ARTERIAL - HEMODIALYSIS ACCESS GRAFTS
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
hemodialysis av fistula/access graft
surgically created connection between an artery and vein for hemodialysis
hemodialysis use
removes creatinine, urea and water from the blood of patients w end-stage renal failure
in the pre op assessment for hemodialysis, vessels are measured
inner to inner
av fistula for dialysis
direct connection between artery and vein that is created to allow access point for dialysis port
av graft for dialysis
synthetic tube is connected to artery and vein to allow access point for dialysis port
vessel diameters needed for avf/av graft
native vein >2.5 mm for avf
native vein >4 mm for av graft
native artery >2 mm
requirements for veins before avf/graft
straight course, located within 1 cm of skin surface, free of obstruction
before avf/graft, distal radial artery psv should be _____ cm/s
over 50
what can be performed to assess the feeding artery for appropriate increase in arterial diameter/vessel compliance for fistula placement
reactive hyperemia testing
reactive hyperemia testing for avf/graft
clenching fist increases distal resistance and pulsatility in prox arteries
clench held for 2 min
release fist, resistance should drop distally, flow increases in hand
resistive index is measured, anything over .7 indicates feeding artery will not work
avf/grafts are usually put in the patient’s _____ arm
nondominant
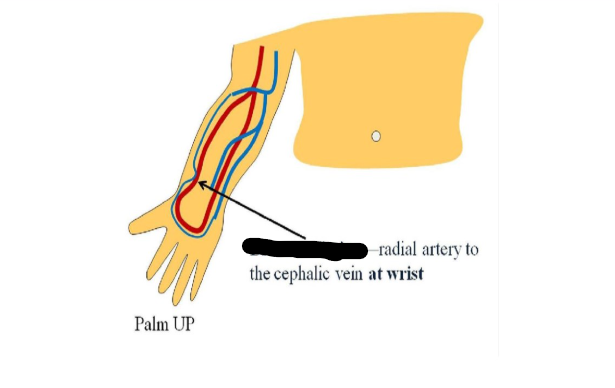
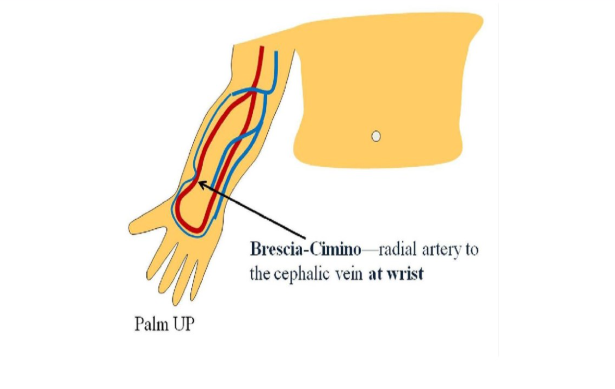
most common avf
brescia-cimino
brescia-cimino
radial artery to cephalic vein @wrist
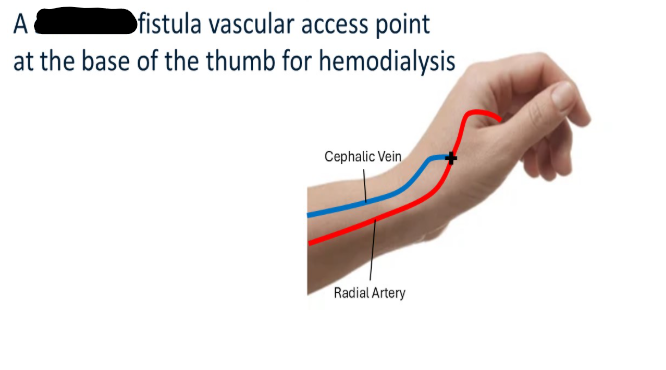
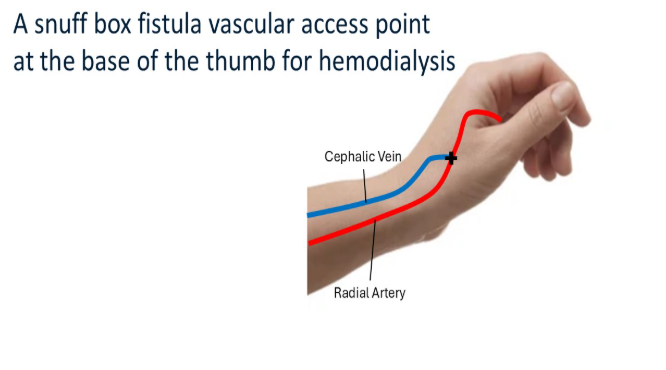
snuffbox fistula
radial artery is connected to the cephalic vein at the distal wrist (snuffbox: triangular depression at the lateral aspect of dorsum of hand)
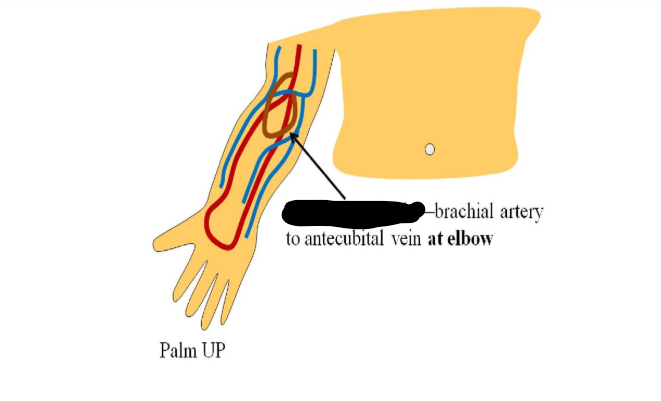
brachiocephalic avf
brachial artery and antecubital vein at elbow
brachiobasilic avf
brachial artery and basilic vein at elbow
radiobasilic avf
radial artery and basilic vein at forearm
when is a synthetic graft used
when native veins are inadequate or avf has failed
drawbacks of synthetic graft
shorter duration of use and lower patency rates than avf
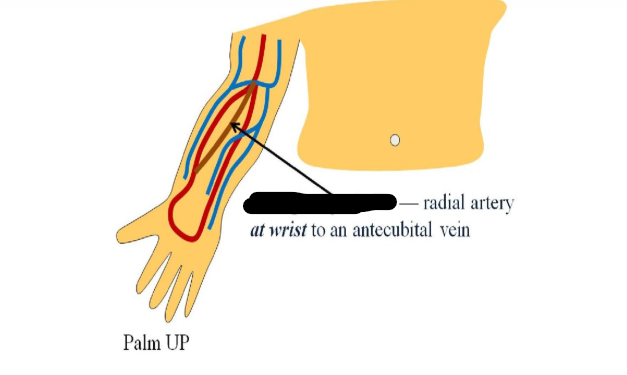
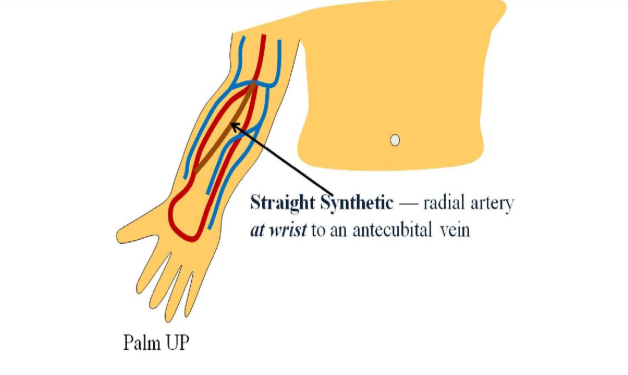
most common type of synthetic graft
straight synthetic, looped synthetic
straight synthetic graft
brachial artery to basilic vein in upper arm
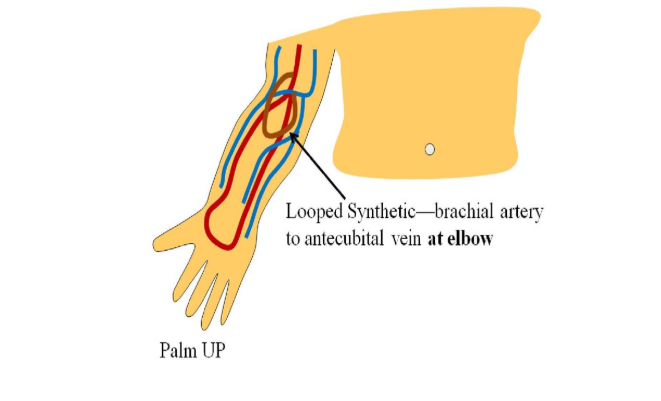
looped synthetic graft
brachial artery to antecubital or cephalic vein at elbow, loop extends distally to wrist
t/f: blood pressure can be taken on an arm with an avf or graft
false
#1 site of stenosis in av graft
venous anastomosis
how should the patient be positioned for evaluation of avf/graft
patient seated or supine w arm extended and supported
arm externally rotated and placed at a 45 degree angle to the body
venous outflow prox to an avf/graft becomes
pulsatile/turbulent due to inflow of arterial flow distally
arterial inflow prox to an avf/graft should be
low resistance w increased diastolic flow
normal psv within graft
100-400 cm/s
normal edv within graft
60-200 cm/s
velocity ratio of _____ at anastomosis is abnormal
over 3.0
if the flow velocity doubles between two points in a graft what is suspected
significant stenosis
what is suspected if the arterial inflow to a graft is triphasic
occlusion
if the venous outflow vein demonstrates a loss of spontaneous flow and phasicity what is suspected
stenosis/obstruction
how is volume flow measured in an avf/graft
obtained in a straight vein segment
measure diameter of vein in area of flow sampling
doppler measurement obtained by opening the sample volume size to include all flow from anterior to posterior wall, trace waveform
flow volume of _____ indicates stenosis
under 500 ml/min
flow volume of _____ indicates chf
over 1200 ml/min
in what kind of avf/graft does steal syndrome most commonly occur
radiocephalic fistula
what will flow look like in a radiocephalic fistula with steal syndrome
distal to the fistula, the ulnar artery will be antegrade and the radial artery will be retrograde (blood travels to hand via ulnar, moves through palmar arch to exit the hand in the radial artery)
what is steal syndrome in the avf/graft most commonly caused by
high volume flow but can sometimes be inflow stenosis