The human genome, what genes are and how they work
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Animal cell
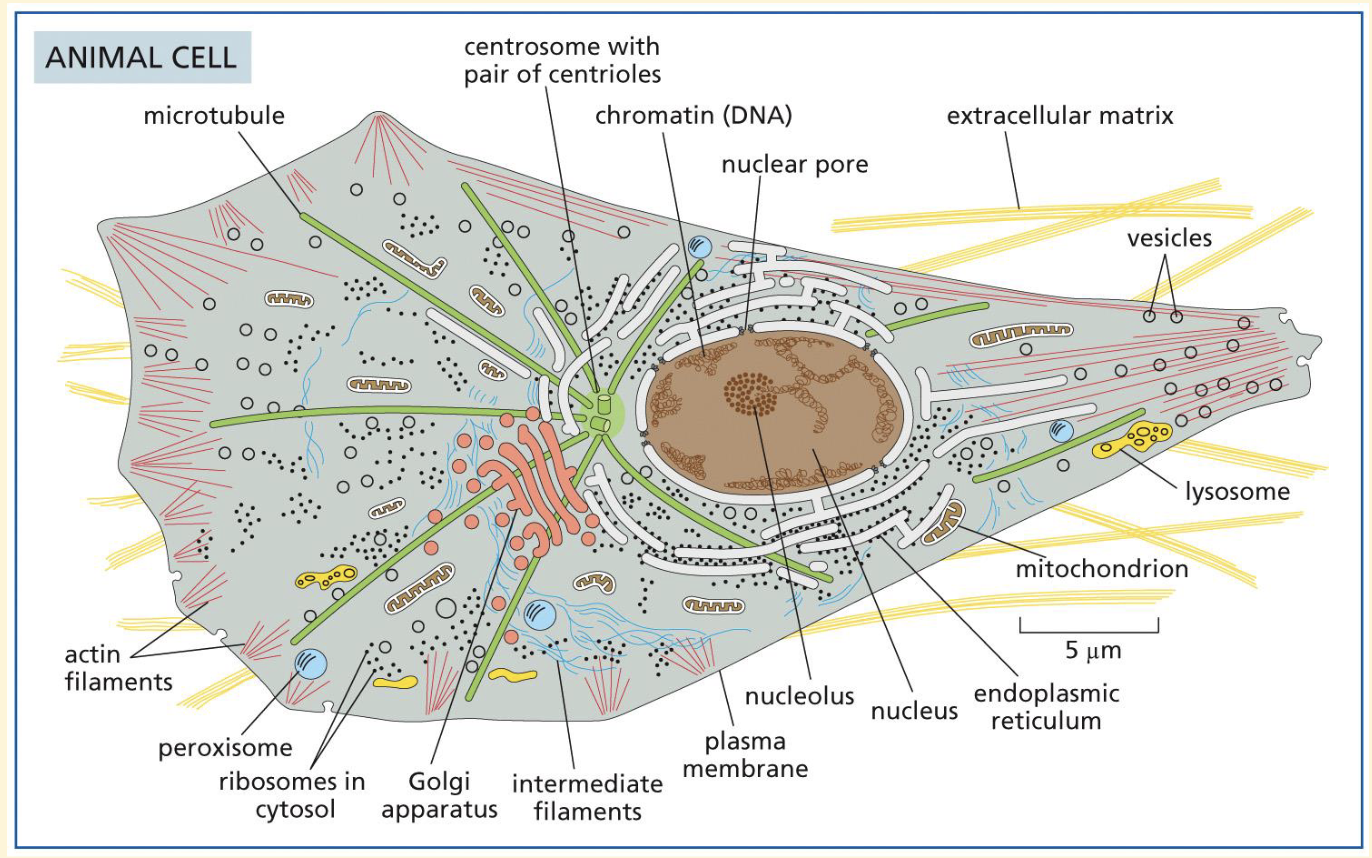
Microtubule defintion and function
Microtubules are rigid, hollow protein cylinders that are essential for maintaining cell shape, transporting organelles and vesicles intracellularly, and forming structures like cilia and flagella
Actin filaments
To form the dynamic cytoskeleton, which gives structural support to cells and links the interior of the cell with its surroundings. Forces acting on the actin cytoskeleton are translated and transmitted by signaling pathways to convey information about the external environment.
To allow cell motility. For example, through the formation and function of Filopodia or Lamellipodia.
During mitosis, intracellular organelles are transported by motor proteins to the daughter cells along actin cables
In muscle cells, actin filaments are aligned and myosin proteins generate forces on the filaments to support muscle contraction. These complexes are known as ‘thin filaments’.
What is chromatin?
(DNA plus associated proteins
What is within a nucleus?
Chromatin
Euchromatin
Heterochromatin
Nucleolus
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear pore
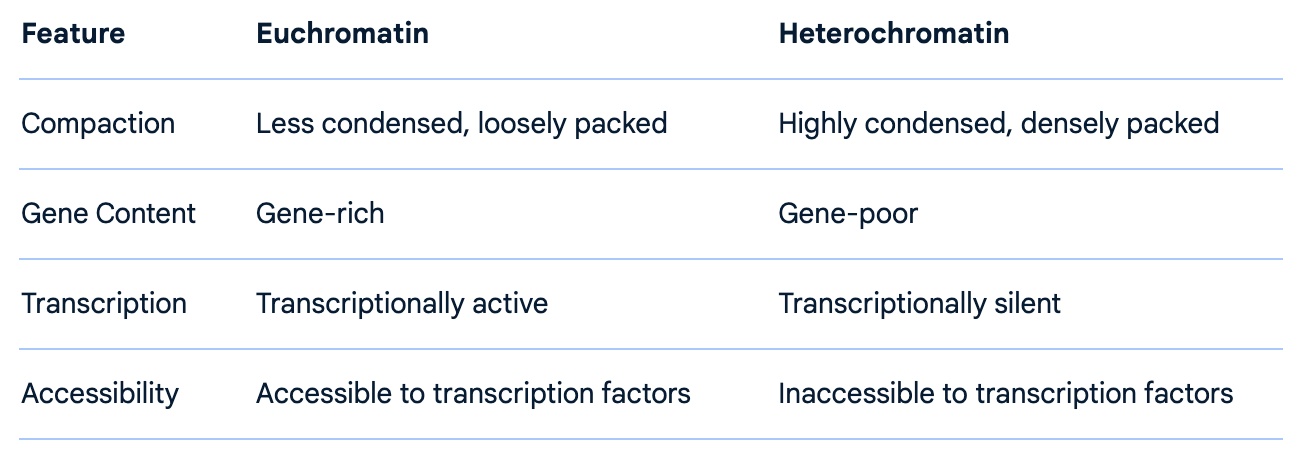
What is euchromatin vs heterochromatin?
Nucleolus function
ribosome biogenesis, which involves the transcription of ribosomal RNA (rRNA), processing of this rRNA, and assembly of ribosomal subunits with proteins to form functional ribosomes.
DNA damage sensing and repair,
pre-mRNA processing,
Nuclear envelope function
Double membrane
Controls entry and exit
Outer membrane has RER on surface
Nuclear pores function
Allows passage of larger molecules
mRNA
DNA replication SEMI CONSERVATIVE
Location and Steps
Nucleus
1. DNA helicase unwinds DNA/double helix, DNA helicase breaks hydrogen bonds;
2. Both strands act as templates;
3. (Free DNA) nucleotides line up in complementary pairs/A-T and G-C;
4. DNA polymerase joins nucleotides (of new strand);
Reject forms hydrogen bonds/joins bases
5. Forming phosphodiester bonds;
6. Each new DNA molecule consists of one
old/original/template strand and one new strand;
Describe and explain how the structure of DNA results in accurate replication.
1 two strands therefore semi-conservative replication (possible);
2 base pairing / hydrogen bonds holds strands together
3 hydrogen bonds weak / easily broken, allow strands to separate;
4 bases (sequence) (exposed so) act as template / can be copied;
5 A with T, C with G / complementary copy;
6 DNA one parent and one new strand;
Transcription
Location and steps
Nucleus
1. Hydrogen bonds (between DNA bases) break;
Ignore DNA helicase.
Reject hydrolysing hydrogen bonds.
2. (Only) one DNA strand acts as a template;
3. (Free) RNA nucleotides align by complementary base pairing;
For ‘align by complementary base pairing’, accept ‘align to complementary bases’ or ‘align by base pairing’.
4. (In RNA) Uracil base pairs with adenine (on DNA)
OR
(In RNA) Uracil is used in place of thymine;
Do not credit use of letters alone for bases.
5. RNA polymerase joins (adjacent RNA) nucleotides;
Reject suggestions that RNA polymerase forms hydrogen bonds or joins complementary bases.
6. (By) phosphodiester bonds (between adjacent nucleotides);
7. Pre-mRNA is spliced (to form mRNA)
OR
Introns are removed (to form mRNA);
Translation
Location and steps
Cytoplasm
1. (mRNA attaches) to ribosomes
OR
(mRNA attaches) to rough endoplasmic reticulum;
2. (tRNA) anticodons (bind to) complementary (mRNA) codons;
3. tRNA brings a specific amino acid;
4. Amino acids join by peptide bonds;
5. (Amino acids join together) with the use of ATP;
6. tRNA released (after amino acid joined to polypeptide);
7. The ribosome moves along the mRNA to form the polypeptide;
DNA (our genetic store) has to fulfil three functions:
1. Encode all info required to make an organism
(DNA to RNA to protein)
2. It must replicate itself accurately
3. It must allow beneficial mutations to be selected
Genetics definition
the study of heredity, the process by which
characteristics are passed from parents to offspring
Gene definition
is a unit of biological information that encodes a
specific protein or regulatory molecule
Precision medicine definition
an emerging data-driven approach for disease
treatment and prevention that takes into account
individual variability in genes, environment, and
lifestyle for each person
How much percentage of genome functional
~ 80% our genome
sequence is ‘functional’
How many genes identical?
Genes 99.9% identical
Structure of DNA
1. Polymer of nucleotides;
Accept ‘polynucleotide’
2. (Nucleotide) consists of deoxyribose, phosphate and an organic/nitrogenous base;
Accept ‘phosphoric acid’ for phosphate
3. Phosphodiester bonds (between nucleotides);
4. DNA double helix held by H bonds
OR
2 strands held by H bonds;
5. (Hydrogen bonds/pairing) between adenine, thymine and cytosine, guanine;
Ignore bases identified with letters (A, T, G, C)
Reject adenosine and cysteine
6. DNA is associated with histones/proteins;
Are DNA strands parallel or antiparallel?
Antiparallel
Why is it antiparallel?

How is DNA condensed?
Supercoiling
DNA sequence highly condensed around histone proteins –multiple levels of folding
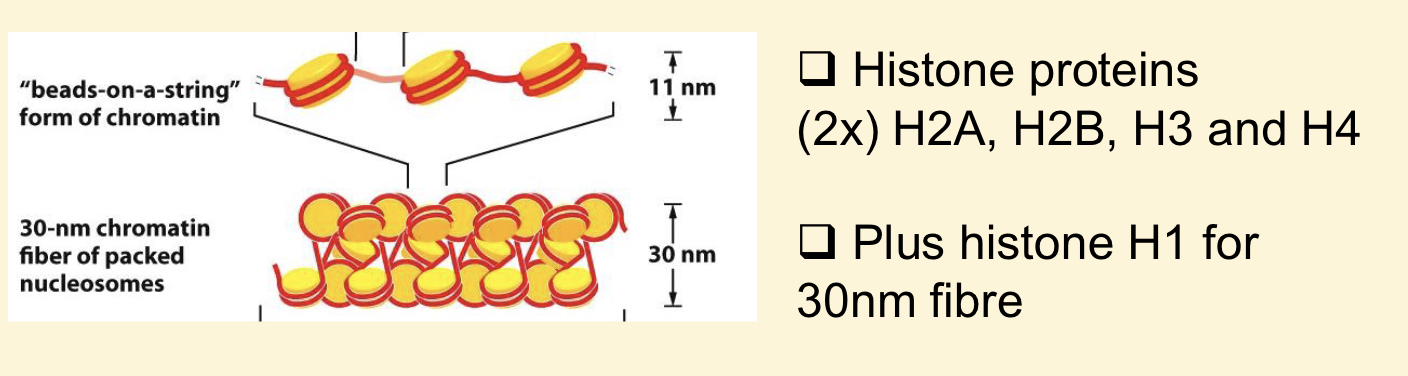
What is the first level of folding?
Nucleosome
Nucleosome key info
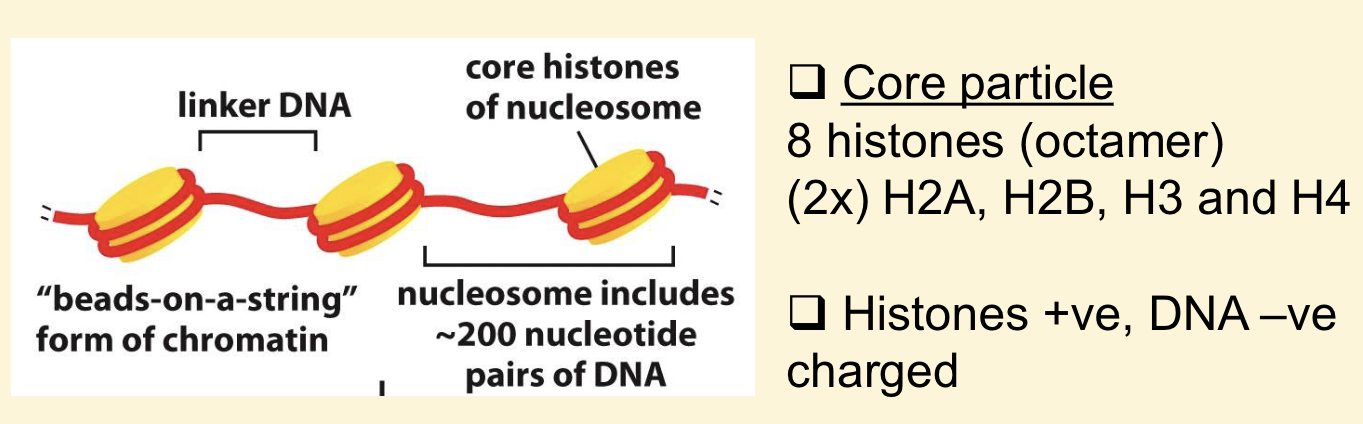
Nucleosome clear structure
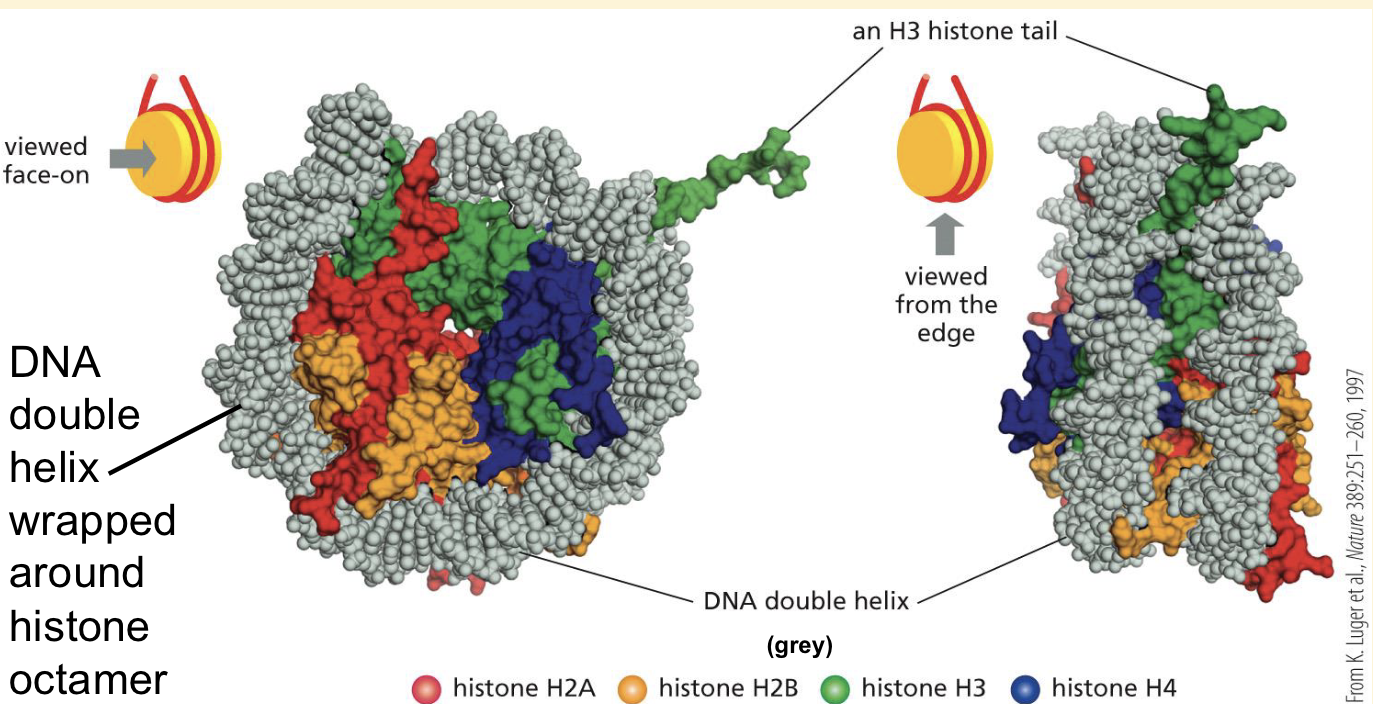
What does the second level of folding require?
H1
Second level of folding
Is DNA condensation highly regulated
Yes
What does DNA condensation allow
Allow access to enzymes for DNA replication or gene expression
2 methods of decondensation
1. Chromatin-remodelling
complexes
2. Histone-modifying
enzymes
(add or remove acetyl,
phosphate or methyl groups)
Does supercoiling affect gene expression?
Yes
What may supercoiling cause?
May cause gene expression to be switched off –
❑ β-globin: severe anaemia
❑ Tumour suppressor genes: cancer
What is epigenetics?
Epigenetics - heritable changes in gene function that cannot
be explained by changes in DNA sequence (e.g. methylation)
– impact of environment. Clinical implications unclear
True or false
Histone modification patterns can be inherited
True
What is Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS)?
Chromatin disease, most lethal
1/100,000
Non-specific symptoms
Intellectual disability
Facial abnormalities
Broad thumbs and broad great toes
❑ RSTS: mutation in histone acetyl-transferases
What is DNA packaged into?
Chromosomes
What is human karyotype used for?
Diagnose diseases