Module 1: Topic 2: Quality Management
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
why is internal QC in lab procedures needed?
to minimise errors and ensure test result accuracy
what does internal QC involve:
rigorous, systematic checks on instrumentation, methodologies and processes used in daily operations
lab equipment is calibrated and functions optimally
What does Quality Control ensure:
ensures an analytical run produces results that are consistent with results from previous internal runs
while remaining an important part of labs quality activities, QC does not ________
guarantee the correct result
What type of errors are usually encountered?
Data input errors - standards, calibration values
Instrument errors - accuracy, precision
Observer errors - reading errors, errors in equipment selection, analysis and interpretation
Environmental errors - external factors affecting measurement
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined?
Repeatability, reproducibility, within-lab responsibility, between-lab reproducibility, stability, bias, drift, resolution, standard uncertainty
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Repeatability
variation among measurements made on the same object using the same conditions (precision)
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Reproducibility:
variation among measurements made on the same sample using diff conditions (instrument, operator, lab)
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Within-lab reproducibility:
precision within a single lab over time
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Between-lab reproducibility:
precision between diff labs
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Stability:
Variation among measurements made on the same object using the same conditions at diff times
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Bias:
diff between measurement average for the same object and its true value
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Drift:
continuous or incremental change over time
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Resolution:
smallest change in a quantity that causes a detectable change in output/indication
How is the uncertainty in measurement defined? Standard uncertainty:
uncertainty expressed as a standard deviation
What are some sources of uncertainty?
weighing uncertainties
volume uncertainties of pipettes
fluctuations of density
temp effects
metrological traceability
homogeneity of the sampling material
matrix of the sampling material
complex steps in preparation of the sample
stability of measuring signal
calibration of measuring device
what type of specimen is suitable for quality controls?
Specimen that has been assayed many times
shelf life/open-vial stability
liquid vs lyophilised
medically relevant levels
challenge range of instrumentation
within-run/vial-to-vial variability
matrix preservatives
What are some properties of QC materials?
sample specially prepared for use as QC
QC can be plasma or serum
can be used to check for accuracy if value has been reliably determined (e.g. reference centre)
should be controls of high, N and low values
at least 1 QC specimen must be used for every batch analysis
large number of specimens: use 1 control for every 20 specimens
same material is used for external QC or as a calibrator
Why should we perform duplicate tests on specimens?
provides way to check precision of routine work
Duplicate testing on specimens detects _____ random errors, but is it not sensitive to _________, nor will it detect ____________
random errors
gradual drift
incorrect calibration
what limitations are there of internal QC?
only detects change in performance between current and “stable” operation
if original determination of mean contained systematic errors, they are not detected
evaluation of original method needs to establish accuracy (as well as recovery and interference
Ongoing comparison studies using external QA are needed to ensure systematic errors do not slowly increase and are undetected
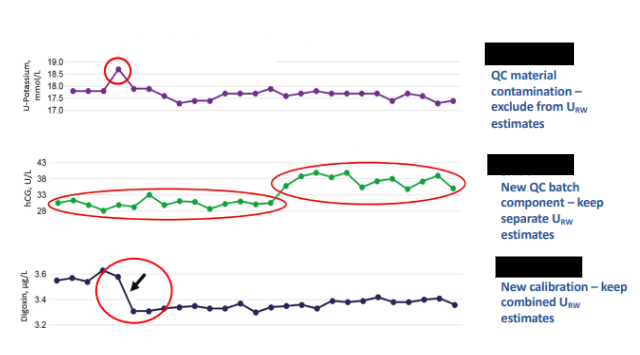
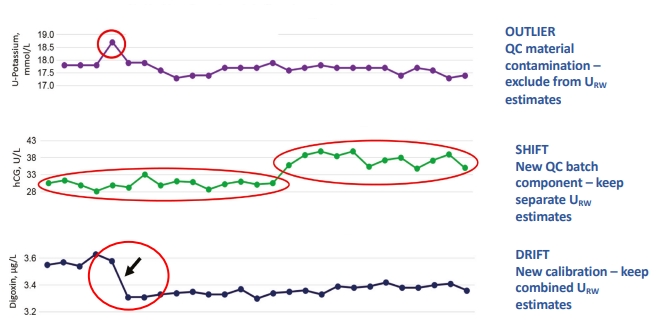
What is External Quality Assurance (EQA) and who performs it?
external comparison of the labs performance against other labs involved in similar activities
evaluation by an outside agency of the performance by a no of labs on material which is supplied specially for the purpose
How is EQA organised?
usually organised on a national or regional basis
The analysis of performance is _______
retrospective
what is the objective of EQA?
objective is to achieve comparability, not necessarily accuracy unless the specimens have been assayed by a reference lab, using methods of known precision, alongside a reference preparation of known value
What are the functions of EQA schemes?
Primary - Measurement
QA material, data collection and analysis
Secondary - Assessment
analytical standards: allowable limits
Tertiary - Corrective action
protocols for dealing with poor performance
evaluation and education
What are the outcomes of EQA schemes?
compare lab results w peer group for:
accuracy
precision
linearity
compare methods and instruments
What is EQA: Profiency surveillance?
critical supervision of all aspects of lab tests
preanalytical: collection, labelling, delivery, storage of specimens before tests
postanalytical: reading and reporting of results
includes maintenance and control of equipment and apparatus
What is EQA: Verification and standardisation
EQA involves validating lab results against those of other accredited labs
measurements are verified and standardised by sending samples to external entities such as RCPA-QAP
EQA ensures alignment with industry standards and enhances reliability of findings
Differences of External QA vs Internal QC?
ensures results from diff labs are comparable using same test, methodology and/or instrument
an external proficiency organisation provides samples, and lab results are evaluated and compared to peers
provides independent external evaluation of labs performance
an investment in reducing risk of reporting incorrect results and minimising potential harm to patients and labs
aids regulatory compliance; labs that participate in EQA may be preferred by their referring clinicians
checks on internal QC and competency of lab staff
What are the three major activities of QAP?
Preventative
Assessment
Correction
What are some Preventative activites of QAP
activities performed before examining specimen that establish systems to promote accuracy in analytical testing
preventative equipment maintenance
instrument calibration
testing of media
induction and training of personnel
What are some Assessment activites of QAP
activities performed during testing to determine whether test systems are performing correctly
assaying standards and controls
maintaining control charts
What are some Correction activites of QAP
activities performed to correct system after an error has been detected
equipment troubleshooting
recalibration of instruments
What agencies address quality?
Royal College of Pathologists of Australasia (RCPA)
National Pathology Accreditation Advisory Council (NPAAC)
National Association of Testing Authorities (NATA)
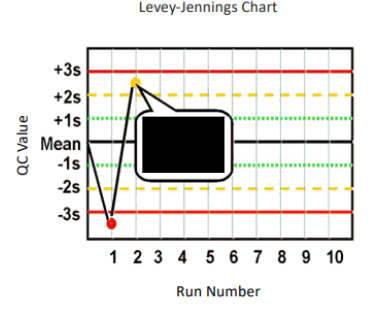
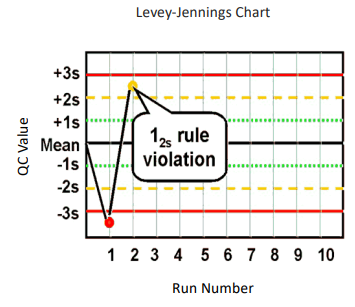
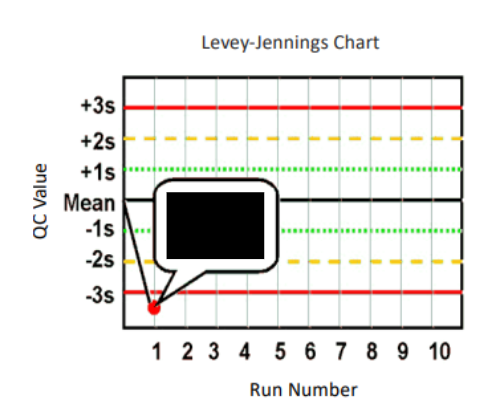
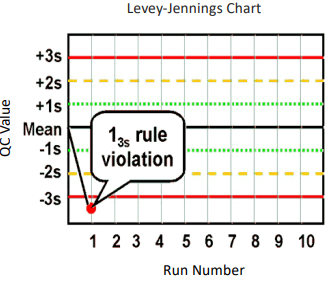
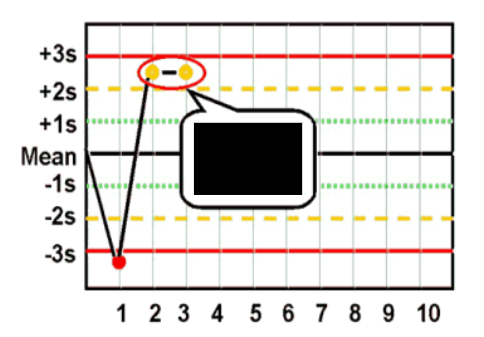
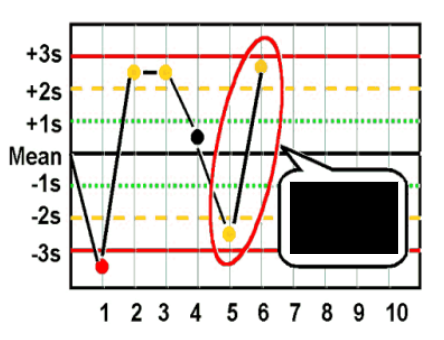
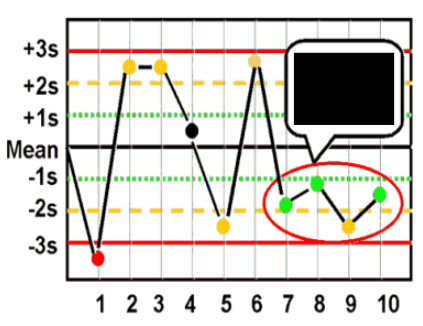
What are Levey-Jennings control charts and what are they used for?
type of control chart used in lab studies to monitor and assess stability and correctness of lab processes over time
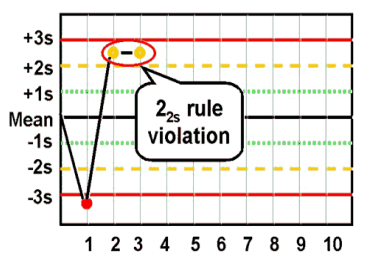
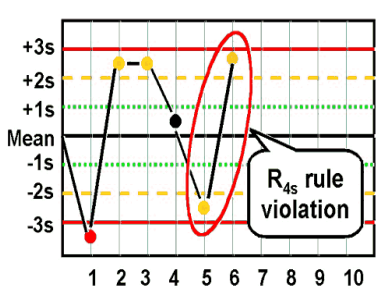
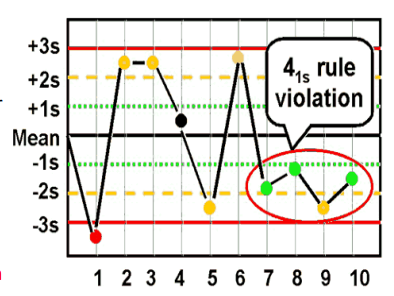
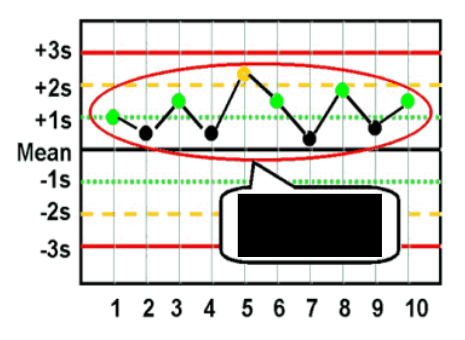
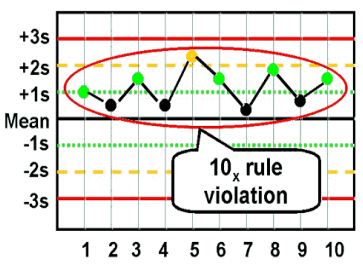
what are the Westgard analysis of quality
12s (warning)
13s (random error)
22s (systematic error)
R4S (random error)
41s (bias)
10x (bias)