domestic breeds, genes, genotypes and phenotypes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
line breeding
Robert Bakewell (1725-1795)
selective breeding
gradual involvement of humans
animals have diversity due to environmental influence
animals that display desired attributes are used in reproduction
Robert Bakewell
pioneer of livestock breeding natural selection, deliberate animal breeding
great variety of breeds
origins of todays livestock breeds
natural selection and evolution
descent with modification from a common ancestor
Charles Darwin- the origins of species
Galton’s conditions of domestication
They should be hardy
they should have an inborne liking to man
they should be comfort-loving
they should be found useful to the savages
they should breed freely
they should be easy to tend
Soay
Sheep
one of the more primitive breeds in the UK
representative of original breed
sheep breed development
Developed for living conditions
eg. mountains, hills, lowland
Hill Ewe- Scottish blackface
standardised for wool
with an average fibre diameter
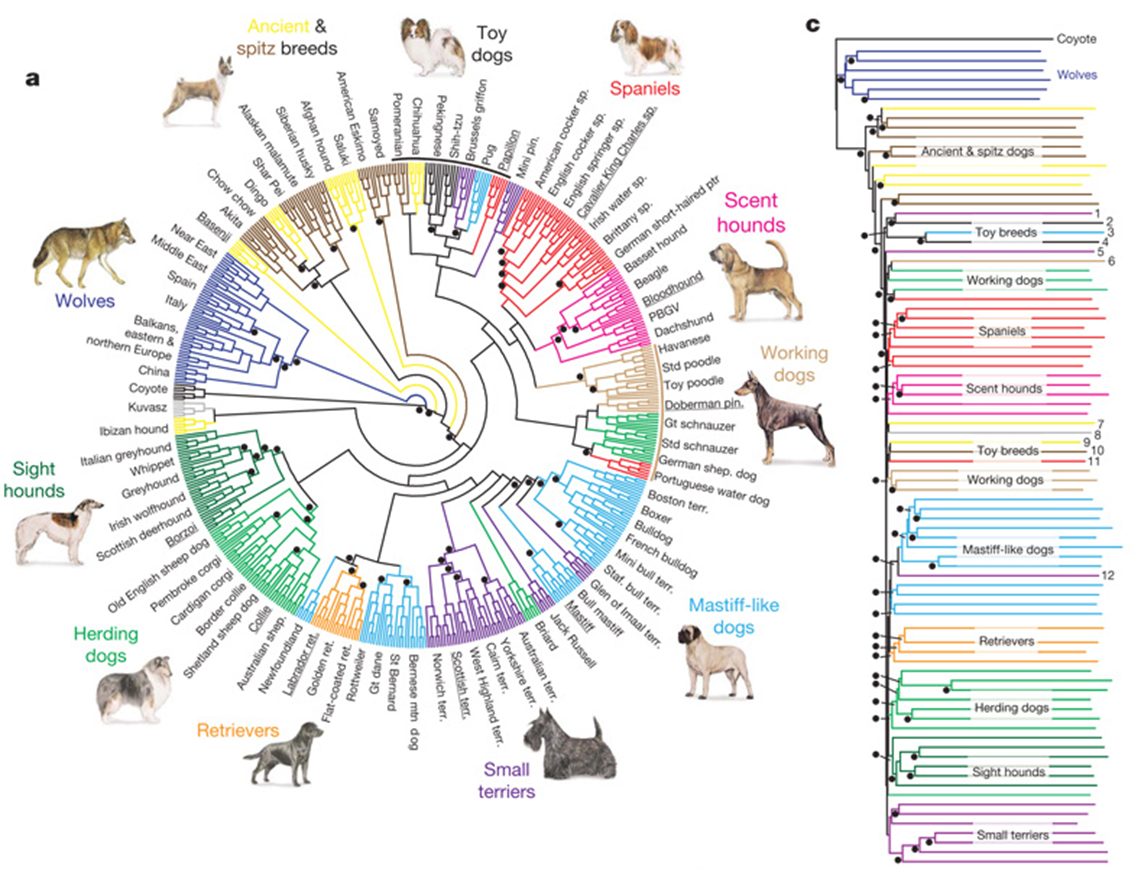
dog breeds- rapid phenotypic evolution under domestication
animal genetics
study of inheritance in animals
Animal breeding
application of principles of animal genetics
the goal is improvement of animals
Breed
a group of domestic animals with a homogeneous appearance, behaviour, and other characteristics that distinguish it from other animals of the same species.
Selecting the best animals
no animal is best for all situations
systems approach
knowledge of traits of importance
how performance interacts with factors
eg. physical environment
gene
The basic physical unit of heredity consisting of a DNA sequence and a specific location on a chromosome
locus
the specific location of a gene on a chromosome
Allele
an alternative form of a gene. One of two or more forms of the same gene
sheep karyotype
haploid number= 54
genotype
the combination of genes at a single locus or at a number of loci
homozygote
a one-locus genotype containing functionally identical alleles
heterozygote
a one-locus genotype containing functionally different alleles
genetic variation and mutations
1) chromosomal mutations
deletion, translocation, duplication and inversions
2) gene mutations
substitution, insertion, deletions. frameshifts
transfer of genetic information through cell division
mitosis- multiplication division
meiosis- re-shuffling of alleles, genetic variation
the benefits of sex
increase the rate of adaptive evolution by accelerating the speed at which beneficial mutations sweep through sexual, as apposed to asexual, populations
sexual reproduction
•Over time, genomes accrue mutations that have either a positive or a negative effect on an individual's fitness (relative benefit or cost of each mutation is indicated by size)
•During sexual reproduction, chromosomes are shuffled by recombination, changing the mutations that are grouped together in offspring. This process enables individual mutations to be independently retained or removed by selection.
additive gene addition or co-dominance
type of gene action
performance of the heterozygous animals is exactly intermediate to the two homozygous types
complete dominance
gene action
a form of dominance in which the expression of heterozygote is identical to the expression of the homozygous dominant genotype
partial dominance
gene action
when the effect of one allele is partially, but not completely, masked by the presence of another allele
over dominance
gene action
when heterozygotes show more extreme performance than either homozygote
sex-linked genes
genes that are lactated on the sex chromosome, rather than the autosome
e.g. Inverdale allele
sex limited
gene action
the trait is only shown in one sex
sex influenced genes
some sheep breeds, the male are horned and the females usually polled
genetic imprinting
gene action
epigenetic phenomenon by which certain genes are expressed in a parent-of-origin specific manner = mono-allelic expression.
e.g callipyge genomic locus in sheep