Ch. 28 (Development + Inheritance) pt.1 + pt.2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
How long is an oocyte viable? Sperm?
Oocyte:
12-24 hours
Sperm:
24-48 hours
How many sperm are released upon ejaculation vs. how many make it to the ovulated oocyte?
Released:
Millions
Survive:
Couple Hundred
What is fertilization?
Sperm chromosomes COMBINE with those of SECONDARY oocyte to form fertilized egg (Zygote)
What mechanism guides sperm towards the oocyte. Be specific.
Chemotaxis guides the sperm towards the oocyte
→ oocyte + Cumulus cells secrete chemoattractants (e.g., progesterone) that guide sperm
Sperm have olfactory receptors
Describe the events the occur during each step required for a sperm to fertilize an egg:
a. Sperm arrive at oocyte
Enzyme on cell surface of sperm acts to digest corona radiata
Sperm heads then bind to sperm-binding receptors in zona pellucida,
causing sperm membrane calcium channels to open
Ca2+ flows into each sperm
(Triggering the following step)
b. Acrosomal reaction
When triggered by calcium influx, enzymes from many sperm are
released that digest holes in zona pellucida
Spermall release enzymes at same time to digest zona pellucida
Many are required to clear a path to oocyte membrane
c. Sperm binds to oocyte membrane receptor
After path has been cleared in zona pellucida, a single sperm forcibly swims towards oocyte membrane
• Acrosomal collar (tip of sperm) on rear portion of acrosomal membrane binds to oocyte plasma membrane sperm-binding receptor
d. Binding causes
Oocyte to form microvilli that wrap around sperm head
Trigger fusing of oocyte and sperm membrane
e. Membrane fusion
Cytoplasmic contents of sperm enter oocyte
Tail and other parts, such as sperm cell membrane/ mitochondria, are left behind
on oocyte cell membrane surface
____________________________ refers to the transfer of genetically determined characteristics from generation to generation, and _____________________________ is the study of the mechanisms responsible for this transfer of information.
Heredity refers to the transfer of genetically determined characteristics from generation to generation, and Genetics is the study of the mechanisms responsible for this transfer of information.
How many sperm are required to break down the corona radiata prior to fertilization? How many sperm are required to fertilize the oocyte?
Break down corona radiate:
HUNDREDS
Fertilize the oocyte:
1
Describe the mechanisms prevents polyspermy?
1) Fast-block (1-3 seconds)
When sperm binds to sperm-binding receptors on oocyte, sodium channels shift RMP to positive (sperm can’t bind to positively charges oocyte plasma membrane)
2) Slow-block (60 seconds after sperm binds)
Ca + surge from oocyte ER that causes
The release of enzymes that destroy the zone pellucid sperm-binding receptors + harden zone pellucida
Has an oocyte completed the process of meiosis by the time it is ovulated? Explain.
NO
Has not completed meiosis by the time it is ovulated
it is arrested in metaphase II of meiosis II and will only complete meiosis upon fertilization by a sperm cell
How many chromosomes are contained with a human zygote? Where do they come from?
# of chromosomes:
46 chromosomes
Come from:
23 from mom
23 from dad
What is cleavage? Where/when does this happen?
Cleavage:
→ series of rapid mitotic cell divisions that occur in the zygote shortly after fertilization.
Embryo travels through uterine tube to uterus + floats freely until it implants
Zygote moves towards uterus
1st cleavage:
after 36 hours + produces 2 daughter cells = BLASTOMERES
after 72 hours, cluster of cells contains 16 or more cells = MORULA
What phase of cleavage is the embryo in upon implantation in the uterus? How many days after ovulation does implantation take place?
→ blastocyst stage of cleavage
6-10 days after ovulation
What is the difference between a morula and blastocyst?
Morula: Solid ball of 16–32 cells, no cavity, forms ~day 3–4.
Blastocyst: Hollow with fluid-filled cavity, inner cell mass + trophoblast, forms ~day 5
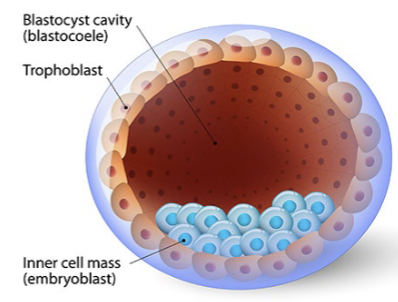
What are the 2 primary structures that make up the blastocyst? Which of these structures will give rise to the embryo?
Trophoblast: Outer layer; forms the placenta.
Inner cell mass: Cluster of cells inside; gives rise to the embryo.
The trophoblast proliferates into 2 layers of cells, the inner cytotrophoblast and the outer syncytiotrophoblast.
What is the fate of each (what do the become/do)?
→ IMPLANTATION: (6-7 days after ovulation)
Trophoblast invades uterine wall
Cytotrophoblast:
Inner layer of cells
gives rise to new trophoblast cells and helps form chorionic villi
Syncytiotrophoblast:
Cells in outer layer
invades the uterine lining, secretes hCG, and helps establish maternal-fetal circulation
What is the significance of hCG? How long is hCG necessary to secrete before it is no longer consequential to the fate of the fetus?
hCG:
crucial for maintaining the corpus luteum, which continues to produce progesterone during early pregnancy, preventing menstruation and supporting the uterine lining for implantation and embryo development
Takeover:
first 8–10 weeks (2 months) of pregnancy, after which the placenta takes over progesterone production, and hCG levels decrease.
What is the placenta? What is the function of the placenta? What types of things can cross the placental barrier?
Placenta:
Organ providing interface btw maternal and fetal circulation
Site of:
Gas exchange
Transfer nutrients to fetus
Transfer of waste from fetus to mother
Fetotoxic substances (ALCOHOL)
Nicotine
Antibiotics
Certain pathogens
The placenta is a contribution of both embryonic and maternal tissues. What structures of the placenta are embryonic/fetal? Maternal?
Embryonic:
Chorion: Derived from the trophoblast (outer layer of the blastocyst), forms the fetal part of the placenta.
Chorionic villi: Finger-like projections from the chorion that invade the uterine wall and facilitate nutrient and gas exchange.
Maternal:
Decidua basalis: endometrium located between chorionic villi and stratum basalis of endometrium
• Decidua capsularis: part of endometrium at uterine cavity face of implanted embryo
• Portion of placenta that expands to accommodate growing fetus
• Villi in decidua capsularis degenerate as fetus grows, while villi in decidua basalis increase in number and branches
• Together chorionic villi and decidua basalis make up placenta
What is the difference between the decidua basalis and decidua capsularis?
Decidua basalis: The part of the decidua located beneath the implanted embryo, where the placenta develops and attaches to the uterine wall.
Decidua capsularis: The part of the decidua that surrounds the fetal side of the embryo, forming a capsule around the growing blastocyst.
What are the 2 layers of the embryonic disc?
In which layer is the primitive streak formed?
Epiblast
Hypoblast
Primitive streak: Epiblast
What is gastrulation?
Embryonic disk transforms into 3 layered embryo (3 primary germ layers are present)
What are the 3 primary germ layers?
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
a. During gastrulation, The first epiblast cells to migrate through the streak displace the hypoblast to form the __________.
b. The __________ is formed next, as more cells migrate in and begin to move laterally.
c. The remaining epiblast cells that do not migrate are now considered the ___________.
Endoderm
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
23. Name the germ layer which contributes the following:
a. the epithelial lining of the digestive, respiratory and urogenital systems _________
b. the majority of the mass of the human body _____________
c. the nervous system and epidermis ______________
Endoderm
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
What is neurulation?
What is the notochord and what role does it play in neurulation?
a. The notochord will eventually be replaced by what structure? The only remnant of the notochord in the adult body is the _____________ ________________.
The notochord is a rod of mesoderm that signals the ectoderm to form the neural tube (neurulation).
It is eventually replaced by the vertebral column (spine).
The only adult remnant of the notochord is the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral discs.
During neurulation, the ______________ folds inward to form ____________ and ____________. The ______________ fuse to form the ___________________.
Neural crest
neural groove
Neural folds
Neural folds
Neural tube
What is spina bifida? Rank the 3 major forms of spina bifida from least to most severe
Neural finds FAIL to FUSE
1) Occulta (mild)
Spine defect/ no outward symptoms (tuft of hair)
2) meningocele
Meninges protrude to form a sac of CFS
3) Myelomeningocele
Meninges protrude to form the sac full of CSF + underdeveloped spinal cord PROTRUDES into the sac
What are somites? What three parts do they subdivide into and what are the fates of each?
Blocks of mesoderm
1) Sklerotome
2) Dermatome
3) Myotome
Between which weeks does the embryonic period end and the fetal stage begin?
Embryonic period: 1-8 weeks
Fetal stage: 9-38 weeks
How many weeks does it take for the fetus to fully form (full term)? Why is the gestational period 40.5 weeks?
Full term = 38.5 weeks
→ Bc it accounts for the last mensturational period
How is the gestational period divided?
1st trimester:
Weeks 0-13
2nd trimester:
Weeks 14-27
3rd trimester:
Weeks 28-40
What type of maternal adaptations occur in the second and third trimesters?
Respiration Rate + tidal volume
Blood volume
Nutrient + vitamin intake
Glomerular filtration rate
Urination
Size of uterus + Mammary glands
What is the technical term for stretch marks and why do they form?
Striae
→ RAPID stretching of dermis
In addition to its role in the nutrition of the fetus, the placenta acts as an endocrine organ. Identify the placental hormones from the descriptions below (hormones may be used more than once):
OPTIONS:
Estrogen
Progesterone
Relaxin
hCG
Prolactin
a. Increases the flexibility of the pubic symphysis and dilates the cervix ___________
b. Used in pregnancy testing ________
c. Secreted by trophoblast cells and later chorion ________________
d. Suppresses FSH and LH, preventing ovulation (2 hormones) _________
e. Promotes fetal growth and viability, as well as uterine enlargement _________
f. Helps prepare the mammary glands for milk production __________
g. During the first trimester, these two hormones are secreted by the corpus luteum to maintain the pregnancy. ____________
h. Prompts corpus luteum to persist, continuing secretion of progesterone and estrogen _______
i. Increases maternal metabolic rate ________
j. During the last two trimesters, these two hormones are secreted by the placenta to help maintain the endometrium and continue the pregnancy ________
a. Increases the flexibility of the pubic symphysis and dilates the cervix → Relaxin
b. Used in pregnancy testing → hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin)
c. Secreted by trophoblast cells and later chorion → hCG
d. Suppresses FSH and LH, preventing ovulation (2 hormones) → Estrogen and Progesterone
e. Promotes fetal growth and viability, as well as uterine enlargement → Estrogen
f. Helps prepare the mammary glands for milk production → Prolactin (and also Estrogen and Progesterone contribute)
g. During the first trimester, these two hormones are secreted by the corpus luteum to maintain the pregnancy → Estrogen and Progesterone
h. Prompts corpus luteum to persist, continuing secretion of progesterone and estrogen → hCG
i. Increases maternal metabolic rate → Thyroid Stimulating hormone
j. During the last two trimesters, these two hormones are secreted by the placenta to help maintain the endometrium and continue the pregnancy → Estrogen and Progesterone
What is parturition?
Forceful expulsion of FETUS
What stimulates contractions in later pregnancy?
Increasing ratio of estrogen - Progesterone (MORE ESTROGEN)
→ Makes myometrium more sensitive to stimuli that promote contractions
What are Braxton-Hicks contractions?
WEAK + IRREGULAR contractions
Caused by:
Decreasing levels of progesterone
What is the bloody show? Is this normal?
YES NORMAL
→ Collection of mucus is expelled from the cervical canal 1-2 days prior to labor
(the mucus BLOCKS enters to the uterus) ← That’s why it forms (MUCUS PLUG)
What event is happening when a pregnant woman’s water breaks? Why does delivery need to follow within 24-48 hours of this event?
Amnionic cavity RUPTURES
→ Amnionic fluid is released
MUST OCCUR TO PREVENT INFECTION
Describe the positive feedback mechanism that helps childbirth progress quickly.
Distention of cervix causes MORE oxytocin + prostaglandin release
Causes greater CONTRACTION force
Causing more distention of cervix
Causing more released oxytocin + Prostaglandin
REPEATES
What is Pitocin and when is it administered?
Drug similar to oxytocin
→ INDUCES LABOR
Given when childbirth is NOT progressing
For the following events, indicate which stage of labor they occur in (Dilation, Expulsion, Afterbirth)
a. This stage lasts from onset of labor until the cervix is fully dilated. __________
b. Strong contractions every 2–3 minutes. __________
c. Longest stage of labor. ____________
d. Baby’s neck extends as head exits perineum followed by delivery of the rest of the body ______
e. Strong contractions continue, causing detachment of placenta. _________
f. Crowning occurs during this stage. __________
g. This stage lasts from full dilation to delivery. __________
Dilation
Expulsion
Dilation
Expulsion
Afterbirth
Expulsion
Expulsion
What is vertex position? Breech?
a. Which is the natural delivery position?
b. Which position might require a Caesarian section?
c. What is a Caesarian section?
Vertex position: (Natural delivery)
USUAL, Head-first presentation
Skull dilates cervix
Breech position: (requires C-section)
Buttock-first
Caesarian Section:
surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through incisions made in the mother's abdomen and uterus.
What is involution of the uterus?
uterus returns to ORIGINAL size
What is lochia?
Vaginal discharge of uterine cells, blood cells, and debris (last up to 2 weeks)
What is preeclampsia?
COMPLICATION of pregnancy
Results in HYPERTENSION + Proteinuria
What is gestational diabetes?
Form of diabetes mellitus that forms during pregnancy (around 24 weeks)
What is the APGAR score? Describe what is being tested?
Physical test performed on baby 1-5 min after birth to assess physical wellness
→ 0-2 points given per category
A → Appearance
P → Pulse
G → Grimace (reflex response)
A → Activity (muscle tone)
R → Respiration
What is colostrum and how does it differ from True milk?
Colostrum:
yellow
low fat
low sugar
high protein
Vitamin A
IgA antibodies (protect against infection)
Real Milk:
Watery
translucent
rich in lactose + protein
Which hormone is involved in the positive feedback mechanism of labor as well as the milk let-down reflex of lactation?
OXYTOCIN
What is a gene?
Segment of DNA
Blueprint for synthesis of proteins
What is genetics and who is considered the father of genetics? In what year did scientists successfully map the first complete human genome?
Study of the mechanism of heredity —> Gregor Mendel
→ 2003
What is the genome?
Complete set of genetic material
→ Includes all DNA + some viruses + RNA
(Maternal & Paternal)
If every nucleated cell has the same genome, why do some cells look and function differently than others?
Alterations in GENE EXPRESSSION between individual cells
Compare and contrast genotype and phenotype.
Genotype:
Genetic makeup of a person for a trait
Ex: (FF, Ff, or ff)
Phenotype:
Physical expresión of genotype (physical, behavioral, biochemical)
ex:
Genotype FF or Fr = Phenotype of freckles
Genotype ff = phenotype NO freckles
If you examine a karyotype, the first 22 pair of chromosomes are known as _______
__________. The 23rd pair of chromosomes is known as your __________.
If you examine a karyotype, the first 22 pair of chromosomes are known as Autosomes. The 23rd pair of chromosomes is known as your sex chromosomes.
Diploid number (46)
Karyotype: individual's complete set of chromosomes
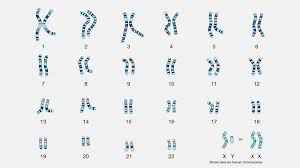
WE ALL HAVE 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
→ 1 pair of sex chromosomes = determine genetic sex (XX= female / XY= male)
→ 22 pairs of autosomes (non-sex chromosomes) Guide expression of most other traits
Define the following terms:
a. homologous chromosomes
b. autosomes
c. sex chromosomes
d. allele
e. homozygous
f. heterozygous
g. dominant
h. recessive
Homologous Chromosomes:
Pairs of chromosomes (one from each parent) that are similar in size, shape, and gene content
Carry the same genes at the same locations (loci), but may carry different versions (alleles) of those genes.
Autosomes:
The first 22 pairs of chromosomes in humans that do not determine sex
They carry genes for various traits unrelated to sex determination
Sex chromosomes
The 23rd pair of chromosomes that determine biological sex. In humans:
XX = typically female
XY = typically male
Allele
Genes that occur at the same LOCUS (location) on homologous chromosomes
Ex: gene for eye color may have a brown allele and a blue allele.
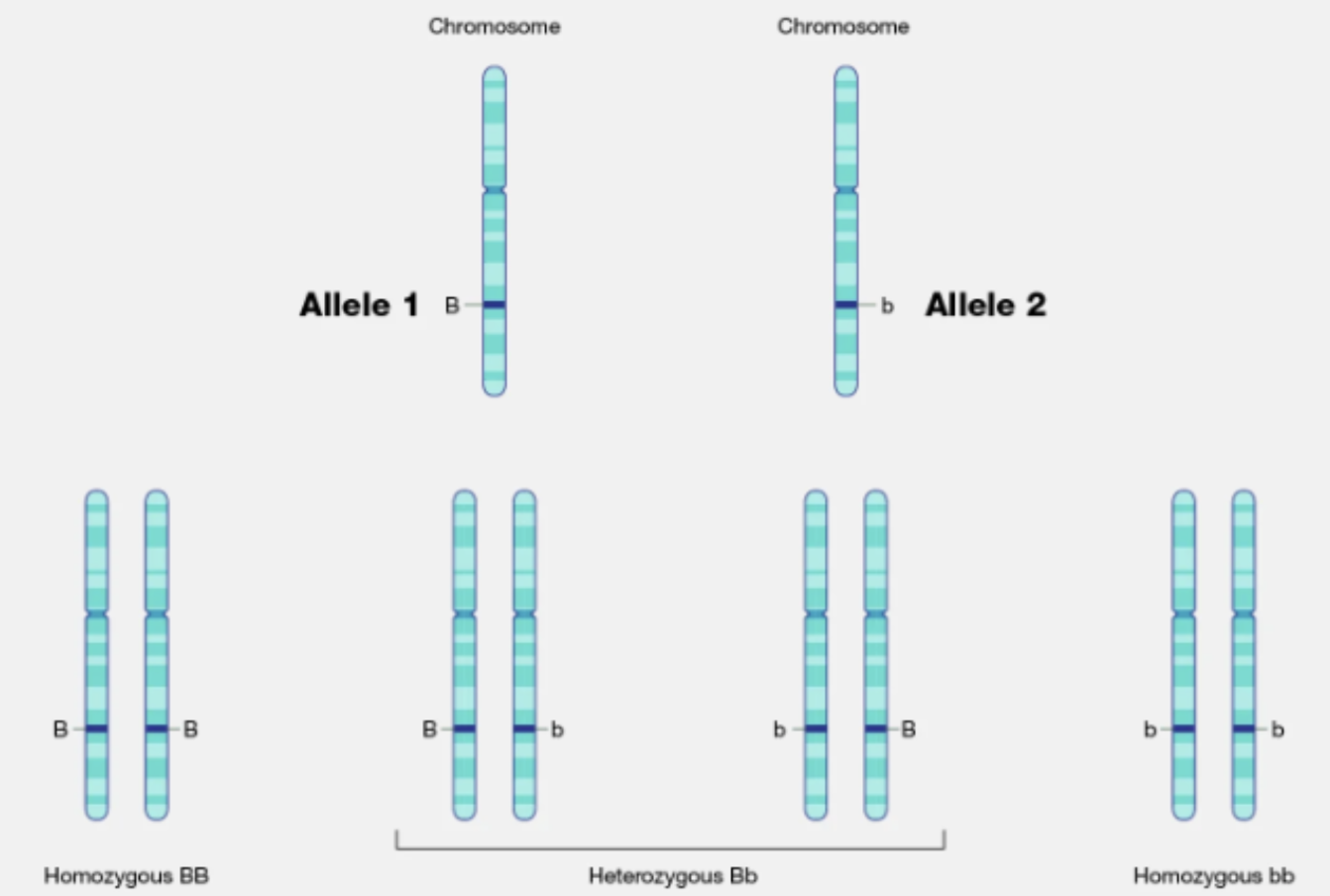
→ Homozygous
Alleles are the same for SINGLE trait
DNA sequence is the SAME for both homologous chromosomes
two identical alleles for a specific gene (e.g., AA or aa).
→ Heterozygous
Alleles are DIFFERENT for single trait
DNA sequence is DIFFERENT on one homologous chromosome than other
two different alleles for a specific gene (e.g., Aa).
Dominant
An allele that masks the effect of a recessive allele. It is expressed in the phenotype even if only one copy is present (e.g., A in Aa).
Recessive
An allele that is only expressed in the phenotype when two copies are present (e.g., aa). It is masked by a dominant allele.
How are dominant and recessive alleles designated?
using uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively:
Dominant alleles → Uppercase letter (e.g., A)
Recessive alleles → Lowercase letter (e.g., a)
What differentiates monogenic (Mendelian) inheritance from polygenic (non-Mendelian) inheritance? What are some examples of traits determined by each type of inheritance?
Monogenic (mendelian) Inheritence:
A trait controlled by a single gene with two alleles, usually following Mendel’s laws (dominant and recessive patterns).
Key features:
One gene = one trait
Follows clear dominant/recessive patterns
Predictable inheritance (like in Punnett squares)
Ex:
Widows peak
Cystic fibrosis (recessive)
Polygenic (non-mendelian inheritance)
A trait controlled by multiple genes, each contributing a small effect to the phenotype.
Key features:
Involves several genes (often on different chromosomes)
Shows a range of variation (continuous traits)
Influenced by environment as well (multifactorial)
Ex:
Skin color
Height
Eye color
Weight
What is segregation? Independent assortment?
Segregation: → separation during meiosis
→ A parent gives just ONE allele for a gene to each gamete they produce
2 alleles of one trait will be separated + distributed to 2 different daughter cells (maternal + paternal)
Ex:: for Tt —allele:
T will go in one daughter cell, and allele t will go in other
• Errors in segregation can lead to cancer, infertility, and Down syndrome
Independent Assortment:
→ During gamete formation, different pairs of alleles segregate independently of each other
Alleles of 2 different traits on 2 different chromosomes are distributed independently of each other
Ex: Bb is on one chromosome, and Jj is on another chromosome, so possibilities of inheritance
are: BJ, Bj, bJ, and bj
• Whether you inherit a B or b is independent of whether you inherit a J or j

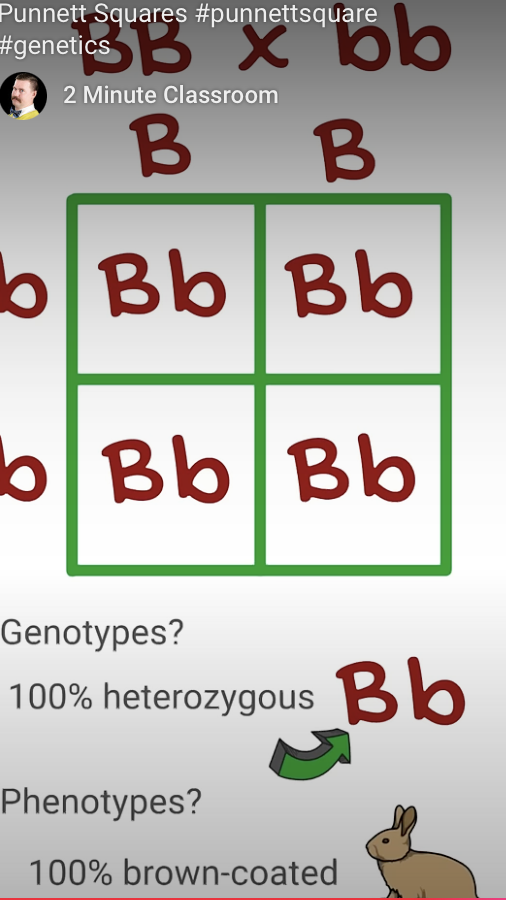
What is a Punnett square? Be able to use one on the exam. Be able to calculate genotypic and phenotypic ratios based on the type of inheritance.
Punnet Square:
tool used to predict the possible genetic outcomes (genotypes and phenotypes) of a cross between two individuals
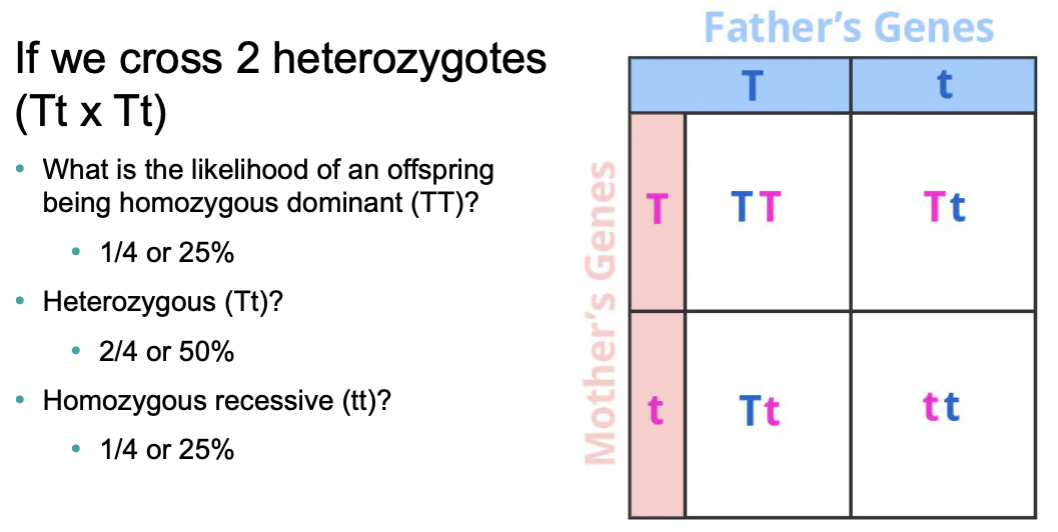
Do the probabilities of offspring inheriting a particular trait change if a mating results in one phenotype rather than another?
No, the probabilities do not change just because a certain phenotype shows up in one offspring.
Compare and contrast the three types of simple inheritance:
a. strict dominance
b. codominance
c. incomplete dominance
Strict dominance:
→ One allele completely MASKS the effect of the other
Dominant allele: Expressed
Recessive allele: Hidden unless 2 copies
Co-dominance:
→ BOTH alleles are fully expressed in the heterozygote (neither is dominant or recessive)
Blood type AB: A + B Alleles are both expressed (AB blood type)
Cattle color: Red (R) + White (W)
Incomplete Dominance:
→ The heterozygous phenotype is a blend of the 2 alleles (Not fully dominant or recessive)
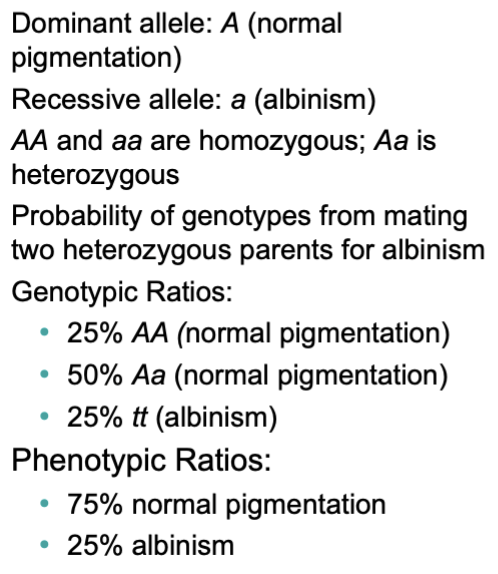
What conditions must exist for a recessive trait to be expressed?
MUST INHERIT 2 RECESSIVE ALLELES
What is a carrier?
a person who has one copy of a recessive allele for a genetic trait or disorder, but does not show the trait in their phenotype.
Complete a Punnett square and list the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the following example of strict dominance:
Free earlobes (F) are dominant to attached earlobes (f). A heterozygous male is mated with a heterozygous female.
Complete a Punnett square and list the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the following example of strict dominance:
A carrier of Tay-Sachs disease (Tt) decides to have a child with a person that is homozygous normal (TT) for this allele. (Hint: Tay-Sachs follows a autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.)
Autosomal Recessive: This means that a person needs two copies of the faulty gene (one from each parent) to actually have the disease.
Sickle cell anemia is an example of incomplete dominance. Assume “S” is a normal shaped blood cell, and “s” is a sickle shaped blood cell. (“SS” = normal, “Ss” = has the sickling trait, and “ss” = has sickle cell disease)
Complete a Punnett square and list the expected phenotypic ratios for the following example of incomplete Dominance:
A man with sickling trait has children with a woman who has the sickling trait.
Incomplete Dominance:
It’s when neither allele is completely dominant over the other.
Instead of one allele masking the other (like in strict dominance), the two alleles blend together in the heterozygous form.
Blood types are determined by three genes...............”A” is a dominant gene, “B” is a dominant gene, and “O” is a recessive gene. There are 4 blood types created by combinations of these genes. AA and AO yield type A blood, BB and BO yield type B blood, AB creates AB blood, and OO creates type O blood.
Complete a Punnett square and list all possible phenotypes for the following example of codominance: A person with type AB blood has a child with a person that has type B blood.
Complete a Punnett square and list all possible phenotypes for the following example of codominance:
A person with type A blood has a baby with a person with type B blood.
Why are X-linked traits expressed differently in males
Males express X-linked traits more often because they have only one X chromosome, so any gene on it (even a recessive one) is automatically expressed.
→ For females, they must have recessive alleles on both X chromosomes in order to express an X-linked condition
Sex-linked inheritance is unique, because the traits are passed on with the X-chromosome only. For the disorders listed, the Y-chromosome does not carry a corresponding gene. When performing a Punnett square for sex-linked traits, be sure to keep track of the % of male offspring and % of female offspring expressing the disorders. For our purposes, a superscript indicates that the chromosome carries the disorder. The lack of a superscript is interpreted as the presence of a normal gene.
Complete a Punnett square and list the % of male and female children which will be normal and the % of male and female children which will express the disorder for the following example of sex-linked inheritance: A female carrier for color blindness (XcX) mates with a man that has normal color vision (XY).
A man with hemophilia (XhY) decides to have children with a woman who is a carrier for hemophilia (XhX). What % of the male and what % of the female offspring would express hemophilia? Are there any carriers produced? If so, what is the sex of the carrier?
What is a pedigree?
Genetic representation of a family tree that diagrams the inheritance of a trait/disease through several generations
What is an amniocentesis?
Chorionic villus sampling?
Why are these tests only administered if there is a known risk of a genetic disorder?
Amniocentesis:
Amniotic fluid is withdrawn after week 14-16
Fluid + cells are examined for genetic abnormalities
Testing takes several weeks (to check for any possible disease the baby may have)
Chorionic villus sampling: (CVS)
Chorionic villi sampled at 8-10 weeks
karyotypes for genetic abnormalities
Can be done earlier than amniocentesis
→ Because testing is INVASIVE + Risky for mother + fetus