Nuclear Chemistry
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
alpha particle α
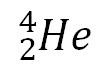
2
New cards
beta particle β
aka electron
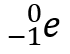
3
New cards
gamma particle γ
high-energy photon, electromagnetic radiation, always accompanied by another particle
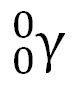
4
New cards
positron
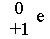
5
New cards
neutron
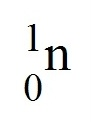
6
New cards
proton
1/1 H
7
New cards
the more energy created...
the more harmful it is to the human body
8
New cards
chemical reactions
reactions involving electrons
9
New cards
nuclear reactions
reactions involving protons and neutrons
10
New cards
radioactive
nucleus becomes unstable and tries to become stable--gives off radiation
11
New cards
1:1 ratio of protons to neutrons
necessary for keeping the nucleus stable
12
New cards
after #20 (calcium) on the periodic table...
more neutrons than protons are needed and it loses the 1:1 ratio
13
New cards
#82 Pb (lead)
the last stable element, all elements afterward are unstable
14
New cards
radioactive decay
when a nucleus is so unstable that it decays to reach a stable nucleus--shedding dangerous particles
15
New cards
spontaneous disintegration of nucleus
happens without any intervention, nucleus disintegrates into a slightly larger nucleus accompanied by the emission of particles, electromagnetic radiation, or both
16
New cards
radioactive series
a series of nuclear reactions that begins with an unstable nucleus and terminates with a stable one
17
New cards
antimatter
positrons are opposite of beta particles/electrons, when combined both are annihlated and create gamma rays