Microbio lec10 Virology Wrap-Up and Introduction to Parasites
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is a characteristic of acute viral infections?
A) Virus remains dormant in host cells.
B) progeny are produced and released rapidly.
C) Infection clears slowly.
D) Virus transforms host cells into cancer cells.
B
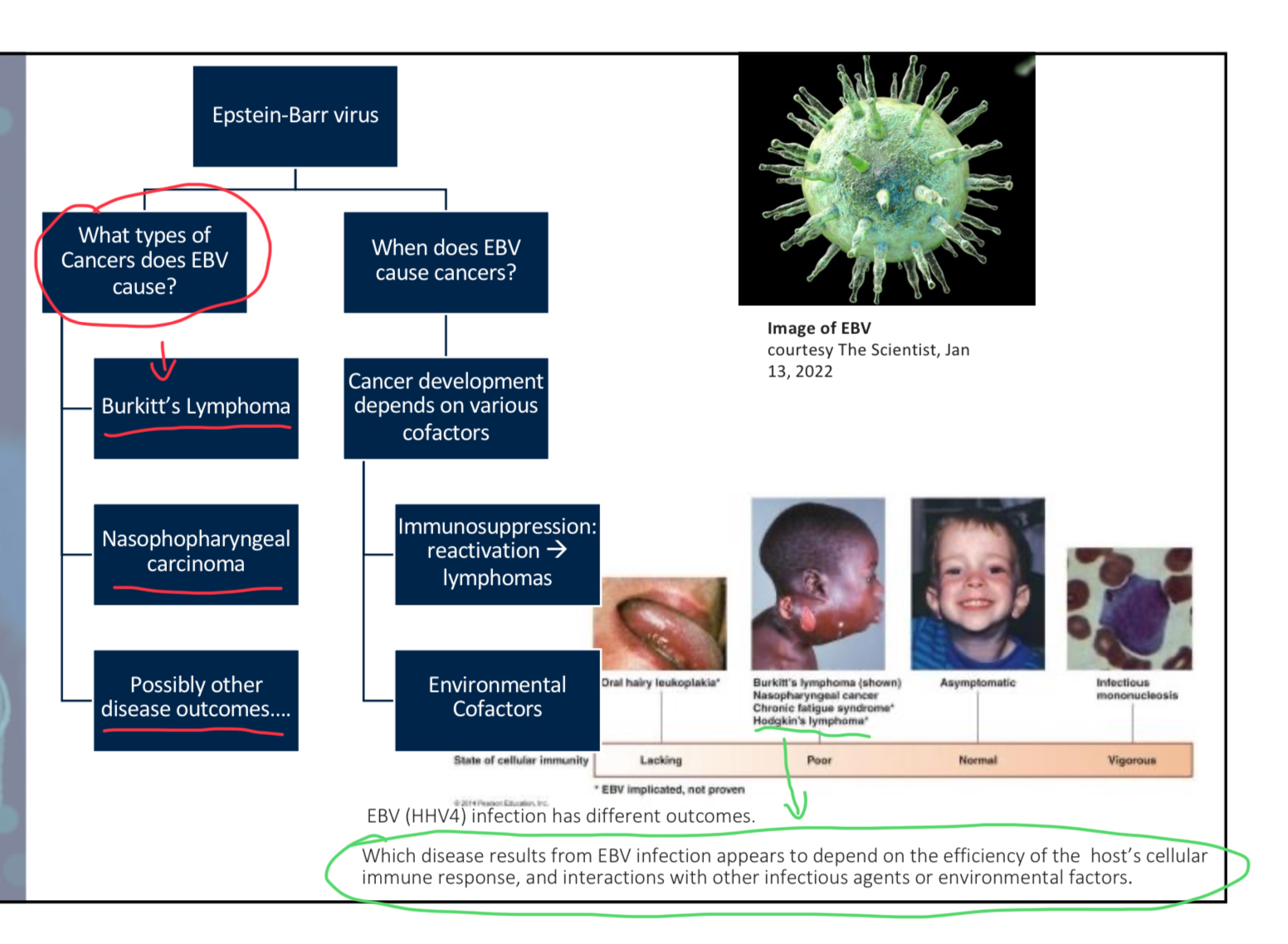
What disease is linked to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection and characterized by poor cellular immunity?
A. Oral hairy leukoplakia
B. Infectious mononucleosis
C. Asymptomatic condition
D. Burkitt's lymphoma
D
p1slide14
Name the 5 types of hepatitis infections and how they’re classified
There’s 5 hepatitis infections A, B, C, D and E
A, C, D, and E are RNA viruses
B is a DNA virus
Co-infection with B and D lead to complete liver damage
What are the structural features of the Hepatitis B
Dane particle: Complete, infectious virion.
Spherical particle: Viral surface antigens only.
Filamentous particle: Angled section.
The spherical and filamentous particle are incomplete viral particles and act as decoy to decrease immune system efficiency
True or False: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes chronic infections that clear slowly.
True (released by exocytosis)
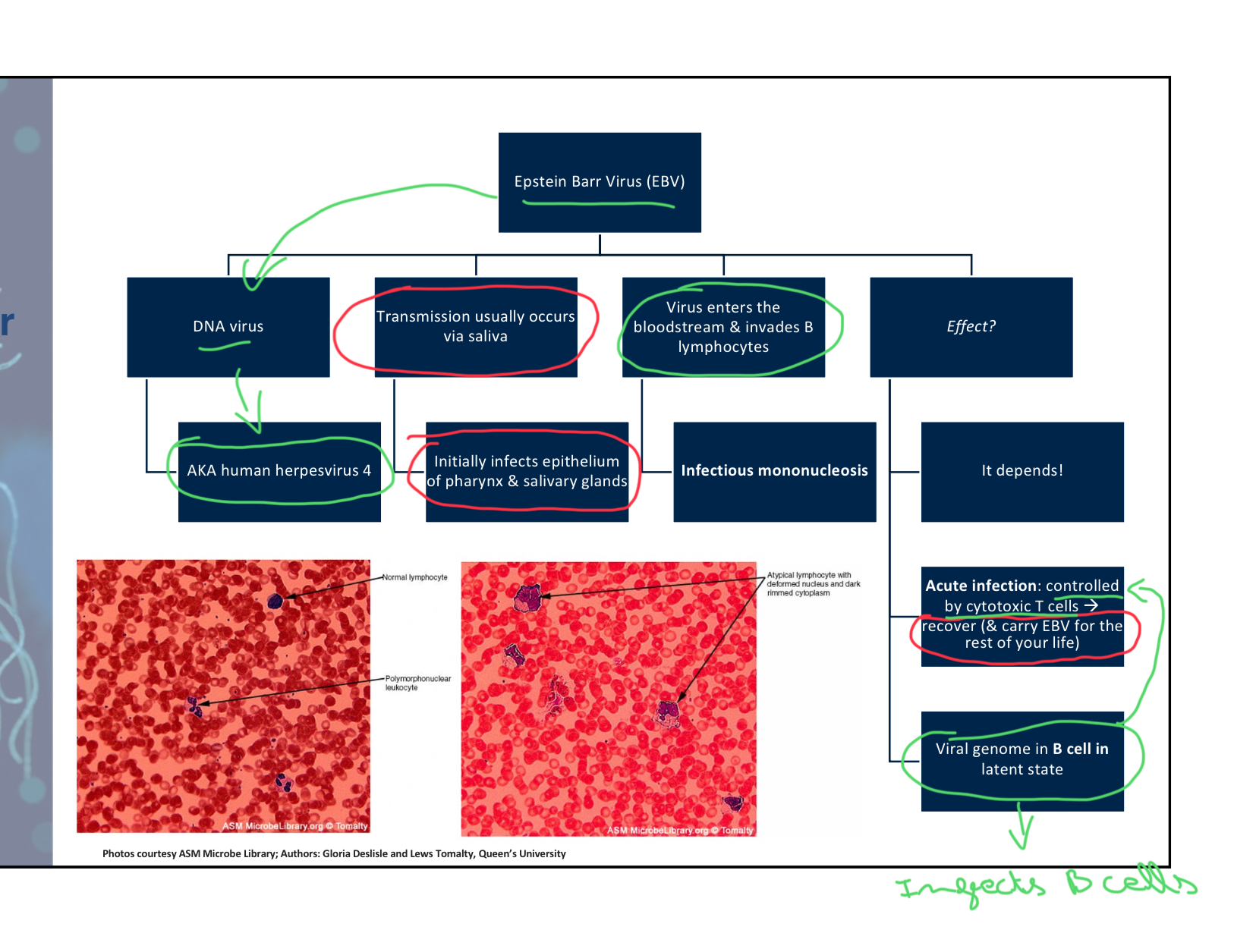
Which virus is known for causing latent infections and can lead to shingles?
A) HSV1
B) HSV2
C) VZV
D) EBV
C (Shingles lesions result from previously acquired VZV infections. Vesicles often form in a “belt” around chest or hips, following a nerve pathway. The vesicles dry and heal but can be very painful and itchy)
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) is also known as _______________________.
Human Herpesvirus 4 (its a DNA virus often transmitted via saliva. It infects epithelium of pharyngeal and salivary glands. It can enter bloodstream infect B cells as well.)
True or False: All strains of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) are oncogenic
False (only certain strains cause cancer ex; HPV16, HPV18 and 31)
Note; HPV is a DNA virus, it infects epithelial cells causing benign warts
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) proteins E6 and E7 target the host cell proteins _______ and _______.
p53 and Rb (these 2 are host cell proteins that regulates cell cycle and cell proliferation)
explain the relationship btw Human T cell leukemia (HTLV) virus and HIV
It’s a relative of HIV which makes it a retrovirus that integrates T cell genome
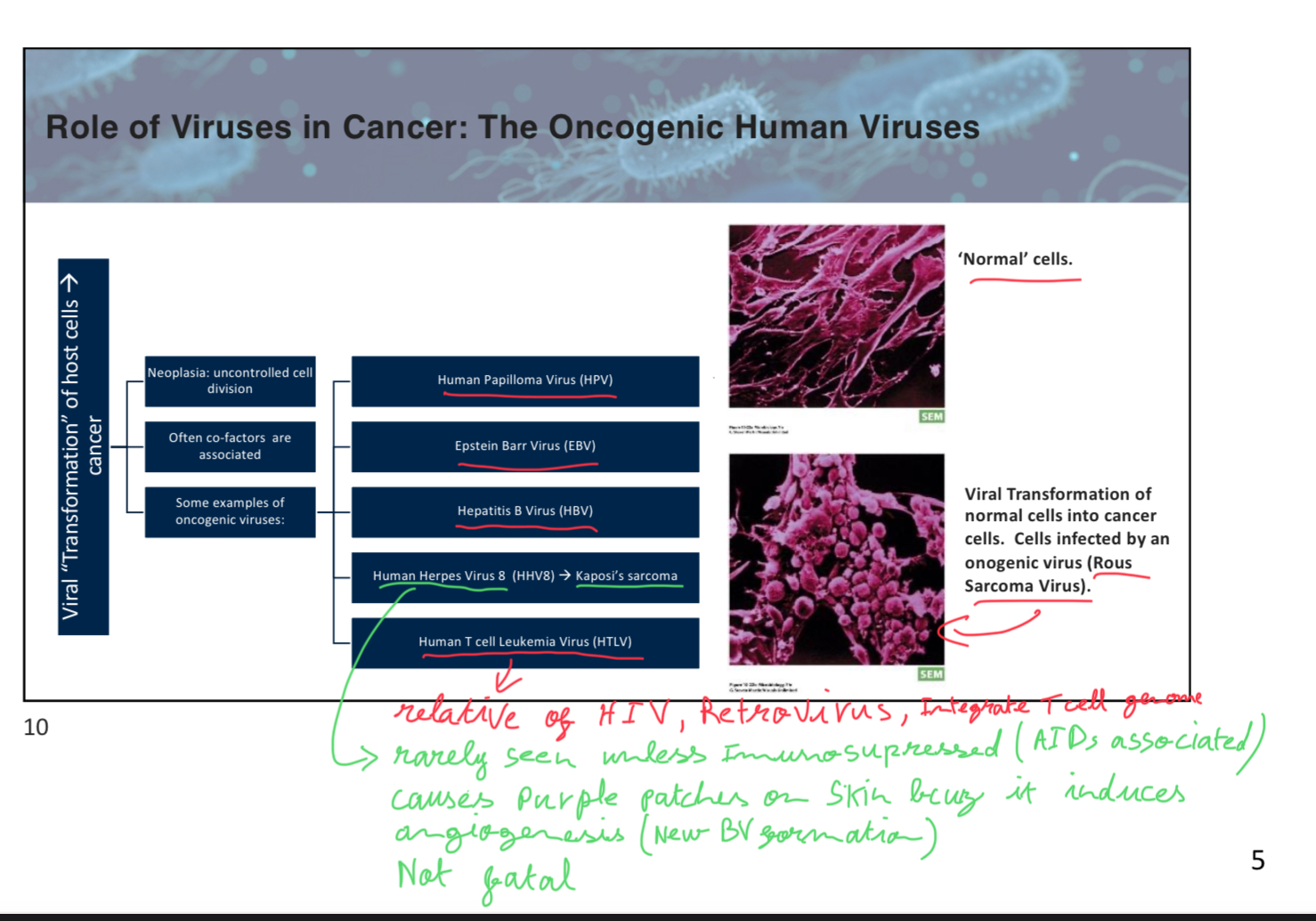
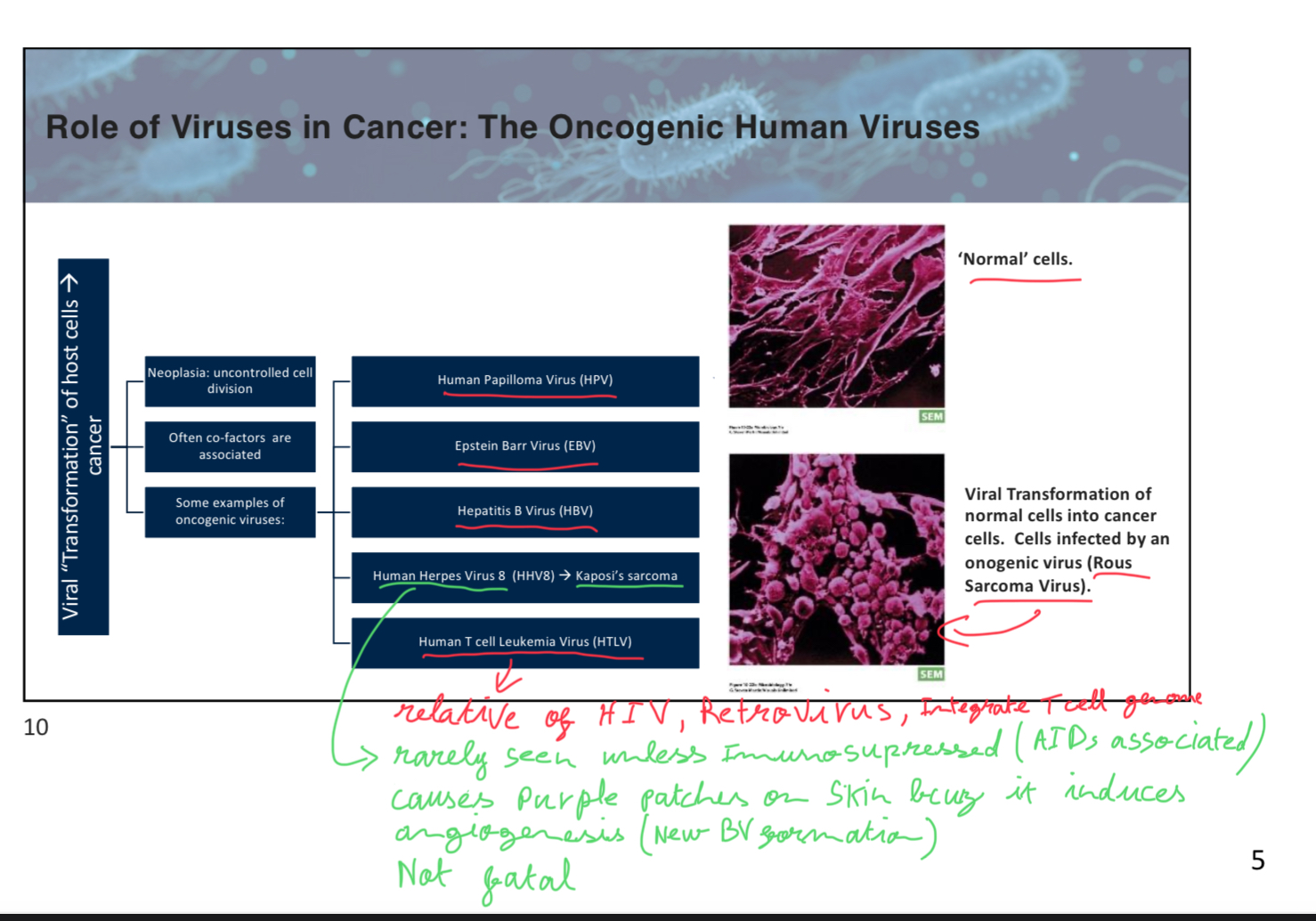
What does Human Herpes virus 8 causes
causes purple patches on skin bcuz it induces angiogenesis (new BV formation). Associated with Kaposi’s sarcoma.
It’s rarely seen unless immunosuppressed (AIDs associated)
Which of the following viruses can transform cells into cancer cells?
A) Leukemia
B) Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
C) EBV
D) All of the above
D
p1slide10
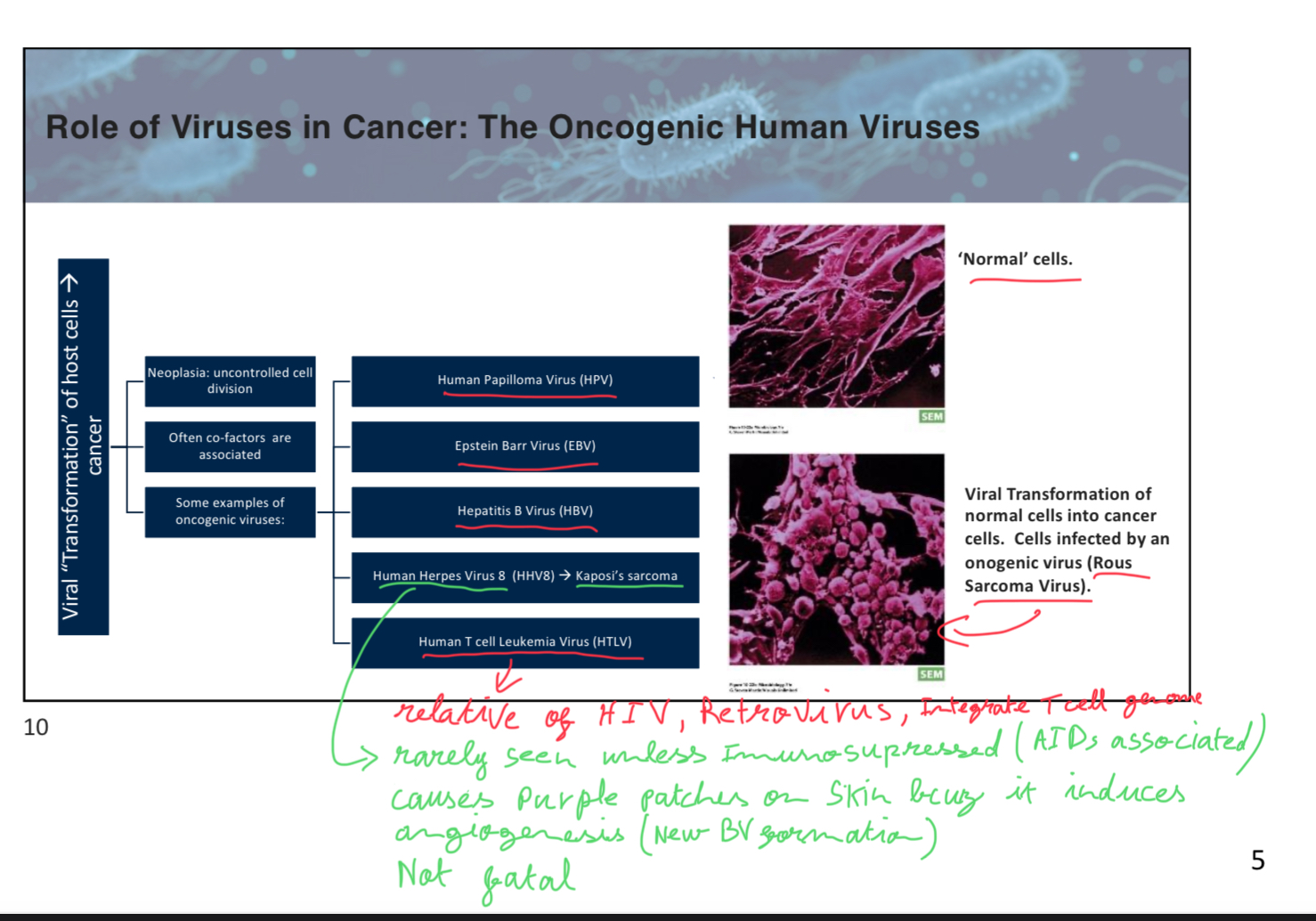
What is the hallmark of the herpesvirus family?
A) Latency
B) Chronic infection
C) Oncogenic transformation
D) Acute infection
A (HSV travels via sensory neurons to ganglia → latent (or replicate slowly) → reactivation (various inducers) → replicates in epithelial cells at original location)
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV1) causes _______________________
Fever blisters aka cold sores
HSV2 causes genital herpes
What is the primary challenge in developing antiviral drugs?
A) Targeting the virus without damaging host cells
B) Ensuring the virus mutates quickly
C) Making the drugs affordable
D) Ensuring the drugs are always effective
A
Which of the following is NOT a stage in the viral replication cycle?
A) Attachment
B) Entry
C) Synthesis
D) Retrosynthesis
D
Amantadine is used to prevent the _________ step of the entry stage in influenza infections.
Uncoating (binds viral protein to prevent it)
Which drug is used to inhibit the release of influenza virus particles from host cells?
A) Oseltamivir
B) Acyclovir
C) AZT
D) Amantadine
A
Acyclovir — blocks synthesis of DNA
AZT — blocks synthesis, RT of HIV
Amantadine — blocks uncoating
Protease inhibitors are used to block viral _______________________ in HIV infections.
Protein assembly
The drug _______________________ acts by binding to CCR5 to prevent HIV entry.
Maraviroc
The combination of __________ and _________ can reduce HIV lvls and slow AIDS progression
Reverse transcriptase and Protease inhibitors
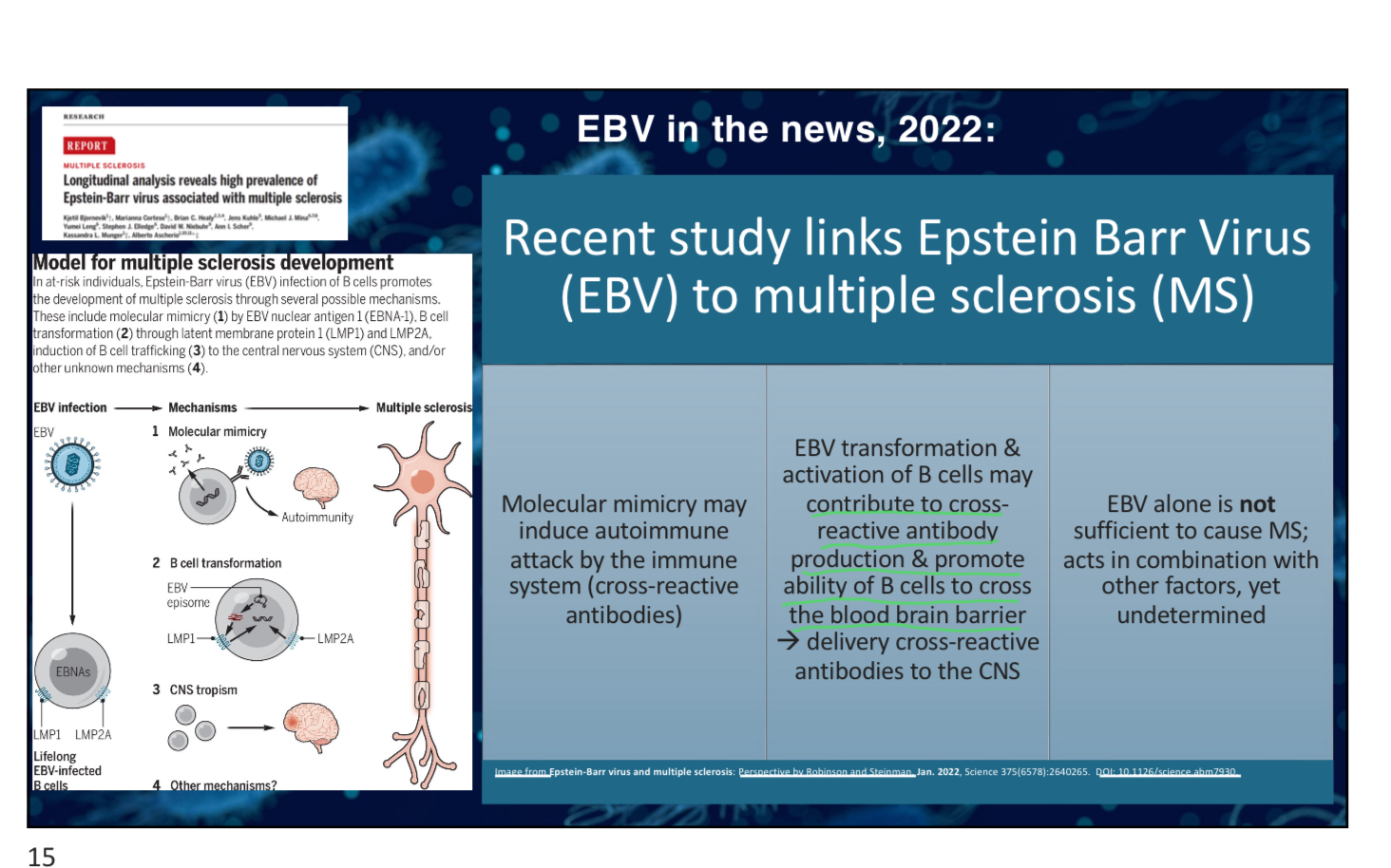
What is the role of ritonavir in combination with protease inhibitors like nirmatrelvir?
A) To decrease the effectiveness of the protease inhibitor
B) To reduce the side effects of the protease inhibitor
C) To increase the dosage of the protease inhibitor
D) To enhance the activity of the protease inhibitor
D
pt1slide34
True/False: Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase are better for antiviral therapy bcuz they are more tolerated than nucleoside RT
True (less side effects)
Describe the mechanism by which oseltamivir (Tamiflu) inhibits the release of influenza virus particles.
Oseltamivir inhibits the release of influenza virus particles by blocking the neuraminidase enzyme, which is necessary for cleaving sialic acid and releasing mature viral particles from host cells.
What is unique about viroids?
A) They are made of DNA only.
B) They are made of RNA only.
C) They are made of both DNA and RNA.
D) They are made of proteins only.
B
pt3slide2
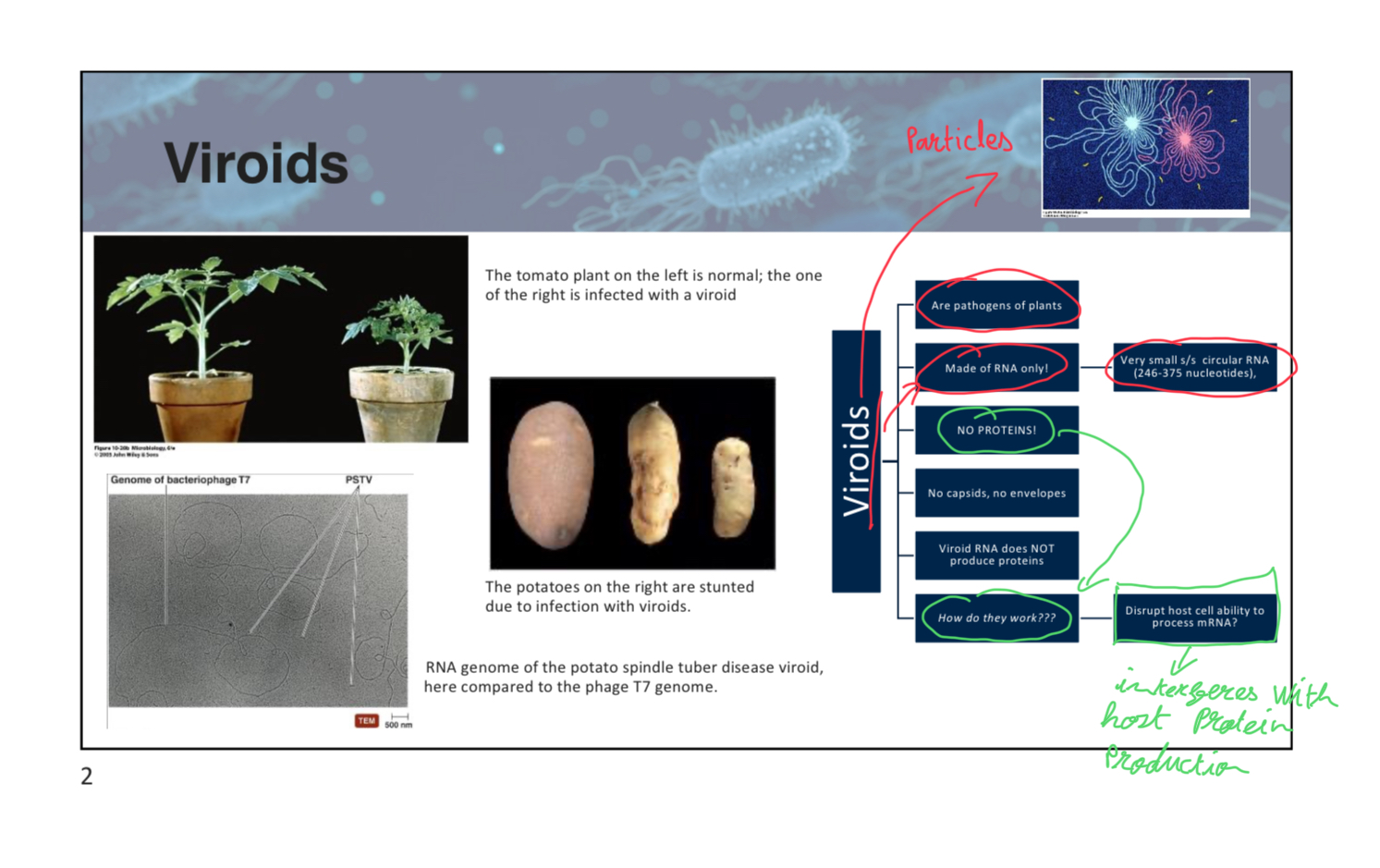
Viroids are pathogens that primarily infect _______________________.
Plants (interferes with host protein production)
What type of diseases do prions cause?
A) Neurological degenerative diseases
B) Cardiovascular diseases
C) Respiratory diseases
D) Gastrointestinal diseases
A (in animals and humans)
pt3slide3
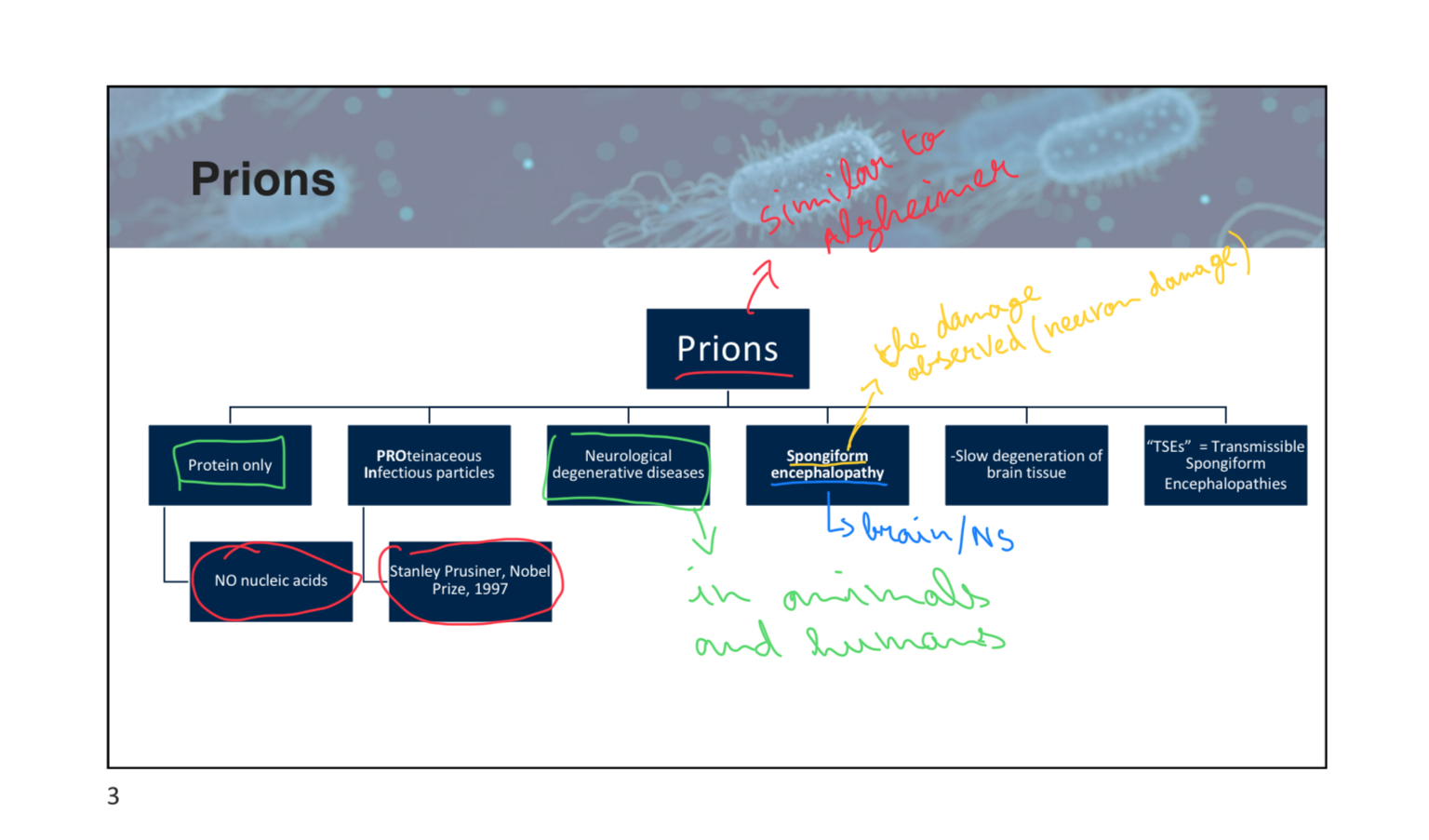
True/False: Prions contain nucleic acids.
False
Which of the following is NOT a type of prion disease?
A) Scrapie
B) Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)
C) Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE)
D) Tuberculosis
D
True/False: Prion diseases are easily inactivated by heat.
False (requires a combination of heat + NaOH treatment)
Describe the mechanism by which prions cause disease, focusing on the role of PrPSc and PrPC.
Prions cause disease by the misfolding of the normal prion protein (PrPC) into an abnormal form (PrPSc). PrPSc can induce normal PrPC to misfold into more PrPSc, leading to the accumulation of these abnormal proteins, which form aggregates that damage nerve cells.
pt3slide13/14
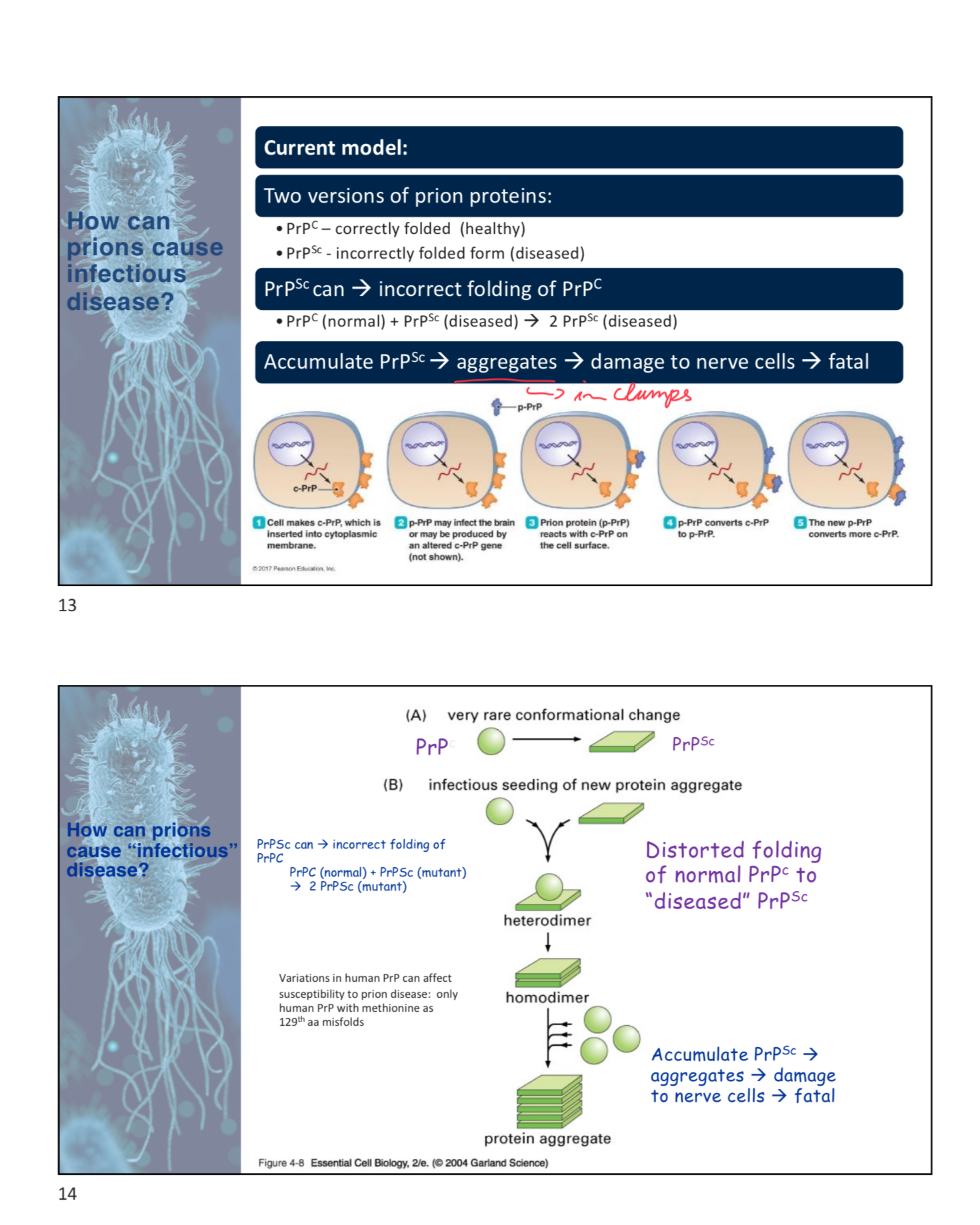
Compare and contrast the transmission methods of Scrapie and Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)
Scrapie is transmitted vertically from mother to offspring in sheep, while Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) is transmitted directly among elk and deer, potentially through saliva, urine, feces, or hair.
Describe the different forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) and their characteristics.
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) comes in three main forms: sporadic (most common), familial (genetic), and iatrogenic (acquired through medical procedures). A variant form, vCJD, is linked to the consumption of BSE-contaminated beef.
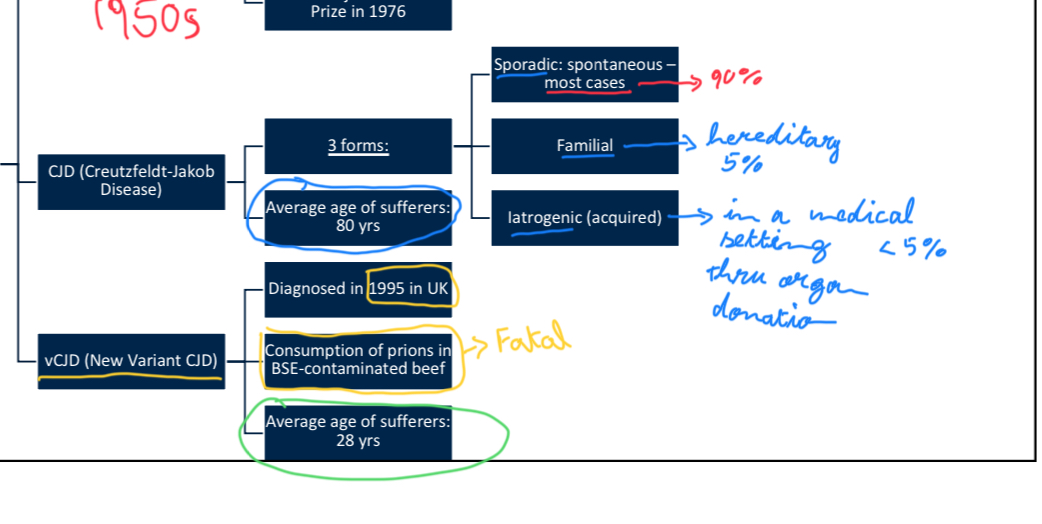
Which of the following list of prions are found in humans:
A) Kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD), Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD)
B) Scrapie, Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)
C) Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE), Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD)
D) Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (vCJD), Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD), Scrapie
A
pt3slide11
What is the primary mode of transmission for Giardia intestinalis?
A) Vector-borne
B) Direct contact
C) Fecal-oral route
D) Airborne
C
Giardia intestinalis trophozoites attach to the host intestinal epithelium using an _______________________ disk.
adhesive
pt4slide12
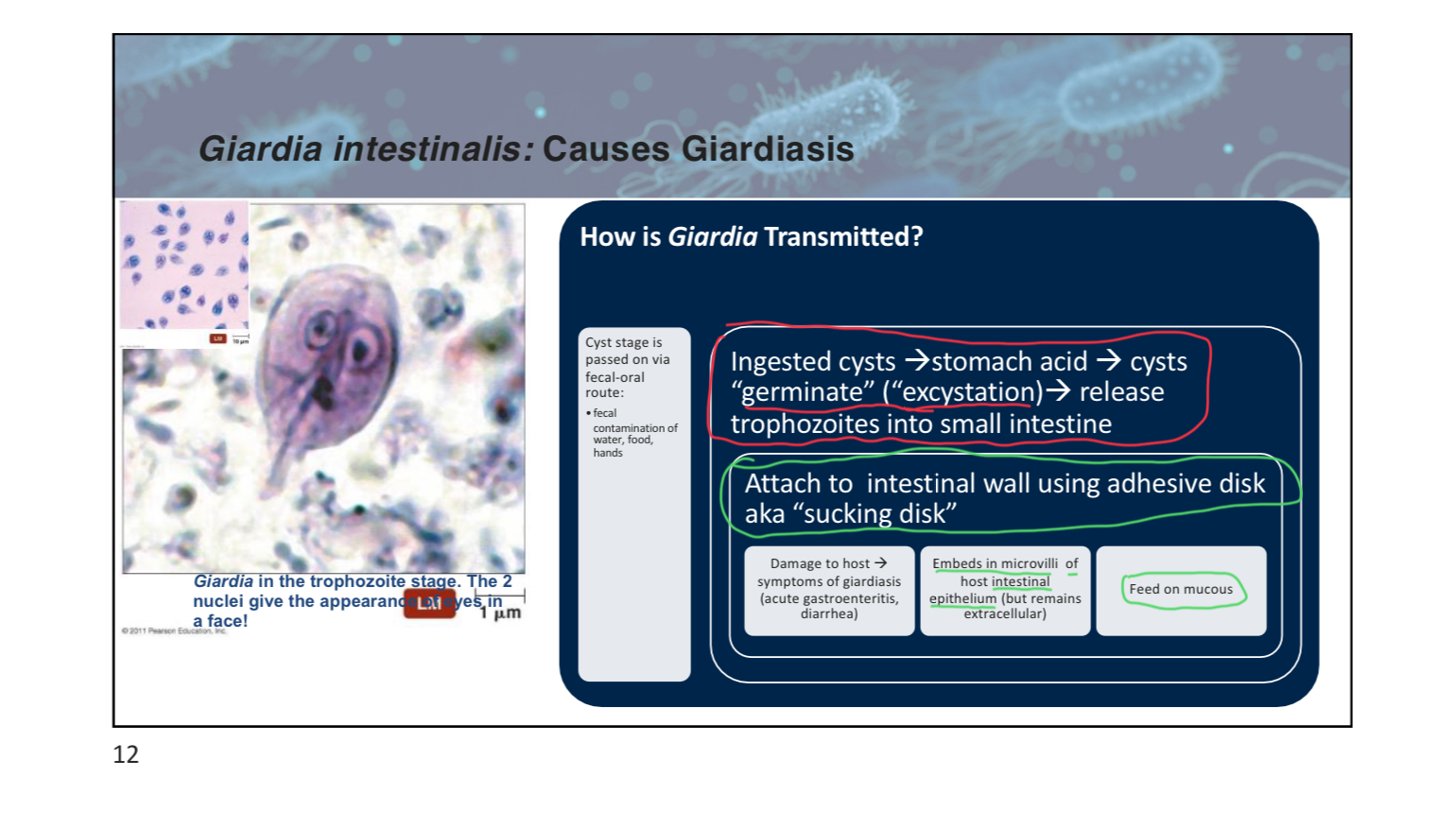
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Giardia intestinalis cysts?
A) Highly resistant to damage
B) Made of cross-linked cyst wall proteins and polysaccharides
C) Motile
D) Can survive for months
C (cyst represent non motile form and is the infective form)
True or False: Giardia intestinalis is an intracellular parasite.
False (is an extracellular parasite, it does not invade host cells but instead remains in the lumen of the small intestine → feeds on mucous)
Which group of protozoans includes Giardia intestinalis?
A) Apicomplexans
B) Flagellates
C) Ciliates
D) Sarcodines
Giardia intestinalis undergoes _______________________ to reproduce in the host.
B (has 4 pairs of flagella and 2 nuclei)
Binary fission (more trophozoite produced)
Explain the process of excystation in Giardia intestinalis and its significance in infection.
Excystation is the process by which Giardia cysts "germinate" upon ingestion, releasing trophozoites into the small intestine, to begin infection.
Outline the life cycle of Giardia intestinalis, including its transmission and replication stages
The life cycle of Giardia intestinalis begins with the ingestion of cysts through the fecal-oral route. Upon ingestion, cysts undergo excystation in the small intestine, releasing trophozoites. These trophozoites attach to the intestinal wall and feed, eventually undergoing binary fission to reproduce. As the infection progresses, trophozoites form new cysts through encystation, which are then excreted into the environment to continue the cycle.
Which of the following water treatment steps is MOST effective at removing Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts?
A) Chlorination/UV radiation
B) UV radiation/filtration
C) Sedimentation/filtration
D) Coagulation
C
Toxoplasma gondii is an apicomplexan, meaning it is _______________.
Not motile
What is the infectious stage of Toxoplasma gondii found in tissue cysts?
A) Sporozoites
B) Tachyzoites
C) Merozoites
D) Bradyzoites
D
True/False: 40% of the population has antibodies against T. gondii
True (it’s very common)
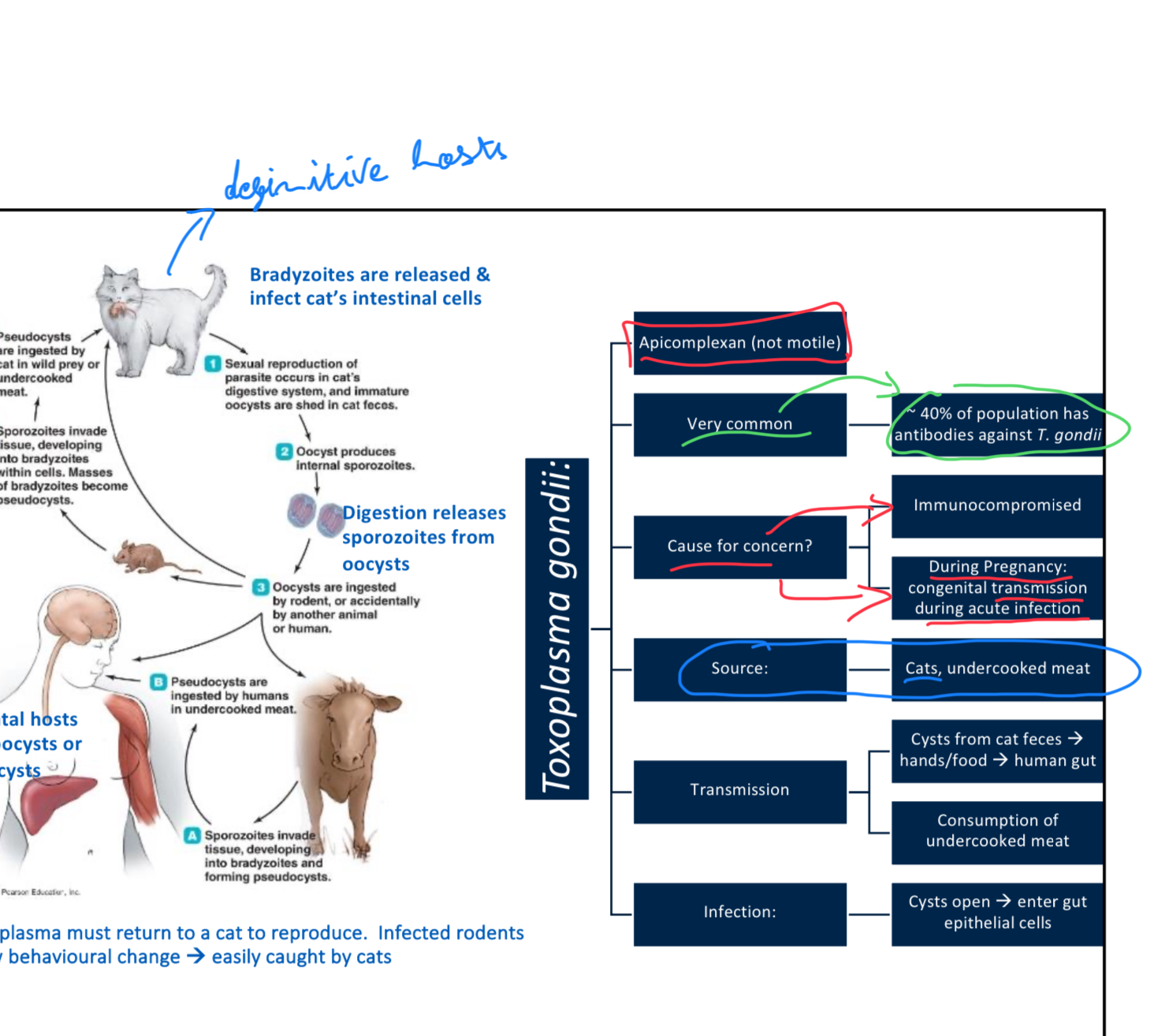
Which of the following is NOT a common route of human infection for Toxoplasma gondii?
A) Consumption of undercooked meat
B) Contact with cat feces
C) Maternal-fetal transmission
D) Mosquito bites
D
Toxoplasma gondii multiplies inside host cells and can invade other cell types, living inside ______________ inside host cells.
Vacuoles
pt5slide14

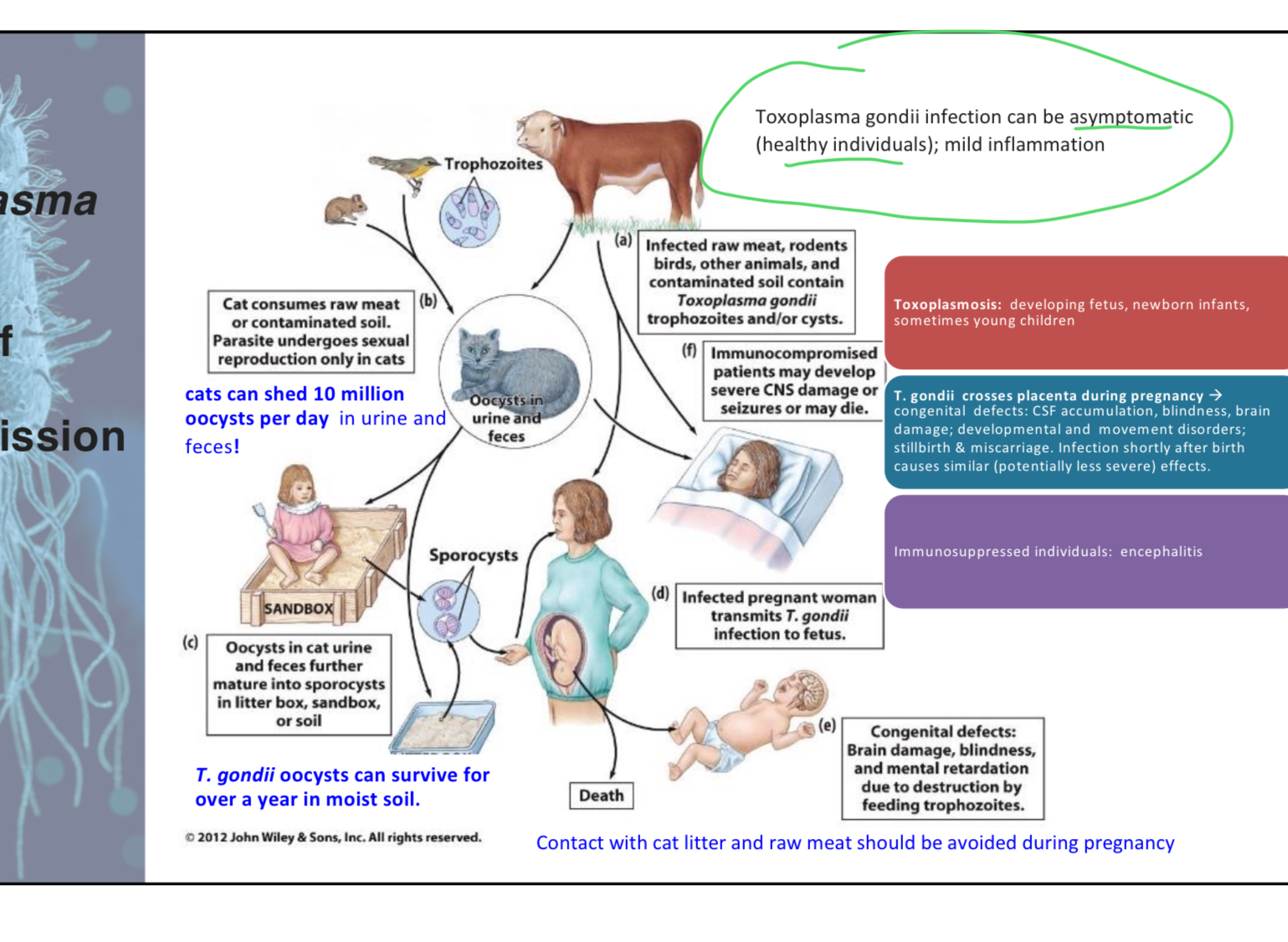
Toxoplasma gondii causes ___________ in AIDS patients
Intracerebral lessions
Note: infection with T. gondii can be life long
Briefly describe the life cycle of Cryptosporidium parvum and how humans become infected.
Humans become infected by ingesting oocysts in contaminated water or food. Oocysts release sporozoites in the intestine, which invade mucosa and attach to intestinal epithelial cells, becoming surrounded by host cell membranes. New oocysts are then released in feces, repeating the cycle.
Explain why Cryptosporidium parvum is difficult to remove from water supplies using traditional disinfection methods like chlorination.
Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts are resistant to chlorine due to their tough structure.
Describe the role of cats in the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii, and explain why they are considered the definitive host.
Cats are the definitive host because Toxoplasma gondii can only sexually reproduce within them. Cats shed oocysts in their feces, which can then infect intermediate hosts.
Which of the following is a characteristic of cestodes (tapeworms)?
A) They have a complete digestive system
B) They are dioecious and reproduce asexually
C) They absorb nutrients through their outer cuticle
D) They are monoecious with single opening for food & waste
C (when they got no digestive system they get nutrients thru their skin)
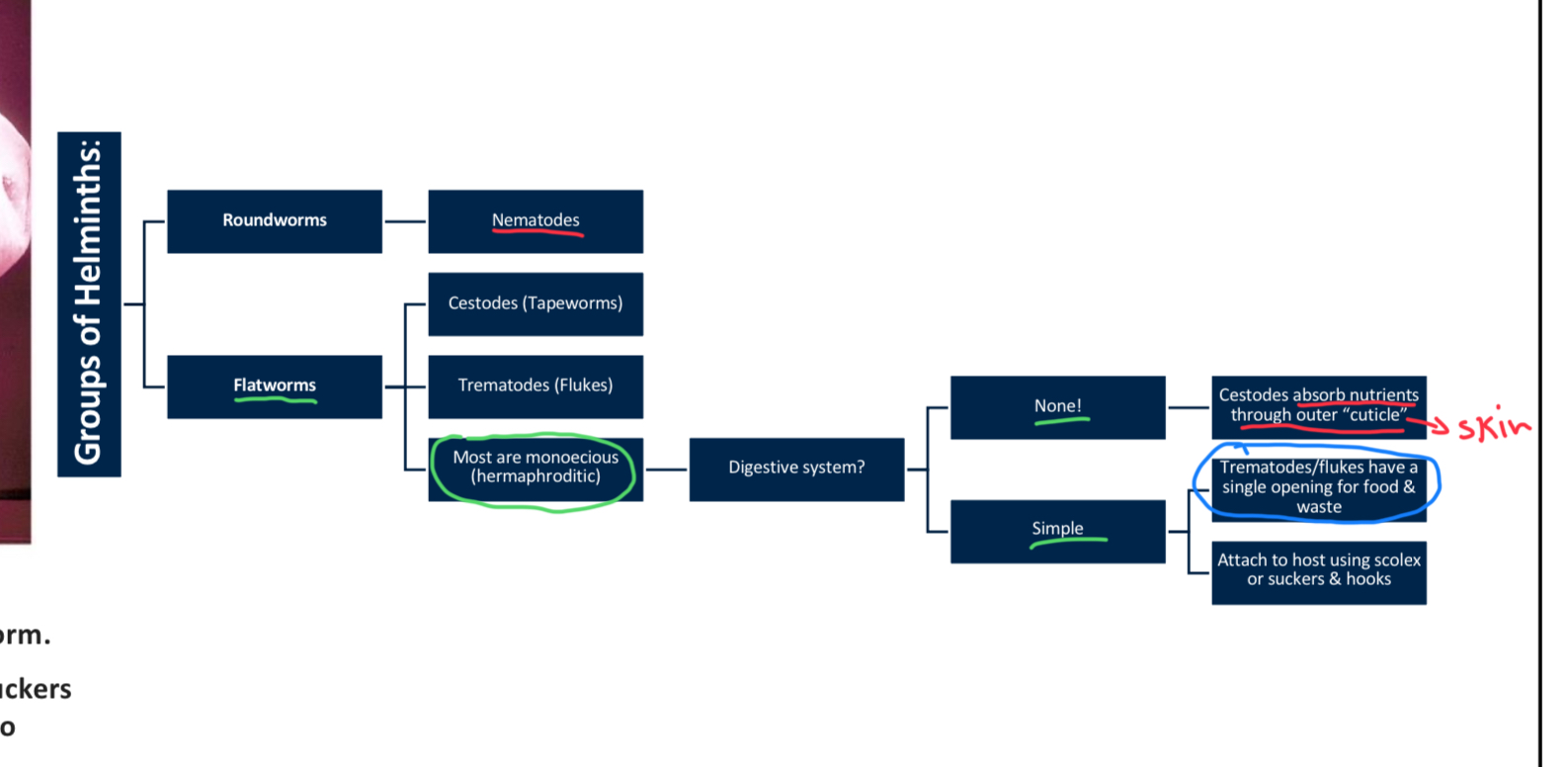
What is the primary function of the scolex in tapeworms?
A) Reproduction
B) Nutrient absorption
C) Egg production
D) Attachment to the host
D
True/False: Nematodes are dioecious, meaning they have distinct male and female worm.
True (in roundworms)
Note: In contrast, monoecious means 1 worm has both male and female reproductive organs (in flatworms)
In your own words explain each of these terms.
A. proglottis
B. Strobilia
C. Gravid
A. A proglottis is a single segment in the body of a tapeworm. Each proglottis contains its own reproductive system, enabling the tapeworm to produce eggs independently within each segment.
B. The strobila refers to the entire segmented body of a tapeworm, excluding the scolex (head) and neck, a chain of proglottids that are continuously produced by the neck region
C. Gravid refers to the state of being full of eggs. In tapeworms, distal proglottids (the segments farthest from the neck) become gravid as they mature, containing thousands of eggs and release the eggs in faces
Which of these is an intermediate host for Taenia saginata?
A) Humans
B) Pigs
C) Cattle
D) Mosquitoes
C (humans are definitive host)
What temperature is required to kill Taenia saginata cysticerci in beef?
A) 45°C
B) 57°C
C) 76.7°C
D) 100°C
B
Which medication is commonly used to treat active taeniasis?
A) Metronidazole
B) Praziquantel
C) Amphotericin B
D) Ciprofloxacin
B (Praziquantel & Nicolasamide can be used to treat active taeniasis. For cysticercosis, treatment is more difficult. For example, Praziquantel is cysticidal (kills cysticerci) but this can lead to inflammation around dying cysts, inducing seizures or other symptoms.)
True/False: Taenia solium can cause cysticercosis if humans ingest its eggs
True (this occurs on rare occasion where humans become intermediate hosts and can damage host nerves, brain and eyes)
True/False: Flukes (trematodes) have a digestive system with two openings for food and waste.
False (they only got 1)
Flukes are grouped according to __________
site of body they parasitize (2 types tissue and blood flukes)
Humans are the only hosts for;
A) Flukes
B) Nematodes
C) Taenia saginata
D) Trichinella spiralis
B
Compare the digestive systems of cestodes, trematodes, and nematodes
Cestodes lack a digestive system and absorb nutrients through their cuticle; trematodes have a simple digestive tract with one opening; nematodes have a more complex digestive system with separate openings for intake and waste.