Microbiology Lab Quiz 7
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are some characteristics of ALL enteric bacteria?
Gram (-)
Rod-shaped
Ferments glucose to acid
Facultative anaerobes (continue growth in the presence of O2
Family of Enterobacteriaceae; led to the establishment of the Total Coliform Rule
Total Coliform Rule
places limits on the # of E. coli that can be present in water that is used for different purposes due to the fact members of the Enterobacteriaceae cause 40-45% of ALL foodborne and waterborne illnesses in the U.S.
Enteric Bacteria
relating to or occurring in the intestines or intestinal ailments (E. coli, Shigella, Salmonella), but some occur in non-intestinal habitats (Yersinia pestis, Proteus mirabilis, Erwinia)
most are considered opportunistic pathogens (E. coli & Proteus vulgaris) and in rare cases trigger septic infections
*Responsible for 40-50% of all nosocomial infections
Escherichia coli
normal inhabitant of human intestines (enteric)
Shigella species
fecal contaminated water; causes dysentery (enteric)
Salmonella species
undercooked chicken/eggs; Most common cause of food poisoning (US-enteric)
Yersinia pestis
rodents, fleas; causes bubonic plague (non-intestinal)
Proteus mirabilis
found in soil; degrades organic material (non-intestinal)
Erwinia species
common plant pathogen; negatively impacts pears, apples, carrots, etc. (non-intestinal)
Opportunistic pathogens
cause diseases (urinary tract infections, pneumonia, & wound infections) in immunocompromised (weakened/impaired immune systems) hosts like AIDS pts, cancer pts, transplant pts, and pregnant women
ex. Proteus vulgaris & Escherichia coli (in rare cases can cause septic infections)
Septic infections
overactive immune response throughout body
occurs in response to bacterial infection
can trigger organ failure and drop in blood pressure which can lead to death
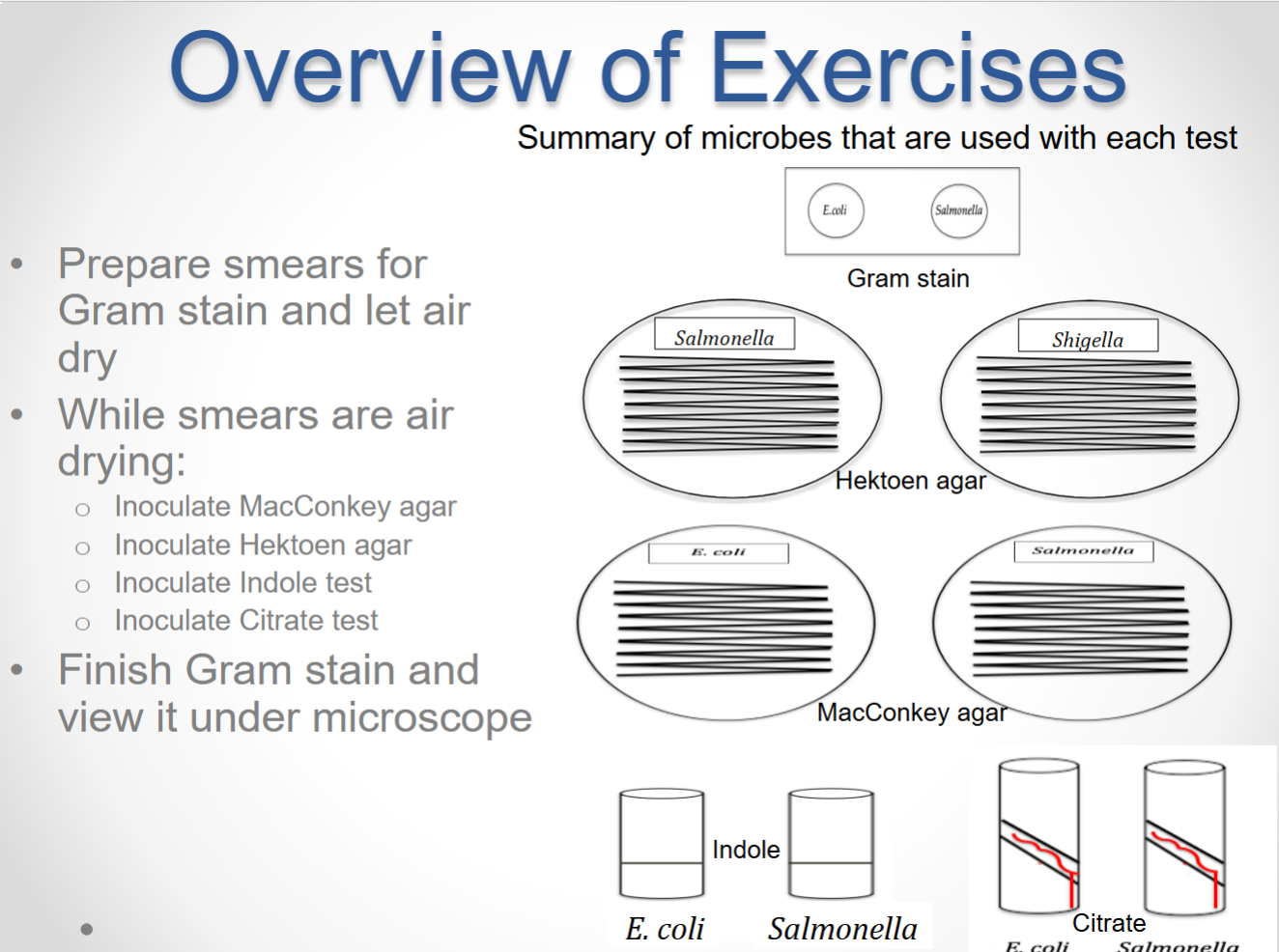
Gram stain
Bacteria: E. coli (-) & Salmonella or S. aureus (+)
Primary stain: Crystal violet
Secondary stain: Safranin
Mordant: Iodine
Decolorizer: Acetone alcohol
MacConkey agar
Selective for Gram - bacteria + Differential (b/t lactose-E. coli & non lactose-Salmonella fermenters) must be checked < or at 24 hrs
Selective component: Bile salts + Crystal violet
Differential component: Lactose
pH indicator: Neutral red (turns pink during lactose fermentation…yellow non)
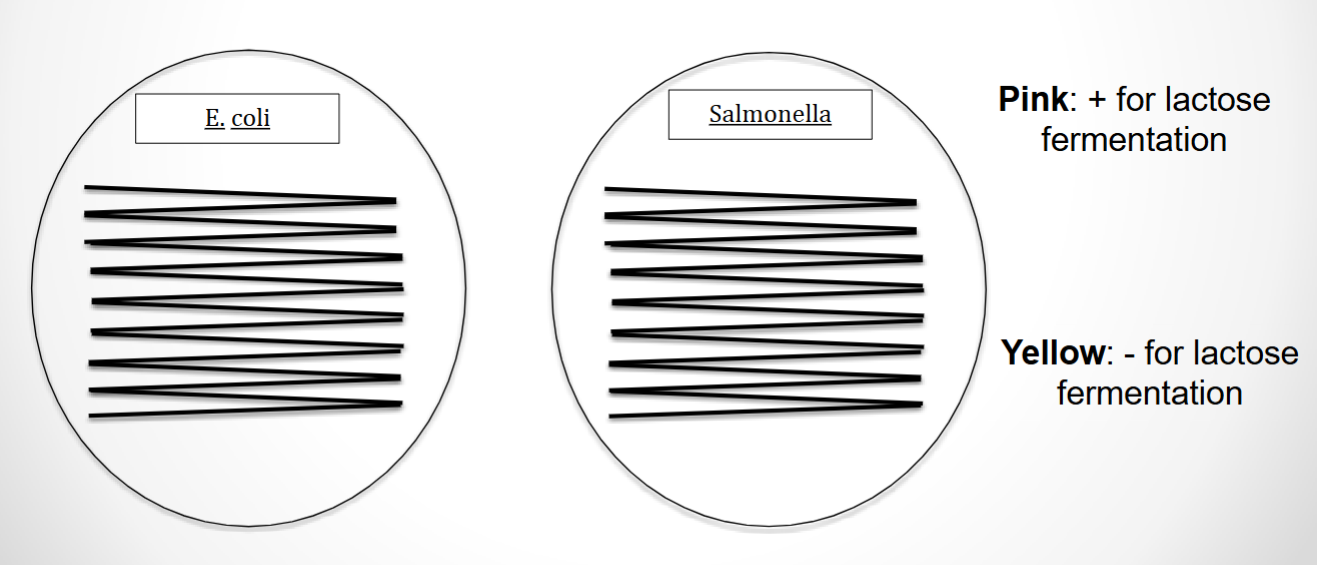

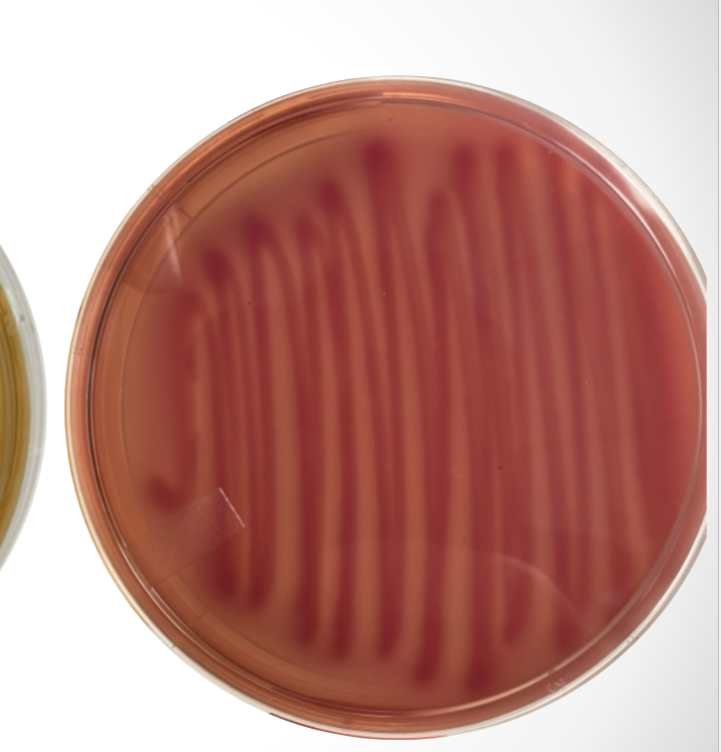
What agar is used in this test? What bacteria was used and what does the reaction suggest?
MacConkey agar, Salmonella, and the reaction suggests that Salmonella is negative for lactose fermentation
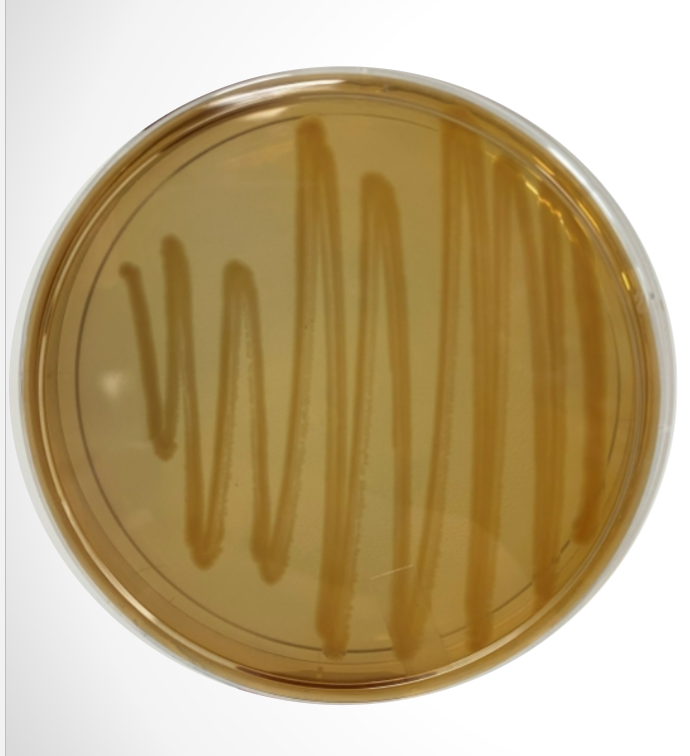
What agar is used in this test? What bacteria was used and what does the reaction suggest?
MacConkey agar, E. coli, and the reaction suggest that E. coli is positive for lactose fermentation
Hektoen agar
Selective for Gram + bacteria & Differential (differentiates b/t microbes that can-Salmonella /cannot produce H2S from sulfur-Shigella)
Selective component: Bile salts
Differential component: Sulfur and Iron
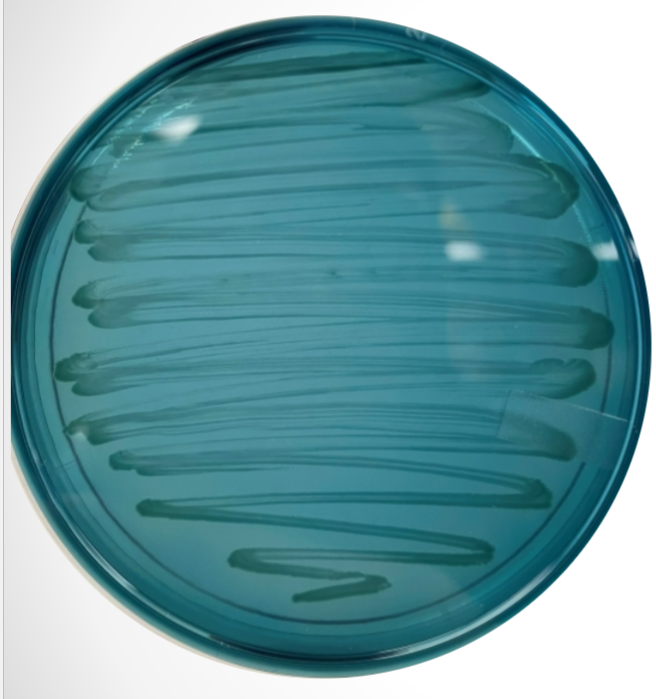
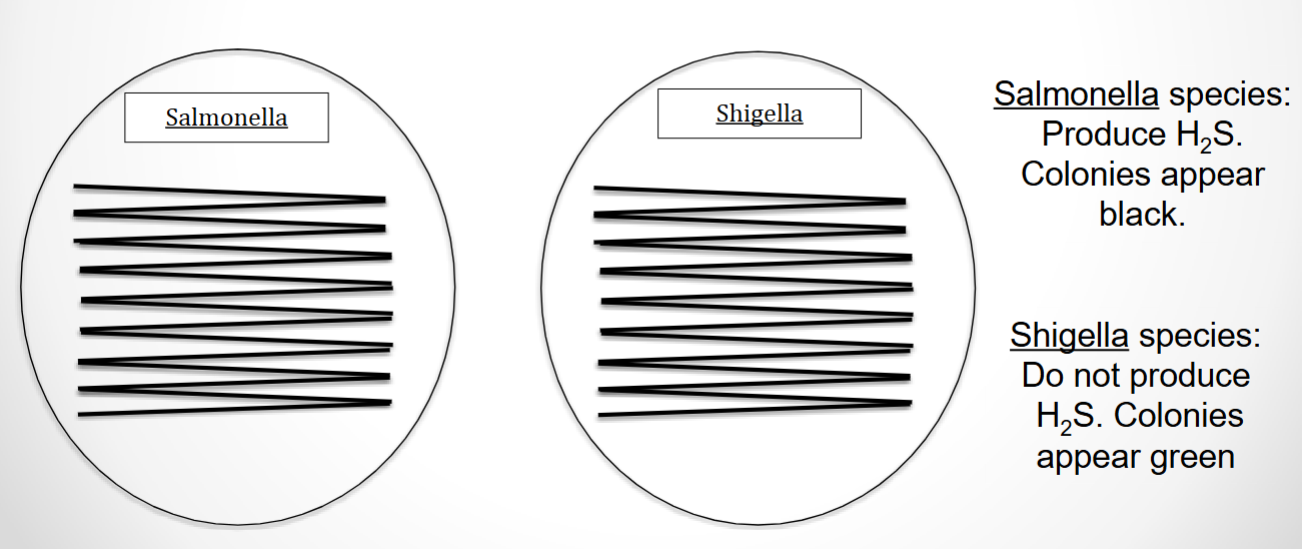

What agar is used in this test? What bacteria was used and what does the reaction suggest?
Hektoen agar, Shigella, and the reaction suggests that Shigella does not produce H2S (colonies appear green)
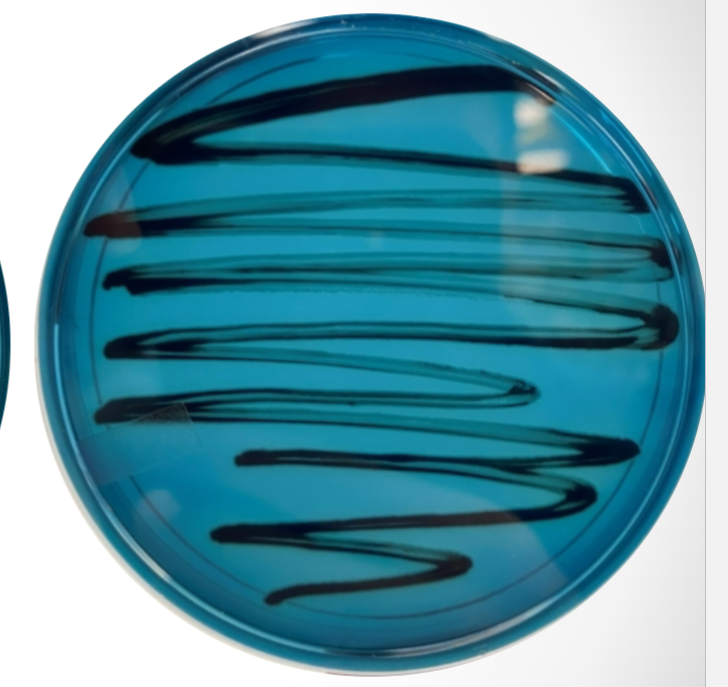

What agar is used in this test? What bacteria was used and what does the reaction suggest?
Hektoen agar, Salmonella, and the reaction suggests that Salmonella does produce H2S from sulfur, which reacts with iron (colonies appear black)
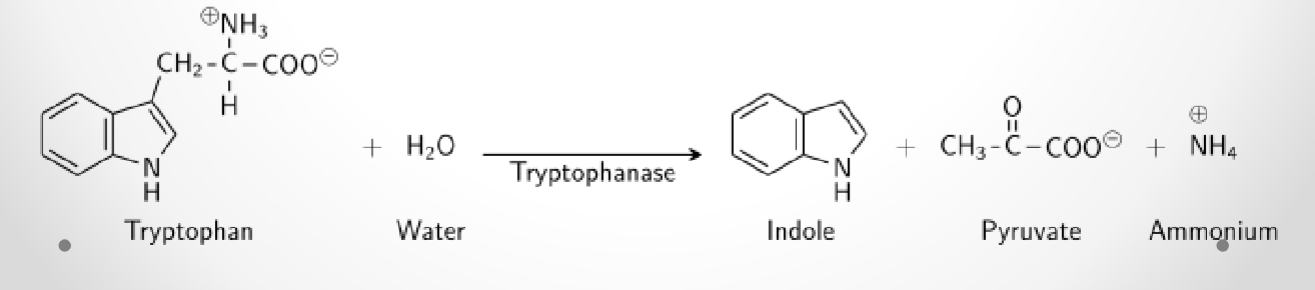
Indole broth
Differential broth (differentiates b/t microbes that does-E. coli / doesn’t-Salmonella produce tryptophanase enzyme)
Differential component: Tryptophan
After 24 hrs of incubation, add 6 drops of Kovac’s reagent to each tube to see reaction.


What medium is used in this test? What bacteria was used and what does the reaction suggest?
Indole broth, E. coli, and the reaction suggests that E. coli is positive for tryptophanase

What medium is used in this test? What bacteria was used and what does the reaction suggest?
Indole broth, Salmonella, and the reaction suggests that Salmonella is negative for tryptophanase
Citrate agar
Selective and Differentiates for microbes that do-Salmonella / don’t-E. coli use citrate as a carbon (food) source
Differential component: Citrate
pH indicator: Bromothymol blue (green at acidic pH & blue at basic pH)
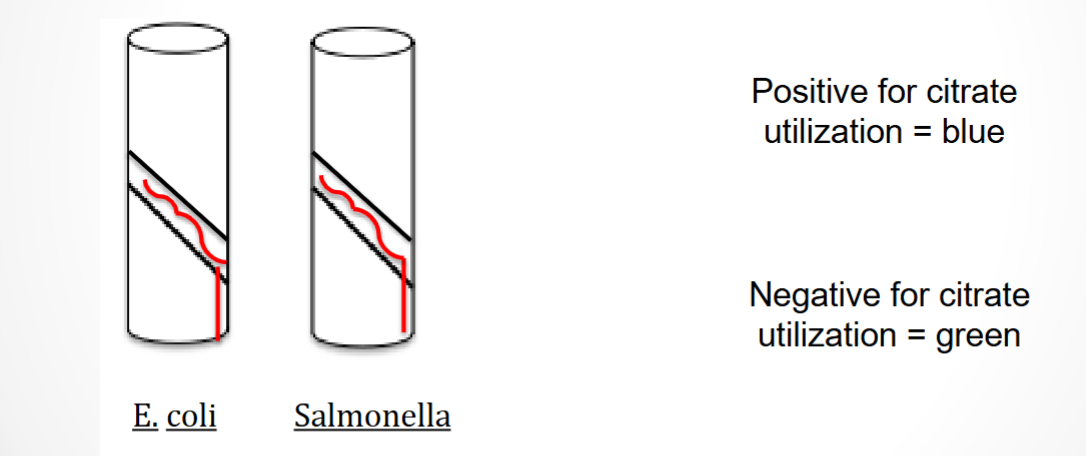

What agar is used in this test? What bacteria was used and what does the reaction suggest?
Citrate agar, Salmonella, and the reaction suggests that Salmonella is positive for citrate utilization as a food source (basic pH)

What agar is used in this test? What bacteria was used and what does the reaction suggest?
Citrate agar, E. coli, and the reaction suggests that E. coli is negative for citrate utilization as a food source (acidic pH)
Overview of Lab 7: