week 2 co2 - aging eye
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What happens to the lids during aging?
dry skin from loss of oily secretions
wrinked and thin due to loss of elasticity
pseudoptosis - overhanging skin
corneal shape changes - less pressure on lids
malposition of lower lid - ectropion and entropion
malposition of punctum - watery eyes
weaker, less efficient blinks - dry eyes, discomfort, Cl intolerance
what happens to the conjunctiva during ageing?
Pigmented areas can appear (racial/complexion-associated melanosis).
Pigment spots may be seen.
Limbal epithelial folds (palisades of Vogt) become less distinct.
Pinguecula (yellowish elastotic degeneration near the limbus) more common.
Conjunctivochalasis (redundant, loose conjunctiva) develops.
Conjunctival cysts may occur (benign epithelial inclusion cysts).
Implications:
Mostly benign and cosmetic.
Pinguecula/pterygium can induce irritation or astigmatism.
Conjunctivochalasis may cause watery eyes and discomfort.
Q: What happens to the tear film with age
Tear production decreases (↓ aqueous & lipid secretion), tear film stability reduces, and evaporation increases.
Implications: Dry eye symptoms, burning/stinging, CL intolerance.
What happens to the cornea with age?
Cornea
Astigmatism shifts WTR → ATR → Change in spectacle Rx
Arcus senilis (lipid at corneal periphery) → Cosmetic, no VA effect
Vogt’s limbal girdle → Cosmetic only
↓ Endothelial cell density → ↓ transparency, ↓ VA & contrast
↓ Sensitivity → Higher injury risk
↓ Metabolism → ↑ fluorescein permeability
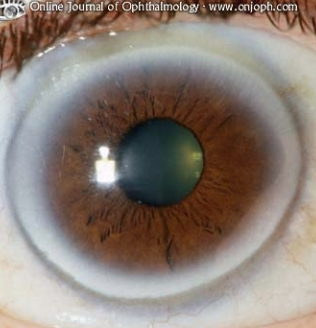
What is this and explain what it is?
arcus senilis
grey-white blurish ring at periphery of cornea
lipid deposits
what happens to normal endothelial cell (ECD) with age?
declines
what is low ECD a risk factor of?
cataract and corneal surgeries
what is polymegethism?
change from uniform cell size to variable cell sizea - indication if distress to endothelium
what happens to the sclera with age?
Yellowing (lipid deposition) → Cosmetic only
Bluish hue (thinning) → Apparent fragility
Loss of elasticity → Reduced structural support
what happens to the anterior chamber with age?
Becomes shallower (lens growth) → ↑ risk of angle closure glaucoma
Pigmentation/thickening of trabecular meshwork → ↑ IOP, risk of glaucoma
Shallow AC → Caution with dilation
What happens to the iris with age?
Depigmentation/atrophy (moth-eaten appearance) → Cosmetic, reduced pupil response
Iris naevi may appear → Usually benign
what happens to the pupil with age?
Senile miosis (smaller pupil) → ↓ retinal illuminance, impaired colour vision, ↑ glare
Persistent pupillary membrane may remain → Usually no clinical impact
What happens to the lens with age?
Thickens & hardens, capsule less elastic → Presbyopia (↓ accommodation)
Lens sclerosis & yellowing → ↓ VA, impaired colour vision (esp. blue-yellow)
Nuclear cataract → ↑ glare, ↓ vision
↓ Light transmission → ↓ retinal illuminance
what happens to the vitreous with age?
Liquefaction of vitreous gel → Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD)
PVD → Floaters & flashes, risk of retinal tears/detachment, possible haemorrhage
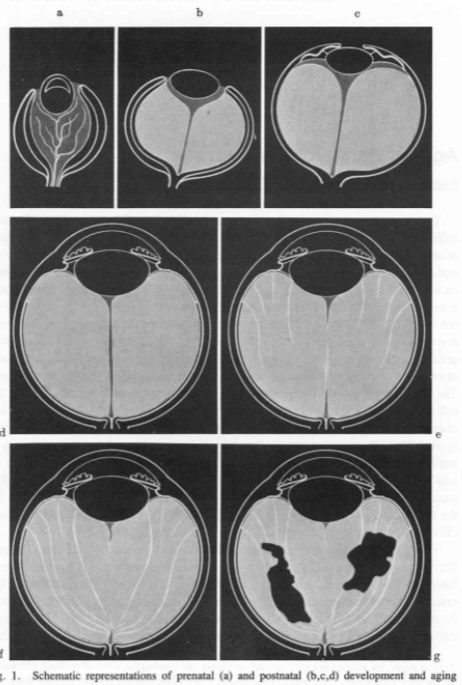
what’s going on here?
increased liquefaction
pockets of fluid
can lead to PVD
what happens to the retina with age?
Narrower/sclerotic vessels (arteriosclerosis) → ↓ retinal perfusion
Lipofuscin accumulation in RPE → Depigmentation, impaired function
Loss of foveal reflex, retinal thinning → ↓ central & peripheral vision
Drusen in macula → ARMD risk
what happens to the choroid with age?
Choroidal crescent → Common benign ageing change
Choroidal atrophy → Reduced retinal support, age-related degeneration
what happens to visual acuity with age?
Stable until ~60, then declines → ↓ VA due to cataract, ARMD, diabetic retinopathy, open angle glaucoma
what happens to refractive error with age?
Refractive Error
Hyperopia increases (40–65 yrs) → More near blur complaints
Myopia may increase after 70 → Often due to cataract/diabetes
Astigmatism shifts WTR → ATR → Change in spectacle Rx
what happens to contrast sensitivity with age?
↓ at mid–high spatial frequencies → Reduced ability to detect fine details, poor vision in low contrast environments
what happens to depth perception with age?
↓ (due to reduced contrast sensitivity) → Difficulty judging kerb heights, ↑ risk of falls
What happens to accomodation with age?
AoA (amp of accom) decreases (presbyopia) → Reduced near vision, need for reading correction
Small pupils increase depth of focus → May mask some presbyopia temporarily
what happens to colour vision with age?
Lens yellowing & ↑ light scatter → Whites appear yellow, blue colours appear darker
Senile miosis + lens changes → ↓ colour discrimination, esp. blue-yellow defects
what happens to glare with age?
↑ due to lens scatter (cataract) → Disability glare (reduced contrast), discomfort glare
what happns with visual fields with age?
Senile ptosis → Field restriction superiorly
Senile miosis & yellowing lens → Reduced peripheral sensitivity
Retrobulbar fat loss → Relative enophthalmos → Field constriction
what happens to dark adaptation with age?
Slower rhodopsin regeneration & ↑ lens scatter → Slower adaptation to dark, higher light threshold needed
what happens to Eye Movements – Versions & Pursuits with age?
Reduced smooth pursuit, restricted horizontal versions → Lag for moving targets, reliance on saccades
what are saccades, espc in age?
ballisitic eye movements
Latency increases → Slower initiation of eye movements
Velocity unchanged → Once initiated, still fast
what happens with Vergence with age?
Near exophoria increases, ↓ accommodative convergence → Difficulty maintaining near fixation, may need prism/adds
what advice would you give your elderly px?
increase contrast around the house
consider glare, hat with brim
discuss driving - night drivibg and bright sun may be diffuclt