Health cH1/2 BASICS if you dk this it’s over
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
health and wellbeing
the state of a persons physical, social, emotional, mental and spiritual existence characterised by an equilibrium in which the individual feels happy, healthy , capable and engaged
WHO health
Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely the absence cene of disease or infirmity
disease
a physical or mental disturbance involving symptoms, dysfunction or tissue damage
infirmity
the quality or state of being weak or ill ; often associated with old age
Dynamic
Continually changing; it is in a constant state of change
Illness
a subjective concept related to personal experience of a disease or injury
subjective
it means different things to different people
Dimensions of health and wellbeing
these are the components that make up an individual’s overall health and wellbeing. The dimensions are physical, social, emotional, mental and spiritual
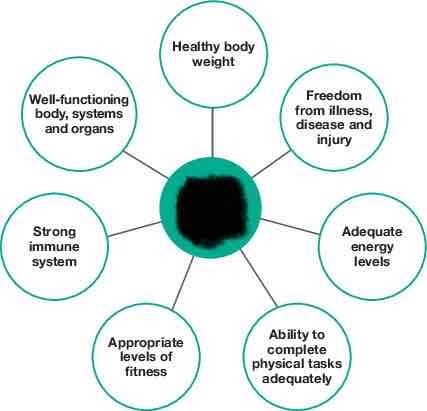
Physical health and wellbeing
relates to the functioning of the body and its systems; it includes the physical capacity to perform daily activities or tasks
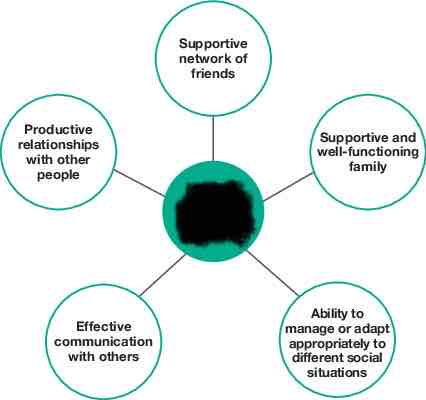
Social health and wellbeing
relates to the ability to form meaningful and satisfying relationships with others and the ability to manage or adapt appropriately to different social situations.
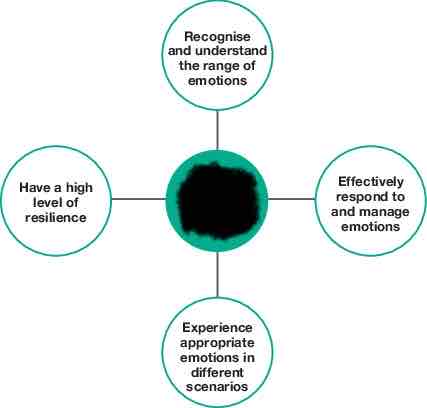
Emotional health and wellbeing
relates to the ability to express emotions and feelings in a positive way.
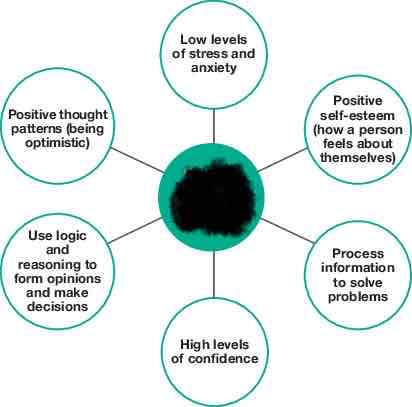
Mental health and wellbeing
the current state of wellbeing relating to a person’s mind or brain and the ability to think and process information.
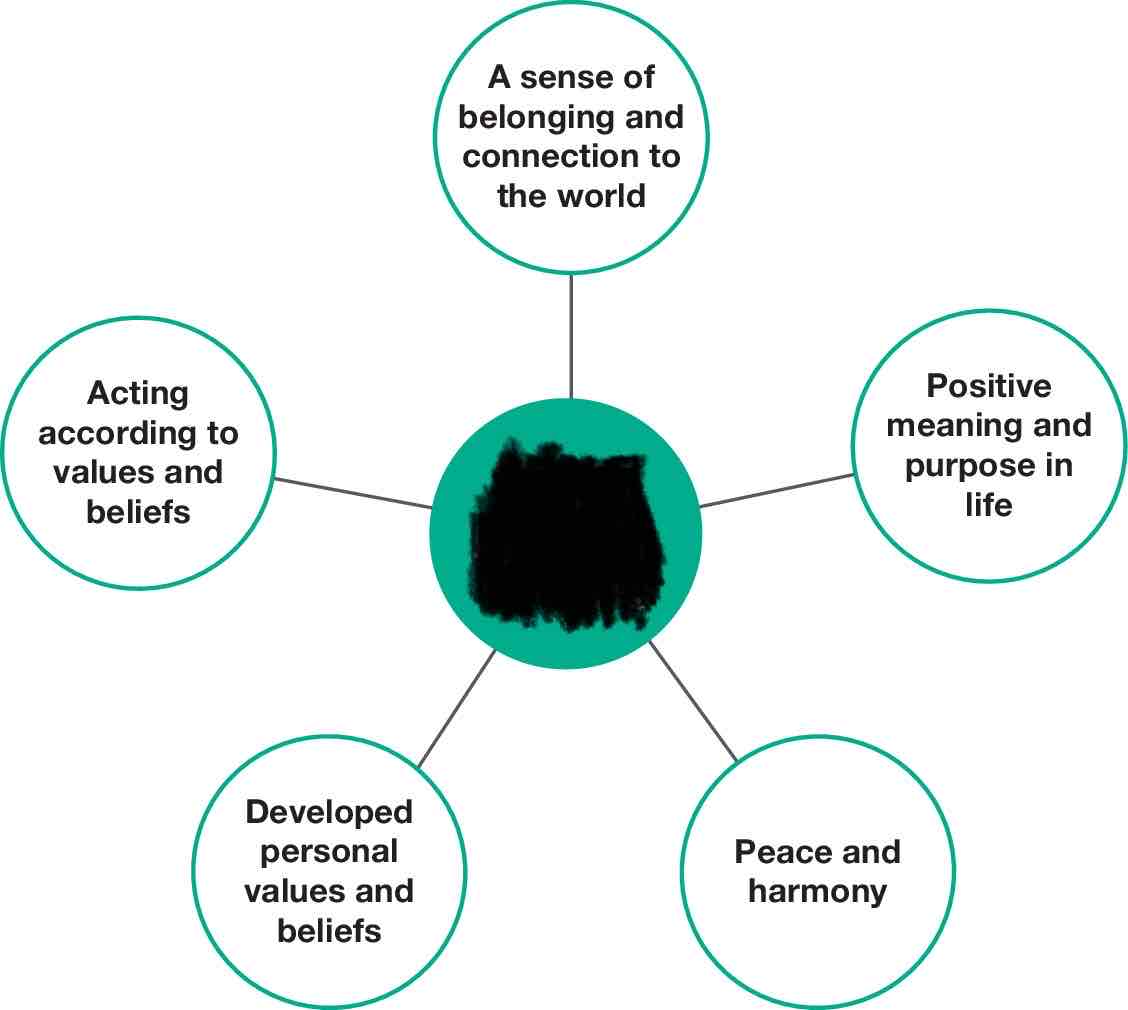
Spiritual health and wellbeing
relates to ideas, beliefs, values and ethics that arise in the minds and conscience of human beings.
Characteristics of physical health and wellbeing
Characteristics of social health and wellbeing
Characteristics of emotional health and wellbeing
Characteristics of mental health and wellbeing
Characteristics of spiritual health and wellbeing
Optimal health and wellbeing
refers to the highest level of health and wellbeing an individual can realistically attain at any particular time.
Interrelationship
The five dimensions of health and wellbeing are interrelated; that is, they all affect each other. Although they will not all be affected in the same way or to the same degree, a change in one will usually have some effect on the other four.
Importance of health and wellbeing as a resource individually
Being healthy can improve quality of life and assist in creating a cycle of wellbeing. It allows individuals to work more effectively and improve their lives, which in turn promotes health and wellbeing.
Individuals can also work productively , reduced healthcare costs, gain an education,exercise and gain an income
Importance of health and wellbeing as a resource nationally
Populations with optimal levels of health and wellbeing experience greater economic benefits such as higher average incomes, greater productivity, less absenteeism from work
Longer healthier lives, health system savings , increased productivity and reduced stress and anxiety in the community
Importance of health and wellbeing as a resource globally
Optimal health and wellbeing can reduce the risk of infectious or communicable diseases spreading between countries.
There is reduced risk of disease transmission between countries, promotes social development and promotes economic development
Prerequisites for health
Peace, Shelter, Education, Food , Income,, Stable ecosystem, sustainable resources , social justice, equity
Peace
The absence of conflict
Shelter
A structure that provides protection from the outside environment
Education
The process of gaining knowledge and building skills, typically in environments such as school and university
Food(security)
When a person has reliable access to adequate quantities of nutritious, safe, and culturally appropriate food at all times, from non-emergency sources.
Income
Money that is earned by an individual through providing labor, producing a good or service or money received from investments which enables them to access various resources
A stable ecosystem
A community that consists of all living and nonliving components of a particular area
Sustainable resources
Meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Social justice
Everyone having equal opportunities and rights,regardless of personal traits such as sex,class and income,ethnicity,religion and age.
Equity
Concept that relates to fairness and social justice,but has a particular focus on disadvantaged groups
Mnemonic for prerequisite of health
People should enjoy edible food inclusion some sustainable stew
Health status
An individual’s or a population’s overall health, taking into account various aspects such as life expectancy, amount of disability and levels of disease risk factors.’
Health indicators
standard statistics that are used to measure and compare health status (e.g. life expectancy, mortality rates, morbidity rates , burden of disease and self assessed health status)
Self assessed health status
An individual’s own opinion about how they feel about their health, their state of mind and their life in general.
Life expectancy
The number of years of life , on average, remaining to an individual at a particular age if death rates do not change
Health adjusted life expectancy
The average length of time an individual at a specific age can expect to live in full health; that is, time lived without the health consequences of disease or injury
Mortality
The number of deaths in a population in a given period
Mortality rate
tthe measure of the proportion of a population who die in a one-year period
Infant mortality rate
The number of deaths of infants between birth and their first birthday per 1000 live births.
Under 5 morality rate
The number of deaths of children under five years of age per 1000 live births.
Maternal mortality rate
tthe number of mothers who die as a result of pregnancy, childbirth or associated treatment per 100 000 women who give birth
Morbidity
Ill health in an individual and levels of ill health within a population
Incidence
Refers to the number of new cases of a disease/condition in a population during a given period
Prevalence
The total number or proportion of cases of a particular disease or condition present in population at a given time
Burden of disease
A measure of the impact of diseases and injuries, specifically it measures the gap between current health status and an ideal situation where everyone lives to an old age free of disease and disability.
Disability adjusted life years
a measure of burden of disease. One DALY is equal to one year of healthy life lost due to illness and/or death. DALYs are calculated as the sum of the years of life lost due to premature death and the years lived with disability for people living with the health condition or its consequences
Years of life lost
A measure of how many years of expected life are lost due to premature death
Years lost due to disabiliary
A measure oh how many healthy years of life are lost due to disease, injury or disability
Smoking
A practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream