Anti-depressants
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Chemical involved in anti-antidepressants
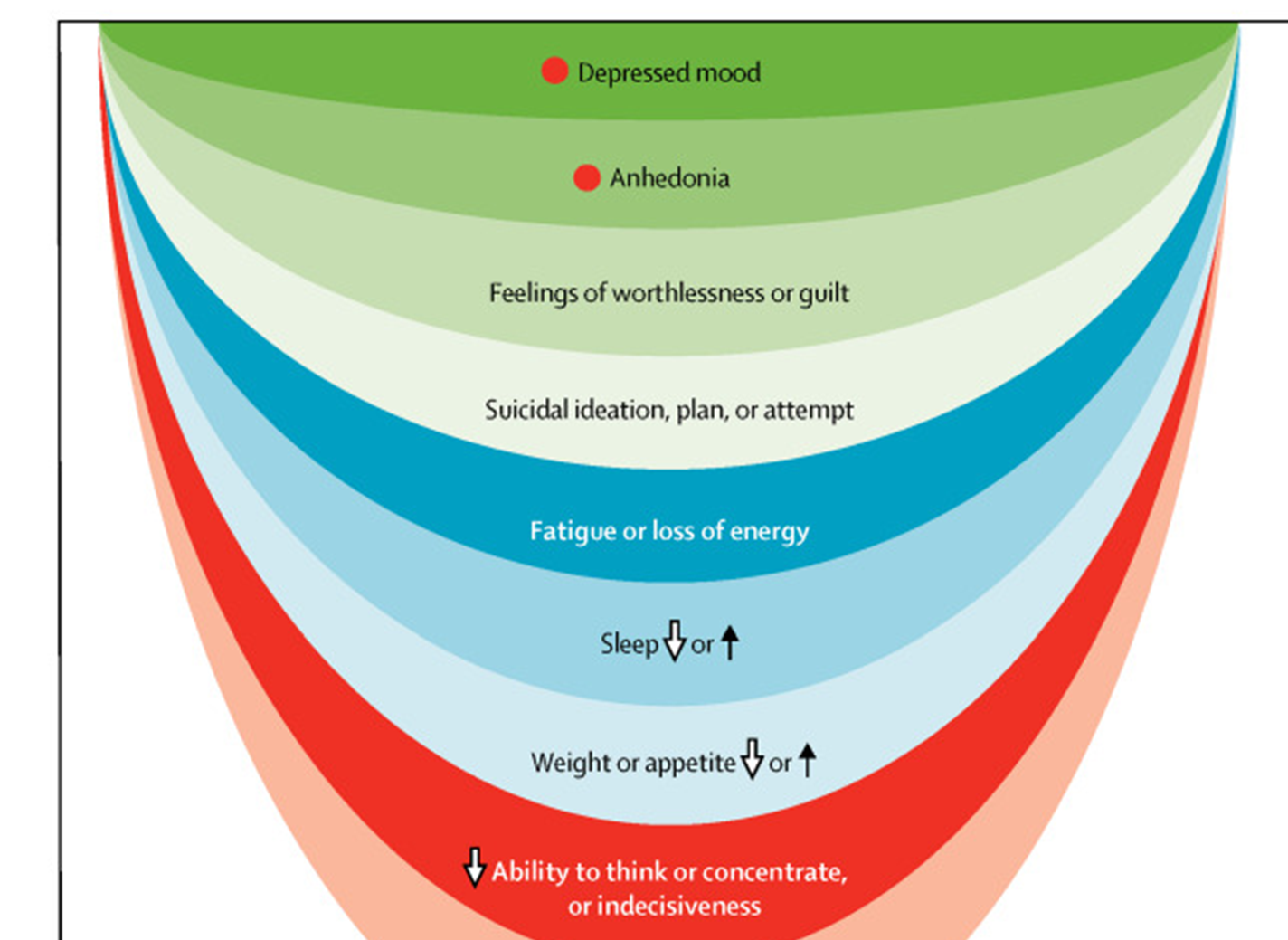
Antidepressants primarily work by increasing the activity of neurotransmitters in the brain, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, which help regulate mood.
Side effects of AD
Feeling agitated, shaky, anxious, sickly, indigestion, stomach/headache, diarrhoea, constipation, loss of appetite, dizziness, insomnia, reduced sex drive, erectile dysfunction, difficulties achieving orgasm during sex/ masturbation.
Conditions with similar symptoms to depression
Is important to know past medical history before prescribing because there conditions that have similar symptoms to depression like: thyroid problems, menopause, hormone issues, vitamin deficiency, low libido.
Its important
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
It is the most commonly prescribed antidepressant. They work by increasing the concentration (amount) of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin helps to regulate mood, memory, pleasure, sleeping, eating, learning and cell communication. It is also licenced for anxiety and OCD.
Examples of SSRIs
-Setraline
-Citalopram
-Fluoextine
-Paroxetine
-Escitalapram
Selective serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
they are a class of antidepressants that increase serotonin and norepinephrine levels. They increase the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain by blocking the reabsorption of neurotransmitters in the brain to increase their availability
Examples of SNRIs
-Venlafaxine
-Duloxetine
-Milnacipran
SSRIs vs SNRIs
-SNRIs is newer and stronger than SSRIs
-SNRIs side-effects can be stronger and overdose can be more dangerous
-SSRIs block the reuptake of only serotonin, while SNRIs block the reuptake of both serotonin and noradrenaline (also called norepinephrine
-Venlafaxine tends to be used when SSRIs haven’t worked
-Serotonin, Reuptake (think about recycling), Inhibitors (think about stopping)
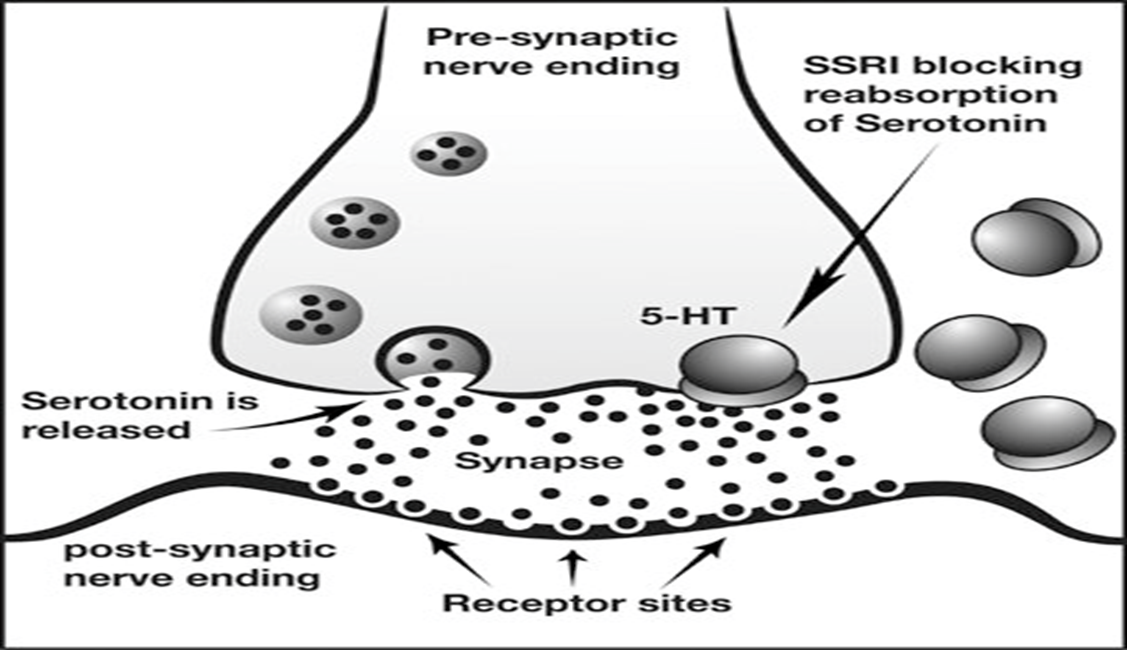
(no need to remember the pic content)
Tricyclics
They work by blocking the reuptake of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine in the increases the levels of these chemicals and helps regulate mood, attention, and pain.
Tricyclics are rarely prescribed as front line treatment as they are very lethal in overdose, and have quite unpleasant side-effects.
Tend to see them in older people who have been on them for many years.
TCAs also used to treat nerve pain, so always check what condition the patient was prescribed the drug for.
Types of tricyclics
-Amitriptyline (can be used for neuro pain)
-Trazodone
-Doxepin
Monoamine Oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
They work by blocking the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which increases the levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain. (They are rarely ever prescribed)
Noradrenaline and specific serotonergic antidepressants (NASSAs)
Another type of antidepressant that works by blocking certain alpha-2 adrenergic receptors and specific serotonin receptor.
Example of noradrenaline and specific serotonergic antidepressants
Mirtazapine (in small doses can help with insomnia )
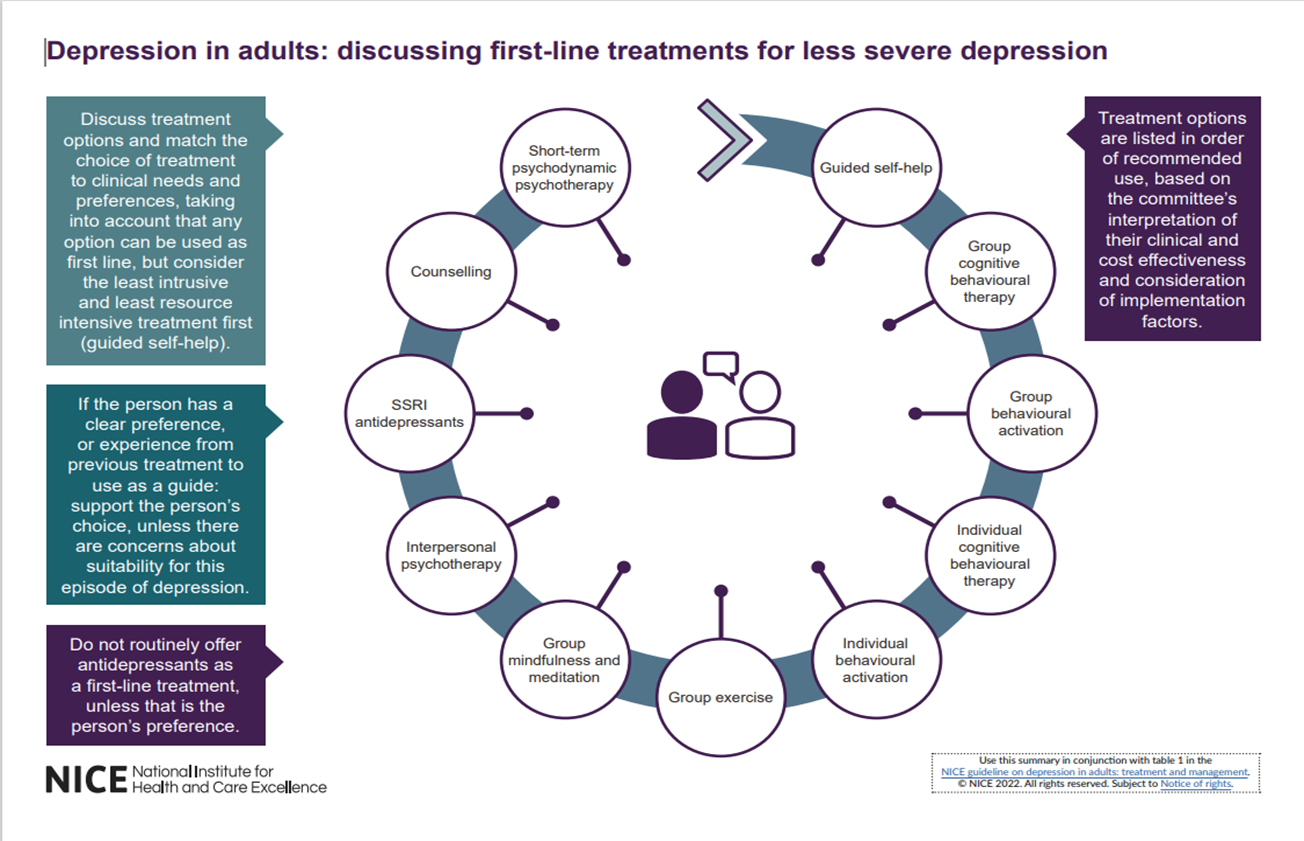
When should anti-depressants be prescribed?
Should avoid medication unless someone is quite impaired by their depression. Depression is now split into ‘less severe’ and ‘more severe’. Screening tools include PHQ-9 and the GAD -7
First-line treatments for less severe depression
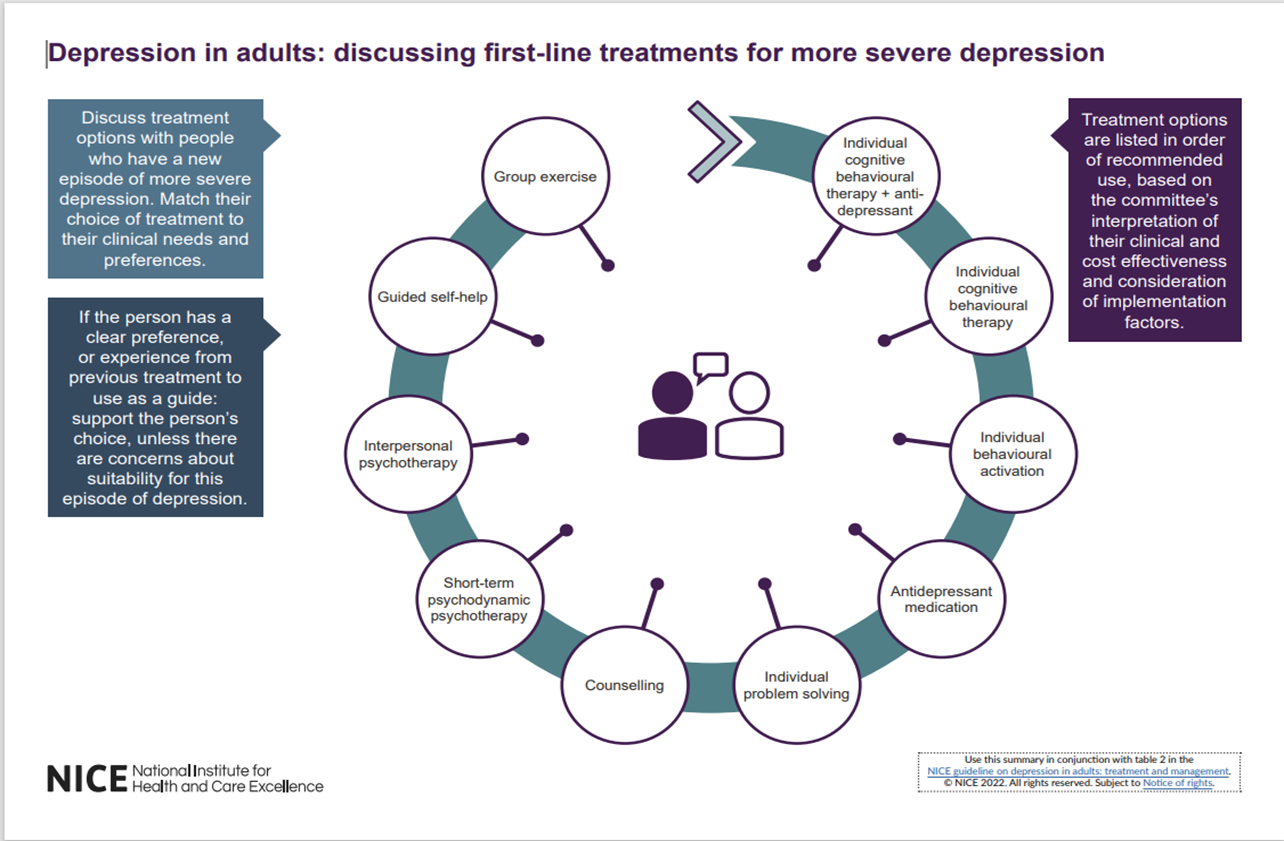
First-line treatments for more severe depression
Physical health promoting
They can impact cardiac health, that is why base lines are important to look out for
•Many antidepressants prolong the QTc
•Prolonged QTc can result in fainting
•Ventricular fibrillation (VF)
•Death
•The longer you have prolonged QTc the bigger the risk of serious complications.
Escalation of ECG
Men QTc over 430- escalate
Women QTC over 450- escalate
Hyponatreamia
A low concentration of sodium in the blood. Defined as sodium levels below 135 mmol/L.
Some SSRIs can also cause hyponatremia.
Symptoms of hyponatremia
Nausea, vomiting, headache, coma, seizures, confusion, restlessness, muscle weakness, loss of energy, fatigue etc.