Basics of Chemistry (A&P)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What substances cannot be broken down into simpler forms (because they are elements)
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Elements
a single substance (periodic table)
Molecules
a combination of two or more atoms (same element) held together by chemical bonds
Compounds
a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms (different elements) held together by chemical bonds
Mixture
substance composed of two or more components that are physically intermixed (no bonds)
Solutions
homogeneous mixtures of components (gas, liquid, or solid)
Solvent
substance present in the greatest amount
Solute
substance present in smaller amount dissolve in the solvent
What is the body chief’s solvent
water
Concentration
the percent of solute dissolved in solution
Chemical bonds
electrons are found in electron shells orbiting the nucleus of an atom; the outermost shell (valence shell) participates in chemical reactions. Atoms will try to achieve a complete valence shell
What are the different types of chemical bonds
Ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds
Ionic bonds
electrons donated from one atom to another (NaCl)
Covalent bonds
electrons are shared between atoms
Hydrogen bonds
not true bonds but weak attractive forces between a hydrogen atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule… they are important in maintaining shape and structure of molecules
What is the most abundant and important inorganic compound found in living
Water
What are the important properties of water?
High heat capacity, temperature stability, polar solvent, cohesion and adhesion, density
What causes chemical reactions to occur?
When electrons are donated or shared
Metabolism
Sum of all chemical reactions that occur in the body
Anabolic reactions
“Building up” reactions; requires input of energy. A.k.a. dehydration, synthesis reactions.
Catabolic reactions
“Breaking down” reactions; generally release energy. Aka hydrolysis reactions.
What does the rate of chemical reactions depend on?
Concentration of reactants, temperature, size of molecules involved in reaction, and presence of catalysts (in the body, this means enzymes)
What are the major elements that make up the human body?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
Inorganic substances
Do not contain carbon
Examples of Inorganic substances
Water, salt, acids and bases
Organic substances
Contain carbon (life)
Examples of Organic substances
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Electrolytes
Salts that exist as charged particles in a solution

What kind of compound is salt?
Ionic compound; when dissolved it disassociate into ions

What are the common ions in the body?
Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-
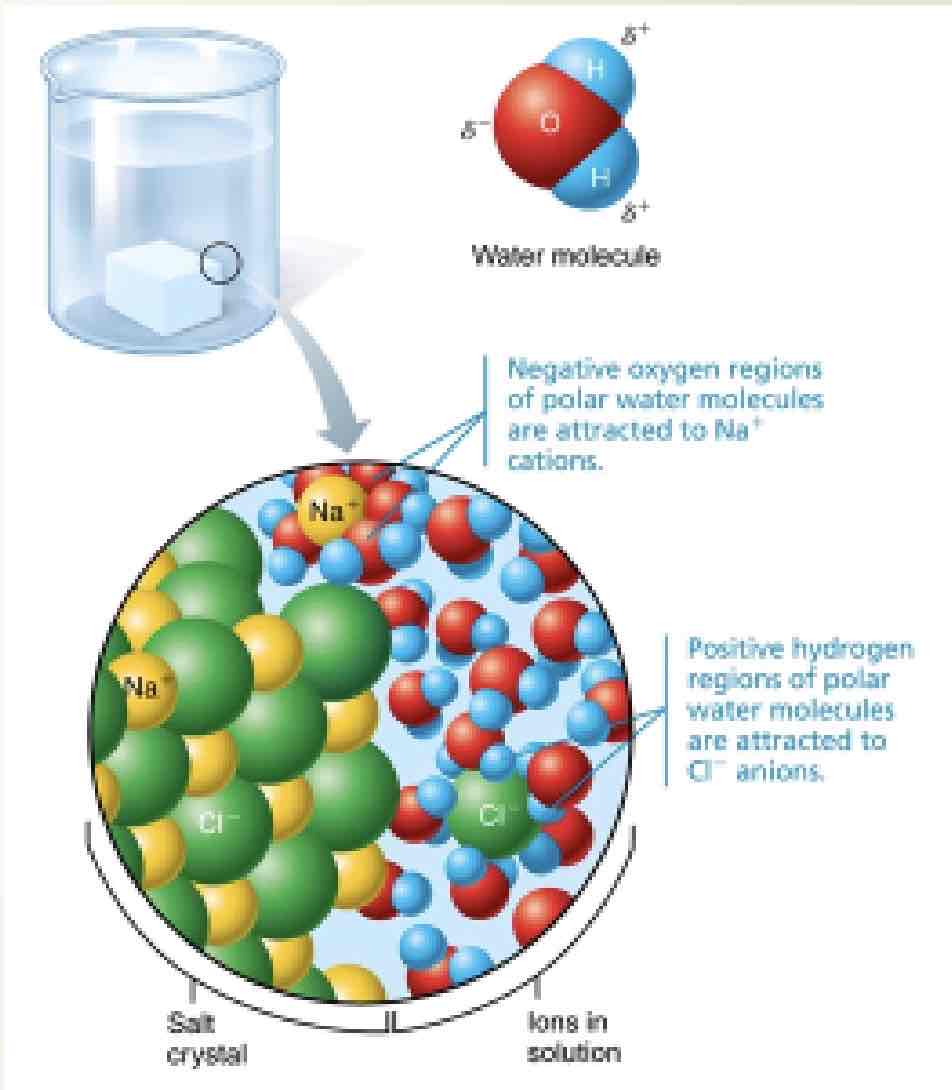
What is the role of salt in the body
Impulse conduction, muscle contraction, and fluid balance
Acids
Are proton donors; they release H+ in solution
Bases
Are proton acceptors; they bind H+ in solution
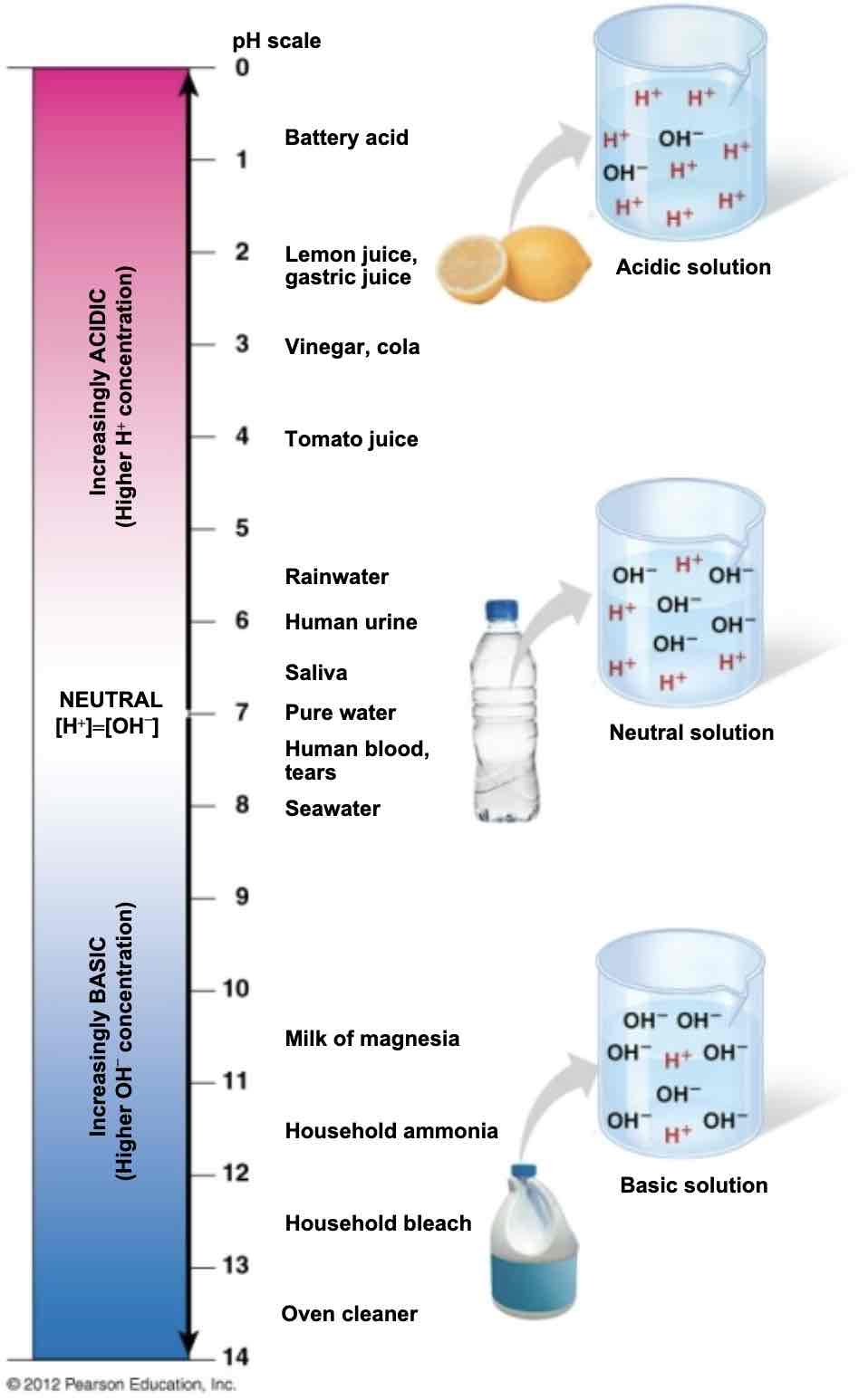
What does the pH scale measure?
It measures the concentration of hydrogen ions, (H +) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14
Lower pH
More H + in solution = more acidic
Higher pH
Less H + in solution = more basic (alkaline)
What is the pH of our blood?
It is maintained at a pH of 7.35- 7.45
What is a buffer system?
It is a mechanic that ensures that the pH stays within this range; buffer systems minimize changes in pH by accepting or donating H+ to the solution
Many biological molecules are macromolecules (macro=large) which can exist as…
Polymers and monomers
Polymer
Long chain like molecules made up of subunits called monomers
Monomers
The smallest form of a macromolecule
How are macromolecules formed?
Dehydration synthesis, and broken down by hydrolysis
What are the four macromolecules of the body?
Carbohydrates fats, proteins, and nucleic acids
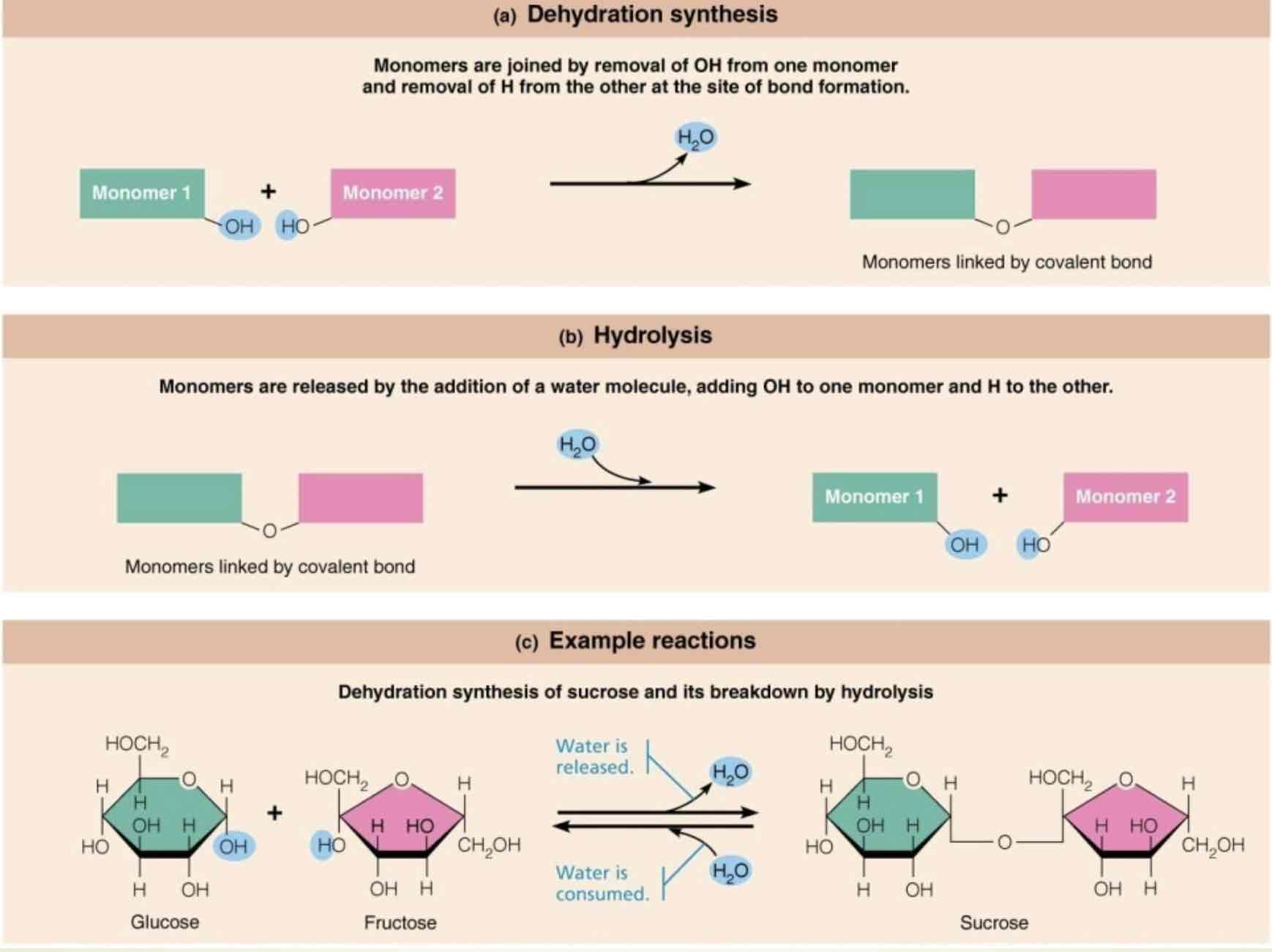
Dehydration synthesis
Monomers are joined by removal of OH from one monomer and removal of H from the other at the site of bond formation
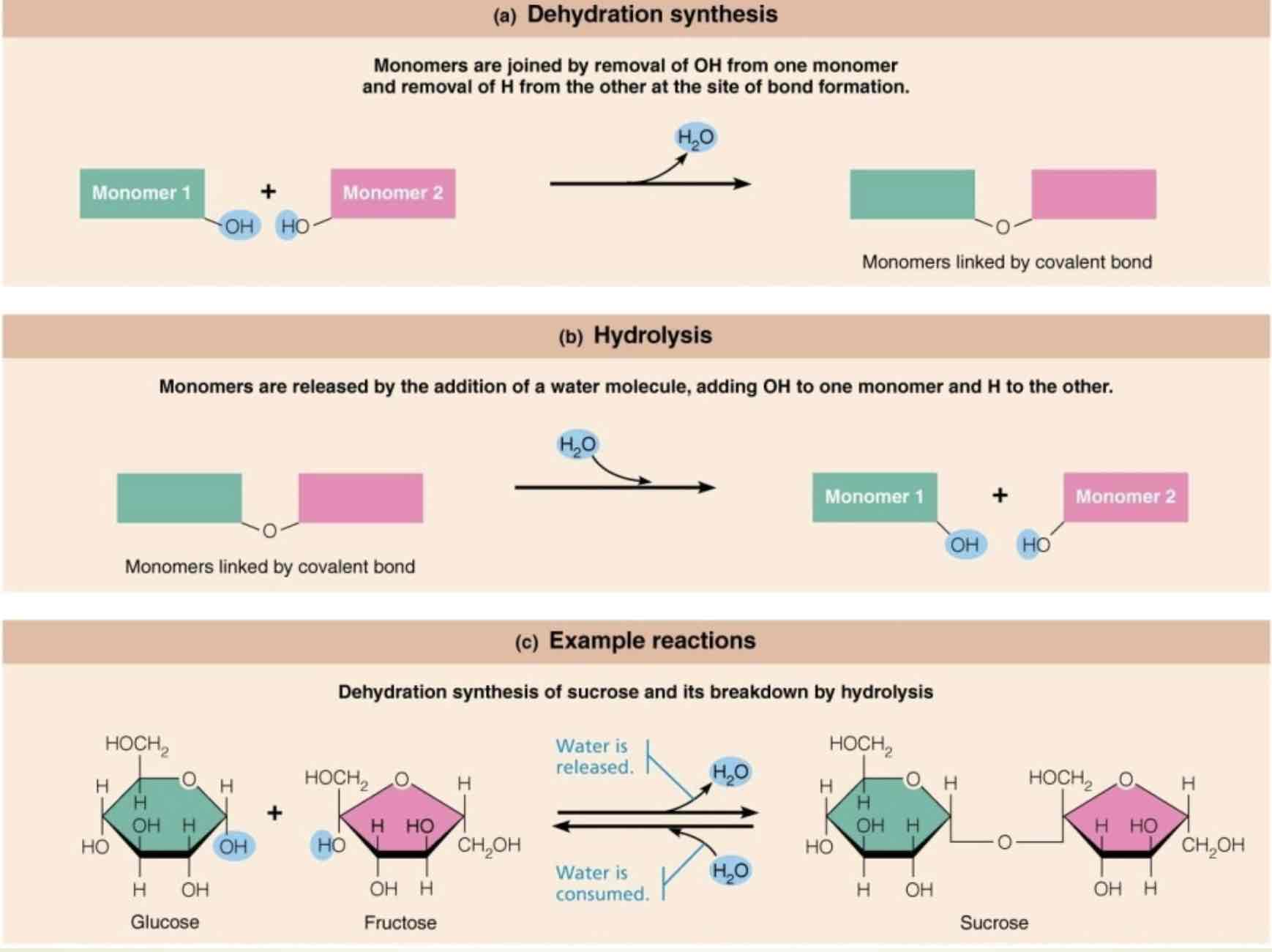
Hydrolysis
Monomers are released by the addition of a water molecule, adding OH, to one monomer and H to the other
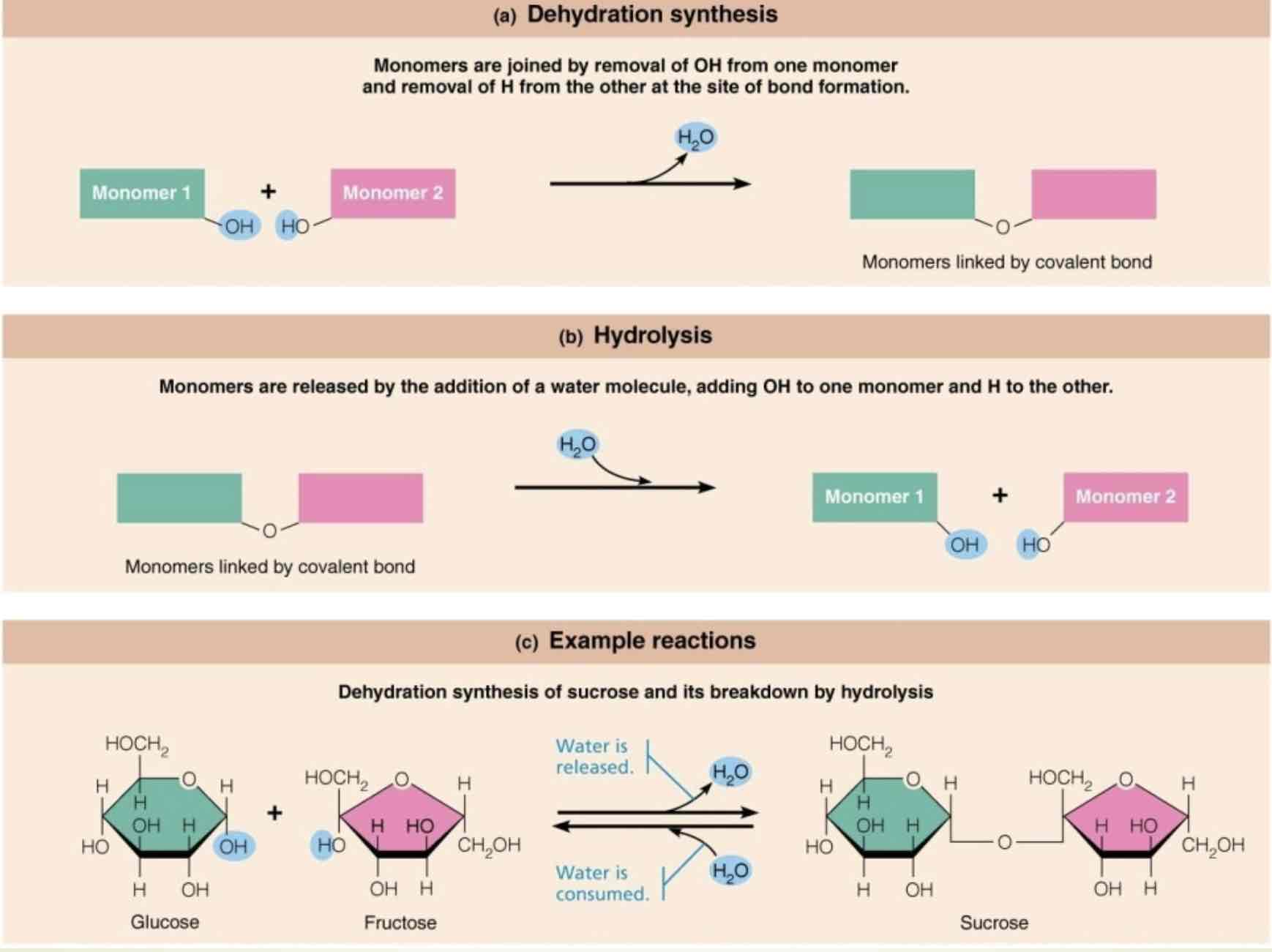
An example of dehydration synthesis
Dehydration synthesis of sucrose, and it’s breakdown by hydrolysis
Why are macromolecules important to the body?
Provides building blocks for making new body components (hormones cells, fibers, etc) and energy source for cellular respiration to produce ATP (our body’s, energy currency)
We ingest polymers, however
Our digestive track can only absorb monomers
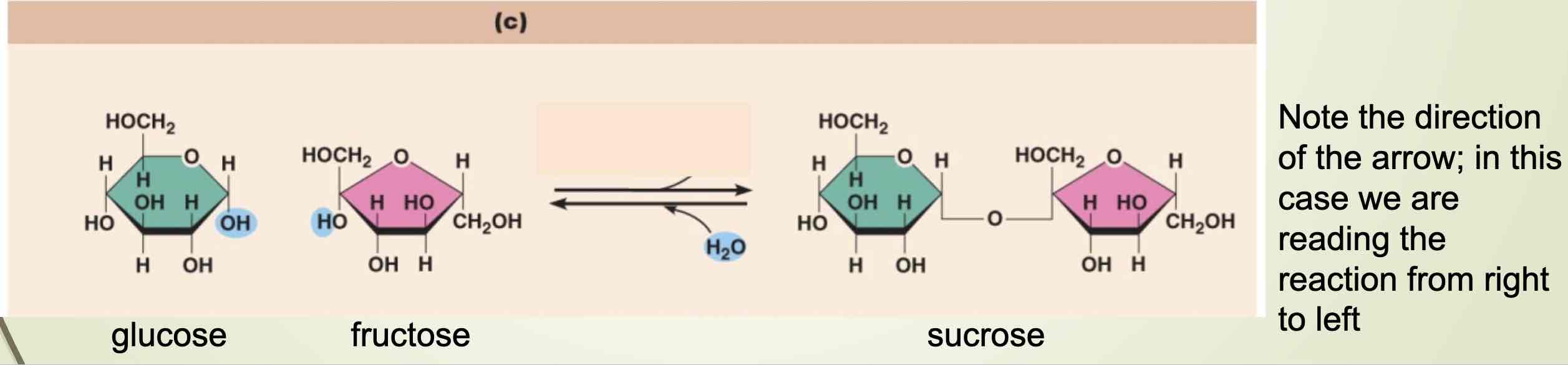
How do we break down food like table sugar(sucrose) into its monomers
Hydrolysis
Carbohydrates
Provide an easily used energy source for the body
Monomer
Monosaccharide (simple sugars); examples: glucose, fructose, and galactose
Disaccharides
Are double sugars
Examples of disaccharides
Sucrose: table sugar: glucose + fructose
Lactose: dairy sugar: glucose + galactose
Maltose: glucose + glucose
Polymer poly saccharide(long chains of glucose)
Glycogen: in animals, stored in the liver and muscles
Starch and cellulose: in plants
Examples of polysaccharides
Plant polysaccharides: starch and cellulose
Animal polysaccharides: glycogen
Lipids
Insulate and protect body organs, build cell membranes and provide stored energy
Examples of lipids
Fatty acids triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids
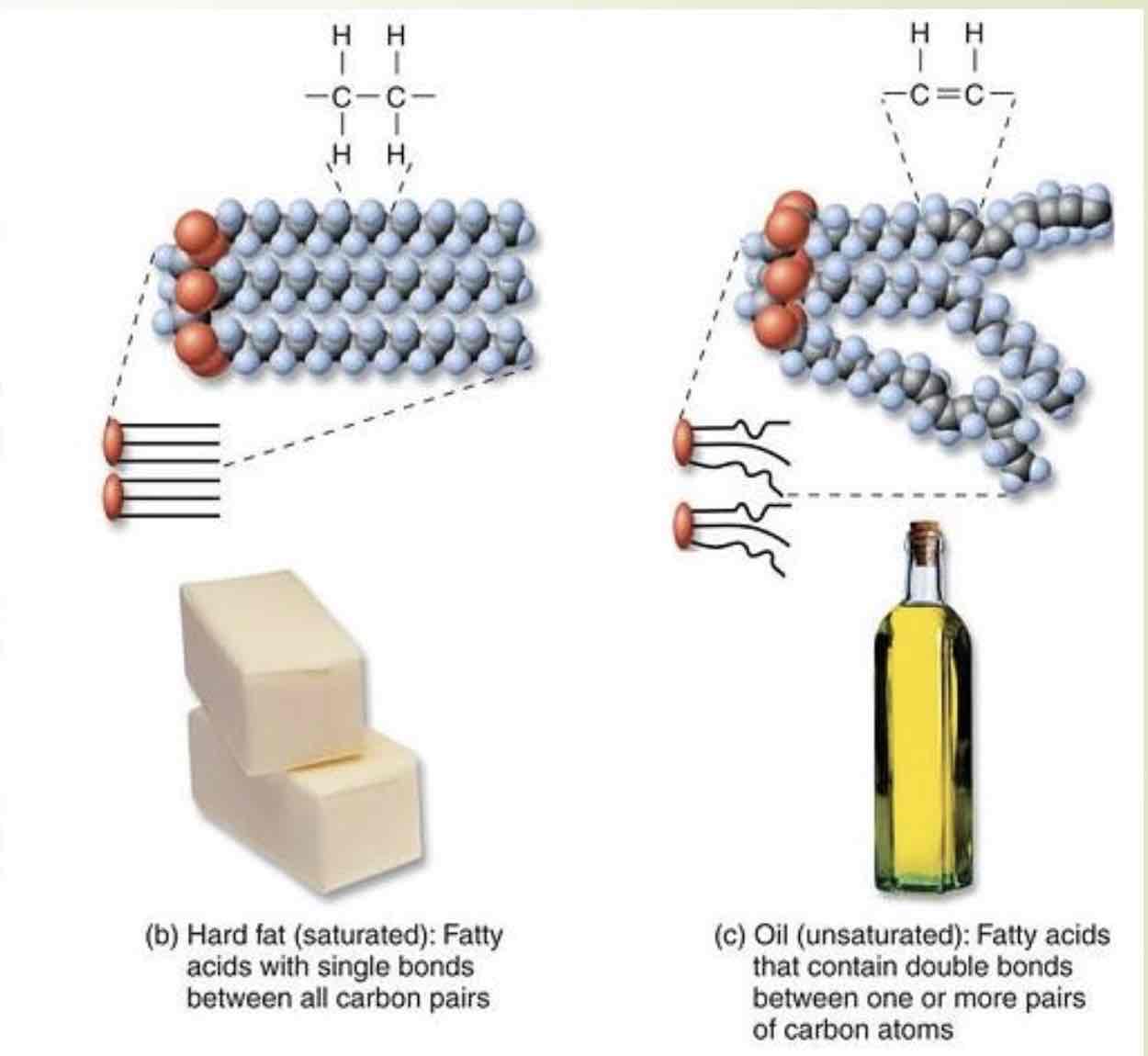
Triglycerides
Long-term energy storage, cushioning and insulation. Fatty acids. Nonpolar hydrophobic. Can be saturated or unsaturated
Saturated:solid at room, temperature; animal fats, unhealthy in large amounts.(butter, fat in meat and eggs.)
Unsaturated:liquid at room temperature;vegetable and nut oils;healthier
Efficient way to store energy:(9 kcal/g vs 4 kcal/g for proteins and carbs)
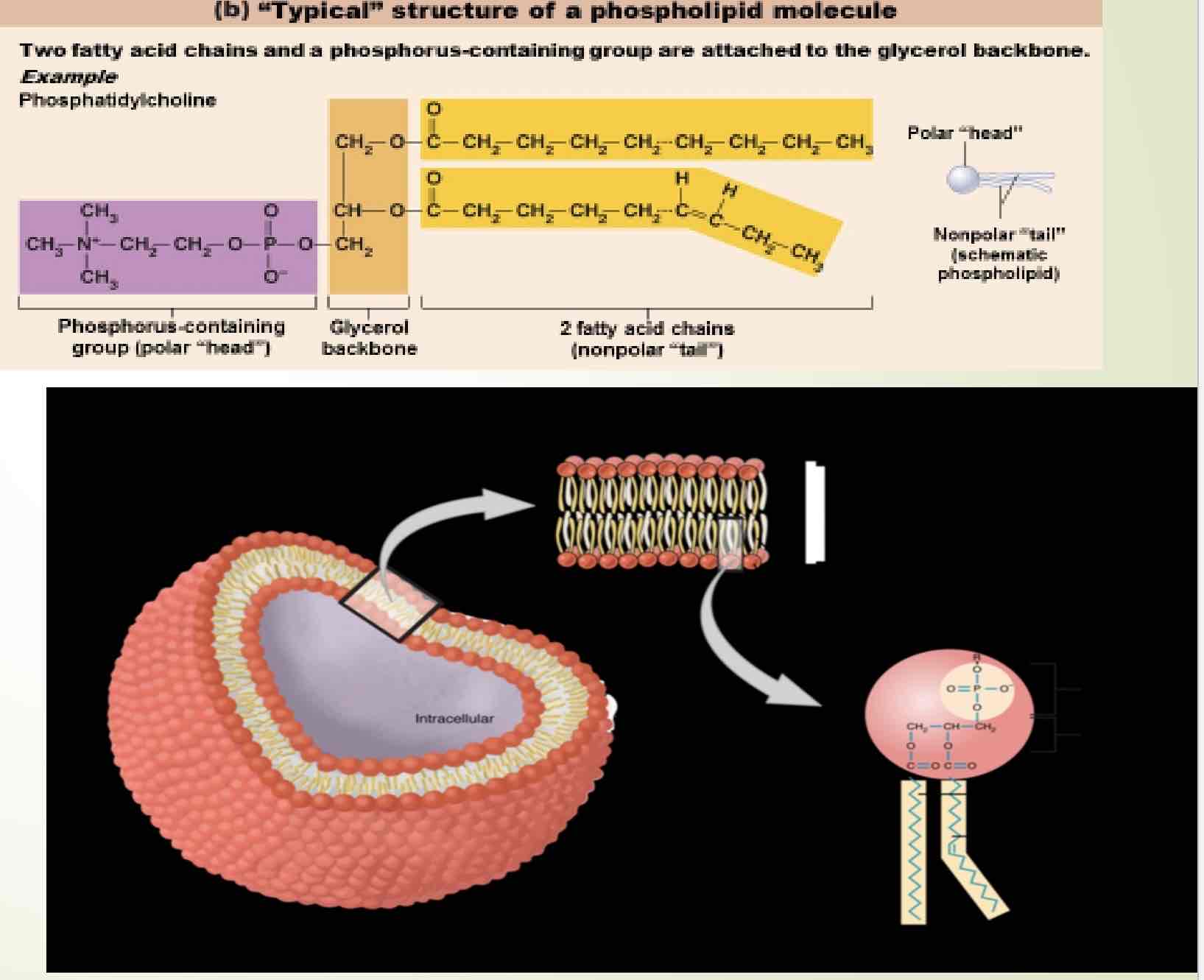
Phospholipids
Major component of cell membranes; most are unsaturated.
Polar end(phosphate head) interacts with water
Nonpolar end(fatty acid tails) shielded from water
Steroids
Composed cell membranes, serve as hormones and basis of vitamin D
Nonpolar: made of four interlocking hydrocarbon rings with little oxygen
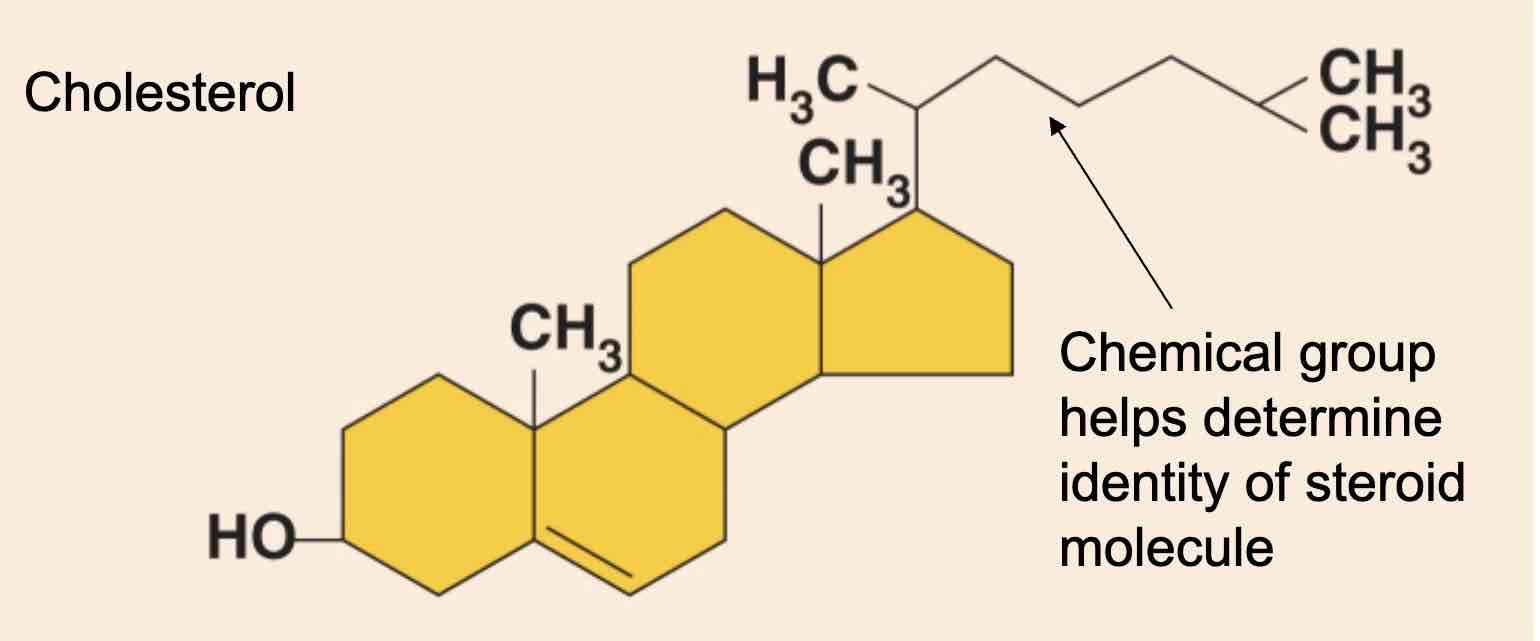
What is the most important steroid?
Cholesterol; it is the basis for all steroids in the body; steroids differ by the chemical groups, attached to the rings
Proteins
Monomer: amino acid
Polymer: polypeptide
Structure of an amino acid
Central carbon, amino and carboxyl
Radical group
Chemical group that is attached to the central carbon, and determines an amino acid to chemical behavior
What type of bond holds amino acids together?
Peptide bond (holds 2 amino acids together)
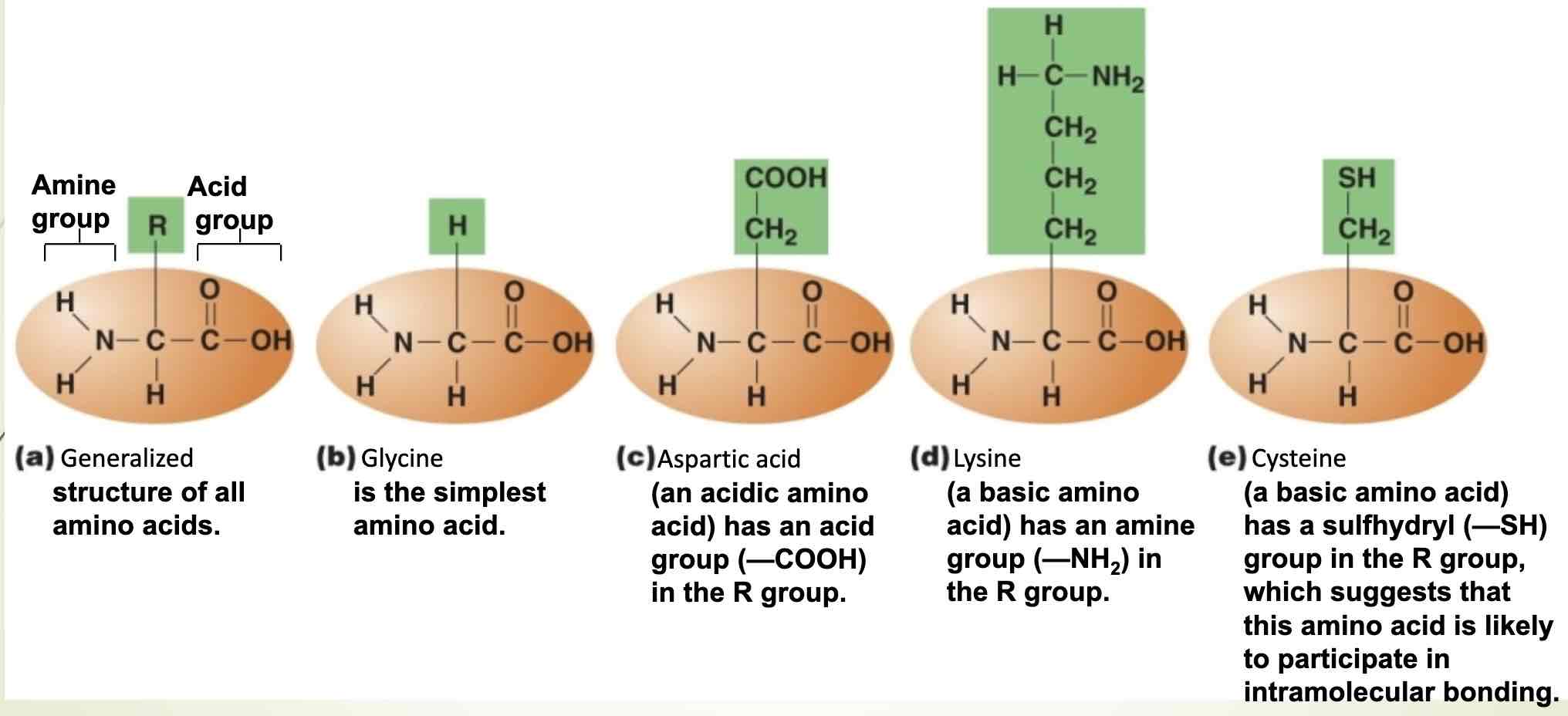
Radical groups of amino acids determine their chemical behavior(structure determines function)
Protein structure
Most proteins are large molecules that contain hundreds to thousands of amino acids. Proteins fold upon themselves to form unique shapes, proteins shape determines proper functioning.
Denaturation
Proteins have an optimal environment in which they function. If conditions are not optimal, they may slow or stop working, example high temperature, or acidity.
Protein function depends on
Structure
Fibrous proteins
Structural strand like insoluble and stable. Examples collagen, keratin, And contractile proteins of muscle
Globular proteins
Functional; compact and spherical. Water soluble.
Fxns:
Hormones(insulin/growth hormone) communication
Immunity(antibodies/complement) protected against disease
Transport(hemoglobin) carry substances in the body
Enzymes(lactase) increases the rate of chemical reactions in the body
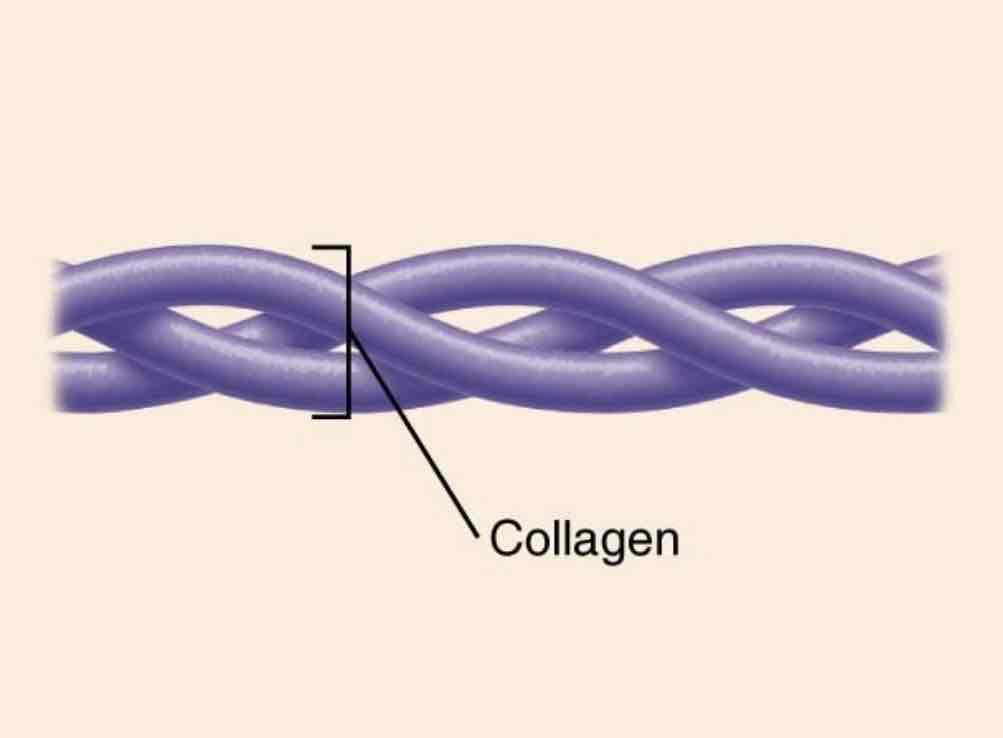
Structural proteins
Function: Mechanical support
Example: collagen found in all connective tissue is the single most abundant protein in the body. It is responsible for the tensile strength of bones, tendons, and ligaments.
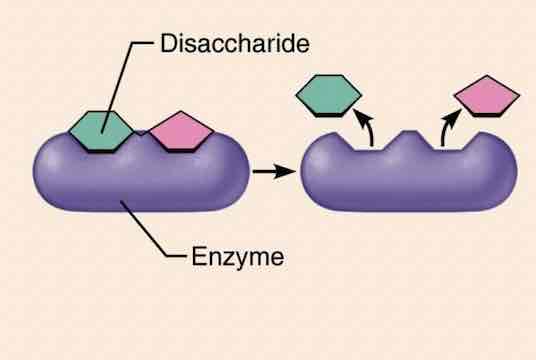
Enzymes proteins
Function: catalyst. Proteins enzymes are essential for virtually every biochemical reaction in the body.
Examples: disaccharides hydrolyze disaccharides, proteases hydrolyze proteins, and oxidases oxidize food fuels
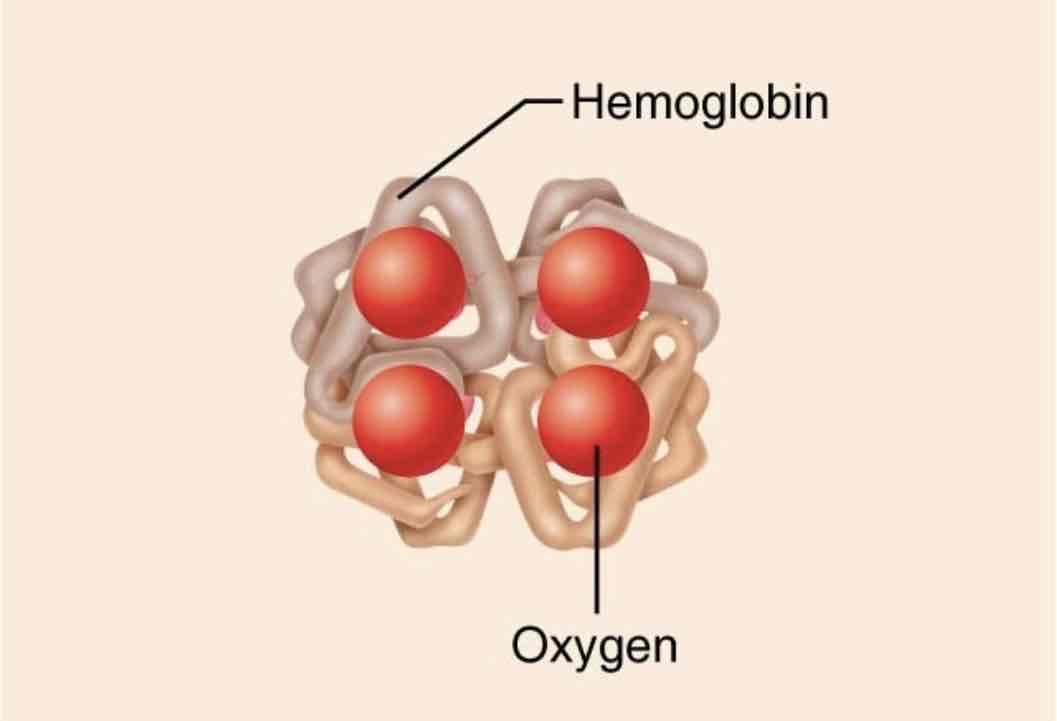
Transport proteins
Function: moving substances(in blood or across plasma membranes)
Examples: hemoglobin transports oxygen in blood. Some plasma membrane proteins transport substances (such a ions) across the plasma membrane
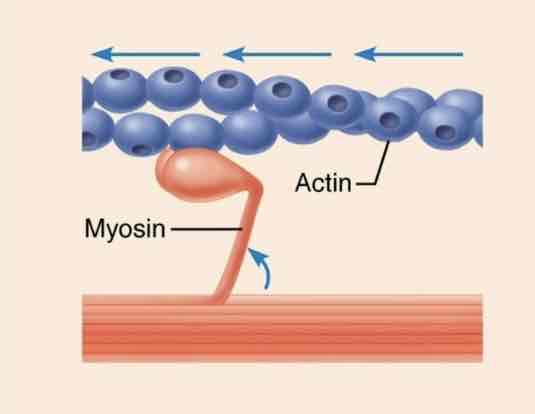
Contractile proteins
Function: movement
Example: actin and myosin cause muscle cell contraction and function in cell division in all cell types.
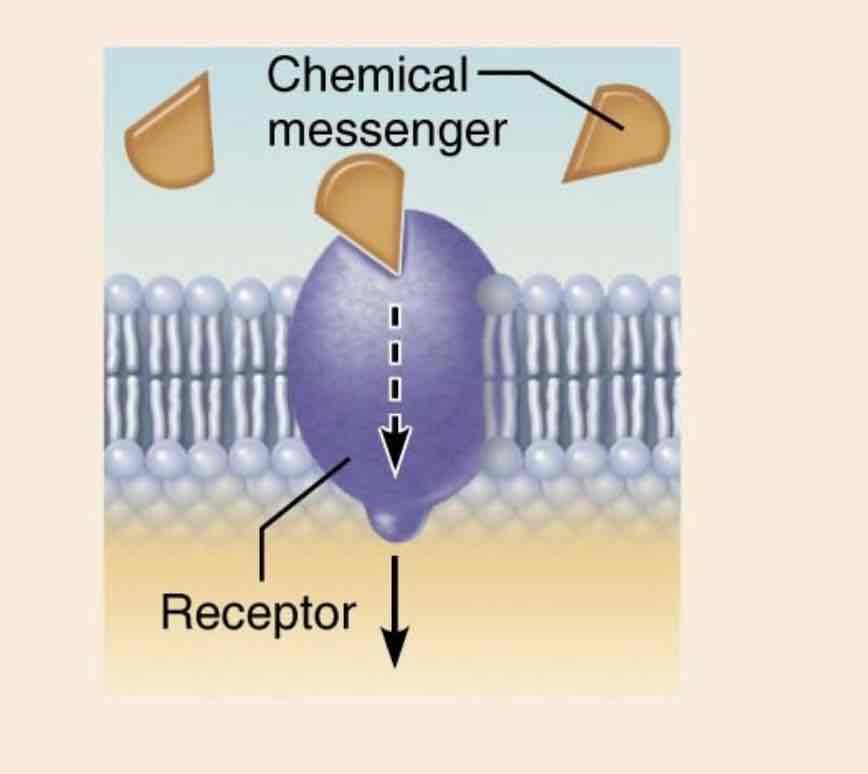
Communication proteins
Function: transmitting signals between cells. Can act as chemical messengers (e.g. hormones) or as receptors in the plasma membrane.
Example: insulin(a protein) acts as receptor to regulate blood sugar levels
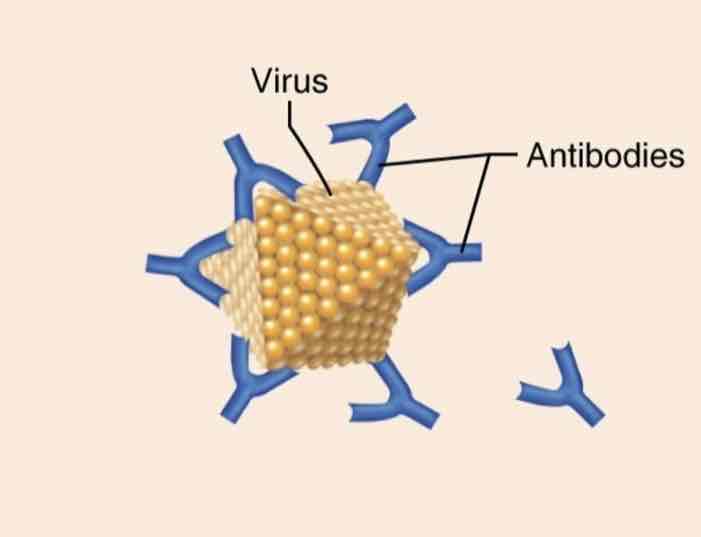
Defensive proteins
Function: protect against disease
Example: antibodies released by certain immune cells are specialized proteins that bind and inactivate foreign substances (e.g. Bacteria, toxins, and viruses.)
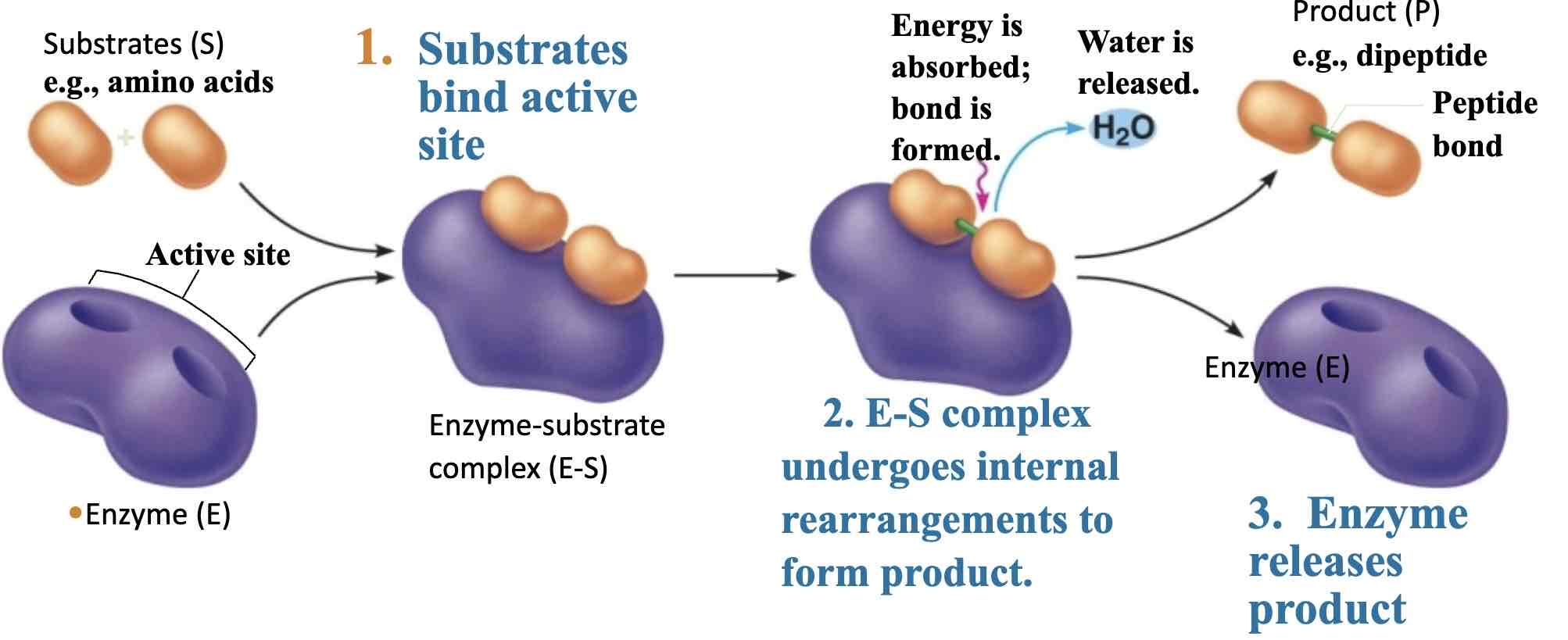
Characteristics of enzymes
Reusable: specific for a substrate (substrate interacts with enzyme at the active site)
Optimal conditions
Enzyme function: lower the activation energy(amount of energy required to start a reaction)
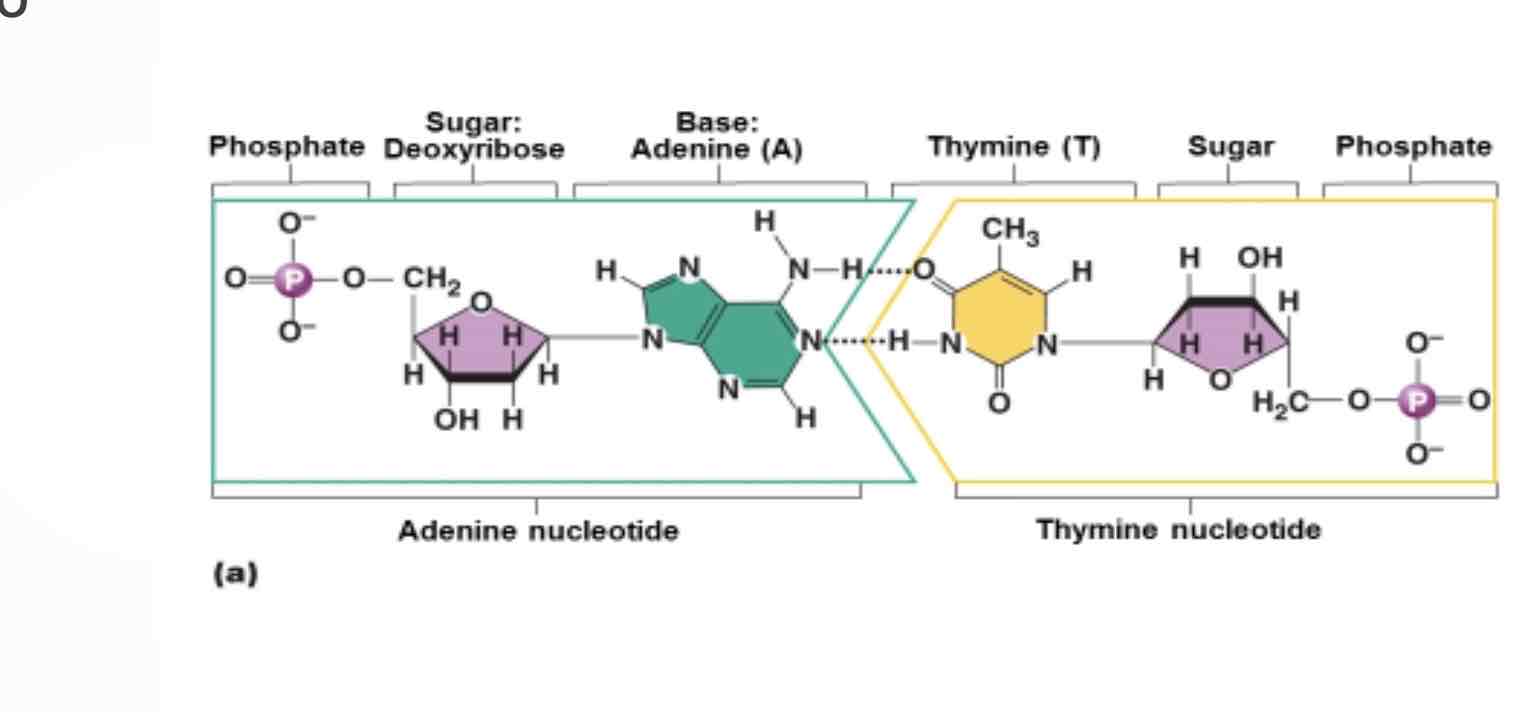
Nucleic acids
Deoxyribonucleic acid(DNA)
Ribonucleic acid(RNA)
Function: stores transmits, and helps to express genetic information
Monomer: nucleotide
Made up of: phosphate group, pentose(five carbon sugar), nitrogenous base(guanine, cytosine, adenine, thymine(DNA only), uracil(RNA only)
Nitrogenous bases are complementary to one another: they are held in place by hydrogen bonds
Add a nine pairs with I mean in DNA; with uracil in RNA.
Guanine pairs with cytosine in both DNA and RNA.
Differences between DNA and RNA (DNA)
Double stranded and helical, specifies proteins structure, pentose sugar: deoxyribose, nitrogenous bases:a,t,g,c
Differences between DNA and RNA (RNA)
Single stranded, three different types: messenger, ribosomal, and transfer RNA. Out DNAs instructions for proteins synthesis, pentose sugar: ribose. Nitrogenous bases: A,U,G,C
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Our body’s fuel. ATP is made in our cells by a process called cellular respiration.
Glucose + O2 → H2O +CO2 + ATP
What does phosphorylation do
This is how ATP powers work in the cell. It transfers a phosphate group to another molecule to power a specific process.