Laboratory Equipments
5.0(6)Studied by 113 people
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Last updated 3:10 AM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
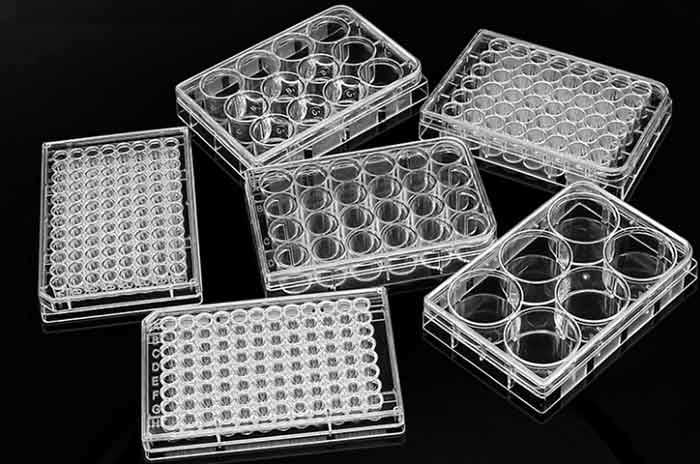
Well Plate
This is made of plastic or ceramic and is used to hold several small amounts of liquids for reactions and analysis.

2
New cards
Beakers
Appearance - cylindrical container with a flat bottom, most have a spout
Uses - to hold and measure liquids, heating them over a Bunsen burner's flame, titration experiments
* commonly used as containers
Uses - to hold and measure liquids, heating them over a Bunsen burner's flame, titration experiments
* commonly used as containers

3
New cards
Griffin Beakers
Type of Beaker
*“Low-Form Beaker”*
Appearance - standard beaker
Uses - daily lab uses
*“Low-Form Beaker”*
Appearance - standard beaker
Uses - daily lab uses

4
New cards
Berzelius Beakers
Type of Beaker
“*Tall-Form Beaker”*
Appearance - tall and thin, height is double the diameter
Uses - titration experiments
“*Tall-Form Beaker”*
Appearance - tall and thin, height is double the diameter
Uses - titration experiments

5
New cards
Crystallizer
Type of Beaker
*“Flat Beaker”*
Appearance - typically don’t have measurement markings
Uses - crystallization, hot-bath heating
*“Flat Beaker”*
Appearance - typically don’t have measurement markings
Uses - crystallization, hot-bath heating

6
New cards
Philips Beaker
Type of Beaker
Appearance - Slopping walls and narrow towards the mouth, slightly conical shape
Uses - mainly use for viscous liquids, daily lab uses
Appearance - Slopping walls and narrow towards the mouth, slightly conical shape
Uses - mainly use for viscous liquids, daily lab uses

7
New cards
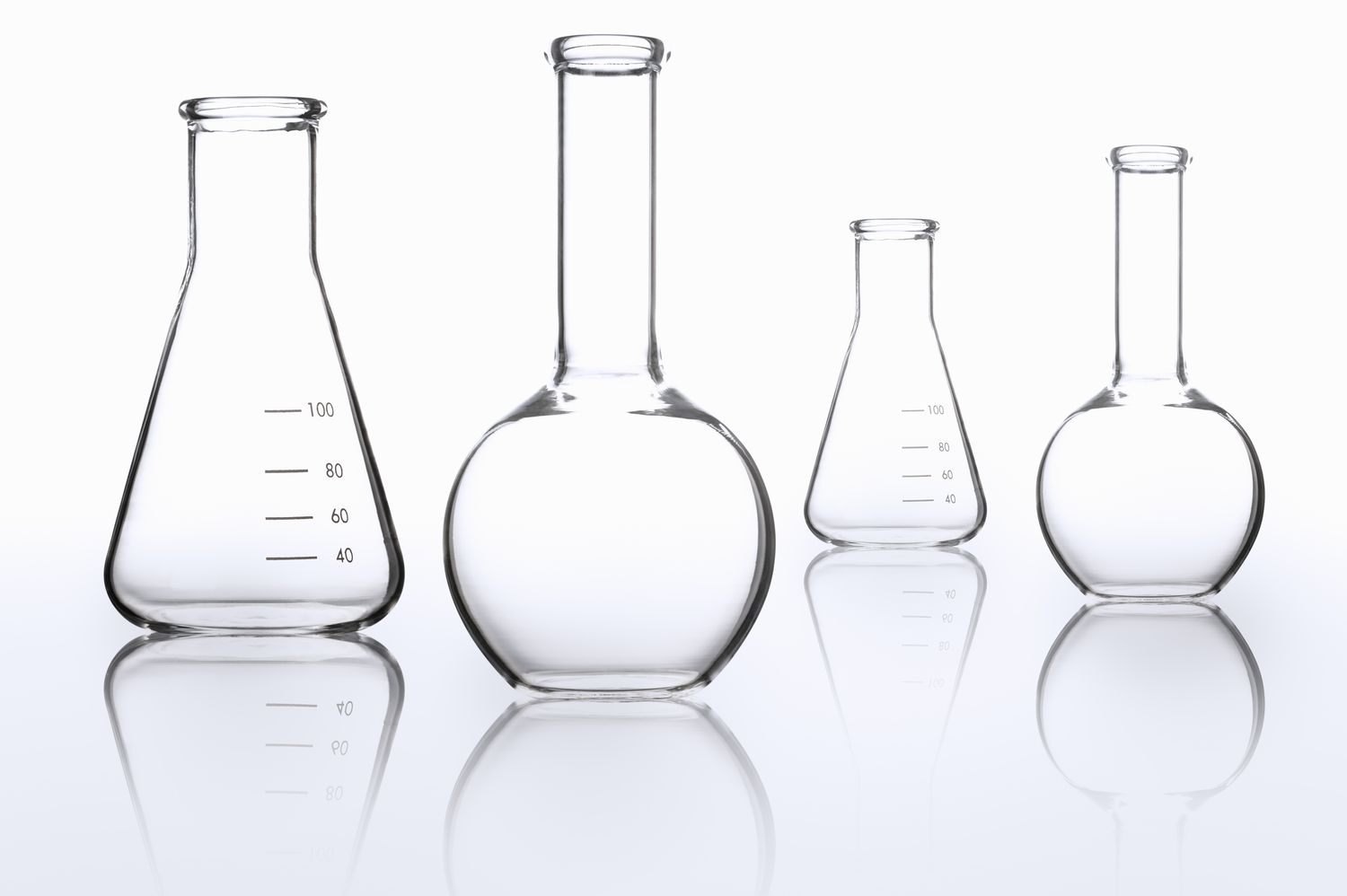
Flask
Appearance - usually made of glass, has a wider body and narrow neck
Uses - to make and hold solutions, to measure chemicals, to contain chemical reactions like boiling, precipitation and analysis,
Uses - to make and hold solutions, to measure chemicals, to contain chemical reactions like boiling, precipitation and analysis,

8
New cards
Erlenmeyer Flask
Type of Flask
“*Conical Flask”*
Appearance - Conical shape, short neck
Uses - it’s designed so that its contents can be swirled easily without spilling out, boiling liquids, titration experiments
* used as reaction vessels
“*Conical Flask”*
Appearance - Conical shape, short neck
Uses - it’s designed so that its contents can be swirled easily without spilling out, boiling liquids, titration experiments
* used as reaction vessels

9
New cards
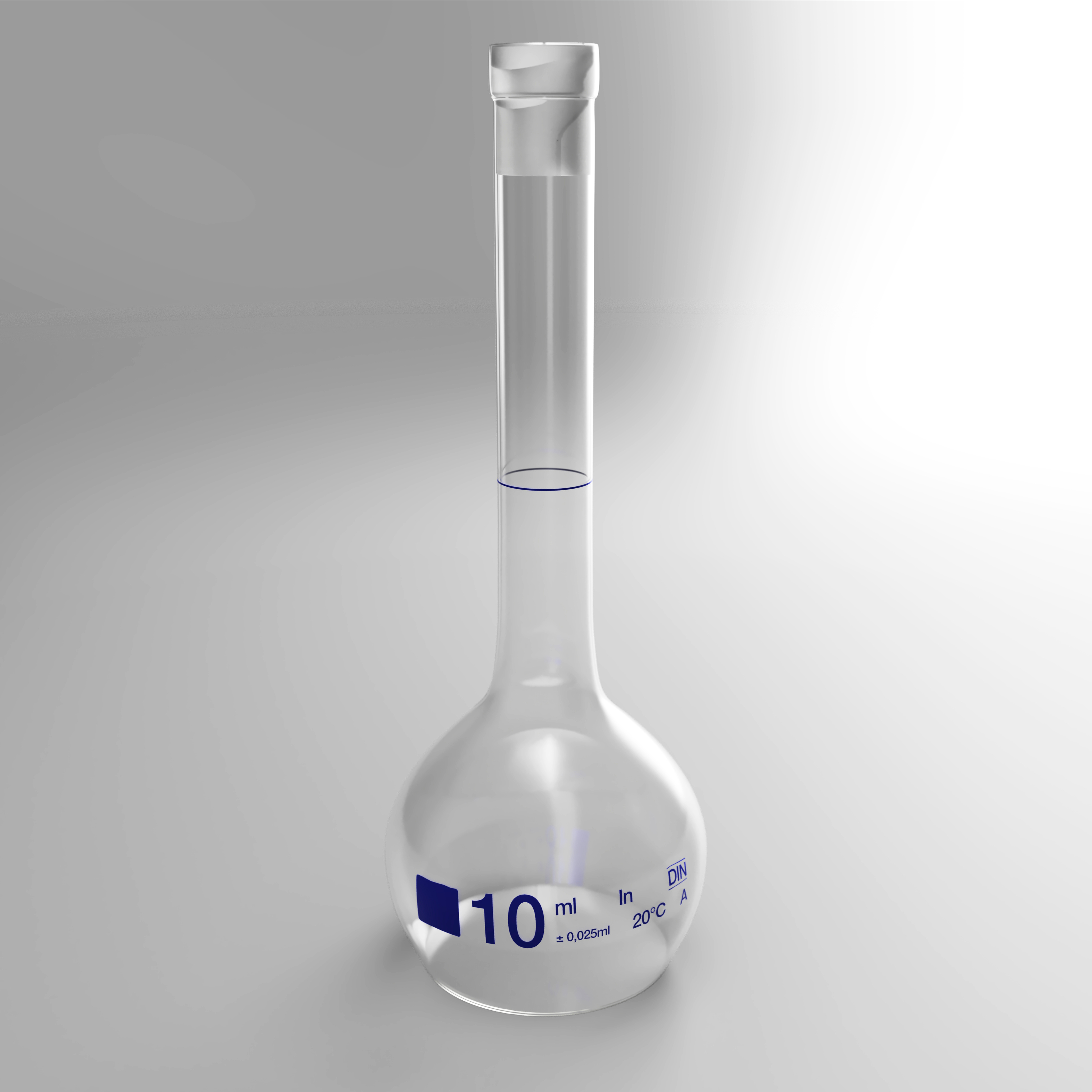
Volumetric Flask
Type of Flask
Appearance - long neck, pear-shaped, flat bottom
* The flask's label also indicates the nominal volume, tolerance, precision class, relevant manufacturing standard and the manufacturer's logo.
Uses - precise dilutions and preparation of standard solutions,
* more accurate than graduated cylinders and beakers
* often used when solutions containing dissolved solids of known concentration are needed
Appearance - long neck, pear-shaped, flat bottom
* The flask's label also indicates the nominal volume, tolerance, precision class, relevant manufacturing standard and the manufacturer's logo.
Uses - precise dilutions and preparation of standard solutions,
* more accurate than graduated cylinders and beakers
* often used when solutions containing dissolved solids of known concentration are needed

10
New cards
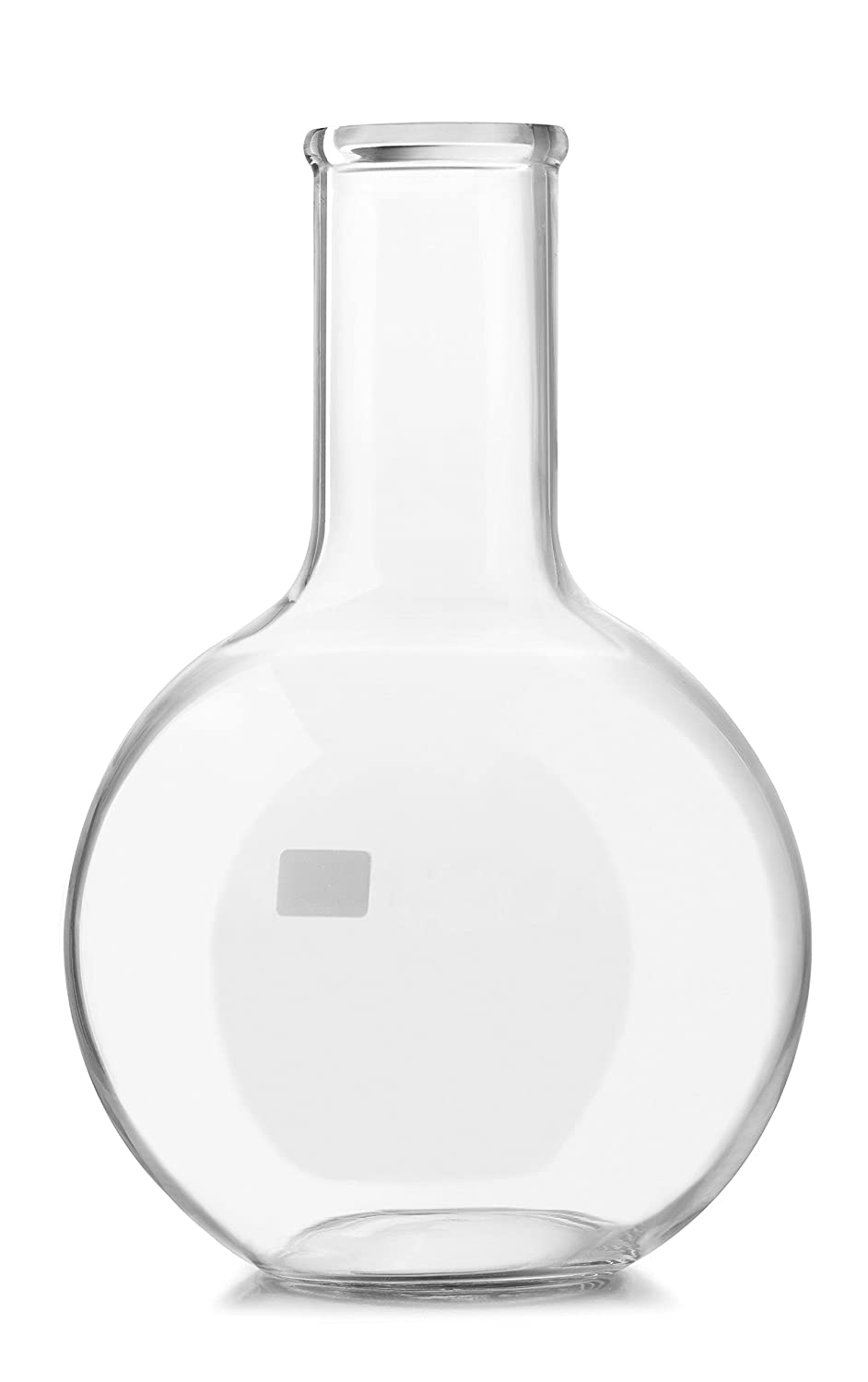
Round-Bottom Flask
Type of Flask
Appearance - Spherical bottoms, shorter neck than volumetric
Uses - distillation, chemical reactions, heating liquid sample, and storage
Appearance - Spherical bottoms, shorter neck than volumetric
Uses - distillation, chemical reactions, heating liquid sample, and storage

11
New cards
Büchner flask
Type of Flask
*Filtering Flask or Bunsen flask or Sidearm flask*
Appearance - conical shape with a flat bottom, tapered neck, and a sidearm for use in vacuum filtration.
Uses - rapid filtration of liquids
* Used with Buchner funnel and a hose to a source of vacuum in *vacuum-assisted liquid filtering*
*Filtering Flask or Bunsen flask or Sidearm flask*
Appearance - conical shape with a flat bottom, tapered neck, and a sidearm for use in vacuum filtration.
Uses - rapid filtration of liquids
* Used with Buchner funnel and a hose to a source of vacuum in *vacuum-assisted liquid filtering*

12
New cards
Florence Flask
Type of Flask
Appearance - round bottom, wider and longer neck than round-bottom flask, no glass joint in the neck,
Uses - useful as a reaction vessel as well as for heating solutions
Appearance - round bottom, wider and longer neck than round-bottom flask, no glass joint in the neck,
Uses - useful as a reaction vessel as well as for heating solutions

13
New cards
Desiccator
Appearance - glass container with sealable enclosure
Uses - preserving moisture-sensitive chemicals; protect chemicals that are hygroscopic or which react with water from humidity
Uses - preserving moisture-sensitive chemicals; protect chemicals that are hygroscopic or which react with water from humidity

14
New cards
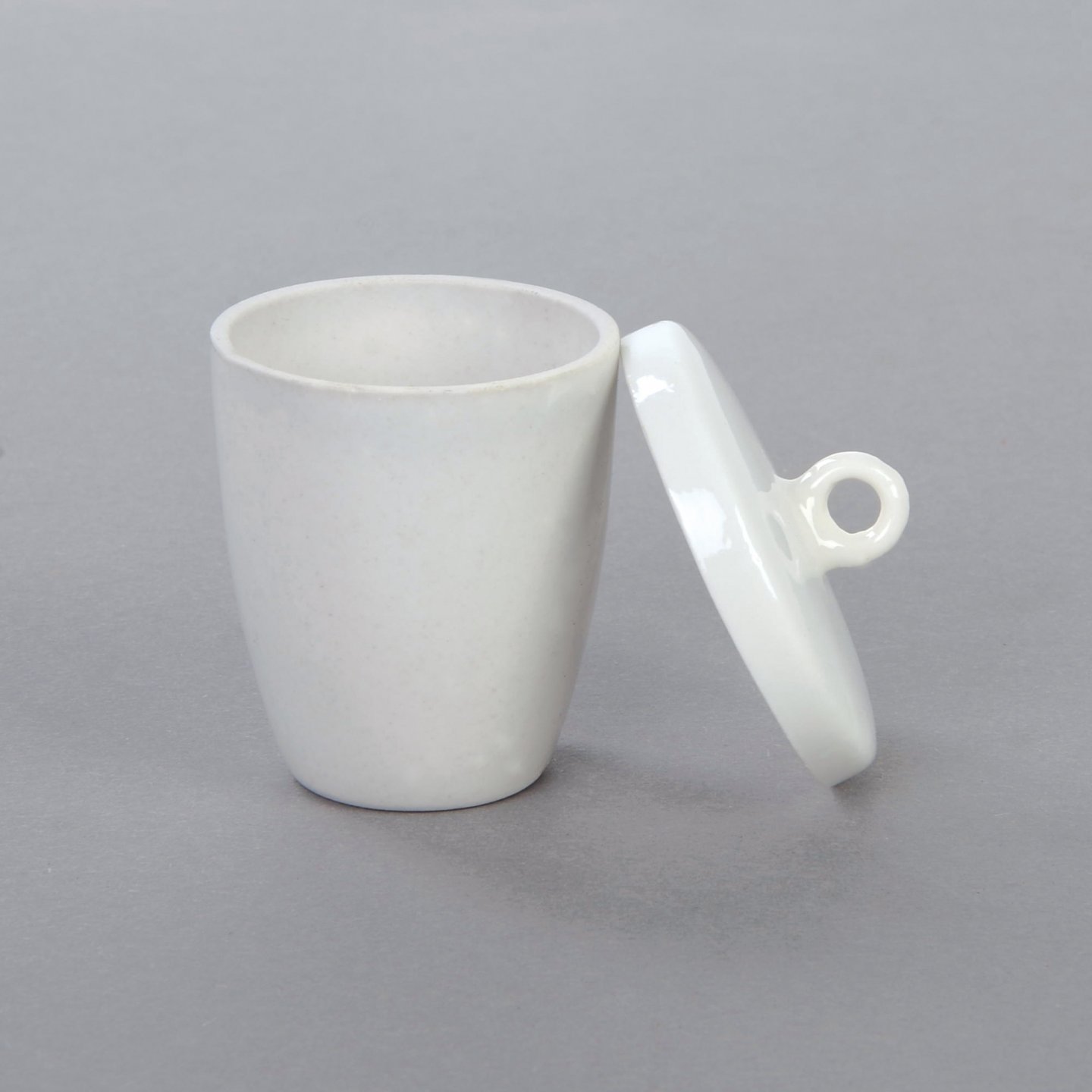
Crucible
Appearance - cup-shaped with lid, usually made of porcelain
Uses - used to contain chemical compounds when heating them to very high temperatures
* needs to be heat-treated before its first use
Uses - used to contain chemical compounds when heating them to very high temperatures
* needs to be heat-treated before its first use

15
New cards
Kipp’s Apparatus
*“Kipp Generator”*
Appearance - made of glass; consists of three vertically stacked chambers, roughly resembling a snowman
Uses - for preparation of small volumes of gases.
Appearance - made of glass; consists of three vertically stacked chambers, roughly resembling a snowman
Uses - for preparation of small volumes of gases.

16
New cards
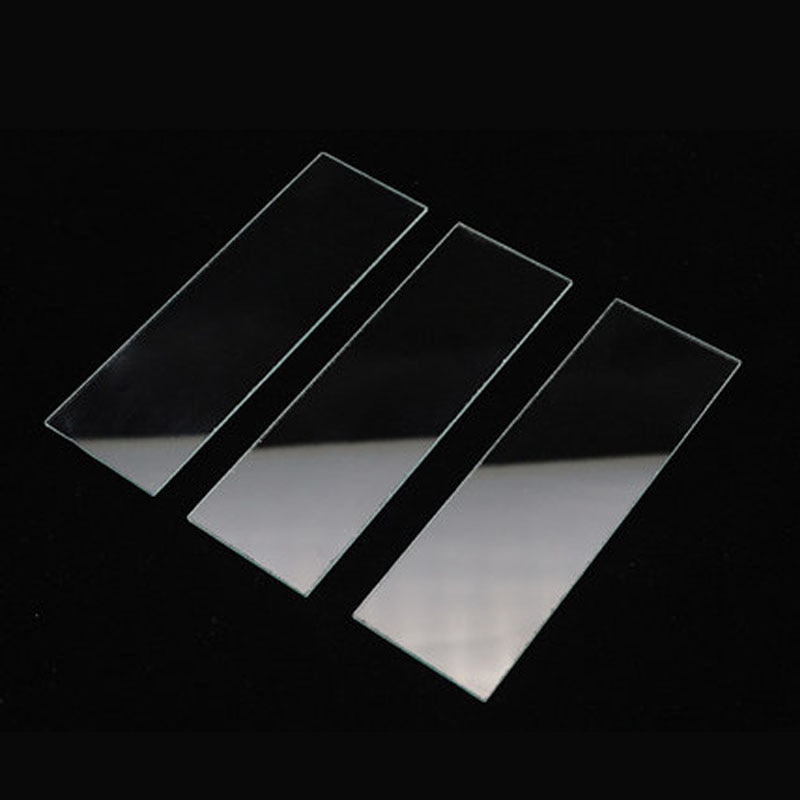
Microscope Slide
Appearance - Rectangle thin flat glass
Uses - to hold objects or view samples for examination under a microscope
Uses - to hold objects or view samples for examination under a microscope

17
New cards
Cover Slip
Appearance - a thin flat piece of glass, smaller than M. Slide
Uses - placed over a specimen on a microscope slide, to hold the specimen in place and protect it from contamination from the environment.
Uses - placed over a specimen on a microscope slide, to hold the specimen in place and protect it from contamination from the environment.

18
New cards
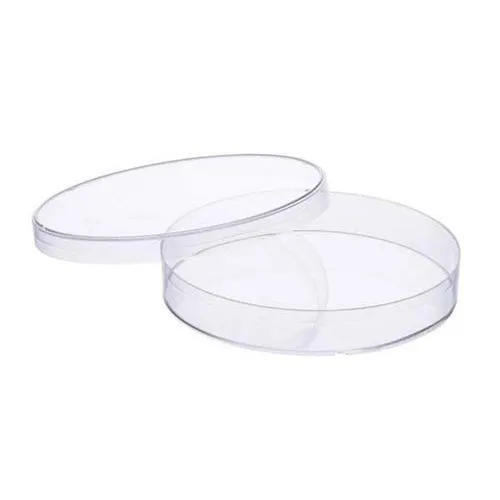
Petri Dish
Appearance - shallow transparent lidded dish, made with glass or plastic
Uses - to culture different types of cells, including bacteria and molds.
Uses - to culture different types of cells, including bacteria and molds.

19
New cards
Watch Glass
Appearance - circular piece of glass, slightly concave
Uses - *evaporate liquids* and cover beakers during sample preparation
Uses - *evaporate liquids* and cover beakers during sample preparation

20
New cards
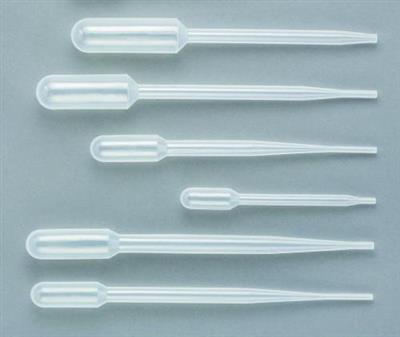
Beral Pipette
Type of Pipette
*“Transfer Pipettes”*
Appearance - Plastic Pipette, graduated or non-graduated
Uses - Non-quantitative transfer, transfer a *larger amount of liquid* where accuracy is not important,
* Disposable
*“Transfer Pipettes”*
Appearance - Plastic Pipette, graduated or non-graduated
Uses - Non-quantitative transfer, transfer a *larger amount of liquid* where accuracy is not important,
* Disposable
21
New cards
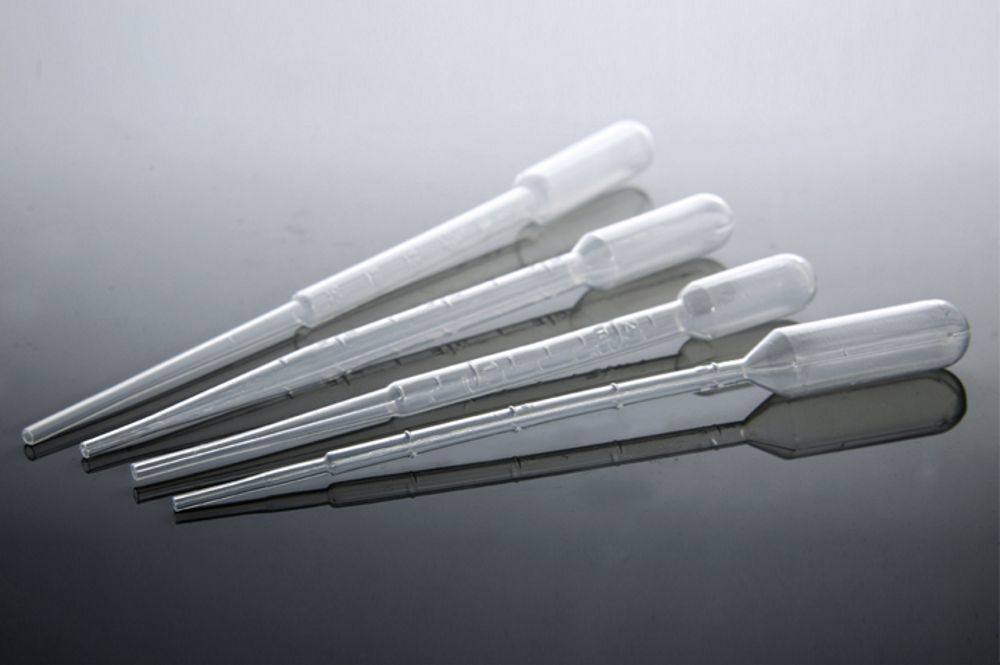
Pasteur Pipette
Type of Pipette
“Glass Pipette”
Appearance - thin glass transfer pipette, usually not-graduated
Uses - transfer small amounts of liquids
* needs a rubber bulb to draw liquid
* higher precision and more accuracy as compared to the Beral pipette
* dropper or eye dropper
“Glass Pipette”
Appearance - thin glass transfer pipette, usually not-graduated
Uses - transfer small amounts of liquids
* needs a rubber bulb to draw liquid
* higher precision and more accuracy as compared to the Beral pipette
* dropper or eye dropper

22
New cards
Volumetric Pipette
Type of Pipette
“Bulb Pipette”
Appearance - long slender necks, equipped with a large *bulb* with a *single graduation mark*
Uses -
to transfer the volume of liquid for use in creating a solution or dilution, prepare solutions for titration
can be used to investigate chemical properties and analyze reactions
* highly accurate for specific volume
“Bulb Pipette”
Appearance - long slender necks, equipped with a large *bulb* with a *single graduation mark*
Uses -
to transfer the volume of liquid for use in creating a solution or dilution, prepare solutions for titration
can be used to investigate chemical properties and analyze reactions
* highly accurate for specific volume

23
New cards
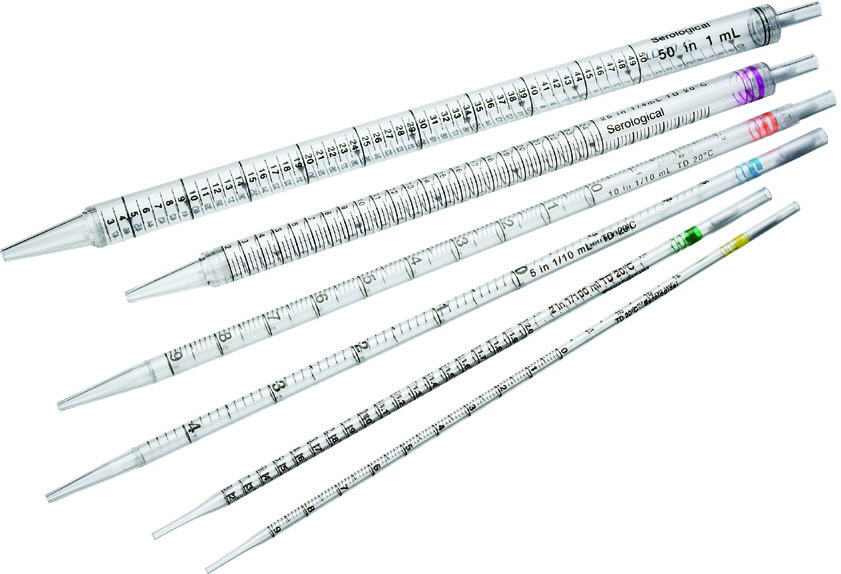
Serological Pipettes
Type of Pipette
*“Blow-out pipettes”*
Appearance - graduated, long and straight tube, uses pipette bulb, pen-like
* designed to be blown out by either external air pressure or gravitation force
* requires a vacuum source for liquid dispensing
Uses - transferring liquid in milliliter volumes, useful for mixing solutions and cell suspensions
* offer clear ascending and descending graduation
*“Blow-out pipettes”*
Appearance - graduated, long and straight tube, uses pipette bulb, pen-like
* designed to be blown out by either external air pressure or gravitation force
* requires a vacuum source for liquid dispensing
Uses - transferring liquid in milliliter volumes, useful for mixing solutions and cell suspensions
* offer clear ascending and descending graduation
24
New cards
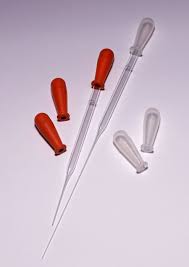
Teat Pipette
“*Dropper”*
Combination of Pasteur pipettes and bulb
Combination of Pasteur pipettes and bulb
25
New cards
Pipette Bulb
Appearance - bulb, usually made of rubber
Use - to create a vacuum or apply pressure to the liquid contents of a pipette; to collect, transfer, and dispense liquids
Use - to create a vacuum or apply pressure to the liquid contents of a pipette; to collect, transfer, and dispense liquids

26
New cards
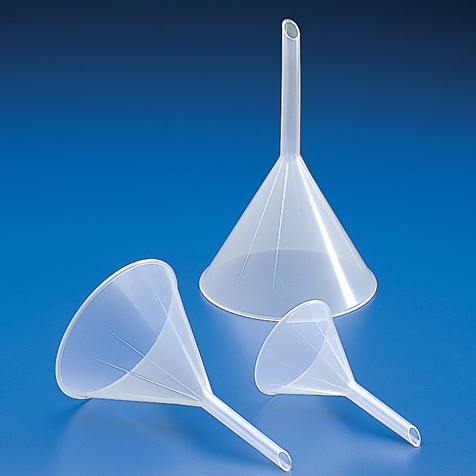
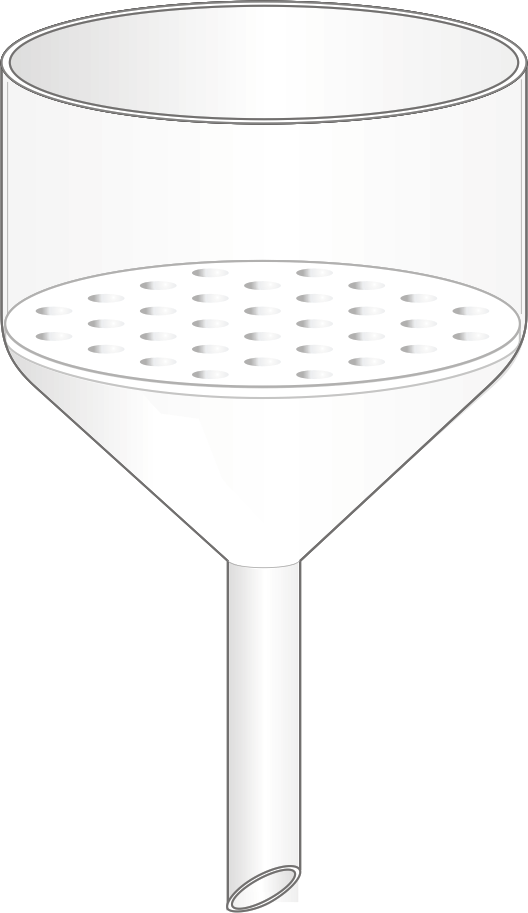
Funnel
Appearance - a tube or pipe that is wide at the top and narrow at the bottom
Uses - filtering, filling, decanting or transferring liquids or powders from one vessel to another
Uses - filtering, filling, decanting or transferring liquids or powders from one vessel to another

27
New cards
Büchner Funnel
Type of Funnel
Appearance -cylindrical construction with a large, fritted (or perforated) top opening consisting of many tiny holes
Uses - separate solids from liquids, *vacuum-assisted liquid filtering*, removes moisture and helps to collect recrystallized compounds
* Filter Funnels
* often used with Buchner flask
* proceeds more quickly than other funnels
Appearance -cylindrical construction with a large, fritted (or perforated) top opening consisting of many tiny holes
Uses - separate solids from liquids, *vacuum-assisted liquid filtering*, removes moisture and helps to collect recrystallized compounds
* Filter Funnels
* often used with Buchner flask
* proceeds more quickly than other funnels
28
New cards
Hirsch Funnel
Type of Funnel
Appearance - similar to Buchner but smaller and have sloping walls
Uses - used to filter and collect solids from a small volume of liquid (1-10 ml)
* Filter Funnels
Appearance - similar to Buchner but smaller and have sloping walls
Uses - used to filter and collect solids from a small volume of liquid (1-10 ml)
* Filter Funnels

29
New cards
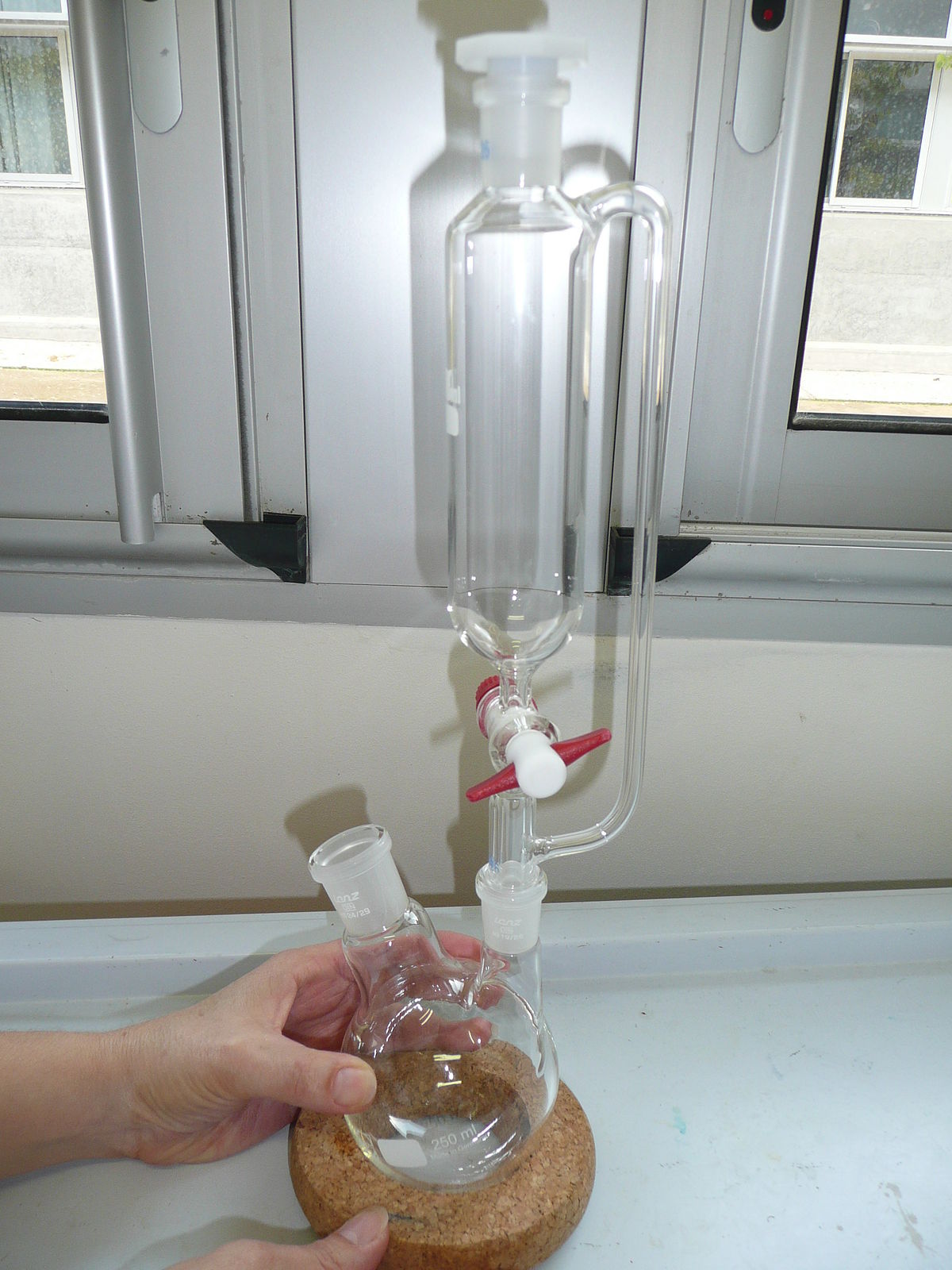
Dropping Funnel
Type of Funnel
Appearance - glass tube with a large cylindrical bulb in the middle, have a valve in the bottom, narrow at the bottom and have a wide opening at the top
Uses - transfer fluids, *used to add or drop liquids* to a reaction mixture, useful for adding reagents slowly
* stopcock (valve) allows the flow to be controlled
* Pressure equalizing funnel, addition funnels
* can be graduated or non-graduated
Appearance - glass tube with a large cylindrical bulb in the middle, have a valve in the bottom, narrow at the bottom and have a wide opening at the top
Uses - transfer fluids, *used to add or drop liquids* to a reaction mixture, useful for adding reagents slowly
* stopcock (valve) allows the flow to be controlled
* Pressure equalizing funnel, addition funnels
* can be graduated or non-graduated

30
New cards
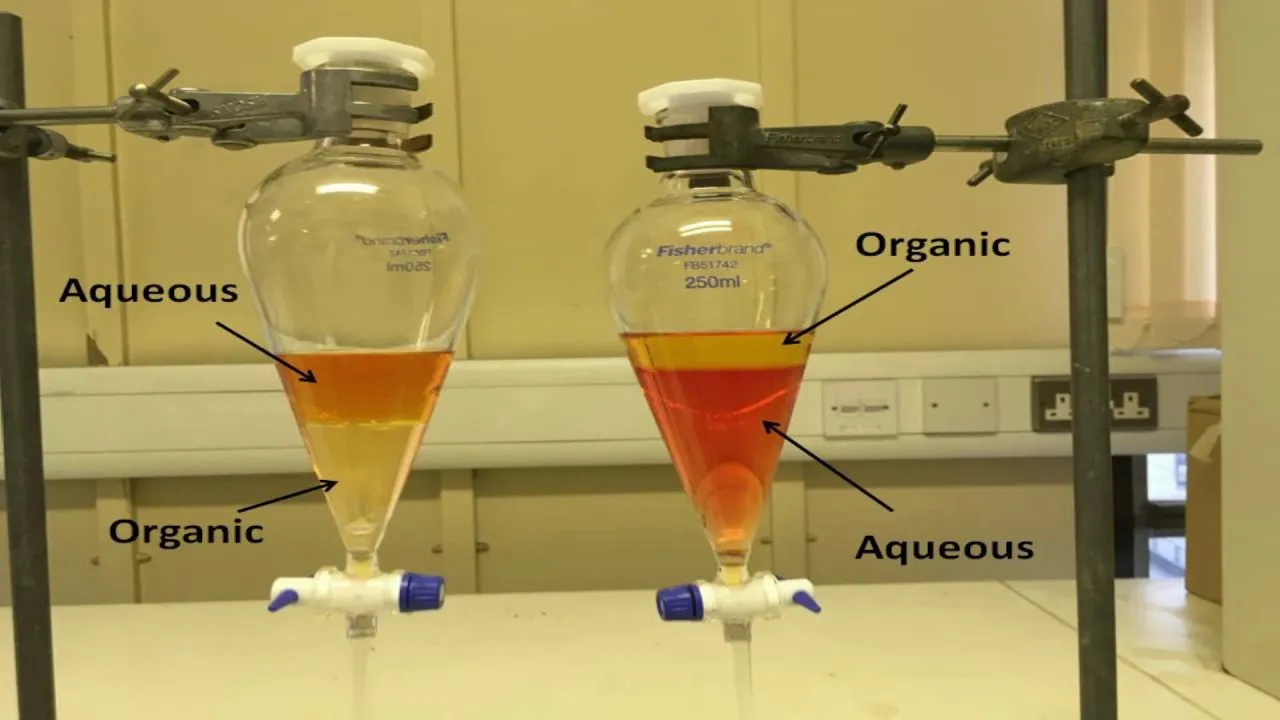
Separating Funnels
Type of Funnel
Appearance - wide at the bottom and have a narrow opening at the top, Squibb or pear shape
* have a stopper on top to prevent spills
* have a stopcock(valve)
Uses - separate immiscible liquids, separate low-density liquid and high density
* not designed for filtration (solid from liquid)
Appearance - wide at the bottom and have a narrow opening at the top, Squibb or pear shape
* have a stopper on top to prevent spills
* have a stopcock(valve)
Uses - separate immiscible liquids, separate low-density liquid and high density
* not designed for filtration (solid from liquid)

31
New cards
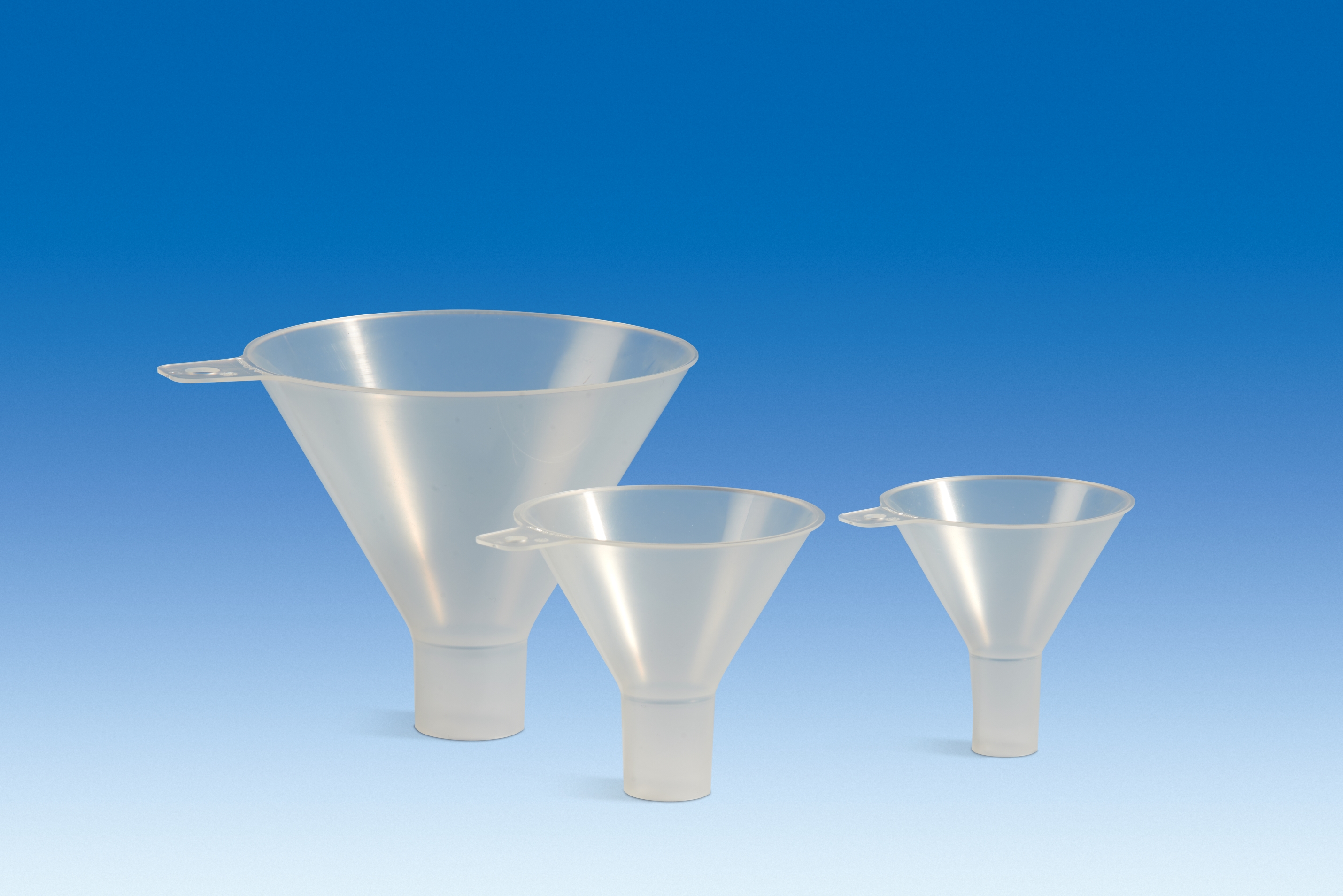
Powder Funnel
Type of Funnel
Appearance - typical funnels but have a wider spout and short neck
Uses - to channel liquids or fine-grained chemicals (powders) into labware with a narrow neck or opening,
* enable the clean transfer of powders, granulated materials, or other solids
Appearance - typical funnels but have a wider spout and short neck
Uses - to channel liquids or fine-grained chemicals (powders) into labware with a narrow neck or opening,
* enable the clean transfer of powders, granulated materials, or other solids

32
New cards
Weighing Funnel
Type of Funnel
Appearance - have a wide opening, flat bottoms, and are designed to fit narrow neck vessels.
Uses - weighing and transporting powder
* one flat side for stability, ensuring that the funnel will not roll-off
Appearance - have a wide opening, flat bottoms, and are designed to fit narrow neck vessels.
Uses - weighing and transporting powder
* one flat side for stability, ensuring that the funnel will not roll-off

33
New cards
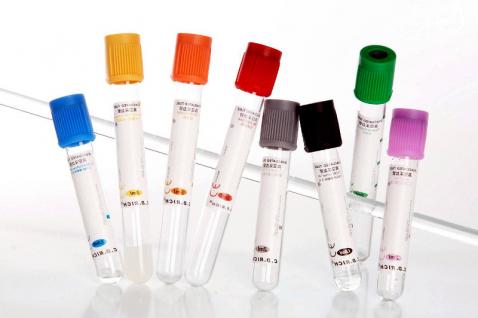
Test Tubes
*“culture or sample tube”*
Appearance - finger-like length of glass or clear plastic tubing, open at the top and closed at the bottom
* spherical bottom and vertical sides reduce mass loss when pouring, make them easier to wash out, and allow convenient monitoring of the contents
* narrow neck of test tube slows down the spreading of gases to the environment
Uses - to hold, mix, or heat small quantities of solid or liquid chemicals; to culture, or grow, samples of various organic materials such as bacteria, mold, and yeast
* Boiling Tube - larger tube for boiling substances
Appearance - finger-like length of glass or clear plastic tubing, open at the top and closed at the bottom
* spherical bottom and vertical sides reduce mass loss when pouring, make them easier to wash out, and allow convenient monitoring of the contents
* narrow neck of test tube slows down the spreading of gases to the environment
Uses - to hold, mix, or heat small quantities of solid or liquid chemicals; to culture, or grow, samples of various organic materials such as bacteria, mold, and yeast
* Boiling Tube - larger tube for boiling substances
34
New cards
Spirit Lamp/ Alcohol Burner
Appearance - small jar with a tank for fuel and comes with a lid which has a tiny hole to hold a single wick
Uses - used to produce open single flame (2 inches), can be used for flame sterilization
* Typical fuel is denatured alcohol, methanol, or isopropanol
* cap is used as a snuffer for extinguishing the flame
Uses - used to produce open single flame (2 inches), can be used for flame sterilization
* Typical fuel is denatured alcohol, methanol, or isopropanol
* cap is used as a snuffer for extinguishing the flame

35
New cards
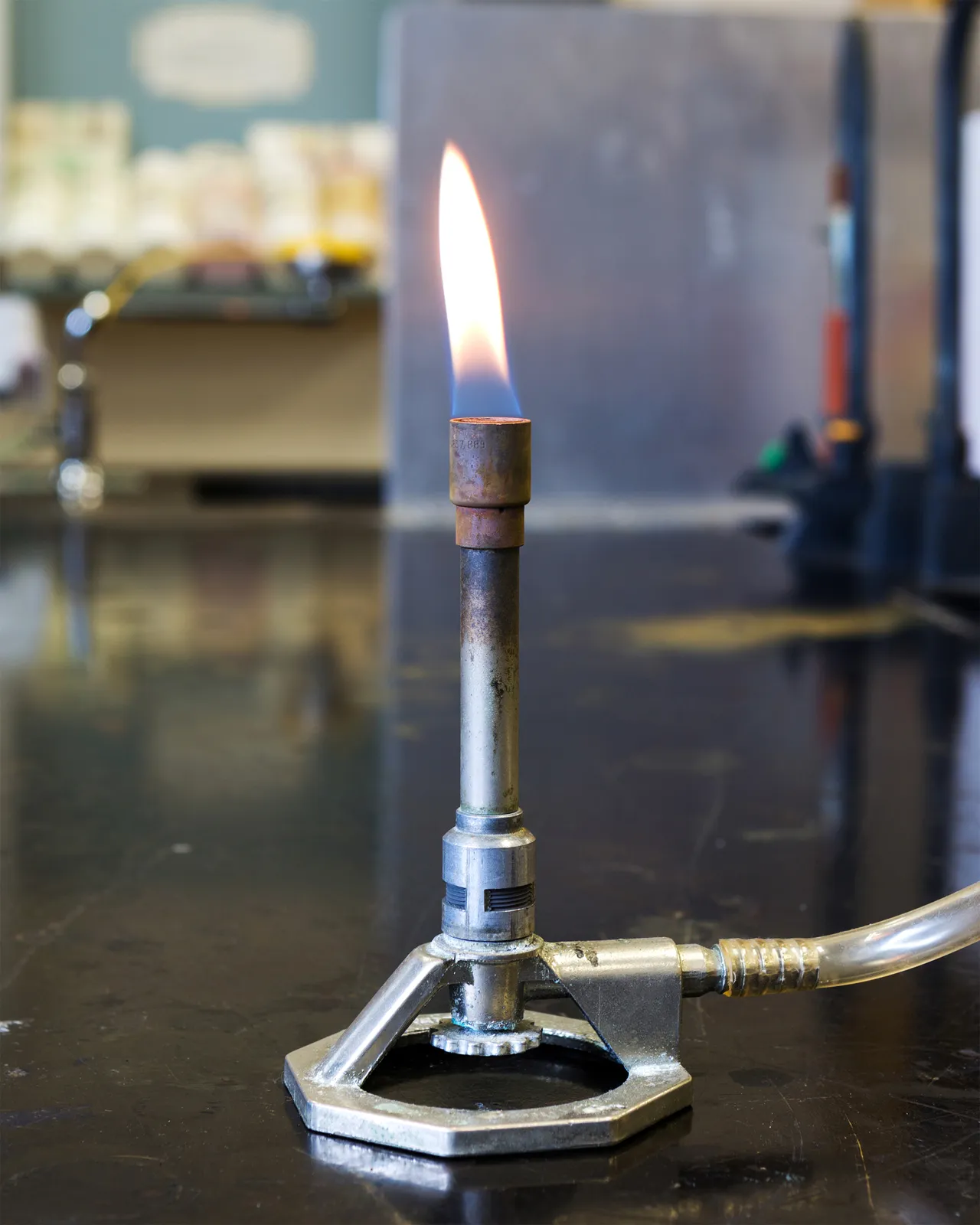
Bunsen Burner
Appearance - air gas burner
Used - for heating, sterilization, and combustion
* The gas can be natural gas (which is mainly methane) or a liquefied petroleum gas, such as propane, butane, or a mixture.
* the burner is placed underneath a laboratory tripod, which supports a beaker or other container
* alternative burners; teclu, meker, tirrill
Used - for heating, sterilization, and combustion
* The gas can be natural gas (which is mainly methane) or a liquefied petroleum gas, such as propane, butane, or a mixture.
* the burner is placed underneath a laboratory tripod, which supports a beaker or other container
* alternative burners; teclu, meker, tirrill

36
New cards
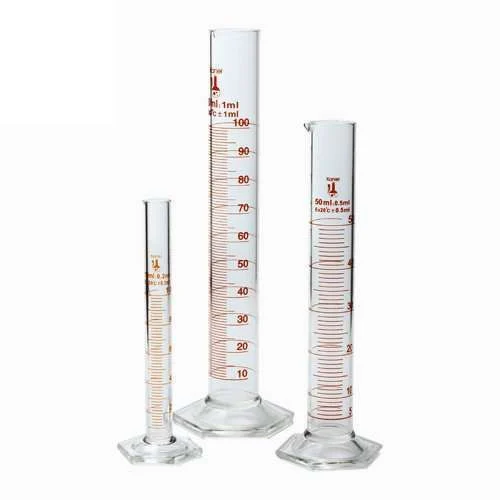
Graduated Cylinder
Measuring Cylinders
Appearance- long and slender containers with measurement, *tall cylindrical beakers*
Uses - used to measure the volume of a liquids, chemicals or solutions, can measure displacement
* more precise and accurate than the common laboratory flasks and beakers
Appearance- long and slender containers with measurement, *tall cylindrical beakers*
Uses - used to measure the volume of a liquids, chemicals or solutions, can measure displacement
* more precise and accurate than the common laboratory flasks and beakers

37
New cards
Mortar and Pestle
Appearance - Bowl and Pestle commonly made of stone, ceramic, or wood
Uses - crush up solid chemicals into smaller pieces, or to grind solids into fine powder, makes it easier to dissolve solids into solvents
Uses - crush up solid chemicals into smaller pieces, or to grind solids into fine powder, makes it easier to dissolve solids into solvents

38
New cards
Tripod Stand
Appearance - three-legged platform, commonly triangular or circular, tall enough for a __bunsen burner__
Uses - basic heating experiments, platform to support and hols flask and beakers
Uses - basic heating experiments, platform to support and hols flask and beakers

39
New cards
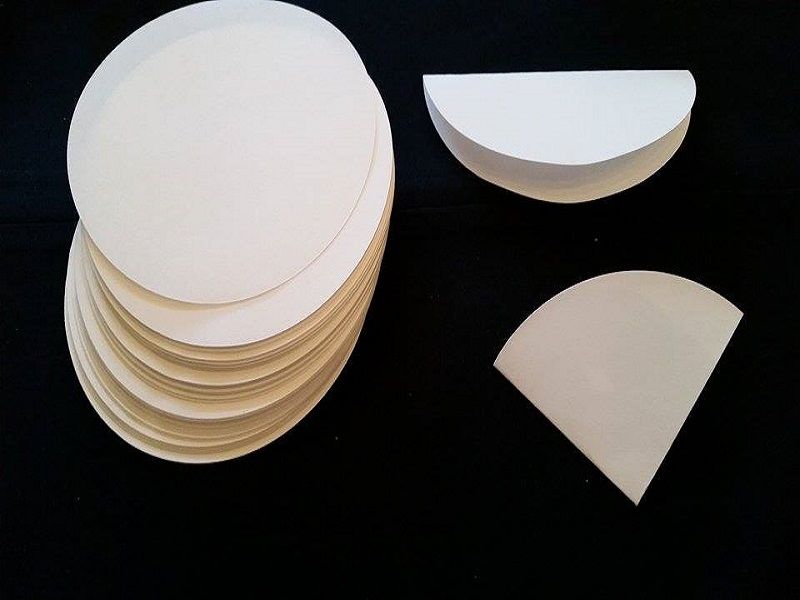
Filter Paper
Appearance - Circle paper with tiny pores
Uses - separate fine substances from liquids or airflow as a semi-permeable barrier
Uses - separate fine substances from liquids or airflow as a semi-permeable barrier

40
New cards
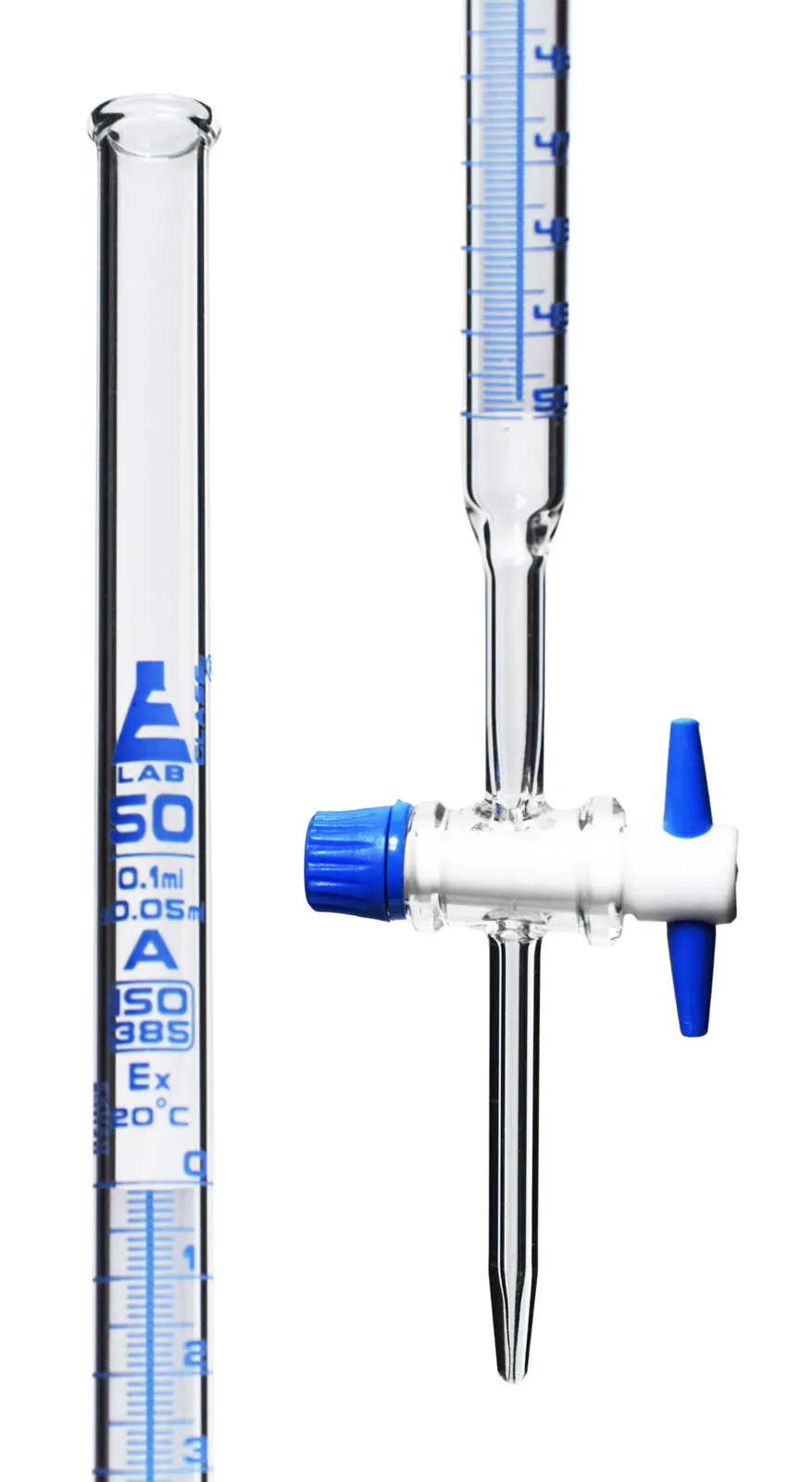
Burette
Appearance - graduated glass tube with a stopcock(valve)
* stopcock is at top; gas burette, at bottom; liquid burette
Uses - quantitative chemical analysis to measure the volume of a liquid or a gas, used for titration
* stopcock is at top; gas burette, at bottom; liquid burette
Uses - quantitative chemical analysis to measure the volume of a liquid or a gas, used for titration

41
New cards
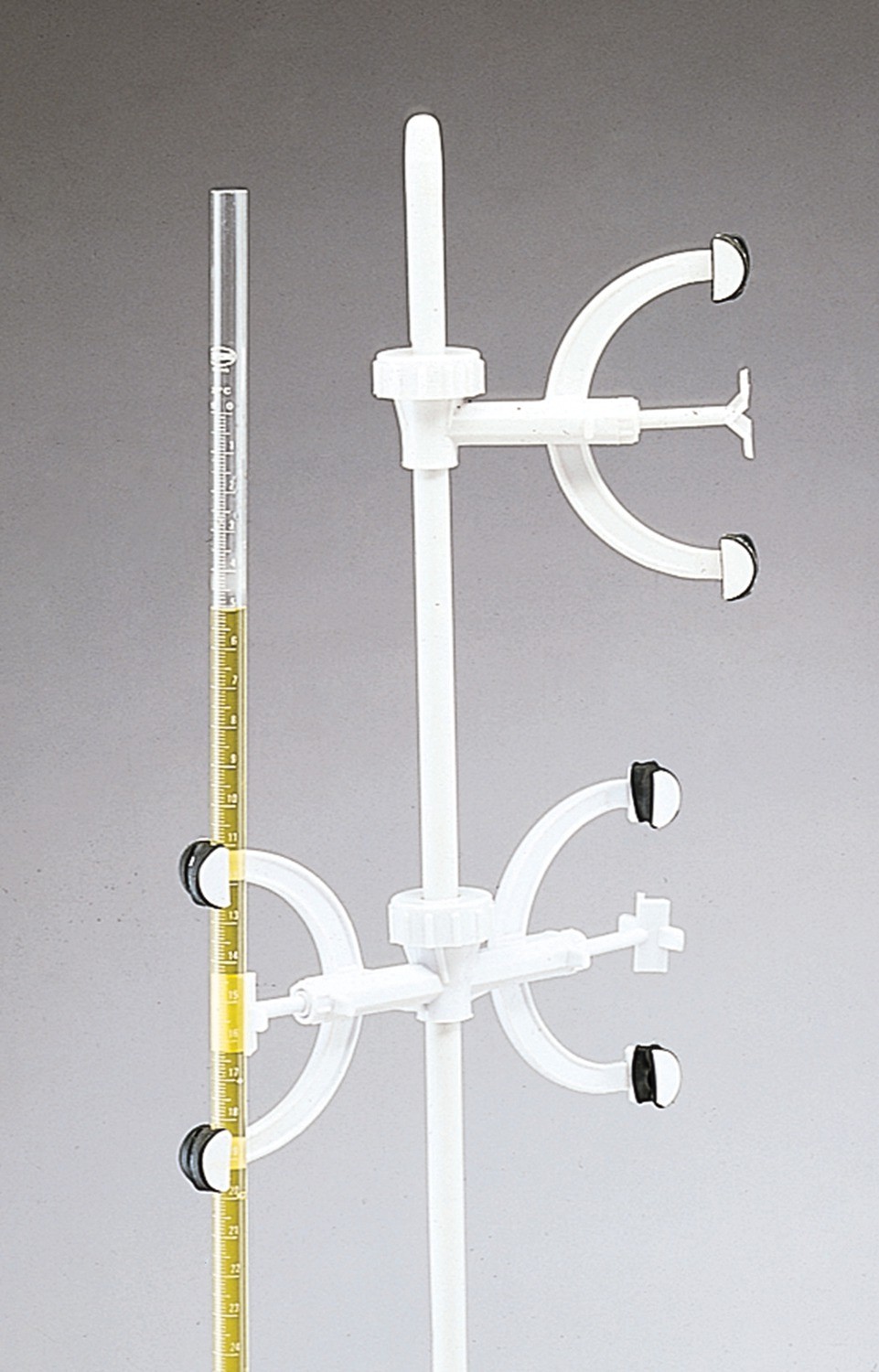
Burette Clamp
Appearance - single or double Y-shaped items, with a C-shaped opening, which have spring action clamps
Uses - specifically to hold and secure a burette on a stand
Uses - specifically to hold and secure a burette on a stand
42
New cards
Utility Clamp
Appearance - attached to a medal rod or the ring stand
Uses - used to fasten or support apparatus such as a beaker, and flasks, etc.
* Two/Three - Prong Extension Clamps, Fixed-Position Clamps, Closed-Yoke Clamps, Fixed-Position Clamps
Uses - used to fasten or support apparatus such as a beaker, and flasks, etc.
* Two/Three - Prong Extension Clamps, Fixed-Position Clamps, Closed-Yoke Clamps, Fixed-Position Clamps

43
New cards
Ring Clamps
“*iron ring”*
Appearance - conjoined metal ring and radially extending rod
Uses - used to hold separatory funnels and secure funnels when filtering or pouring liquids
* have superior thermal resistance and offer some of the most stability you can get out of a stand clamp
Appearance - conjoined metal ring and radially extending rod
Uses - used to hold separatory funnels and secure funnels when filtering or pouring liquids
* have superior thermal resistance and offer some of the most stability you can get out of a stand clamp

44
New cards
Ring Stand
“*Clamp/retort/support stand”*
Appearance - heavy base and a vertical rod
Uses - stability when different clamps and iron rings are attached, distillations, filtration, and titration experiments
Appearance - heavy base and a vertical rod
Uses - stability when different clamps and iron rings are attached, distillations, filtration, and titration experiments

45
New cards
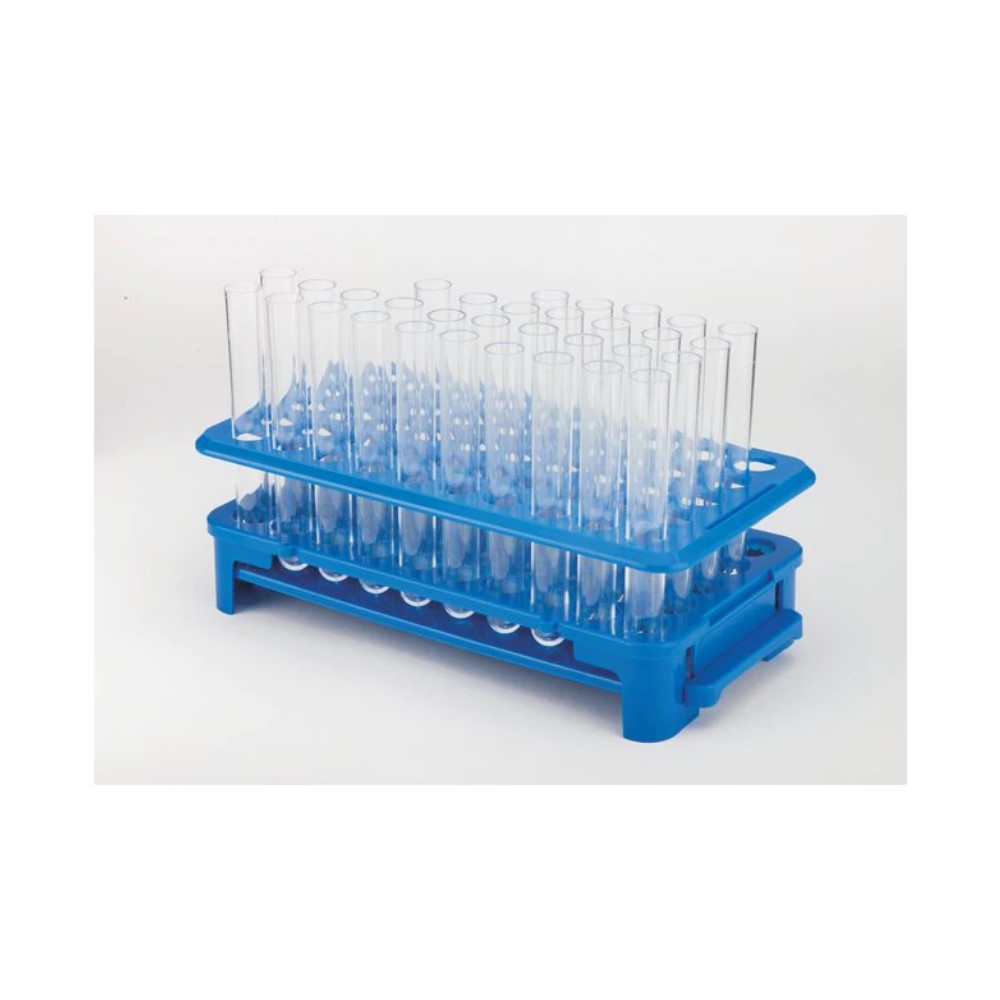
Test Tube Stand/Rack
Used to hold upright multiple test tubes at the same time

46
New cards
Test Tube Holder/Clamp
Appearance - similar to a tongs
Uses - to hold test tubes when it is not supposed to be touched
Uses - to hold test tubes when it is not supposed to be touched

47
New cards
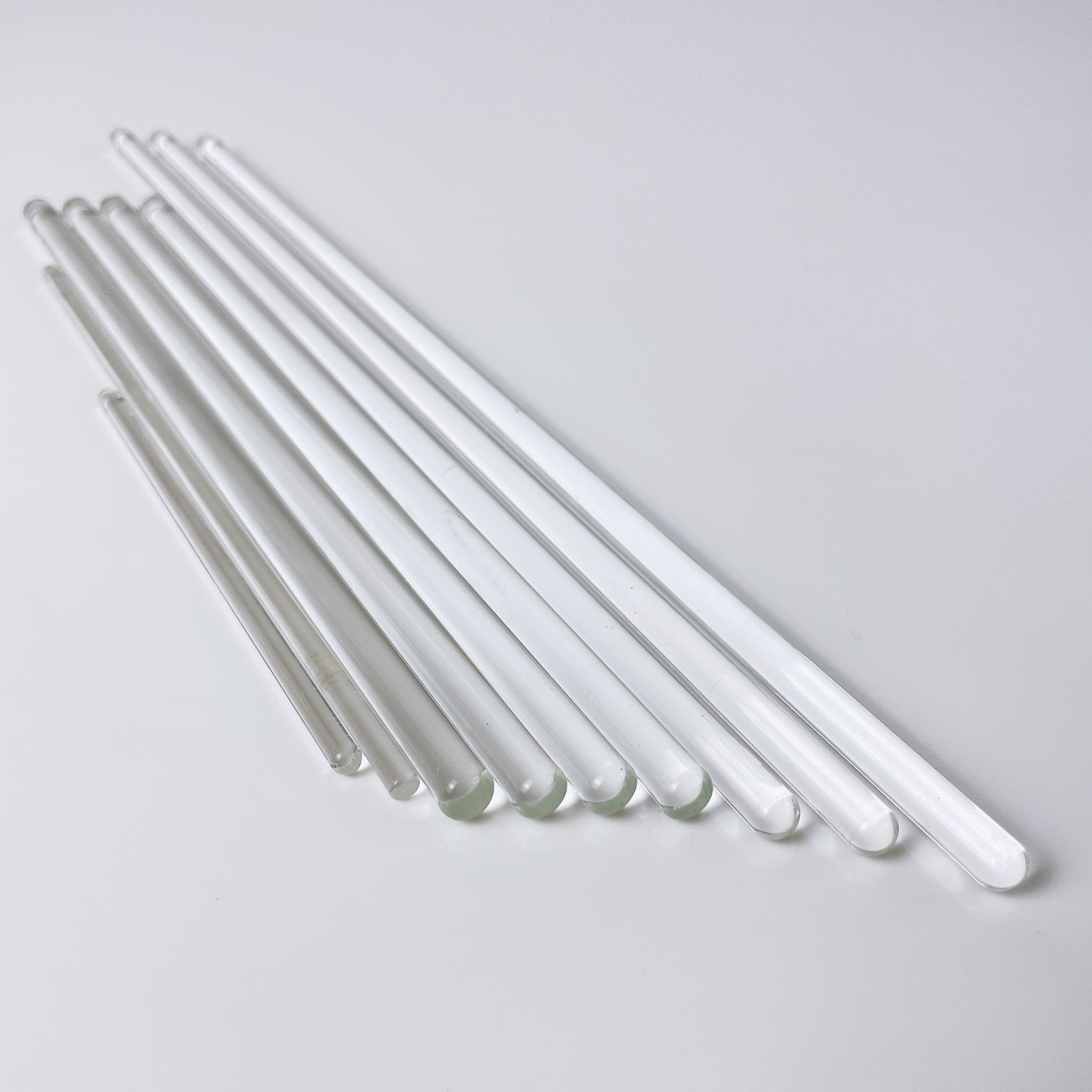
Glass Rod
*“Stirring Rod”*
Used to mix chemicals and liquids for laboratory purposes
Used to mix chemicals and liquids for laboratory purposes

48
New cards
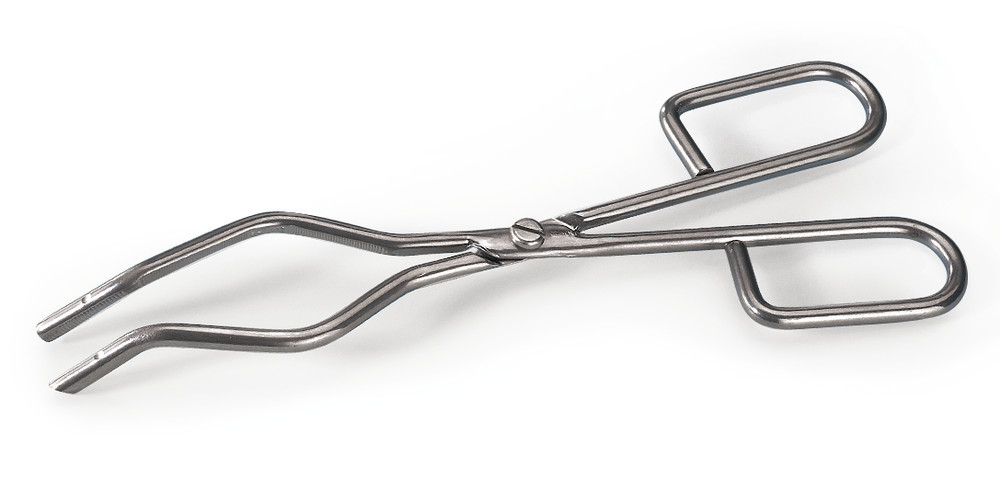
Crucible Tongs
a scissor-like tool used to grip and lift objects instead of holding them directly with hands.

49
New cards
Spatula/Scoopula
__spatula__-like scoop utensil; *used for scraping, transferring, or applying powders and paste-like chemicals or treatments.* Many spatula brands are also *resistant to acids, bases, heat, and solvents*, which make them ideal for use with a wide range of compounds.

50
New cards
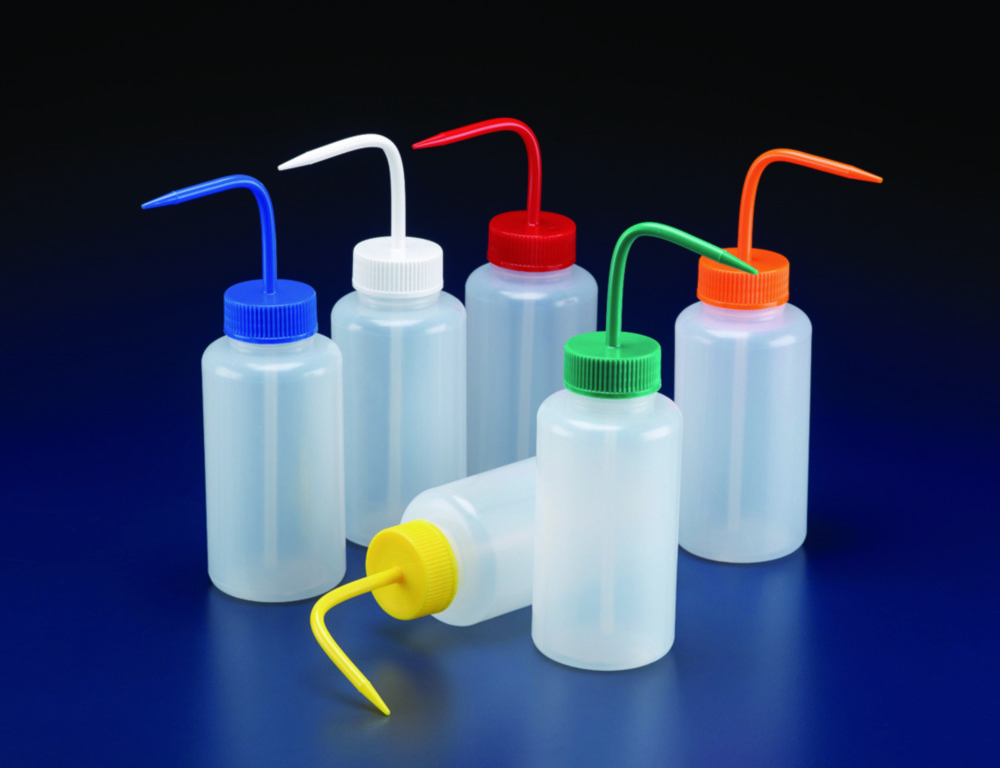
Wash Bottle
a squeeze bottle with a nozzle, *used to rinse various pieces of laboratory glassware*, such as test tubes and round bottom flasks

51
New cards
Beaker Tongs
tongs with rubber grips shaped to hold a beaker

52
New cards
Ceramic Fabric Squares
asbestos-free *insulating squares* that are ideal for protecting laboratory bench tops against heat

53
New cards
Rubber Stoppers
“*Rubber Bungs*”
used to seal bottles, tubes and many other containers
used to seal bottles, tubes and many other containers
54
New cards
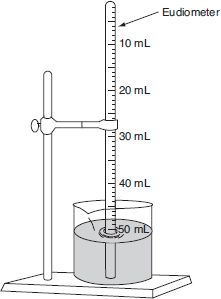
Eudiometer
“*Glass Collecting Tube”*
Appearance - Large glass tube, graduated
Uses - used to measure changes in volume of gases during chemical reactions
Appearance - Large glass tube, graduated
Uses - used to measure changes in volume of gases during chemical reactions
55
New cards
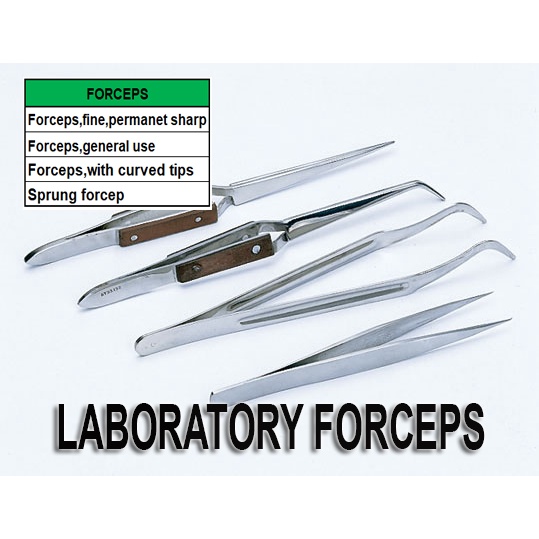
Forceps
small tool that is used to hold or pick up small objects
“*tweezers”*
“*tweezers”*
56
New cards
Pneumatic Through
a piece of laboratory apparatus *used for collecting gases*, such as hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.

57
New cards
RUBBER TUBING
* Rubber tubing is often connected to a condenser, which is a laboratory tool *used in the process of distillation;*
* helps cool water to flow in and out of the condenser and helps the heated water vapor in the condenser return to its liquid state;
* *used to circulate and transport liquids and gases*
* helps cool water to flow in and out of the condenser and helps the heated water vapor in the condenser return to its liquid state;
* *used to circulate and transport liquids and gases*

58
New cards
Safety Googles/Glasses
worn in the lab to protect the eyes
59
New cards
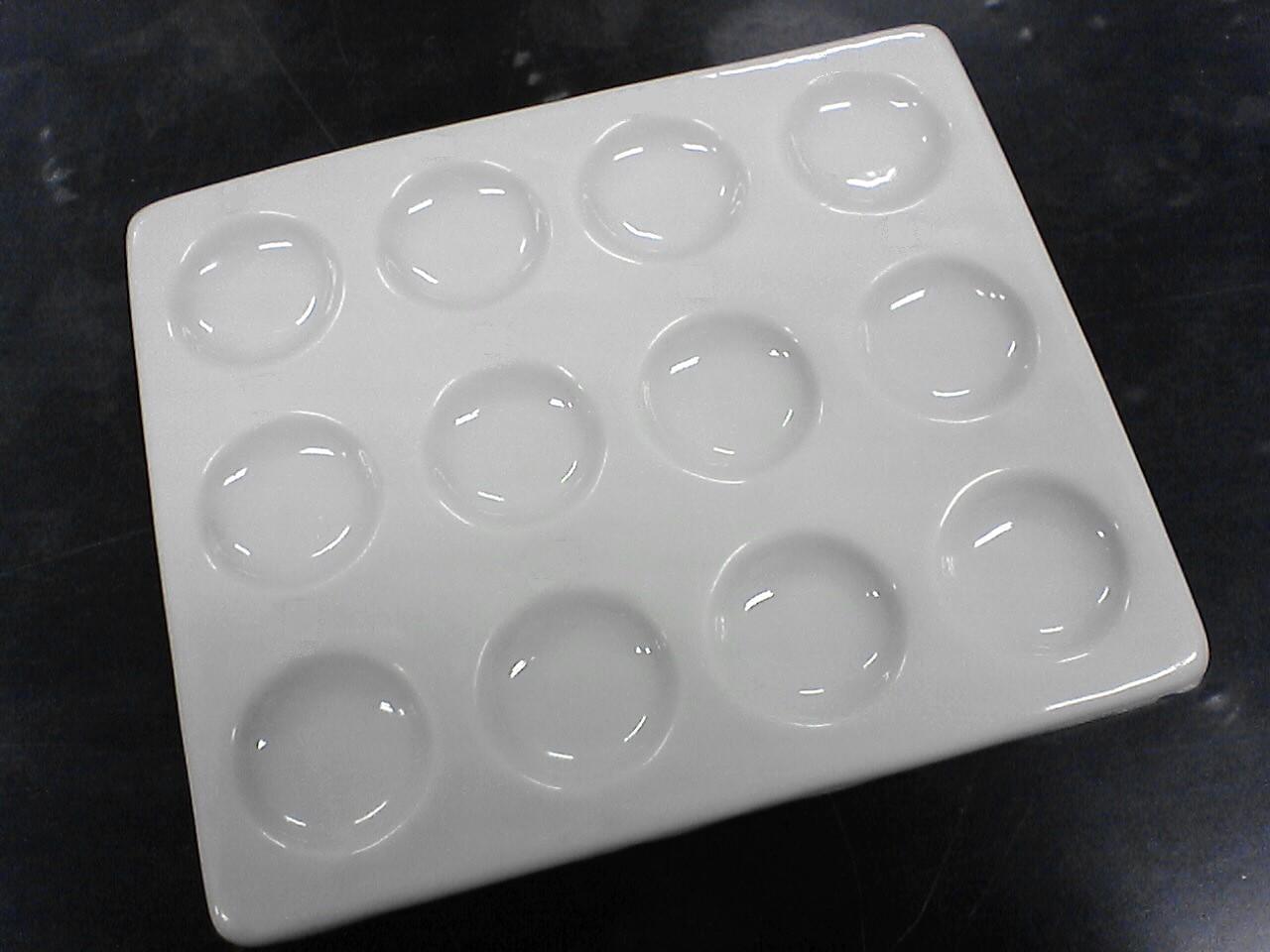
Spot Plate
“*Reaction/culture plates"*
lab instrument designed to facilitate the testing of multiple samples
lab instrument designed to facilitate the testing of multiple samples

60
New cards
Thermometer
used to measure the boiling point and freezing point during science experiments.

61
New cards
Wire Gauze
\
* used to spread the heat of a burner flame and to support glassware
* Intended for flat-bottomed glassware such as beakers, and flasks.
* made of iron wire strands with or without ceramic interior cores
* used to spread the heat of a burner flame and to support glassware
* Intended for flat-bottomed glassware such as beakers, and flasks.
* made of iron wire strands with or without ceramic interior cores

62
New cards
Reagent bottle
*“media bottles or graduated bottles”*
* containers made of glass, plastic, borosilicate or related substances, and topped by special caps or __stoppers__
* They are intended to contain chemicals in liquid or powder form for laboratories and stored in cabinets or on shelves.
* containers made of glass, plastic, borosilicate or related substances, and topped by special caps or __stoppers__
* They are intended to contain chemicals in liquid or powder form for laboratories and stored in cabinets or on shelves.

63
New cards
Simple/Dissecting Microscope
* uses a single lens for magnification

64
New cards
Compound Microscope
* uses 3-5 lenses
* 'monocular and binocular
* 'monocular and binocular

65
New cards
Weigh Boat
economical containers for *weighing liquid or powdered samples* in the laboratory

66
New cards
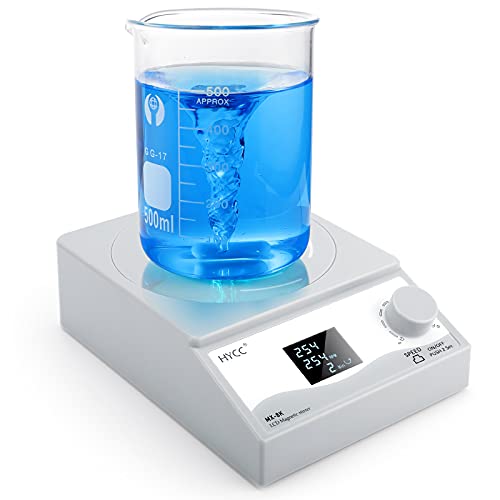
Magnetic Stirrer
* consists of a rotating magnet or a stationary electromagnet that creates a rotating magnetic field.
* This device is used to make a stir bar, immerse in a liquid, quickly spin, or stirring or mixing a solution
* This device is used to make a stir bar, immerse in a liquid, quickly spin, or stirring or mixing a solution

67
New cards
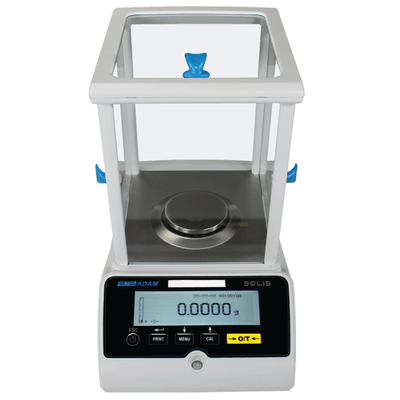
Digital Balance
* “*electronic balance”*
* is used to precisely and accurately *measure the weight of materials*
* The use of electronic balance includes scientific and pharmaceutical research, bakeries, and chemical laboratories
* is used to precisely and accurately *measure the weight of materials*
* The use of electronic balance includes scientific and pharmaceutical research, bakeries, and chemical laboratories

68
New cards
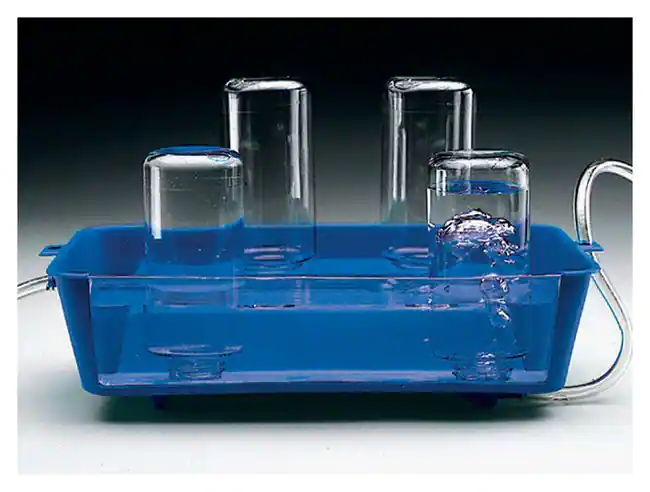
Water Bath
* container filled with heated water
* used to incubate samples in water at a constant temperature over a long period of time
* used to incubate samples in water at a constant temperature over a long period of time

69
New cards
Digital Conductivity Meters
“*Digital Conductometer”*
* measures the electrical conductivity in a solution
* reliable and accurate test instruments for measurement of Conductivity of aqueous solutions
* measures the electrical conductivity in a solution
* reliable and accurate test instruments for measurement of Conductivity of aqueous solutions

70
New cards
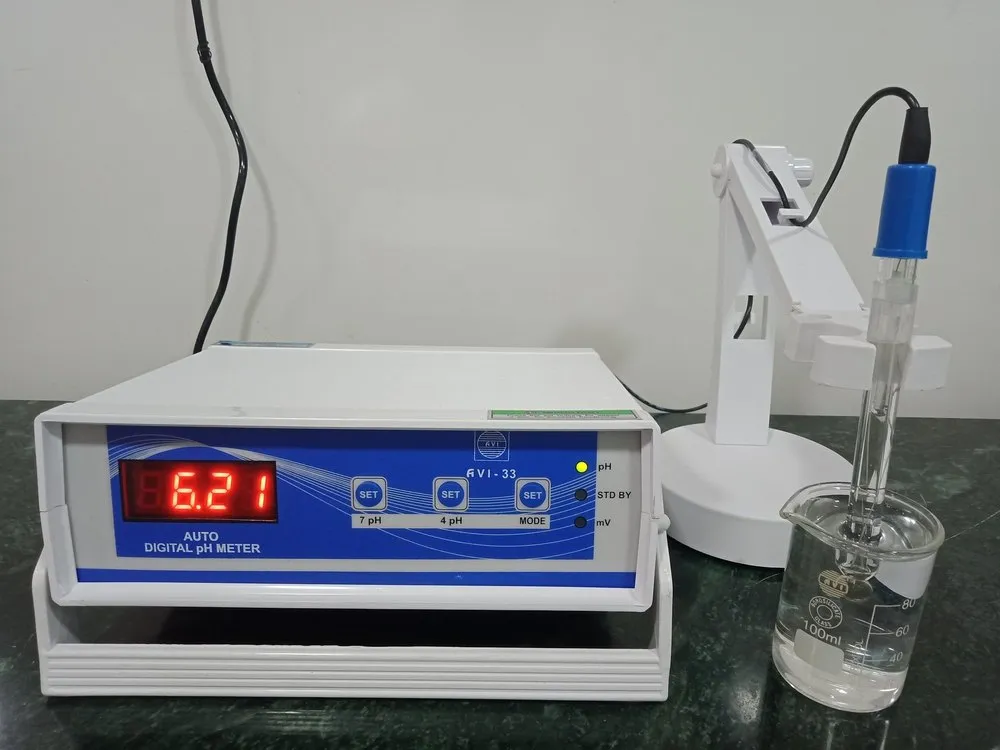
Digital pH meter
a scientific instrument that measures the hydrogen-ion activity in water-based solutions, indicating its acidity or alkalinity expressed as pH
