Class 11 Bottom-up Processes (Productivity and Food Webs)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Biomass
total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level
'how much "stuff" there is'
Productivity
the rate at which a biologically relevant material accumulates over time
'how much "stuff" there is over time'
Mussel ___ increases with phytoplankton ___
Mussel productivity increases with phytoplankton biomass
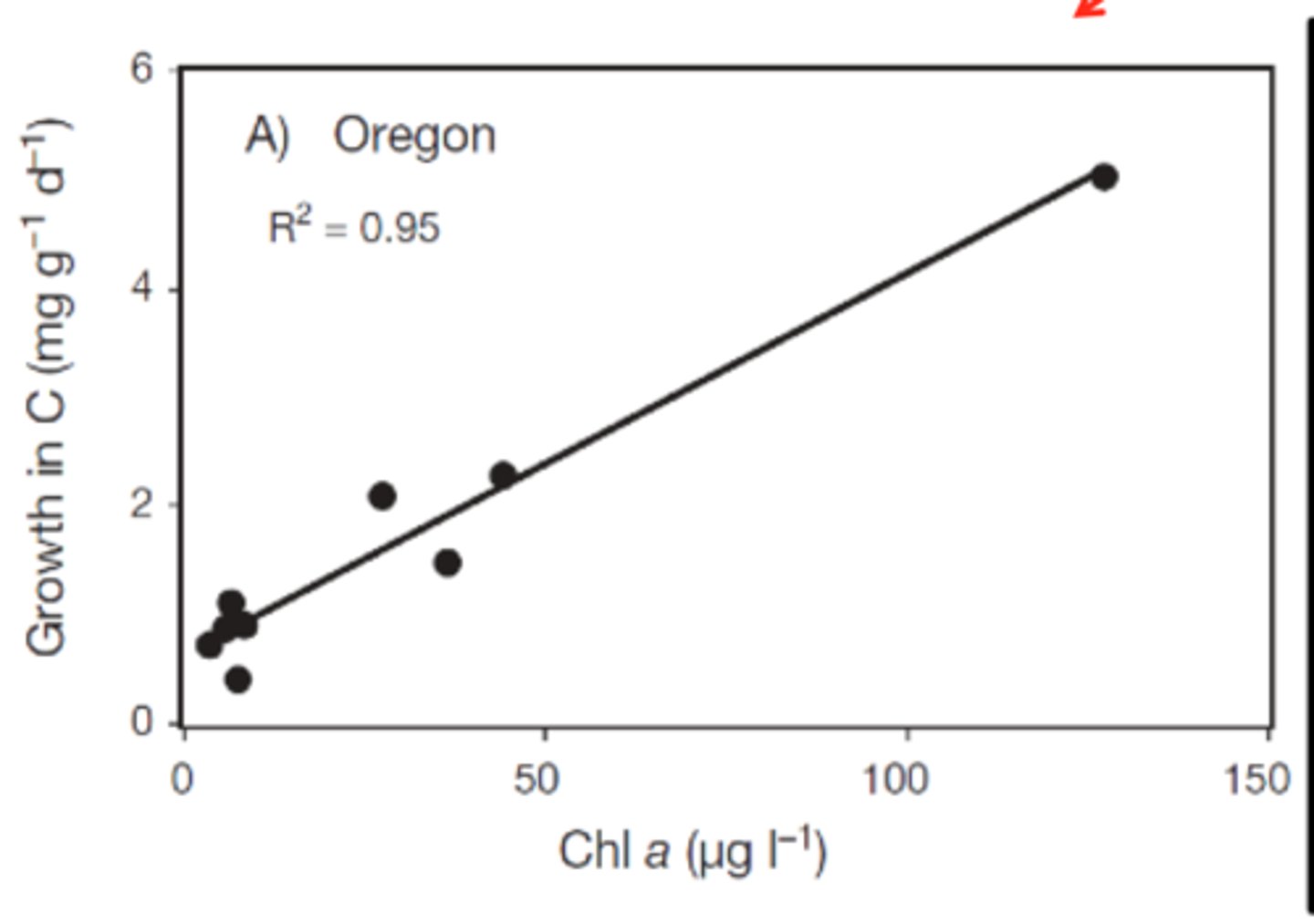
Tidepool _____ can also increase as _____ declines
Tidepool productivity can also increase as biomass declines
primary productivity
growth at the base of the food chain
secondary productivity
growth at higher trophic levels
food chain
A simplified, linear diagram that uses a single organism at each trophic level to illustrate the main pathway of carbon through a system
trophic level
a species or group of species that feeds on one or more other species
food web
a diagram that shows the overall feeding relationships between organisms in an ecological community
Omnivory
feeding on multiple trophic levels
Bottom-up perspective
Available biomass at the base of the food chain can determine abundances of organisms at higher trophic levels
Gross primary production (GPP)
the total amount of carbon fixed (or oxygen produced) by photosynthesis
Net primary production (NPP)
the total amount of carbon fixed (or oxygen produced) by photosynthesis minus the loss associated with respiration
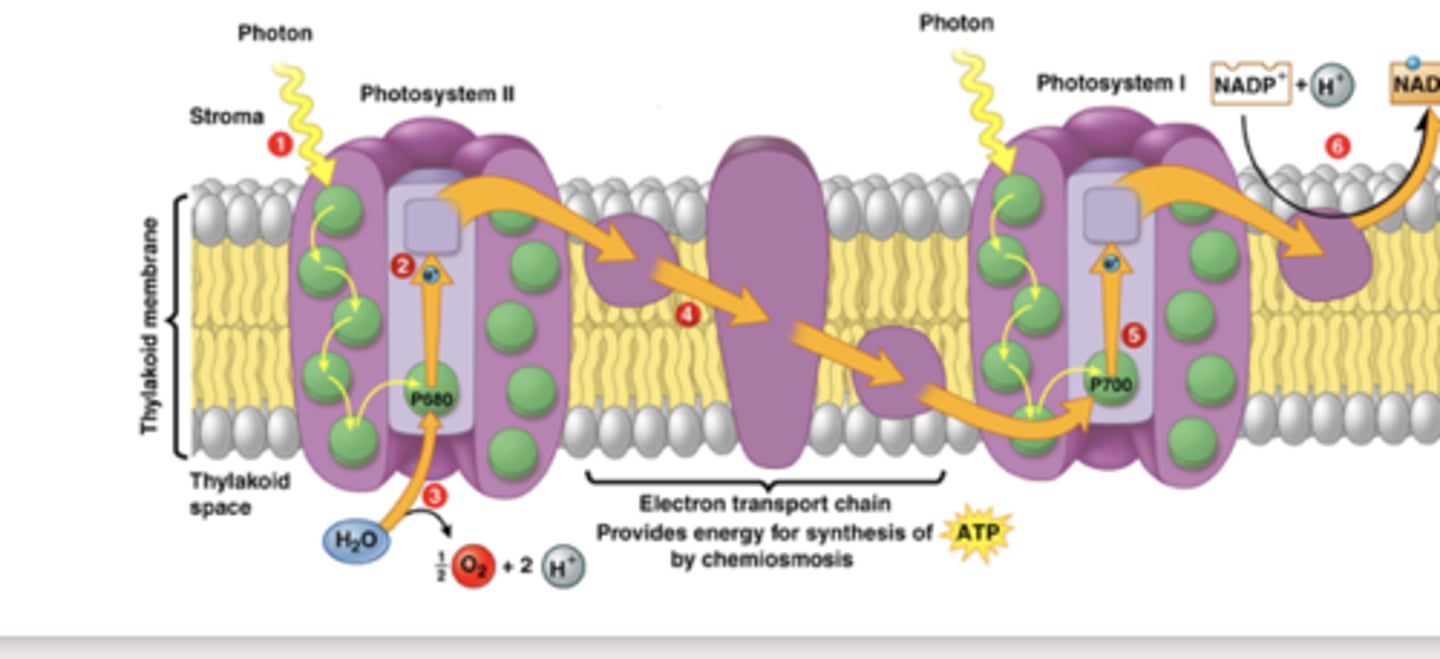
Pulse Amplitude Modulated (PAM) Fluorometry
shines a light on an autroph, then measures the rate of electron transport as proxy for primary productivity
Remote sensing
measure ocean color based on satellite images to observe changes in primary productivity over time
El Nino
an irregularly occurring and complex series of climatic changes affecting the equatorial Pacific region and beyond every few years, characterized by the appearance of unusually warm, nutrient-poor water off northern Peru and Ecuador, typically in late December.
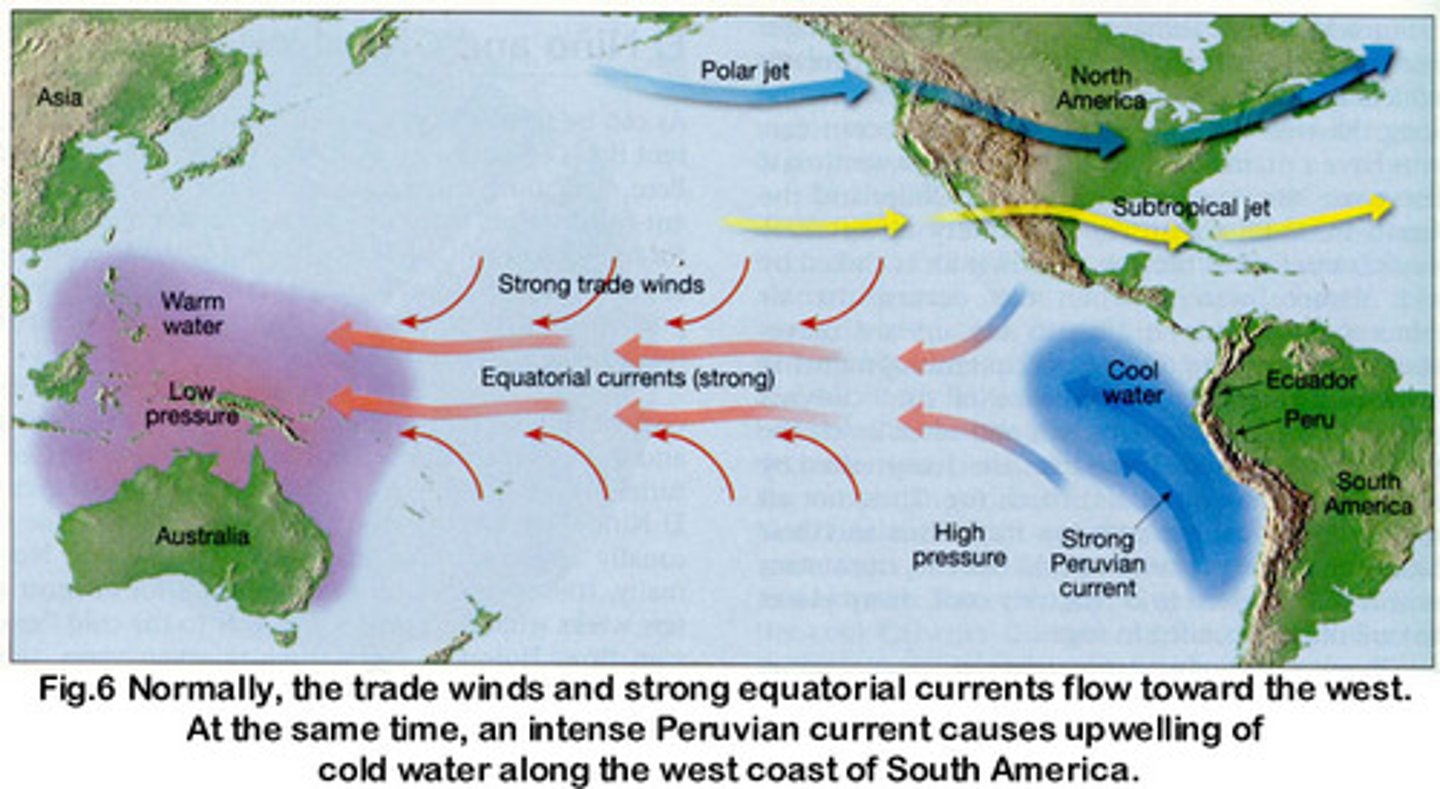
Tradewind
any of the nearly constant easterly winds that dominate most of the tropics and subtropics throughout the world, blowing mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere, and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere.
top-down perspective
the abundance and behavior of species at the top of the food chain can influence the populations and distribution of organisms further down the chain