BIOL 120 Final Exam
1/531
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
532 Terms
A __________ is information from the environment that is converted to a sensory signal in the body.
Stimulus
A __________ is a cell that is capable of detecting stimuli and communicating this information to the central nervous system.
Sensory receptor
__________ is the conversion of an environmental stimulus (such as light energy) to an electrical communication system within the body.
Sensory transduction
A __________ is a series of proteins within a cell that passes a signal along from one molecule to another until a final reaction occurs.
Signal transduction pathway
__________ is the tendency for repeated stimuli to become less noticed over time.
Sensory adaptation
Which part of the eye gives the eye its color?
Iris
When light levels suddenly increase, our eyes adjust quickly by reducing the size of the __________.
Pupil
The receptor potential is the __________.
Membrane potential produced in the receptor cell by sensory transduction
__________ is an example of sensory adaptation.
Ignoring the feeling of shoes on your feet
In all types of chemoreceptors, receptor cells develop receptor potentials in response to __________.
Chemicals dissolved in fluid such as blood or saliva
Standing out in center field, a baseball player watches a hitter's bat strike the ball and then, slightly later, hears the sound of the impact. What types of sensory receptors did the player just use?
Photoreceptors and mechanoreceptors
Thermoreceptors detect __________.
Temperature
A person who cannot focus well on distant objects has __________.
Nearsightedness
A person who has blurred vision caused by a misshapen lens or cornea has __________.
Astigmatism
A person whose eyeball is shorter than normal suffers from __________.
Farsightedness
Sensory receptors are located in and sound is detected in the __________.
Cochlea
A thermoreceptor in the skin converts heat energy to nerve impulses. This conversion is called __________.
Sensory transduction
The following is an example of what? After two hours of driving the neighborhood ice cream van, you no longer hear the chimes
Sensory adaptation
As light passes into the human eye, it goes through a/an/the __________ first.
Cornea
Which sense is based on detection of electromagnetic activity?
Vision/sight
Fill in the blanks: All animals respond to __________, which are signals from the environment such as light and sound. This response, which can happen very quickly, requires several steps. First, cells called __________ within sensory organs must detect a stimulus. To be communicated throughout the animal body, the sensory information must undergo a process called __________, which converts the sensory information into electrical impulses. The electrical impulses travel as __________ along neurons. The data from the electrical signal is ultimately passed to the __________, which processes the information and formulates a response, such as the movement of a muscle.
Stimuli…sensory receptors…sensory transduction…action potentials…central nervous system
What is the correct order of the parts of the vertebrae eye when light strikes it as it enters the eye?
Cornea, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor, retina
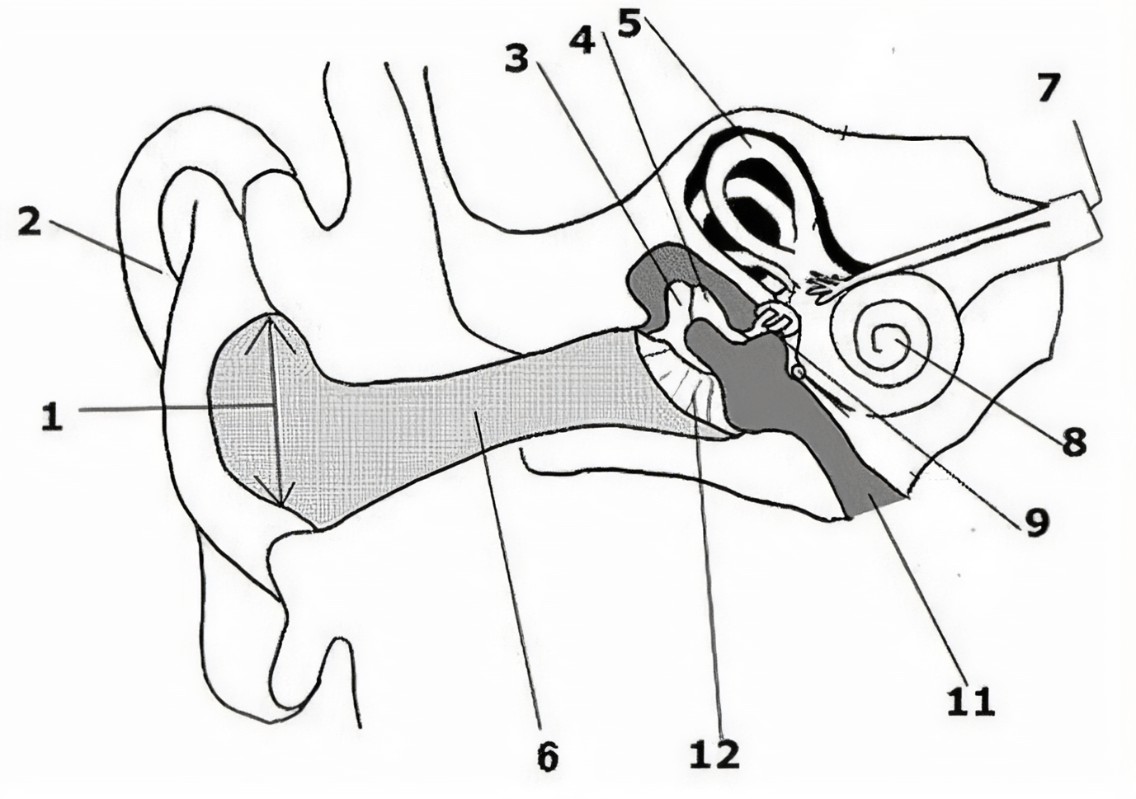
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 1?
Ear drum
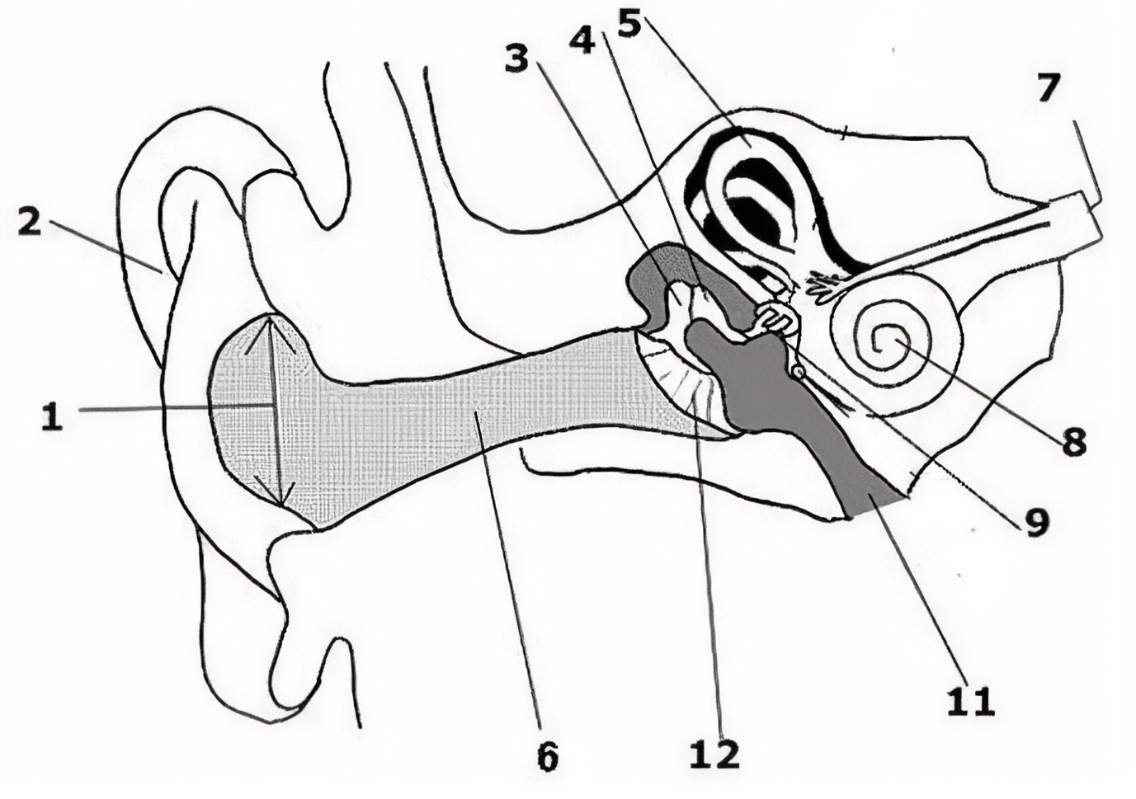
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 2?
Pinna (auricle)
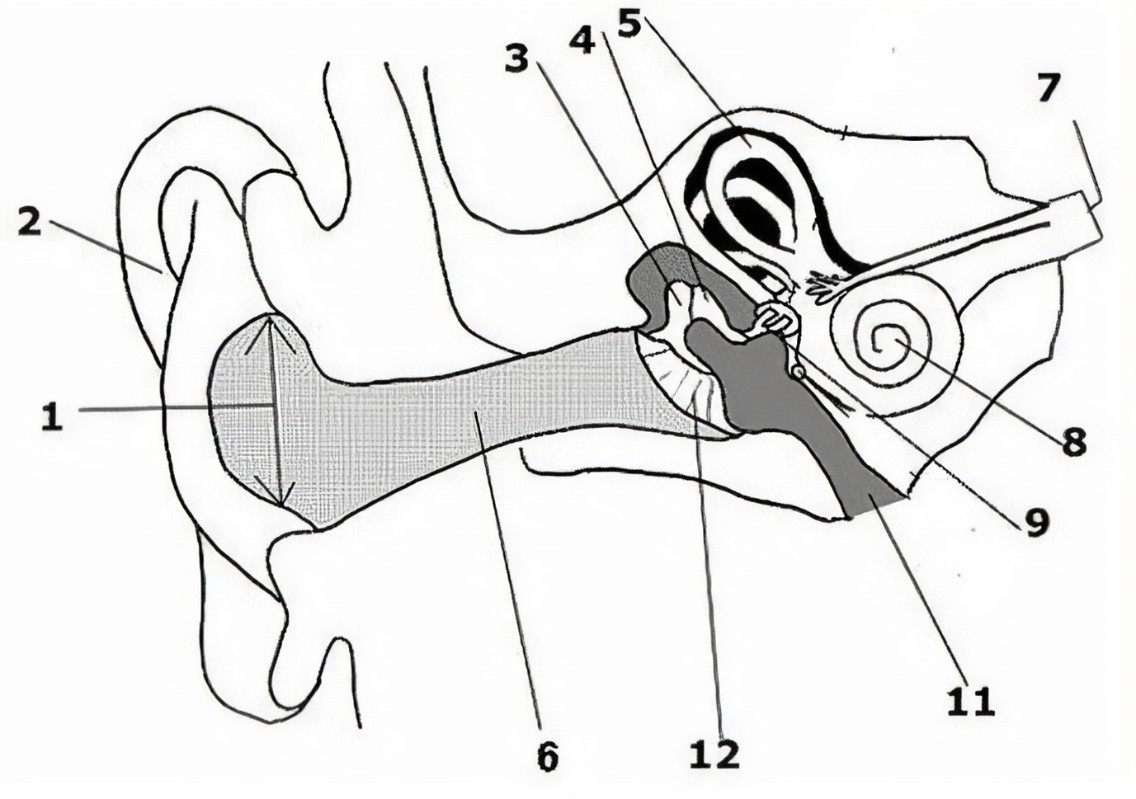
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 3?*
Incus*
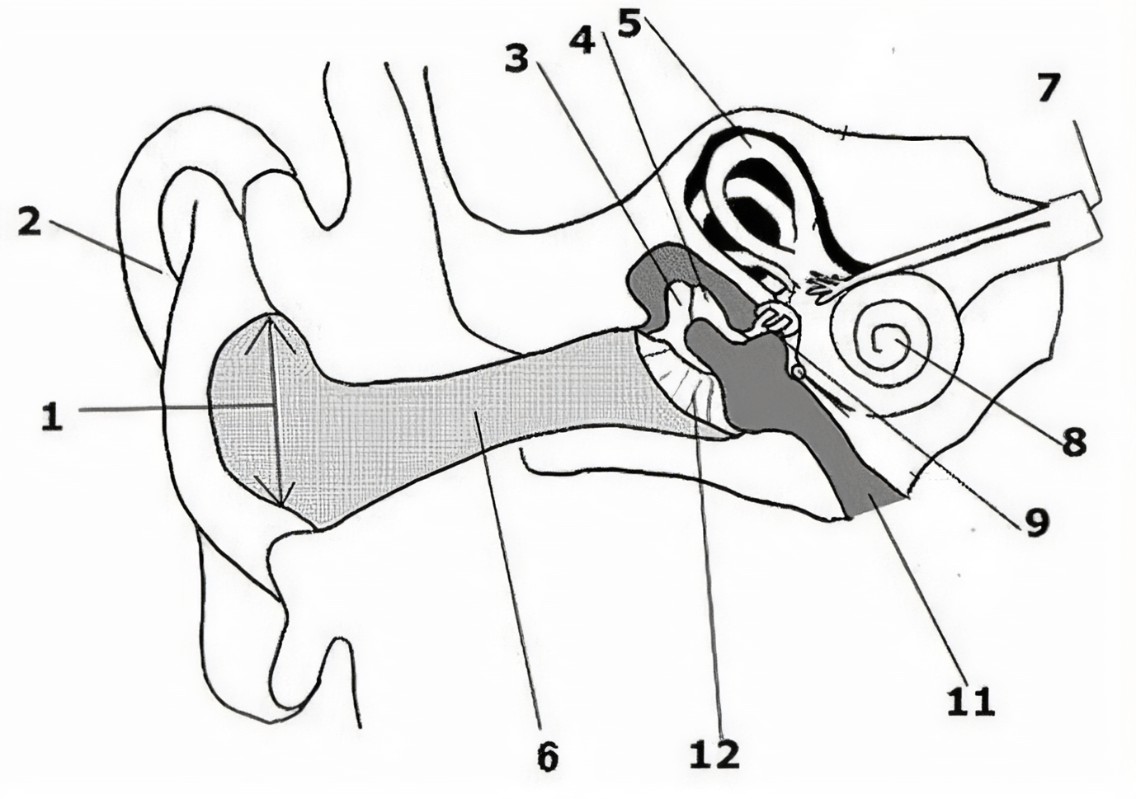
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 4?*
Semicircular canals*
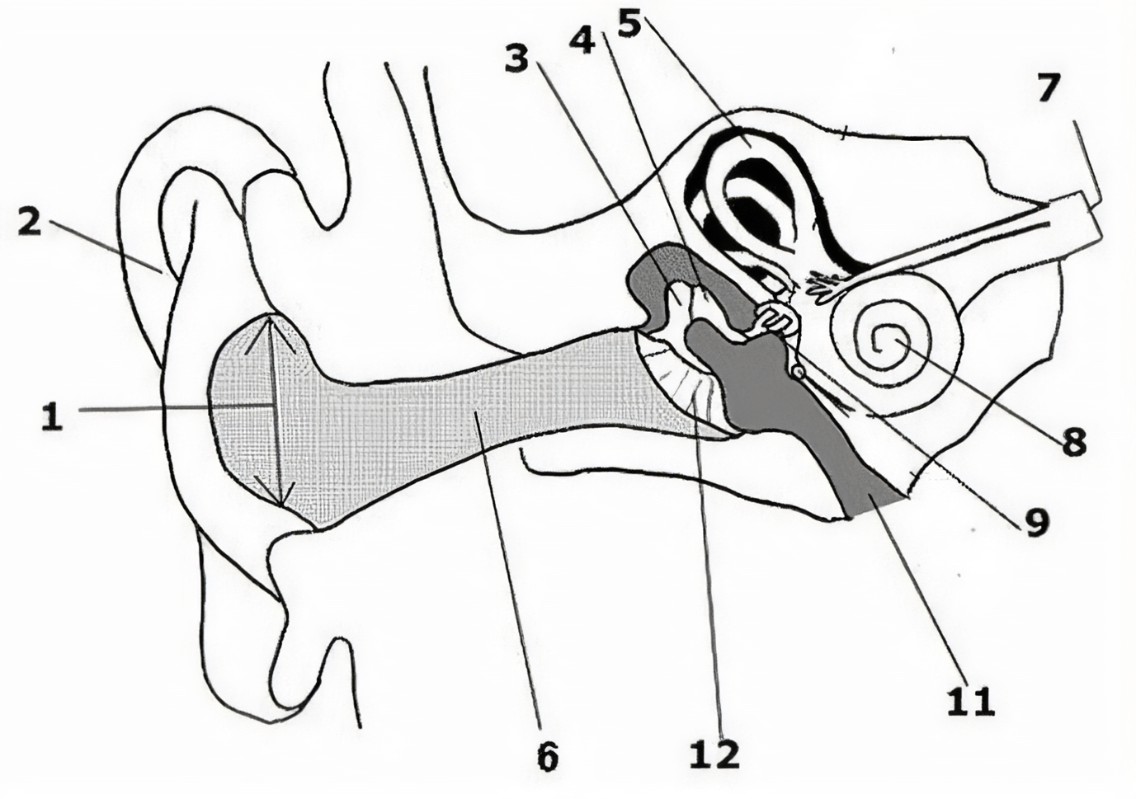
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 5?*
Vestibular nerve*
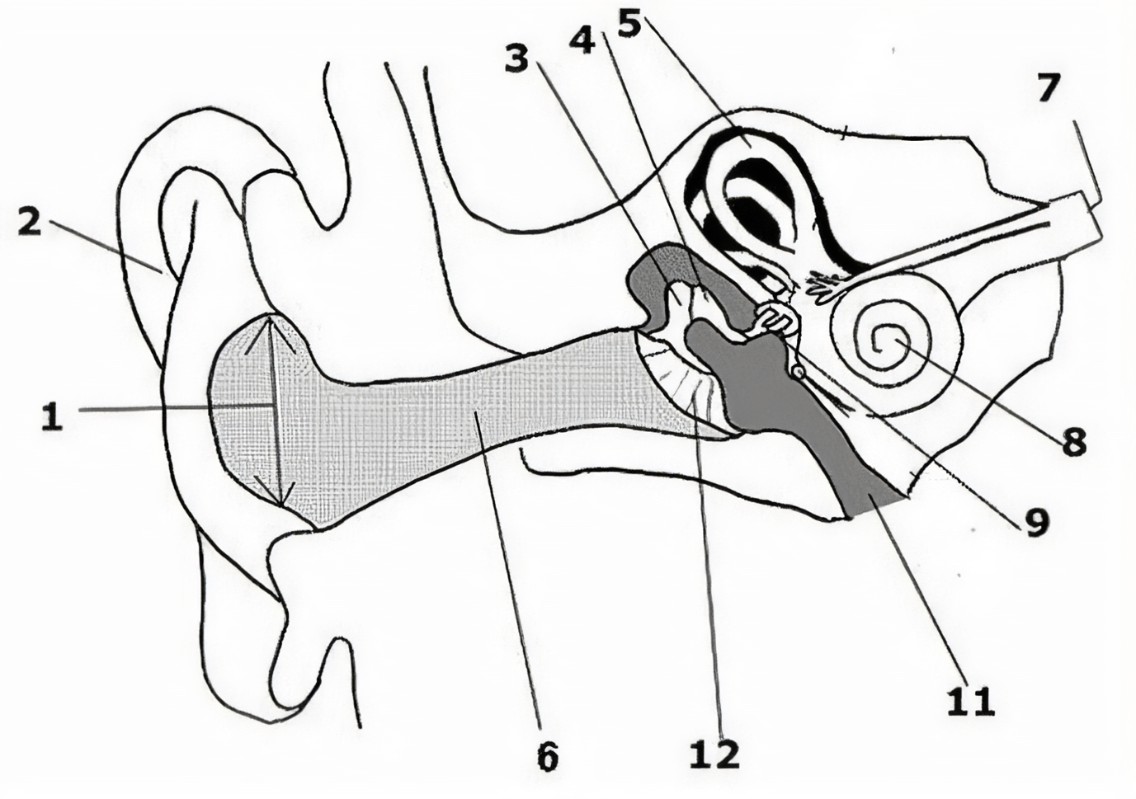
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 6?*
Cochlear nerve*
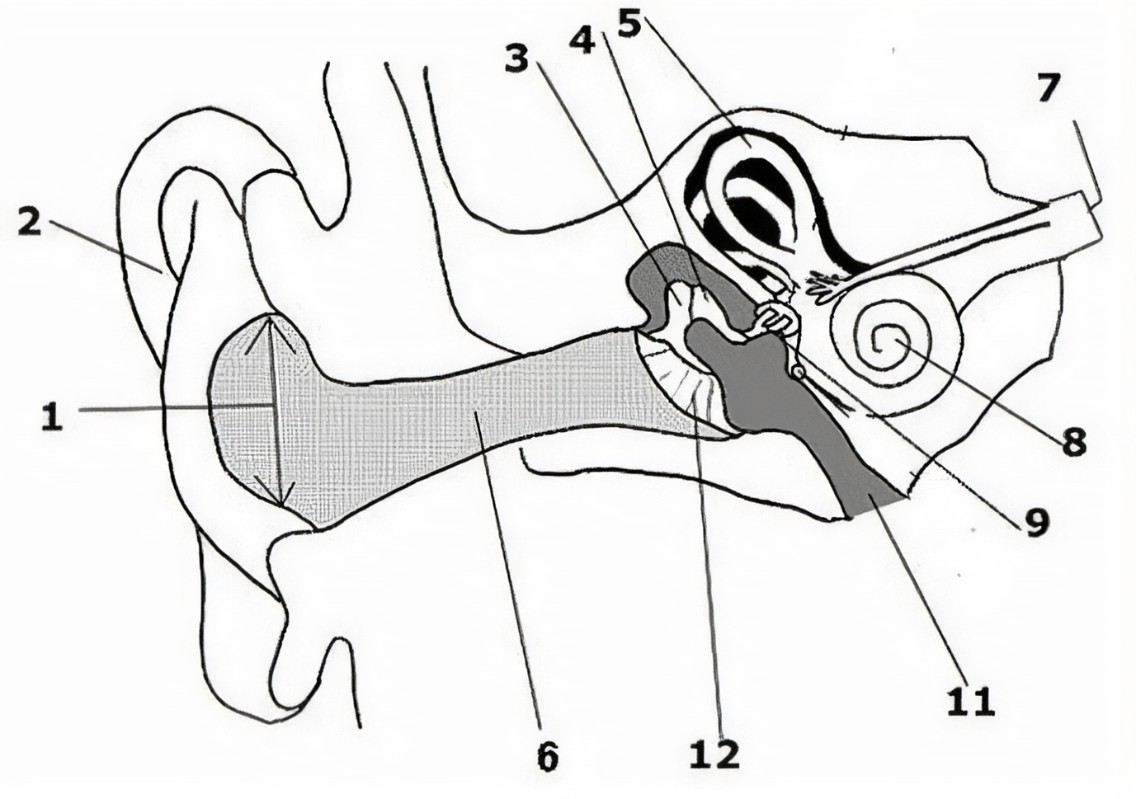
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 7?
Cochlea
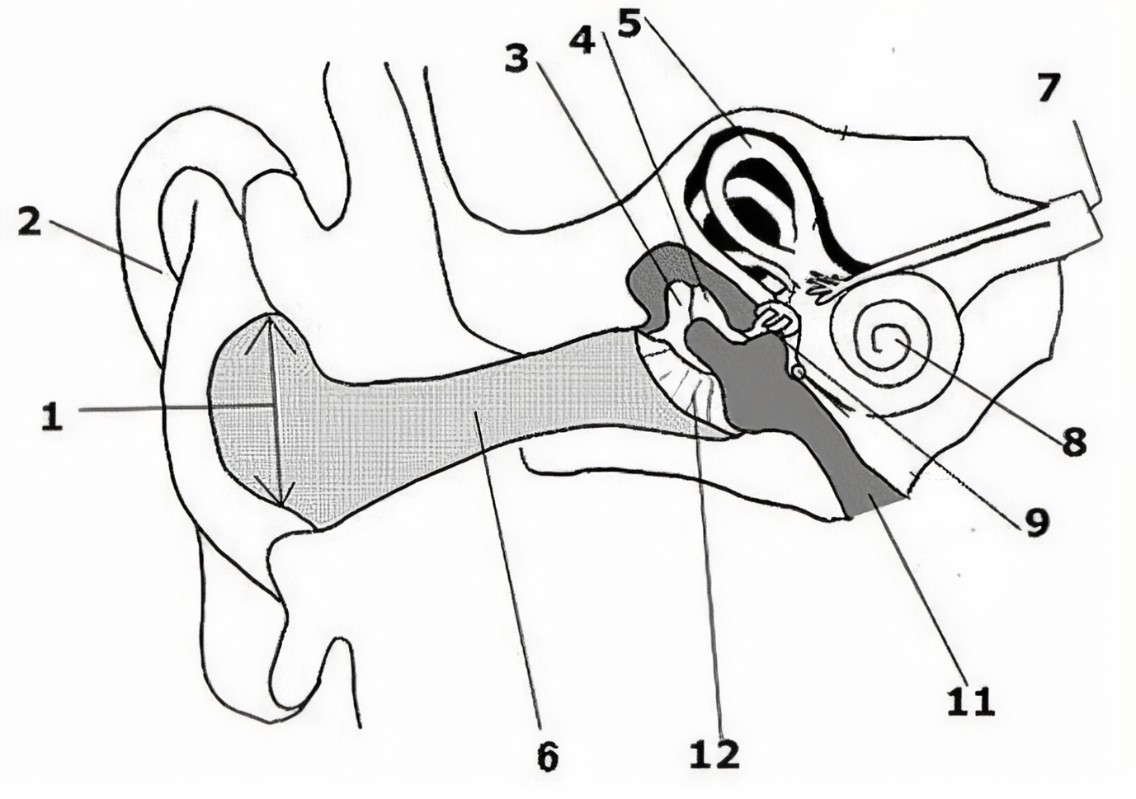
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 8?*
Eustachian tube*
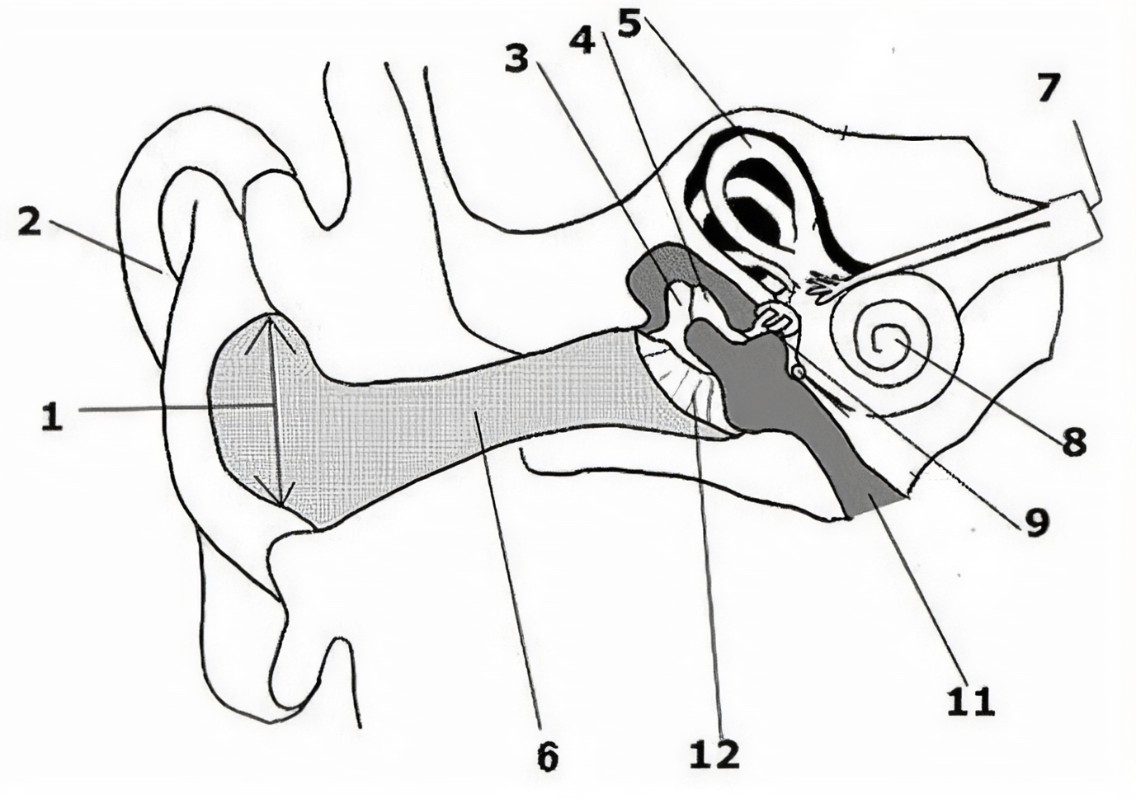
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 9?*
Round window*
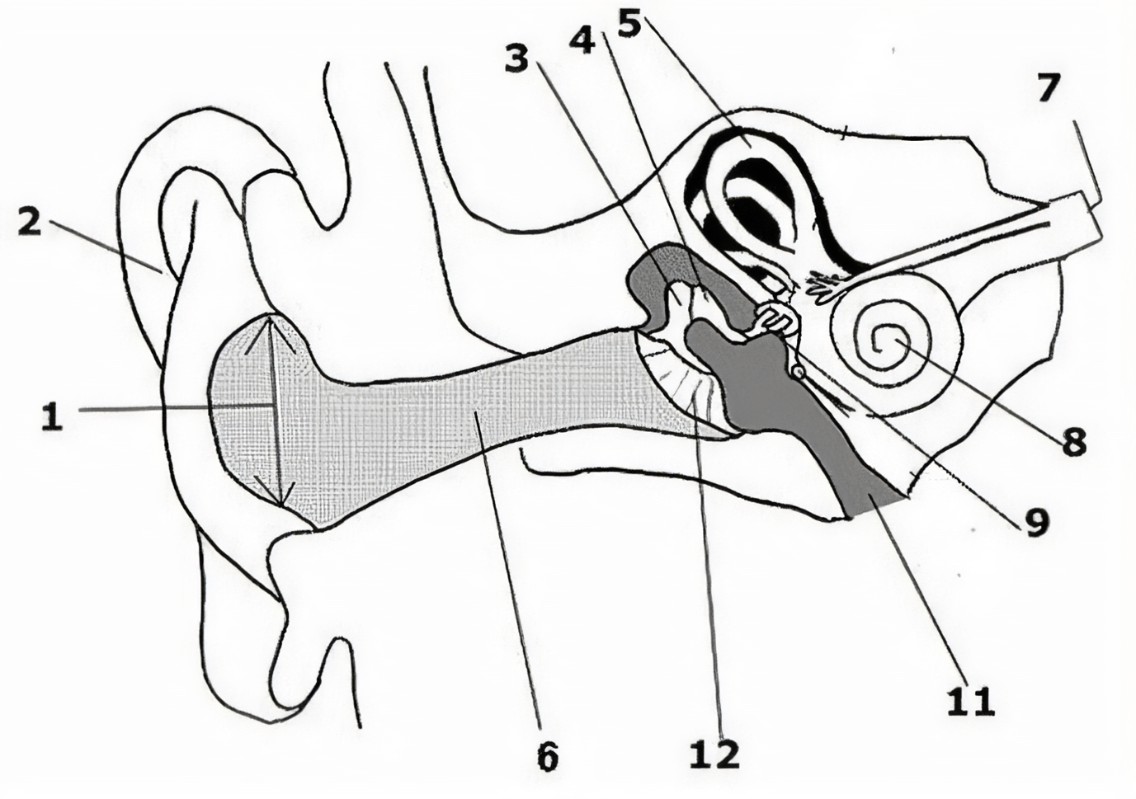
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 10?*
Stapes*
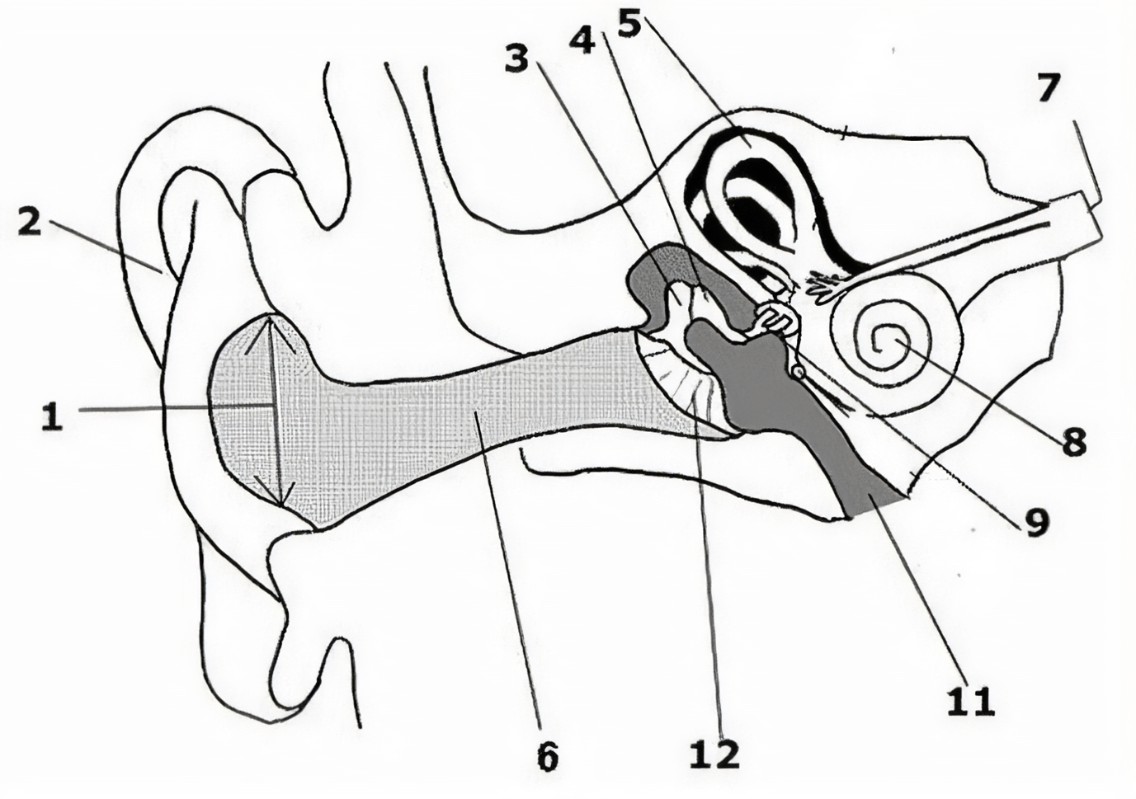
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 11?*
Tympanic cavity (middle ear)*
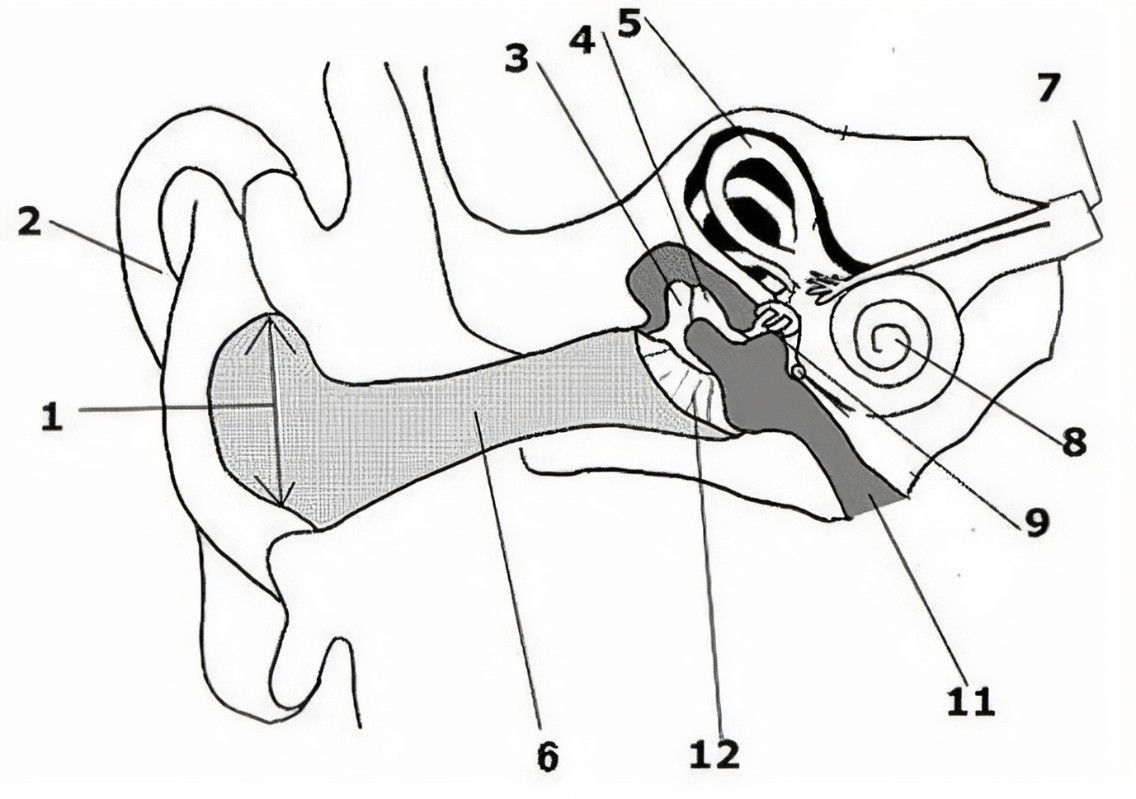
What is the name of the part of the ear corresponding with label 12?*
External auditory canal*
What is the first part of the outer ear?
Auricle (pinna)
What is the last part of the outer ear?*
Eardrum*
How many bones does the middle ear contain?
Three
What are the names of the bones in the middle ear? (Hint: there are three!)
Malleus, incus, stapes
What is the last part of the middle ear?
Stapes
What is the liquid of the inner ear called?*
Perilymph*
Where in the human body is the inner ear found?*
The temporal bone of the skull*
What separates the middle and outer ear?*
The oval and round windows*
What nerve connects the inner ear to the brain?*
The vestibulocochlear nerve*
What is the name for the white of the eye?
Sclera
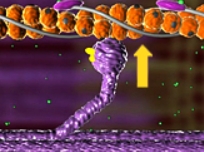
What stage of the sliding-filament model is shown here?
Bind
What occurs in the ‘bind’ stage of the sliding-filament model?
The myosin head binds to actin
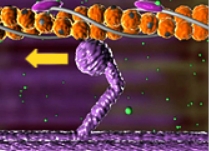
What stage of the sliding-filament model is shown here?
Power stroke
What occurs in the ‘power stroke’ stage of the sliding-filament model?
The myosin head pulls the actin filament. This shortens the sarcomere.
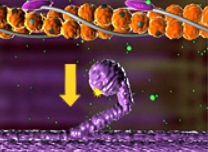
What stage of the sliding-filament model is shown here?
Detach
What occurs in the ‘detach’ stage of the sliding-filament model?
ATP binds to the myosin head. The myosin head is released from the actin filament.
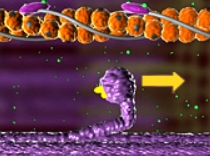
What stage of the sliding-filament model is shown here?
Extend
What occurs in the ‘extend’ stage of the sliding-filament model?
The breakdown of ATP causes the myosin head to extend.
Fill in the blanks: When you bend your elbow, a muscle that is connected to the forearm bone by __________ pulls the forearm toward the shoulder. The upper arm bone is connected to the forearm bone by __________, forming a __________ joint, which moves only in one plane. Rotation at the elbow is enabled by a __________ joint between the upper and lower arm bones. The shoulder has a greater range of movement than the elbow because of the __________ joint where the upper arm joins the shoulder blade.
Tendons…ligaments…hinge…pivot…ball-and-socket
Which part of the bone contains/stores fat?
Yellow bone marrow
The joint that allows you to rotate your forearm so that your hand changes from a palm up position to a palm down position must be a __________ joint.
Pivot
What best helps a broken bone heal?
Returning the broken bone parts back to their natural shape and them immobilizing the bone
Muscles are connected to bones by __________.
Tendons
Functionally, what is the muscle fiber’s fundamental unit of contraction?
Sarcomere
A thick filament is made up of __________.
Myosin
According to the sliding-filament model of muscle contraction, a sarcomere contracts when its __________.
Thin and thick filaments slide past each other
What structure would probably have the largest motor units?
A motor unit in the thigh to control leg movements
A(n) __________ is the contractile unit of the skeletal muscle.
Sarcomere
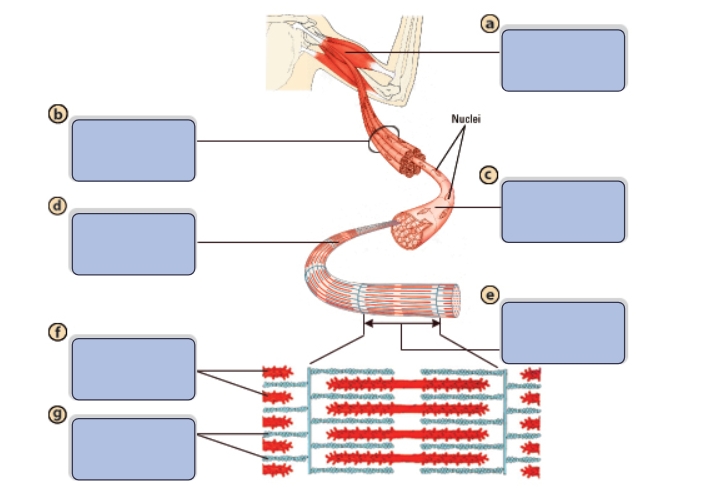
What is the name of structure a?
Muscle
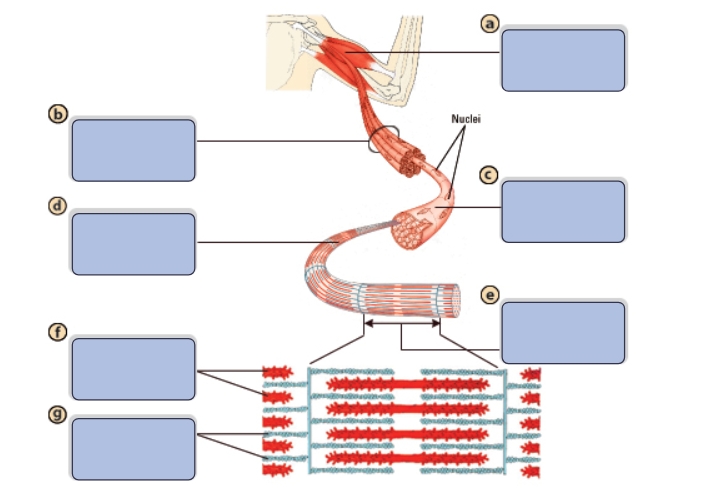
What is the name of structure b?
Bundle of muscle fibers
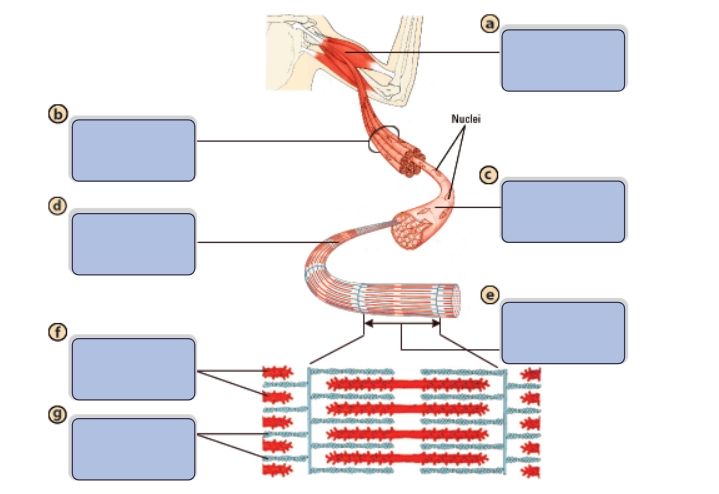
What is the name of structure c?
Single muscle fiber (cell)
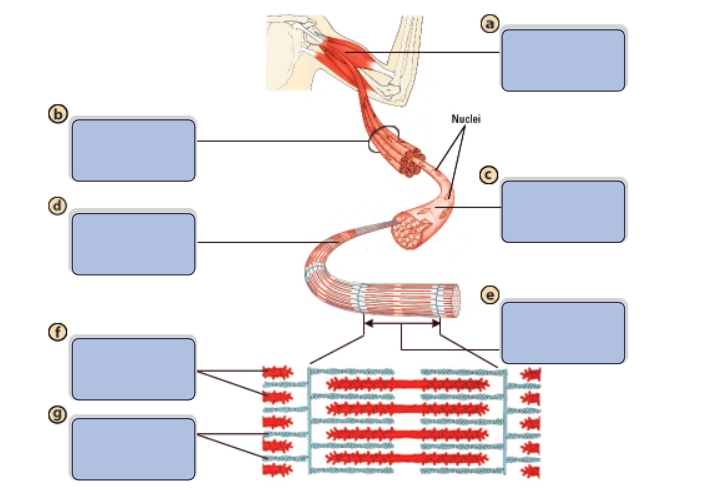
What is the name of structure d?
Myofibril
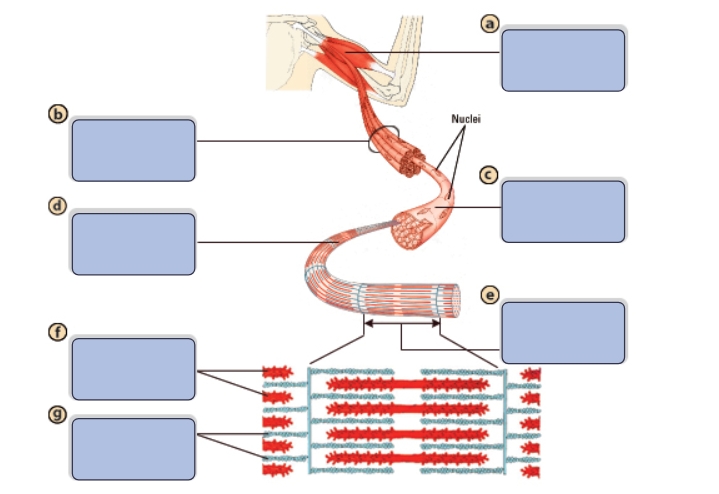
What is the name of structure e?
Sarcomere
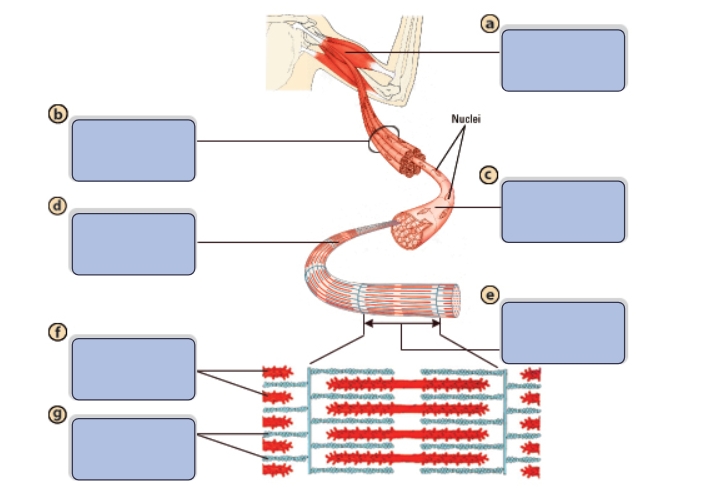
What is the name of structure f?
Myosin (thick filaments)
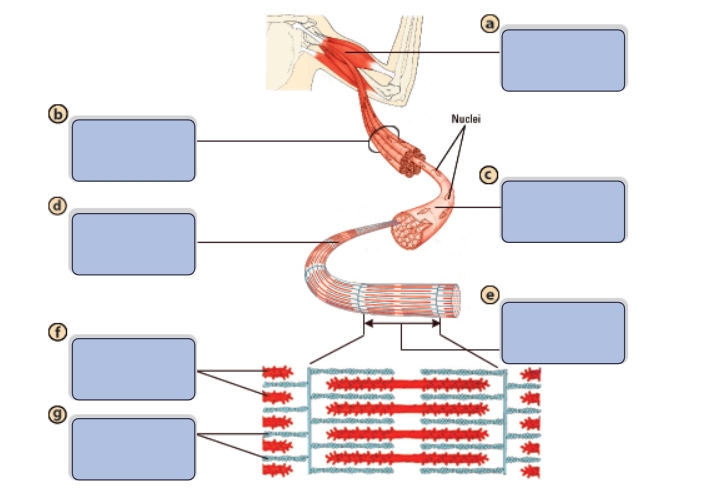
What is the name of structure g?
Actin (thin filaments)
A muscle consists of many long fibers called __________.
Muscle fibers
Muscle fibers have bundles of proteins called __________.
Myofibrils
Myofibrils have contractile units called __________.
Sarcomeres
Sarcomeres are arranged in bands of __________ and __________ __________.
Thin…thick filaments
Thin filaments are made up of __________.
Actin
In general, hormones that bind to plasma membrane receptors __________.
Cannot pass through cell membranes
When a cell responds to a particular steroid hormone it would be expected to have __________.
A receptor inside the cell that binds the hormone
Which system usually transports hormones?
The circulatory system
Why do only some cells have a response to a hormone that is transported throughout the entire body?
Only some cells have the receptors for any particular hormone
Which gland secretes releasing hormones?
The hypothalamus
Which hormone(s) is/are responsible for the “fight-or-flight” response to danger?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) triggers the release of __________ in response to stress.
Glucocorticoids
__________ are the main male hormones.
Androgens
What hormone promotes water retention by the kidneys?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Which hormone opposes the action of parathyroid hormone?
Calcitonin
Which hormone stimulates hormone production by the ovaries and testes?
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Which hormone stimulates milk production?
Prolactin
In __________ diabetes, target cells do not respond normally to insulin.
Type 2
In __________ diabetes, no insulin is produced.
Type 1
In __________ diabetes, glucose levels remain higher than normal.
Both type 1 and type 2
What is the correct order of the sequence of events that occur in the body after eating a sugary snack?
Blood glucose becomes high…pancreas releases insulin…insulin binds to receptors on target cells…cell takes in glucose…blood glucose returns to normal
The hypothalamus is part of what?
The brain
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is made by the __________ and released by the __________.
Hypothalamus…posterior pituitary
Which structure exerts primary regulation of the concentration of sugar in the blood?
Pancreas
What hormone causes a rise in the concentration of glucose in the blood?
Glucagon
Which gland is located near the kidneys?
Adrenal glands
In the presence of stress, which gland is most likely to be active?
Adrenal
The development of __________ may be stimulated by estrogen.
Breasts
The hypothalamus is the master control center of the __________ system.
Endocrine
You look down on the trail where you have been hiking. A rattlesnake is coiled and rattling its tail. Which of the following hormones is likely to be one of the first secreted as a direct response to this situation?
Epinephrine
Which hormone can relieve swelling and pain from inflammation but will also suppress immunity?
Cortisol