Naplex Prep: RxPrep/UWorld - Diabetes
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Which of the following statements about glucagon is correct?
Is produced by the alpha cells in the pancreas and work when BG is low
Hyperglycemia is due to:
decreased insulin secretion
decreased insulin sensitivity
or both
Types of Diabetes:
Type 1
It must be treated with insulin
Absolute insulin deficiency
It is diagnosed with very low or absent C-peptide levels
It is caused by an autoimmune destruction of beta cells in the pancreas
c peptide
produced when insulin is released. t1d have low or none since no insulin is being produced
Type 1 diabetes
Diagnosis (what tests can be done?) + why
Islet antibodies (autoimmune)
C peptide - only produced when insulin is released. So no insulin releasing = low/no c peptide
Types of Diabetes:
Type 2
It is due to insulin deficiency and insulin resistance
Strongly associated with obesity, physical activity, family history and presence of other comorbid conditions
Sarah has been diagnosed with GDM. She has implemented lifestyle modifications but is unable to reach blood glucose goals. what is the preferred treatment in GDM? (after lifestyle)
Insulin is preferred treatment to control blood glucose in a pregnant patient if lifestyle modification are not adequate
Types of Diabetes:
Gestational Diabetes - Management (4)
lifestyle first
insulin is DOC, used if needed
Metformin and glyburide (not preferred, but may be considered)
Types of Diabetes:
Gestational Diabetes - Risks to baby
macrosomia (larger baby)
hypoglycemia at birth
obesity and type 2
Types of Diabetes:
Prediabetes - Treatment Options (broad)
Diet & Exercise
Metformin
Annual Monitoring for Dm and CVD
Types of Diabetes:
Prediabetes - Treatment Options
Who is eligible for Metformin?
BMI > 35
25-59 yrs old
gestational DM Hx
what are the risk factors for type 2 diabetes? 11
age (older)
Physical Inactivity
Overweight (BMI >25 kg/m2 or > 23 kg/m2 in Asian Americans)
High-risk race/ethnicity:
(African American, Latino/Hispanic American, Native American, Asian American or Pacific Islander)
History of gestational diabetes mellitus
A1C > 5.7%
First-degree relative with diabetes
HDL < 35 mg/dL and/or TG > 250 mg/dL
Hypertension(> 140/90 mmHg or taking medication
CVD history or smoking history
Conditions that cause insulin resistance (e.g., acanthosis nigricans, polycystic ovary syndrome)
what are the symptoms of high blood glucose? 7
Polyuria (excessive urination)
Polydipsia (excessive thirst)
Polyphagia (excessive hunger)
Fatigue
Blurry Vision
Erectile Dysfunction
Vaginal Fungal Infection
There are three types of tests used to identify if prediabetes or diabetes is present:
Hemoglobin A1C (or simply A1C) indicates the average BG over approximately the past 3 months
Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) gives the BG at that moment, and is taken after fasting for > 8 hours
The OGTT determines how well glucose is tolerated by measuring the BG level 2 hours after drinking a liquid that is high in sugar
Screening & Testing:
Who should be Tested
everyone with a BMI >/= 25 kg/m2 in (>/= 23 kg/m2 in Asian Americans) + one other risk factor
>/= 35yrs old
symptoms
Diagnostic criteria for diabetes:
A1C: > 6.5%
FPG (mg/dL): > 126
OGTT 2 hr BG (mg/dL): > 200
Diagnostic criteria for pre-diabetes:
alc, fpg, ogtt levels
A1C: 5.7 - 6.4%
FPG (mg/dL): 100 - 125
OGTT 2 hr BG (mg/dL): 140 - 199
Glycemic targets in diabetes - not pregnant
a1c, pre and post prand
A1C: < 7%
Preprandial (mg/dL): 80 - 130
2 - hr PPG (mg/dL): < 180
Glycemic targets in diabetes - pregnant
a1c, pre and post prand
dont use a1c in preg!!
Preprandial (mg/dL): < 95
1 - hr PPG (mg/dL): < 140
2 - hr PPG (mg/dL): < 120
Glycemic control (A1C or another test) should be measured:
Quarterly (every 3 months) if not yet at goal
Biannually (every 6 months or twice per year) if at goal
An A1c of 6% is equivalent to an eAG of _____, with each additional 1% increases the eAG by about ____-
126 mg/dL, 28 mg/dL
HINT: an A1C of 7% is 126 + 28 = 154 eAG
Microvascular diabetes complications includes:
Retinopathy
Diabetic kidney disease (i.e., nephropathy)
Peripheral neuropathy (i.e., loss of sensation, often in the feet), INCREASE risk for foot infections and amputations
Autonomic neuropathy (gastroparesis, loss of bladder control/UTIs, erectile dysfunction)
Macrovascular diabetes complications includes:
Coronary artery disease (CAD), including MI
Cerebrovascular disease including stroke (CVA)
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
DM Anti-platelet Therapy (Aspirin)
Aspirin 75 - 162 mg/day (usually given as 81 mg/day) is recommended for ASCVD secondary prevention (e.g., post MI)
Not recommended for primary prevention
CAD/PAD: aspirin + low dose rivaroxaban can be added
Used in pregnancy to decrease risk of preeclampsia
DM Diabetic Retinopathy monitoring
T2D: eye exam with dilation in diagnosis
If retinopathy repeat annually
Diabetic Neuropathy Treatment
timeline and types of tests that must be done
treatment (3)
Annually: a 10 g monofilament test and 1 other test to assess sensation
Comprehensive foot exam at least annually
Treatment option: Pregabalin (Lyrica), Duloxetine (Cymbalta), Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin)
Vaccines required, in addition to all childhood vaccines:
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Influenza
Pneumovax
age 2-64years: PPSV23 x 1
-- when 65+ years, give another (if 5+ years since previous)
Diabetic Foot Care Counseling
Every day: wash dry and examine feet. Moisturize the top and bottom of feet, but not between the toes
Each office visit: take off shoes to have feet checked
Annual foot exam by a podiatrist
Trim toenails with file; do not leave sharp edges from the clippers
Wear socks and shoes. Elevate feet when sitting
According to the ADA,what is the recommended treatment for cholesterol control?
( who should be treated with high vs mod intensity; add on? how often monitoring?)
High Intensity Statin (Atorvastatin 40 -80 mg or Rosuvastatin 20 - 40 mg daily) for:
Diabetes + ASCVD
Age 50 - 75 years with multiple ASCVD risk factors
Moderate Intensity Statin for:
Diabetes + Age 40 -75 years (no ASCVD)
Diabetes + Age < 40 years + ASCVD risk factors
Add on Treatment (to Maximally Tolerated Statin)
Ezetimibe if ASCVD 10 yr risk > 20%
Icosapent ethyl (Vascepa) if LDL is controlled but TGs are 135 - 499 mg/dL
Monitoring lipid panel annually and 4 -12 weeks after starting a statin or increasing the dose
Comprehensive Care:
weight loss
goal weight loss of ___% of body weight
waist circumference
goal of >/= 5% body weight
waist circumference < 35 inches for females and < 40 inches for males
1 carbohydrate serving = ____ grams
15 grams (1 small fruit, 1 slice of bread, 1/3 cup cooked rice/pasta)
DM Non-Drug Treatment:
Physical activity
150 min/week (over 3 days), with resistance training 2x week
stand q30min
Comprehensive Care:
Cholesterol Control what's high and mod intensity?
high intensity:
- rosuvastatin 20-40 mg
- atorvastatin 40-80 mg
moderate intensity:
- rosuvastatin 5-10 mg
- atorvastatin 10-20 mg
- simvastatin 20-40 mg
Comprehensive Care:
Blood Pressure Control
goal
treatment if albuminuria
no albuminuria
ADA guidelines
- < 130/80 mmHg if higher risk of CVD
- <140/90 mmHg for most
albuminuria
- acei or arb
diabetes and HTN, no albuminuria
- thiazide, CCB, ACEI or ARB
Diabetic Kidney Disease
what and when to check
Check Urine Albumin and eGFR:
Annually if normal kidney function
Twice yearly if reduced kidney function (eGFR 30 - 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or urine albumin > 300)
Which of the following products are likely to be found in over the counter decrease BG products? 3 (are they rec'd?)
Cinnamon
Alpha Lipoic Acid
Chromium
Magnesium
Panax/American Ginseng
NOT rec'd per guidelines
Comprehensive Care:
Bone Health
bone mineral density (DXA scan) q2-3 yrs if >65 or risks
treat if t = <2 or fracture
Treatment algorithm for t2dm
a1c <8.5
8.5-10
>10 (also bg>300, weight loss, sx of hyperglycemia)
dual, mono, etc.
monotx (oral or non insulin injectable)
2 drugs (oral or non insulin injectable)
insulin (regimen can be changed once controlled)
Drug Treatment Options for T2DM:
ASCVD or High risk
1st line
if a1c not at goal
1st line: SGLT2i (dapa, cana, empagliflozin only, if egfr >20) or GLP1 agonist (dulaglutide, lira, SC semaglutide; preferred if egfr <30)
add sglt2i or glp-1 (if not yet started), TZD (NO HF)
Drug Treatment Options for T2DM:
HF
1st line
if cant use
SGLT2i (cana, empag, dapa only, egfr >20)
if eGFR adequate <20
use GLP-1RA with CVD benefit (dula, lira, SC semaglutide)
Drug Treatment Options for T2DM: CKD
1st line
a1c not at goal
1st line: SGLT2i (preferred) (dapa, cana, empagliflozin only, if egfr >20) or GLP1 agonist (dulaglutide, lira, SC semaglutide; preferred if egfr <30)
add glp-1 (if not yet started)
Drug Treatment Options for T2DM:
efficacy for glucose reduction
very high or high efficacy

Drug Treatment Options for T2DM:
efficacy for weight loss
very high or high efficacy
intermediate
neutral
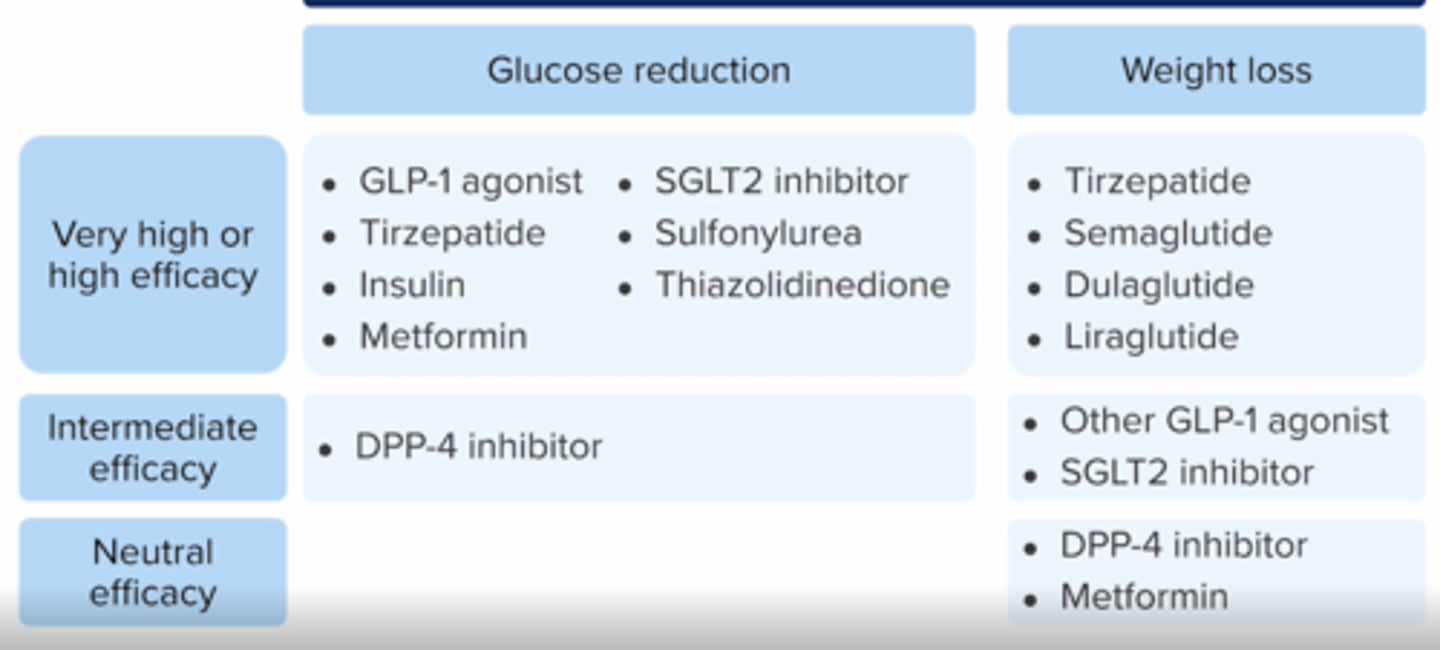
Drug Treatment Options for T2DM:
Minimize hypoglycemia
use: dpp4-i, glp1-ra, SGLT2i, TZD
A1C > 6.5%: add different class from above; keep adding
Drug treatment options for T2DM:
combos to avoid + why
DPP4i + glp1 (both increase glp1 hormones)
SU + insulin ( high risk of hypoglycemia)
What is the mechanism of action of Metformin
(Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Fortamet, Glumetza, Riomet)?
DECREASING hepatic glucose production, DECREASING intestinal absorption of glucose and INCREASING insulin sensitivity
meftformin effect on alc
1-2%, weight neutral, no hypoglycemia
Metformin has many boxed warnings, including which of the following?
Lactic Acidosis - risk INCREASE with renal impairment , Contrast dye, Excessive alcohol
Metformin has many contraindications, including which of the following? (2)
eGFR < 30
Acute or Chronic Metabolic Acidosis
Metformin is not recommended to start if eGFR is _____
30 -45
Side effects of Metformin includes:
GI Effect: Diarrhea, Nausea, Flatulence, and Cramping, Vitamin B12 deficiency (cobalamin)
what lab should be monitored (deficiency) when metformin is used long term?
Can cause vitamin b12 deficiency when used long term
monitor q1-2 years
Metformin levels may increase with _____
kidney impairment
decreased fxn = increased metformin (primarily eliminated through kidney)
Which of the formulations of metformin should patients be informed about a ghost capsule in the stool?
er formulations ->
Glumetza
Fortamet
Glucophage XR,
True or False: Intravacular iodinated contrast media can INCREASE risk of lactic acidosis. Discontinue Metformin before the imaging procedure. Metformin can be restarted 48 hours after procedure if eGFR is stable.
True
True or False: The combination of Metformin and Topiramate can INCREASE the risk of metabolic acidosis
True
Metformin (Fortamet
Glumetza)
initial dosing
titrating
max
1000mg BID = 2000mg/day

KH has just been started on Metformin. How should she be counseled to take it?
with a meal to decrease GI side effects
What are the SGLT2i drugs?
the flozins
canagliflozins (invokana)
dapagliflozin (farxiga)
empagliflozin (Jardiance)
ertugliflozin
bexagliflozin
SGLT2I:
effect on a1c
decrease by 0.7-1% with minimal hypoglycemia, unless w insulin
What is the mechanism of action of the Sodium Glucose Co - Transporter 2 Inhibitors [Canagliflozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), Empagliflozin (Jardiance), Ertugliflozin (Steglatro)]?
Expressed in the proximal renal tubules, is responsible for the reabsorption of filtered glucose
Reduce reabsorption of glucose and INCREASE urinary glucose excretion and thereby DECREASING blood glucose concentrations
Sodium Glucose Co - Transporter 2 Inhibitors [Canagliflozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), Empagliflozin (Jardiance), Ertugliflozin (Steglatro)]
when to avoid in kidney dx? (egfr)
<20
Sodium Glucose Co - Transporter 2 Inhibitors [Canagliflozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), Empagliflozin (Jardiance), Ertugliflozin (Steglatro)] has many warnings, including which of the following? (7)
Ketoacidosis
Gential Mycotic Infections
Urosepsis
Pyelonephritis
Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum
Hypotension
Acute Kidney Injury
Side effects of Sodium Glucose Co - Transporter 2 Inhibitors [Canagliflozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), Empagliflozin (Jardiance), Ertugliflozin (Steglatro)] includes:
Weight Loss
INCREASE Urination
INCREASE Thirst
Hypoglycemia (low risk)
INCREASE Mg/PO4
Canaglifozin (Invokana) has additional safety concerns compared to other agents in its class. Which of the following safety concerns are specific for Canaglifozin (Invokana)?
Increased risk of leg and foot amputations, hyperkalemia risk, and risk of fractures
True or False: Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), Empagliflozin (Jardiance), and Ertugliflozin (Steglatro)] are contraindicated in patients with a eGFR < 30
True
True or False: Canaglifozin (Invokana), Dapagliflozin (Farxiga), and Empagliflozin (Jardiance) have shown reductions in HF and CKD progression
True
SGLT2i - drug interactions
which drugs should be used with caution/monitored?
diuretics
raas inhibitors
NSAIDs
increase volume depletion -> aki, hypotn
What is the mechanism of action of the Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-l) agonists [Liraglutide (Victoza), Dulaglutide (Trulicity), Exenatide (Byetta), Semaglutide (Ozempic), Exenatide extended release (Bydureon, Bydureon BCise, Lixisenatide (Adlyxin)]?
INCREASE glucose-dependent insulin secretion, DECREASE glucagon secretion, slows gastric emptying, improves satiety and can result in weight loss
Which GLP1/glp-gip are for T2Dm and which are for weight loss only?
Liraglutide
- Victoza DM
-Saxenda - Weight Loss (WL)
Semaglutide
-Ozempic Rybelsus (oral version) DM
- Wegovy WL
gip/glp: Tirzepatide
-Mounjaro DM
-Zepbound WL
DM ONLY
Dulaglutide (Trulicity)
Exenatide (Byetta)
Exenatide extended release (Bydureon, Bydureon BCise)
Lixisenatide (Adlyxin)
Which of the following GLP-1 agonist have a boxed warning risk of thyroid C- cell carcinomas?
All except Exenatide (Byetta) and Lixisenatide (Adlyxin)
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-l) agonists [Liraglutide (Victoza), Dulaglutide (Trulicity), Exenatide (Byetta), Semaglutide (Ozempic), Exenatide extended release (Bydureon, Bydureon BCise, Lixisenatide (Adlyxin)] has many warnings, including which of the following?
Pancreatitis
Not recommended in patients with severe GI disease, including Gastroparesis
Patients using Liraglutide (Victoza) should be counseled regarding the rare, but possible risk of:
Pancreatitis
A patient has a new prescription for Exenatide ER (Bydureon). The pharmacist should counsel that the drug can cause which adverse effect:
Serious injection site reaction (e.g., abscess, cellulitis, necrosis) with or without SC nodules
Which of the following statements are true concerning [Liraglutide (Victoza), Dulaglutide (Trulicity), Exenatide (Byetta), Semaglutide (Ozempic), Exenatide extended release (Bydureon, Bydureon BCise, Lixisenatide (Adlyxin)]?
do not use with ____
which have ascvd benefit
Do not use with DPP-4 inhibitors
Liraglutide (Victoza), Dulaglutide (Trulicity), Exenatide (Byetta), Semaglutide (Ozempic) have demonstrated ASCVD benefit
Sam has a new prescription for Exenatide (Byetta). How should she be counseled to take this medication?
Take twice daily, within 60 minutes of your meals
Which GLP -1 agonists requires a separate purchase of pen needles? (HINT: ELL)
Exenatide (Byetta)
Liraglutide (Victoza)
Lixisenatide (Adlyxin)
Sulfonylureas (SUs) and meglitinides are known as ____________; they work by :____
what must be present for these drugs to work?
insulin secretagogues
stimulating insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cells to decrease postprandial blood glucose
Pancreas MUST still be able to make insulin for drugs to work!!
Insulin secretagogues:
SUs and meglitinifes are most helpful on what type of glucose levels (pre/post prandial, long ating, etc)
POST prandial
bc the body needs help to produce enough insulin to handle the influx of glucose
Insulin Secretagogues: Sulfonylureas
Glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL, Glipizide XL)
Glimerpiride (Amaryl)
Glyburide
micronized glyburide (glynase)
Insulin Secretagogues:
meglitinides
repaglinide
nateglinide
Insulin secretagogues:
differences b/t SUs and meglitiniddes
onset/duration of action; how to remember generic names , a1c decrease
SUs
longer acting
start with g, end with ide
a1c: decrease 1-2%
meglitinides
shorter
end in glinide
a1c: decrease 0.5-1.5
What is the mechanism of action of Glimepiride (Amaryl)?
Stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta cells to decrease postprandial BG
Patients should avoid Sulfonylureas (SUs) [Glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL), Glimepiride (Amaryl), Glyburide, Micronized Glyburide (Glynase)] if they have:
sulfa allergy
Insulin Secretagogues:
What are possible side effects from these medication?
Hypoglycemia (glucose independent!!)
Weight gain
Nausea
Which of the following statements are true concerning Sulfonylureas [Glipizide (Glucotrol, Glucotrol XL), Glimepiride (Amaryl), Glyburide, Micronized Glyburide (Glynase)]?
which SUs have longer acting and increase risk of hypoglycemia? (hint: beers criteria)
which formulation may have a ghost tablet?
Glimepiride (Amaryl) and Glyburide is not preferred in elderly due to hypoglycemia risk
Glipizide (Glucotrol XL) îs an OROS formulation and can leave a ghost tablet in the stool
Insulin Secretagogues:
SUs;meglitinides
how are they taken? any exceptions?
SUs:
with 1ST meal of day, HOLD IF NPO (HYPOGLYCEMIA!!)
Glipizide IR should be taken 30 mins before a meal
meglitinides:
short acting - take 30 min before EVERY MEAL (up to tid)
can skip if skip a meal
Side effects of Meglitinides [Repaglinide
(Prandin) and Nateglinide (Starlix)] includes:
Hypoglycemia
Weight gain
Headache
URTIs
Sam has a new prescription for Repaglinide
(Prandin) 1 mg TID #30. How should the pharmacist counsel the patient to take the medications?
If you plan to skip a meal, skip the dose for that meal
Take your dose 15 - 30 minutes prior to a meal
SUs and meglitinides should NOT be taken with :
INSULIN!
meglitinides:
Repaglinide (Prandin) is contraindicated with
Gemfibrozil and Clopidogrel
DPP4i:
which ones? 4
sitagliptin (januvia)
Linaglitpin (tradjenta)
saxagliptin (onglyza)
Alogliptin (nesina)
What is the mechanism of action of the Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors [Sitagliptin (Januvia), Linagliptin (Tradjenta), Saxagliptin (Onglyza), Alogliptin (Nesina)]
Prevent the enzyme DPP-4 from breaking down incretin hormones, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-l) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)
Help to regulate blood glucose levels by INCREASING insulin release from the pancreatic beta cells and DECREASING glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha cells
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors [Sitagliptin (Januvia), Linagliptin (Tradjenta), Saxagliptin (Onglyza), Alogliptin (Nesina)] has many warnings, including which of the following?
Pancreatitis (if have hx of alcoholism or hypertriglyceridemia use w caution)
Severe Arthralgia (joint pain)
Acute Renal Failure (rare)
which dpp4i is NOT renally cleared (doesn't need renal adjustments)?
linagliptin (tradjenta)
what are specific risks/warnings for saxagliptin and alogliptin (dpp4is)?
risk of HF for both, but warning added to whole class
risk of hepatotoxicity for alogliptin only
DPP4i have a (low/high) risk for hypoglycemia
low risk. increase insulin secretion. glucose dependent so if no glucose (food) present, then no insulin there.
What is the mechanism of action of the Thiazolidinediones [Pioglitazone, (Actos) Rosiglitazone (Avandia)]?
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARy) agonists that cause INCREASE peripheral insulin sensitivity (INCREASE uptake and utilization of glucose by the peripheral tissues, also known as insulin sensitizers)
what are the TZDs?
Pioglitazone (Actos)
TZDs effect on a1c
decrease 0.5-1.4%