Inhibition and Kinetics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is an inhibitor?
special agents that can bind to enzymes and inhibit or block their activity
competitive inhibition
inhibitor competes with substrate for binding at active site of enzyme
substrate outcompetes inhibitor at high levels of concentration
how does competitive inhibition affect vmax?
vmax stays the same
how does competitive inhibition affect km?
Km increases
uncompetitive inhibition
only binds ES complex not free enzyme
binds at site other than active site after substrate binds
how does uncompetitive inhibition affect vmax?
vmax decreases
how does uncompetitive inhibition affect Km?
Km decreases
non-competitive inhibition
inhibitor binds to allosteric site
can bind to E or ES
prefers to bind to E because of higher affinity
binding doesn’t prevent substrate from binding to enzyme
how does non-competitive inhibition affect vmax?
vmax decrases
how does non-competitive inhibition affect Km?
Km stays the same
mixed inhibition
can bind to E and ES
prefers E
how does mixed inhibition affect vmax?
vmax decreases
how does mixed inhibition affect Km?
Km increases

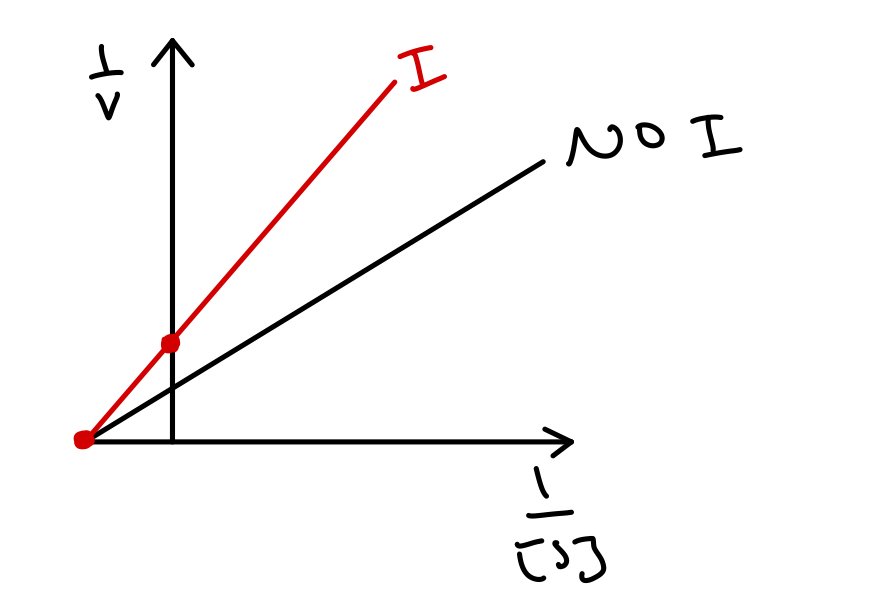
what type of inhibitor does this reciprocal plot represent?
competitive inhibition
what type of inhibitor does this reciprocal plot represent?
non-competitive inhibition
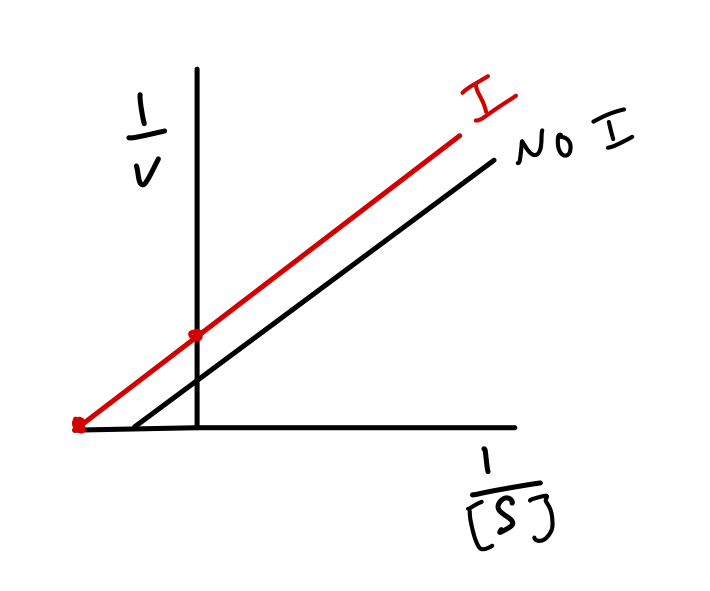
what type of inhibitor does this reciprocal plot represent?
uncompetitive inhibition