Pathophysiology Exam 3
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:27 AM on 10/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
leukemia
-Cancer of white blood cells
-Acute is rapid onset, chronic is usually noticed via blood count
-can occur at different locations along the differentiation cascade
-produces immature cells
-Acute is rapid onset, chronic is usually noticed via blood count
-can occur at different locations along the differentiation cascade
-produces immature cells
2
New cards
acute lymphocytic leukemia
-most common in children
-affect the lymphocytic line in the bone marrow
-majority are B cell in origin in young adults and children (80%)
-20% is T cell in origin
-affect the lymphocytic line in the bone marrow
-majority are B cell in origin in young adults and children (80%)
-20% is T cell in origin
3
New cards
acute myelocytic leukemia
-often associated with deletion of 5q
-petechiae is usually present
-echymoses
-orificial bleeding (abnormal bleeding causes low platelets and RBC with elevated WBC)
-at risk for infection because WBC are immature
-petechiae is usually present
-echymoses
-orificial bleeding (abnormal bleeding causes low platelets and RBC with elevated WBC)
-at risk for infection because WBC are immature
4
New cards
Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia
-philadelphia chromosome translocation between chromosome 9 and 22
-abnormal and excessive accumulation and overgrowth of mature granulocytes in the bone marrow
-predominantly a disorder of adults, but can affect children
-abnormal and excessive accumulation and overgrowth of mature granulocytes in the bone marrow
-predominantly a disorder of adults, but can affect children
5
New cards
Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia stages
-chronic (2-8 years)
-accelerated (granulocytes increase)
-acute or blast crisis (orificial bleeding, fatigue, ineffective WBC)
-accelerated (granulocytes increase)
-acute or blast crisis (orificial bleeding, fatigue, ineffective WBC)
6
New cards
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
-incompetent lymphocytes
-usually a disease of older males
-75% survival rate, usually involves lymph nodes like spleen/liver
-usually a disease of older males
-75% survival rate, usually involves lymph nodes like spleen/liver
7
New cards
etiology of leukemia
-exact cause is unknown (idiopathic)
-chemical: exposure to benzene, chemotherapy medications, methyl methacrylate
-viral (retroviruses)
-radiation: hiroshima, chernobyl have increased incidence (radiation eliminates bones)
-genetic (Philadelphia chromosome, trisomy 21)
-chemical: exposure to benzene, chemotherapy medications, methyl methacrylate
-viral (retroviruses)
-radiation: hiroshima, chernobyl have increased incidence (radiation eliminates bones)
-genetic (Philadelphia chromosome, trisomy 21)
8
New cards
leukemia pathogenesis
excessive production of one cell line decreases production of other cell lines producing erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
9
New cards
Leukemia manifestations
-anemia (pallor, fatigue, malaise, dyspneic, decreased activity tolerance
-thrombocytopenia (petechiae, easy bruising, bleeding gums, occult hematuria, retinal hemorrhages, intracerebral hemorrhage, epistaxis)
-Leukopenia (infection, abscesses)
-weight loss, anorexia, possible CNS involvement (altered LOC)
-thrombocytopenia (petechiae, easy bruising, bleeding gums, occult hematuria, retinal hemorrhages, intracerebral hemorrhage, epistaxis)
-Leukopenia (infection, abscesses)
-weight loss, anorexia, possible CNS involvement (altered LOC)
10
New cards
platelets
thrombocytes
11
New cards
thrombocytopenia etiology
-Decreased production in bone marrow
-Increased destruction of platelets (d/t antibodies)
-Increased consumption (by the spleen)
-Increased destruction of platelets (d/t antibodies)
-Increased consumption (by the spleen)
12
New cards
thrombocytopenia manifestations
Petechiae, ecchymosis, bleeding from mucous membranes, cutaneous sites, internal organs.
13
New cards
Red Blood Cells
-no nucleus, mitochondria, or ribosomes
-life cycle is 80-120 days
-biconcave disc, allowing for large amounts of O2 to be carried
-produced in the red bone marrow
-life cycle is 80-120 days
-biconcave disc, allowing for large amounts of O2 to be carried
-produced in the red bone marrow
14
New cards
Iron deficiency anemia
-iron is essential for hemoglobin development
-occurs when you lose RBC chronically (blood loss from heavy menstrual cycles, colon cancer)
-weakness, pallor, fatigue
-RBCs are microcytic, hypochromic
-occurs when you lose RBC chronically (blood loss from heavy menstrual cycles, colon cancer)
-weakness, pallor, fatigue
-RBCs are microcytic, hypochromic
15
New cards
pernicious anemia
-(type of megaloblastic anemia) vitamin B12 deficiency
-B12 is absorbed in the terminal ileum and requires intrinsic factor secreted by parietal cells in the stomach
-can be caused by a bowel resection surgery and stomach issues
-diarrhea, fatigue, weakness, bleeding/swollen gums, dyspnea, jaundice
-B12 is absorbed in the terminal ileum and requires intrinsic factor secreted by parietal cells in the stomach
-can be caused by a bowel resection surgery and stomach issues
-diarrhea, fatigue, weakness, bleeding/swollen gums, dyspnea, jaundice
16
New cards
sickle cell disease
Genetic disorder in which red blood cells have abnormal hemoglobin molecules and take on an abnormal shape.
17
New cards
sickle cell etiology
-genetic, autosomal recessive, chromosome 7
-heterozygous carriers can have some symptoms that present at low O2 environments (high altitude, cold)
-heterozygous carriers can have some symptoms that present at low O2 environments (high altitude, cold)
18
New cards
sickle cell pathogenesis
-change in the molecular structure of hemoglobin
-decreases the RBC lifespan
-occludes vasculature
-development of venous thrombosis
-decreases the RBC lifespan
-occludes vasculature
-development of venous thrombosis
19
New cards
sickle cell manifestations
-pain, splenomegaly, stroke
-retinal vessel destruction, blindness
-hepatomegaly, tachycardia
-myocardial ischemia
-retinal vessel destruction, blindness
-hepatomegaly, tachycardia
-myocardial ischemia
20
New cards
Multiple Myeloma
-abnormal proliferation of plasma cells (lesions on skull or spine)
21
New cards
multiple myeloma population characteristics
-greater than 40 years of age
-peak incidence is 60s
-greater incidence in males
-peak incidence is 60s
-greater incidence in males
22
New cards
multiple myeloma etiology
-viral
-genetic
-genetic
23
New cards
multiple myeloma pathogenesis
-excess number of abnormal plasma cells infiltrate the bone marrow
-produce abnormal immunoglobulin called bence jones protein
-demineralization of bone in skull and spine
-produce abnormal immunoglobulin called bence jones protein
-demineralization of bone in skull and spine
24
New cards
multiple myeloma manifestations
-destruction of bine leading to bone pain and pathological fractures
-hypercalcemia
-renal insufficiency due to hypercalcemia and increased blood viscosity
-acute renal failure
-anemia- fatigue
-leukopenia (repeated infections)
-thrombocytopenia (bleeding tendencies)
-hypercalcemia
-renal insufficiency due to hypercalcemia and increased blood viscosity
-acute renal failure
-anemia- fatigue
-leukopenia (repeated infections)
-thrombocytopenia (bleeding tendencies)
25
New cards
Hodgkin's lymphoma
-70% cure rate, even better with early diagnosis
-Half of cases occur between 20 and 40; Incidence is higher in males
-Etiology: Genetic, Exposure to chemical agents, Epstein barr virus
-Starts in single lymph node and spreads to other lymph nodes; Contains Reed-Sternberg cell
-Invades other tissues late in disease process; Prognosis for treatment
-Lymph node enlargement (cervical nodes most common), continuous spread through lymph nodes, Fever, Night sweats, Pruritus, Weight loss, Malaise
-Half of cases occur between 20 and 40; Incidence is higher in males
-Etiology: Genetic, Exposure to chemical agents, Epstein barr virus
-Starts in single lymph node and spreads to other lymph nodes; Contains Reed-Sternberg cell
-Invades other tissues late in disease process; Prognosis for treatment
-Lymph node enlargement (cervical nodes most common), continuous spread through lymph nodes, Fever, Night sweats, Pruritus, Weight loss, Malaise
26
New cards
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
-older adults, greater incidence in males
-etiology: viral infection, radiation, exposure to chemicals
-Pattern of development less defined than Hodgkin’s (More spread early on)
-May invade non-lymph tissue early in disease process (Organ involvement like GI bleeds)
-Prognosis ominous for diffuse disease
-Non Contiguous spread of disease, Involvement of gastrointestinal tract (GI bleed, Perforation, Malabsorption), Testes (Testicular mass), Bone marrow
-etiology: viral infection, radiation, exposure to chemicals
-Pattern of development less defined than Hodgkin’s (More spread early on)
-May invade non-lymph tissue early in disease process (Organ involvement like GI bleeds)
-Prognosis ominous for diffuse disease
-Non Contiguous spread of disease, Involvement of gastrointestinal tract (GI bleed, Perforation, Malabsorption), Testes (Testicular mass), Bone marrow
27
New cards
sleep-wake cycles
-part of normal biological fluctuations known as "circadian rhythms"
-circadian rhythms are under control of the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus (SCN)
-a wide variety of pharmacological agents influence sleep cycles
-circadian rhythms are under control of the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus (SCN)
-a wide variety of pharmacological agents influence sleep cycles
28
New cards
circadian rhythm disruption
-due to phase shift
-jet lag (sleep cycle changes first, then temp cycle, then cortisol 10-12 days later)
-shift work causes an increased risk of chronic health problems (especially DM and weight gain)
-cortisol spikes in the early morning and then later in the afternoon (Max about 1-2 hours before waking)
-jet lag (sleep cycle changes first, then temp cycle, then cortisol 10-12 days later)
-shift work causes an increased risk of chronic health problems (especially DM and weight gain)
-cortisol spikes in the early morning and then later in the afternoon (Max about 1-2 hours before waking)
29
New cards
sleep and temperature
temperature spikes in the evening hours
30
New cards
REM sleep
-Rapid eye movement sleep, a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur.
-Psychologically restorative
-about 90 minutes into the cycle
-the older you get, the harder it is to get REM
-serotonin needed for priming of REM sleep, loss of muscle tone, loss of ability to thermoregulate, eye movements
-Psychologically restorative
-about 90 minutes into the cycle
-the older you get, the harder it is to get REM
-serotonin needed for priming of REM sleep, loss of muscle tone, loss of ability to thermoregulate, eye movements
31
New cards
stage 1 sleep
-Light sleep
-The brain emits alpha waves--> consistent with a relaxed state of wakefulness
-The brain emits alpha waves--> consistent with a relaxed state of wakefulness
32
New cards
stage 2 sleep
A sleep deeper than that of stage 1, characterized by a slower, more regular wave pattern, along with momentary interruptions of "sleep spindles."
33
New cards
stage 3 sleep
third stage of sleep; deep sleep characterized by low frequency, high amplitude delta waves
34
New cards
stage 4 sleep
-the deepest stage of sleep, during which we are least responsive to outside stimulation
-absent in individuals over 70
-absent in individuals over 70
35
New cards
physiological changes during sleep
-decreased clearance of respiratory secretions
-cough reflex diminished
-decreased swallowing and esophageal motility
-decreased glomerular filtration rate
-increased aldosterone production
-decreased temp
-cough reflex diminished
-decreased swallowing and esophageal motility
-decreased glomerular filtration rate
-increased aldosterone production
-decreased temp
36
New cards
sleep deprivation
-causes immune system malfunction
-cognitive decline
-hospitalized patients, anxiety, depression, poor sleep hygiene
-cognitive decline
-hospitalized patients, anxiety, depression, poor sleep hygiene
37
New cards
sleep changes across the lifespan
-sleep stage is 50-60 minutes in infants
-sleep stage is 90 minutes in adults
-decreased sleep requirement over time
-stage 4 sleep is absent in adults over 70
-changes like dementia may be linked to sleep (cognitive functioning)
-sleep stage is 90 minutes in adults
-decreased sleep requirement over time
-stage 4 sleep is absent in adults over 70
-changes like dementia may be linked to sleep (cognitive functioning)
38
New cards
Restorative function of sleep
This theory proposes that the purpose of sleep is to allow the body and nervous system to grow and repair any damage that may have occurred to tissues during the day.
39
New cards
fever manifestations
-increased heart rate
-increased cardiac output
-increased oxygen consumption
-increased respiratory rate
-each 1º rise in temp causes a 10% increase in metabolic rate
-decreased production of albumin
-increased production of acute phase proteins
-altered drug metabolism
-enhanced immune function (fever increases interferon response to kill pathogens)
-increased cardiac output
-increased oxygen consumption
-increased respiratory rate
-each 1º rise in temp causes a 10% increase in metabolic rate
-decreased production of albumin
-increased production of acute phase proteins
-altered drug metabolism
-enhanced immune function (fever increases interferon response to kill pathogens)
40
New cards
hypothermia manifestations
-decreased heart rate
-decreased cardiac output
-development of coagulants
-depressed CNS
-decreased cardiac output
-development of coagulants
-depressed CNS
41
New cards
pain
-it is whatever the patient says it is
-subjective
-best way to regulate pain assessment is numerical scale
-subjective
-best way to regulate pain assessment is numerical scale
42
New cards
spinothalamic tract
nerve pathway from the spine to the thalamus along which pain impulses are carried to the brain
43
New cards
manifestations of pain
-increased heart rate
-increased blood pressure
-increased respiratory rate
-dilated pupils
-pallor and perspiration
-nausea and vomiting
-urine retention
-elevated blood glucose
-increased blood pressure
-increased respiratory rate
-dilated pupils
-pallor and perspiration
-nausea and vomiting
-urine retention
-elevated blood glucose
44
New cards
fast pain
-myelinated A delta fibers
-quick, sharp, stabbing pain
-well localized
-quick, sharp, stabbing pain
-well localized
45
New cards
slow pain
-Unmyelinated C fibers
-dull, achy, diffuse pain
-dull, achy, diffuse pain
46
New cards
nocioreceptors
-pain receptors stimulated by tissue injuries
-distribution is mostly in skin
-distribution is mostly in skin
47
New cards
cutaneous pain
superficial pain usually involving the skin or subcutaneous tissue
48
New cards
somatic pain
Pain that originates from skeletal muscles, ligaments, or joints.
49
New cards
visceral pain
-a poorly localized, dull, or diffuse pain that arises from the abdominal organs, or viscera
-can manifest as referred pain
-can manifest as referred pain
50
New cards
referred pain
-shared pathways cause this
-pancreas to back
-heart to chest, neck, jaw, arms
-gallbladder to right shoulder
-pancreas to back
-heart to chest, neck, jaw, arms
-gallbladder to right shoulder
51
New cards
Autoregulation
-mechanism that attempts to maintain supply of necessary metabolic substrates
-protective mechanism that maintains blood pressure
-blood flow remains constant as long as blood pressure is normal
-A MAP (perfusion pressure) lower than 60 and higher than 140 can cause the brain to lose autoregulation
-traumatic brain injury can cause swelling, blood loss which alters blood pressure and can cause a loss of autoregulation
-dehydration can cause altered blood pressure
-protective mechanism that maintains blood pressure
-blood flow remains constant as long as blood pressure is normal
-A MAP (perfusion pressure) lower than 60 and higher than 140 can cause the brain to lose autoregulation
-traumatic brain injury can cause swelling, blood loss which alters blood pressure and can cause a loss of autoregulation
-dehydration can cause altered blood pressure
52
New cards
factors that affect blood flow
-blood pressure
-carbon dioxide concentration (increased CO2 causes vasodilation and increased blood flow)
-oxygen concentration (decreased O2 concentration causes blood vessel vasodilation)
-carbon dioxide concentration (increased CO2 causes vasodilation and increased blood flow)
-oxygen concentration (decreased O2 concentration causes blood vessel vasodilation)
53
New cards
Monroe Kellie hypothesis
-brain, blood, CSF
-intracranial space is limited; increase in volume causes increase in intracranial pressure; to maintain same intracranial pressure, when there is an increase in one component, there must be a decrease in another component
-if there is no compensation, the increased ICP will cause brain death
-ex. breathing faster to decrease CO2 and vasoconstriction to shunt blood
-intracranial space is limited; increase in volume causes increase in intracranial pressure; to maintain same intracranial pressure, when there is an increase in one component, there must be a decrease in another component
-if there is no compensation, the increased ICP will cause brain death
-ex. breathing faster to decrease CO2 and vasoconstriction to shunt blood
54
New cards
Cerebral perfusion
-should be greater than 50mmHg
-(MAP-intracranial pressure)
-(MAP-intracranial pressure)
55
New cards
intracranial pressure
-the amount of pressure inside the skull
-norm is 0-15 mmHg
-if too high, drain CSF
-norm is 0-15 mmHg
-if too high, drain CSF
56
New cards
reticular activating system
-Located in the upper brain stem; responsible for maintenance of consciousness, specifically one's level of arousal
-in a coma, the reticular activating system goes off and stays off
-in a coma, the reticular activating system goes off and stays off
57
New cards
etiology of intracranial hypertension
-anything that causes closed head pathology
-brain swelling causes increased brain tissue volume (traumatic injury) which interferes with cerebral blood flow
-epidural hematoma
-subdural hematoma
-subarachnoid hemorrhage
-intracerebral hematoma
-hydrocephalus
-brain swelling causes increased brain tissue volume (traumatic injury) which interferes with cerebral blood flow
-epidural hematoma
-subdural hematoma
-subarachnoid hemorrhage
-intracerebral hematoma
-hydrocephalus
58
New cards
manifestations of elevated ICP
-decreased LOC is the earliest indicator
-coma
-if obtunded: posturing (decorticate or decerebrate) is a poor indicator
-lower than 8 on the Glasgow coma scale
-projectile vomiting
-pupils non reactive to light
-visual disturbances (delusions, hallucinations)
-Motor Dysfunction (hemiplegia, hemiparesis)
-Headache
-Aphasia
-Changes in respiratory pattern (Cheyne Stokes, apnea)
-Cushing's Reflex (late sign)
-brainstem death
-brain herniation
-coma
-if obtunded: posturing (decorticate or decerebrate) is a poor indicator
-lower than 8 on the Glasgow coma scale
-projectile vomiting
-pupils non reactive to light
-visual disturbances (delusions, hallucinations)
-Motor Dysfunction (hemiplegia, hemiparesis)
-Headache
-Aphasia
-Changes in respiratory pattern (Cheyne Stokes, apnea)
-Cushing's Reflex (late sign)
-brainstem death
-brain herniation
59
New cards
Cushing's Reflex
decreased heart rate, increased blood pressure (trying to maintain CPP), widened pulse pressure
-pulse pressure means that the systolic and diastolic get farther apart
-systolic increases to try and force blood through the brain
-pulse pressure means that the systolic and diastolic get farther apart
-systolic increases to try and force blood through the brain
60
New cards
Decorticate posturing
characterized by upper extremities flexed at the elbows and held closely to the body and lower extremities that are externally rotated and extended. occurs when the brainstem is not inhibited by the motor function of the cerebral cortex.
61
New cards
Decerebrate posturing
posturing in which the neck is extended with jaw clenched; arms are pronated, extended, and close to the sides; legs are extended straight out; more ominous sign of brain stem damage. Most Severe.
62
New cards
brain death
-loss of brainstem (only "alive" from hospital measures)
-requires multiple criteria: no perfusion, flat EEG, Apnea test
-requires multiple criteria: no perfusion, flat EEG, Apnea test
63
New cards
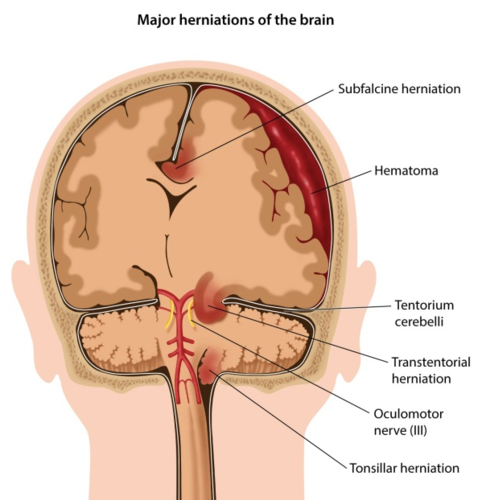
Uncal Herniation
-Uncus of the temporal lobe is displaced downward
Creates pressure on CN III, posterior cerebral artery, and RAS
-temporal lobe moves through the tentorial notch
-causes fixed, blown pupils from CN III pressure
Creates pressure on CN III, posterior cerebral artery, and RAS
-temporal lobe moves through the tentorial notch
-causes fixed, blown pupils from CN III pressure
64
New cards
uncal herniation manifestations
-symptoms of ICP (headache, nausea, vomiting, altered mental status)
-Cushing's Sign
-altered respiratory pattern
-loss of brainstem reflexes
-one pupil blown out, other normal; pupils nonreactive to light
-altered balance
-Cushing's Sign
-altered respiratory pattern
-loss of brainstem reflexes
-one pupil blown out, other normal; pupils nonreactive to light
-altered balance
65
New cards
Epidural Hematoma
-arterial bleeding in the space between the skull and dura layer
-arterial bleeds are more quick moving than venous because each heart beat prevents clotting by pushing blood through the arteries
-arterial bleeds are more quick moving than venous because each heart beat prevents clotting by pushing blood through the arteries
66
New cards
epidural hematoma etiology
-arterial bleed (85% are associated with skull fractures)
-occurs quickly
-baseball to the head, MVA
-occurs quickly
-baseball to the head, MVA
67
New cards
epidural hematoma mechanism
tear in the middle meningeal artery pushes the brain toward midline
68
New cards
epidural hematoma manifestations
-Lucid interval
-ipsilateral pupil change
-contralateral hemiparesis
-increased ICP
-ipsilateral pupil change
-contralateral hemiparesis
-increased ICP
69
New cards
subdural hematoma
-usually venous in origin between the dura and arachnoid layer
70
New cards
Subdural hematoma stages
Acute- symptoms come in 24 hours (elevated ICP symptoms)
Subacute- 2-10 days before symptoms
Chronic- 2 weeks to 2 months later (common in the elderly because they are on anticoagulants and atrophy of brain allows more time before symptoms); sometimes symptoms are mistaken for dementia
Subacute- 2-10 days before symptoms
Chronic- 2 weeks to 2 months later (common in the elderly because they are on anticoagulants and atrophy of brain allows more time before symptoms); sometimes symptoms are mistaken for dementia
71
New cards
subdural hematoma mechanism
tear in the bridging veins
72
New cards
subdural hematoma etiology
72% falls, MVAs
73
New cards
Subdural hematoma manifestations
-headache
-altered levels of consciousness
-no lucid interval
-signs of increased ICP
-drowsy, confusion, agitation, ipsilateral pupil changes (sign of herniation), contralateral hemiparesis
-altered levels of consciousness
-no lucid interval
-signs of increased ICP
-drowsy, confusion, agitation, ipsilateral pupil changes (sign of herniation), contralateral hemiparesis
74
New cards
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
-bleeding into the subarachnoid space (blood mixes with CSF)
-50% mortality
-50% mortality
75
New cards
subarachnoid hemorrhage etiology
-ruptured cerebral aneurysm
-trauma
-trauma
76
New cards
subarachnoid hemorrhage mechanisms
-irritation of the dura can cause signs of meningitis
-decreased absorption of CSF because the blood plugs up arachnoid villi
-can cause communicating hydrocephalus
-decreased absorption of CSF because the blood plugs up arachnoid villi
-can cause communicating hydrocephalus
77
New cards
subarachnoid hemorrhage manifestations
-fever
-photophobia
-nuchal rigidity
-communicating hydrocephalus
-severe headache, blurred vision, diplopia
-sensory and motor deficits
-projectile vomiting
-vasospasm (constricts vessels and causes lack of blood flow and potential stroke)
-photophobia
-nuchal rigidity
-communicating hydrocephalus
-severe headache, blurred vision, diplopia
-sensory and motor deficits
-projectile vomiting
-vasospasm (constricts vessels and causes lack of blood flow and potential stroke)
78
New cards
signs of meningial irritation
-photophobia
-nuchal rigidity
-nuchal rigidity
79
New cards
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
-hemorrhagic stroke
-bleeding in the brain tissue
-bleeding in the brain tissue
80
New cards
intracerebral hemorrhagex etiology
often uncontrolled hypertension (usually in the daytime because BP is higher)
81
New cards
intracerebral hemorrhage manifestations
-elevated ICP symptoms
-coma if pressure gets too high
-coma if pressure gets too high
82
New cards
hydrocephalus
accumulation of fluid in the spaces of the brain, causes increased ICP
83
New cards
communicating hydrocephalus
-difficulty reabsorbing CSF because the arachnoid villi are plugged up
-arachnoid villi may eventually work again
-causes headache nausea, downward deviation of the eyes, impaired balance, increased ICP symptoms
-arachnoid villi may eventually work again
-causes headache nausea, downward deviation of the eyes, impaired balance, increased ICP symptoms
84
New cards
noncommunicating hydrocephalus
-blockage in the CSF drainage system (something obstructs the flow between the ventricles)
-congenital defect between the third and fourth ventricles, tumor
-requires a shunt
-increased ICP symptoms
-congenital defect between the third and fourth ventricles, tumor
-requires a shunt
-increased ICP symptoms
85
New cards
compression force
-tissue is compressed on impact
-ex. brain hits the front of the skull
-ex. brain hits the front of the skull
86
New cards
tension force
-less common
-tissue is pulled apart
-tissue is pulled apart
87
New cards
shearing force
-brain moves at two different rates, causing a shift and tearing down the corpus callosum
88
New cards
Diffuse axonal injury
-due to shearing force (tears corpus callosum)
-damage to nerve cells in the connecting fibers of the brain
-poor prognosis, people generally do not recover/wake up
-damage to nerve cells in the connecting fibers of the brain
-poor prognosis, people generally do not recover/wake up
89
New cards
pattern of head injuries
-damage to frontal lobe and temporal tips
90
New cards
concussions
-shake the brain; momentary interruption of brain function without loss of consciousness
-can occur from any kind of mechanical force that impacts the brain
-can occur from any kind of mechanical force that impacts the brain
91
New cards
concussion manifestations
-repeated concussions can cause residual effects
-momentary loss of reflexes
-arrest of respirations
-amnesia
-headache
-dizziness
-confusion
-visual disturbance
-gait disturbances
-momentary loss of reflexes
-arrest of respirations
-amnesia
-headache
-dizziness
-confusion
-visual disturbance
-gait disturbances
92
New cards
post concussion syndrome
-can last six months to never ending
-headache, dizziness, insonnia, decreased cognitive abilities
-headache, dizziness, insonnia, decreased cognitive abilities
93
New cards
cerebral contusions
-focal injury
-bruising of the temporal tips and frontal lobe (usually)
-bruising of the temporal tips and frontal lobe (usually)
94
New cards
contusion etiology
-head injury
95
New cards
contusion mechanism
-anatomic site often involved is frontal and temporal lobes
96
New cards
contusion manifestations
-loss of consciousness
-loss of reflexes
-stop breathing for a few seconds
-bradycardia
-hemiparesis
-hypotension
-aphasia
-loss of reflexes
-stop breathing for a few seconds
-bradycardia
-hemiparesis
-hypotension
-aphasia
97
New cards
basilar skull fracture
-base of the skull through the sinuses
-transverse sinuses have a risk for infection (meningitis)
-transverse sinuses have a risk for infection (meningitis)
98
New cards
basilar skull fracture manifestations
-CSF leak out of ears and nose
-potential for meningitis
-racoon's eyes (bruising)
-battle sign (mastoid process bruising)
-potential for meningitis
-racoon's eyes (bruising)
-battle sign (mastoid process bruising)
99
New cards
meningitis
inflammation of the meninges
100
New cards
bacterial meningitis etiology
-2/3 of cases are under 5 years old
-haemophilus influenza (not common because children are vaccinated)
-neisseria meningitides (triggered by respiratory/ear infections; common in college; manifests as petechiae on chest/wrist, sepsis)
-streptococcus pneumoniae (older adults)
-E. coli in infants
-haemophilus influenza (not common because children are vaccinated)
-neisseria meningitides (triggered by respiratory/ear infections; common in college; manifests as petechiae on chest/wrist, sepsis)
-streptococcus pneumoniae (older adults)
-E. coli in infants