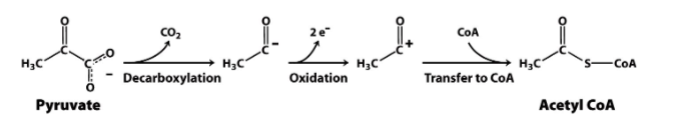
Components of PDH
E1: Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
E2: Dihydrolipoyl Transacetylase
E3: Dihydrolipoyl Dehydrogenase
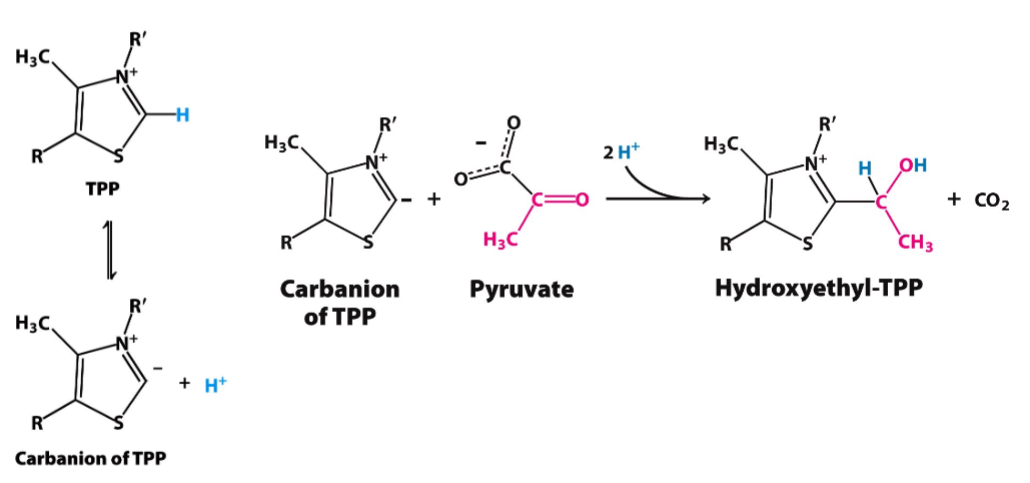
Decarboxylation Mechanism
goal: converts pyruvate to hydroxyethyl-TPP (loss of CO2)
enzyme: pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1)
prosthetic: thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
Oxidation Mechanism
goal: converts hydroxyethyl-TPP to acetyllipoamide
enzyme: pyruvate dehydrogenase (E1)
prosthetic group: Lipoamide (a component of E2)
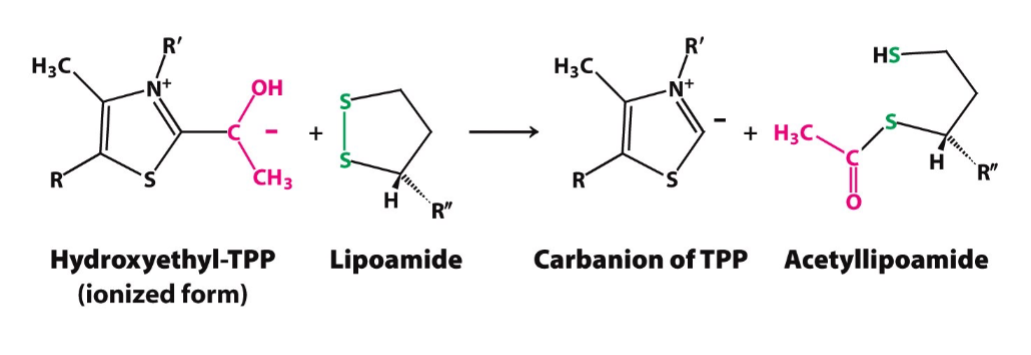
Transfer Mechanism
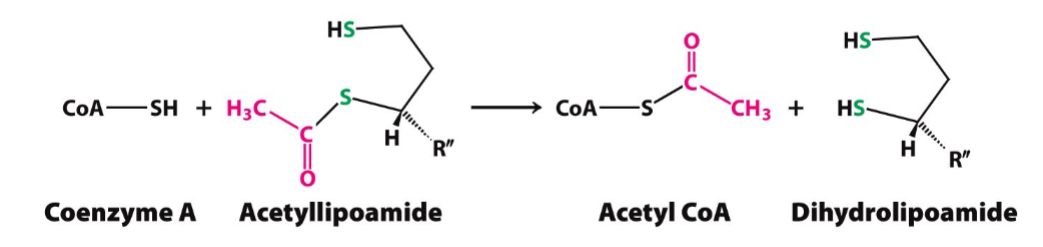
goal: transfers acetyl group from acetyl lipoamide to coenzyme A (CoA)
enzyme: dihydrolipoyl transacetylase (E2)
prosthetic group: coenzyme A
“Reset” Mechanism
goal: oxidation of dihydrolipoamide to lipoamide
enzyme: dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (E3)
prosthetic group: FAD/NAD+
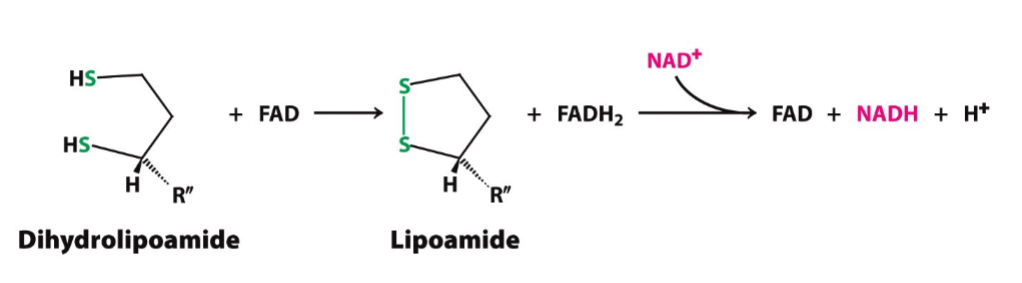
NAD+
can get reduced to NADH
oxidizing agent
FAD
can get reduced to FADH2
oxidizing agent
Structure of PDH (144 subunits)
eight E2 trimers (three subunits each → 24 subunits total)
each E2 trimer is surrounded by an E1 trimer (12×8 = 96 subunits total)
core of eight E2 trimers are surrounded by 12 E3 (aB → 24 subunits)
Functional Domains of E2 Trimer
lipoamide binding domain
E3 interaction domain
transacetylase domain
Beriberi
neurological condition that results from a deficiency in thiamine (vitamin B1), a precursor of TPP
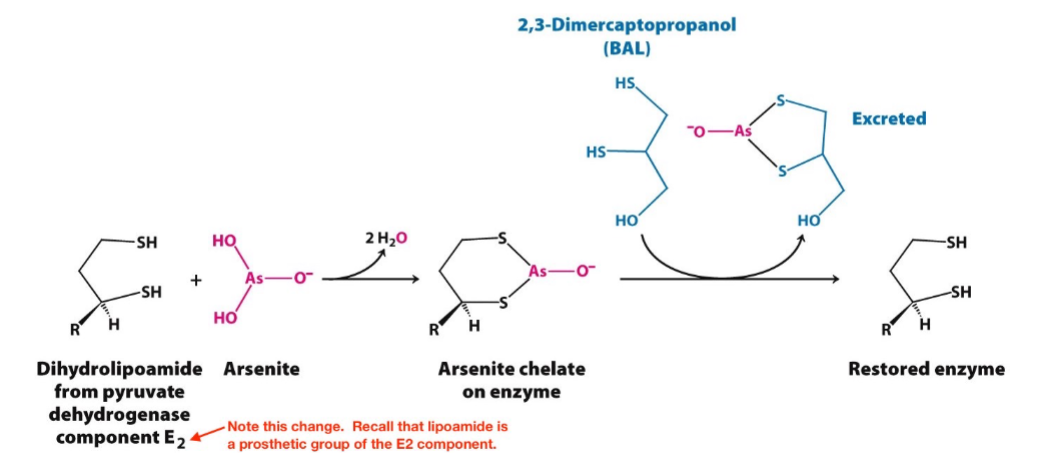
Arsenite Poisoning
inhibits the PDH complex by (reversibly) inactivating the dihydrolipoamide component of E2
Acetyl CoA
main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production