MANGROVES
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What are mangroves?
Various types of trees up to medium height and shrubs that grow in saline coastal sediment habitats in the tropics and subtropics
Thrive in intertidal between seagrass beds and the coast
Extremely productive and provide numerous goods and services both to the marine environment and people
Fisheries (nurseries), timber and land products, costal protection and tourism
How are mangroves interconnected with coral reefs and seagrass beds?
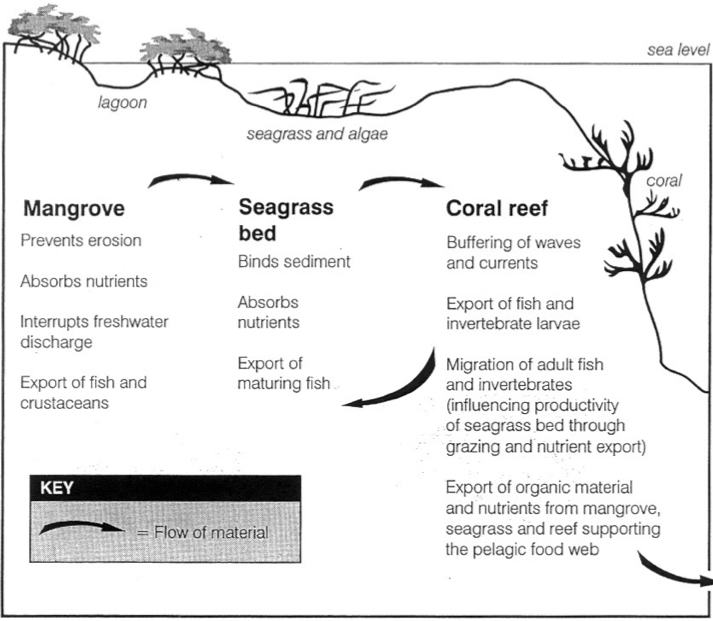
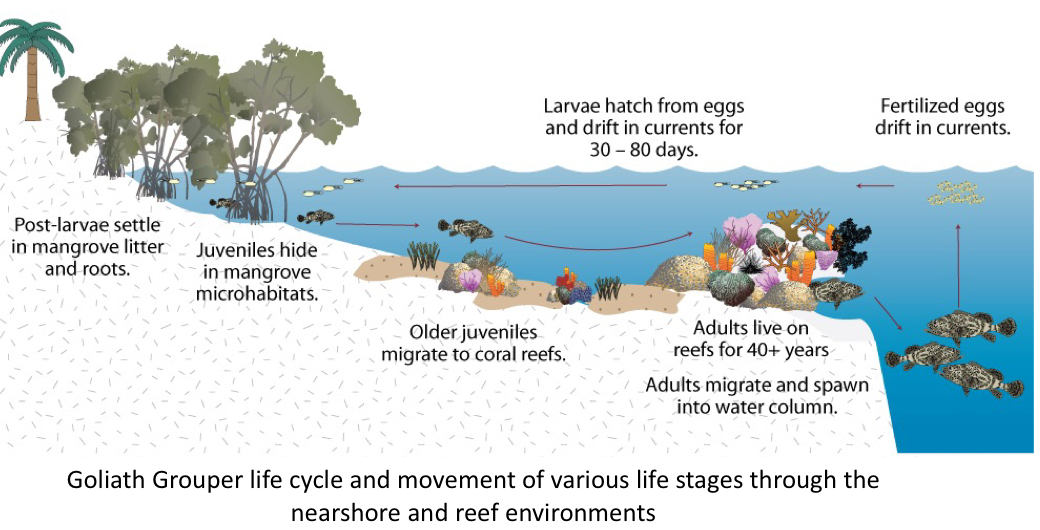
How do mangroves help the Goliath Grouper?
Crucial in juvenile survival because mangroves serve as microhabitats that prevent predation
What are epiphytes?
'Air plants' - plants that grow on top of other plants (typically trees) co-existing in the most harmonious, harmless way
E.g., creepers, orchids, fernsW
Why are mangroves considered blue carbon ecosystems?
Blue carbon is any carbon stored by the ocean
Highly effective at capturing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass and sediments (burial)
CO2 decomposes under anaerobic conditions
Largely due to the deep, organic rich soils
What is carbon storage vs sequestration?
Carbon storage: total amount of carbon contained in a forest or a part of the forest (soil or trees) “stock” or “pool”
Carbon sequestration: the process of removing carbon from the atmosphere and storing it in another form that cannot be immediately released (wood) “rate”
How do mangroves protect the coastline?
Natural barrier against storms
Absorbing and weakening wave energy as well as preventing damage caused by debris movement due to storms or tsunamis
Entangled roots stabilize coastal areas through sediment capture and bio-filtration of nutrients and pollutants
Aerial roots filter sediments and reduce pollutants from sewage and aquaculture in estuaries and coastal waters H
What are the benefits to local communities?
Provide food, medicines, fuel wood, charcoal, and construction materials
What was the evolution of mangroves?
Evolved independently 16 times
Polyphyletic group - set of organisms that have been grouped together but do not share an immediate common ancestor (e.g., sharks and dolphins)
Similar traits due to convergent evolution
~ 55 species in 20 genera in 16 families
Mangal = mangrove community
Mangrove tree root system
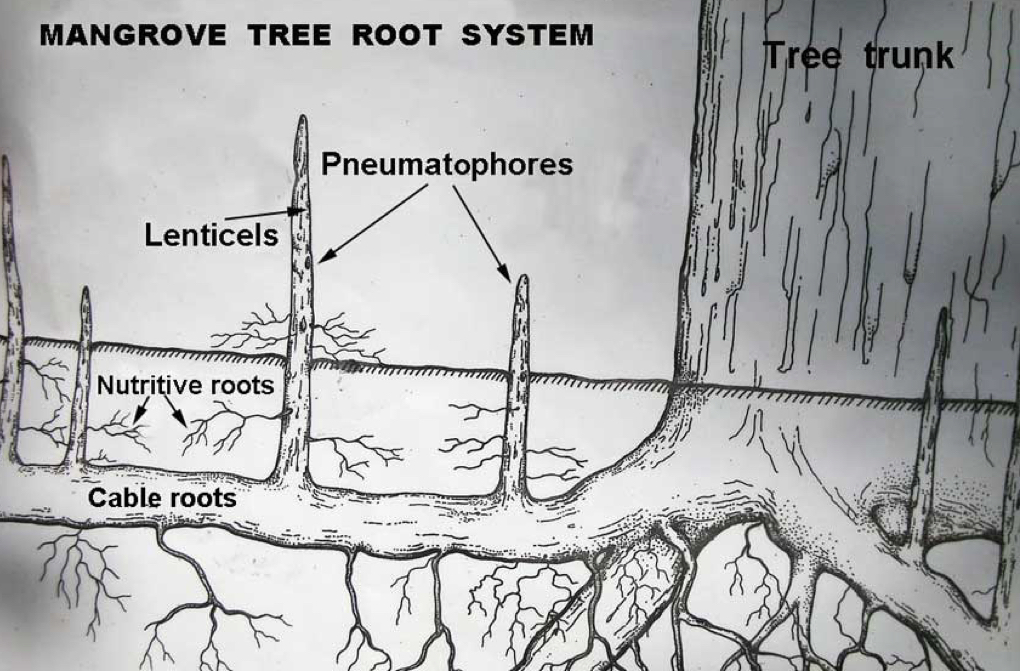
What are aerial roots?
“Breathing roots”
Allow mangroves to exchange gases, including oxygen, with the air
Oxygen content of water is far below that of air
Bacteria in soil can deplete soil oxygen content
Oxygen diffuses through water 10,000 times slower than air
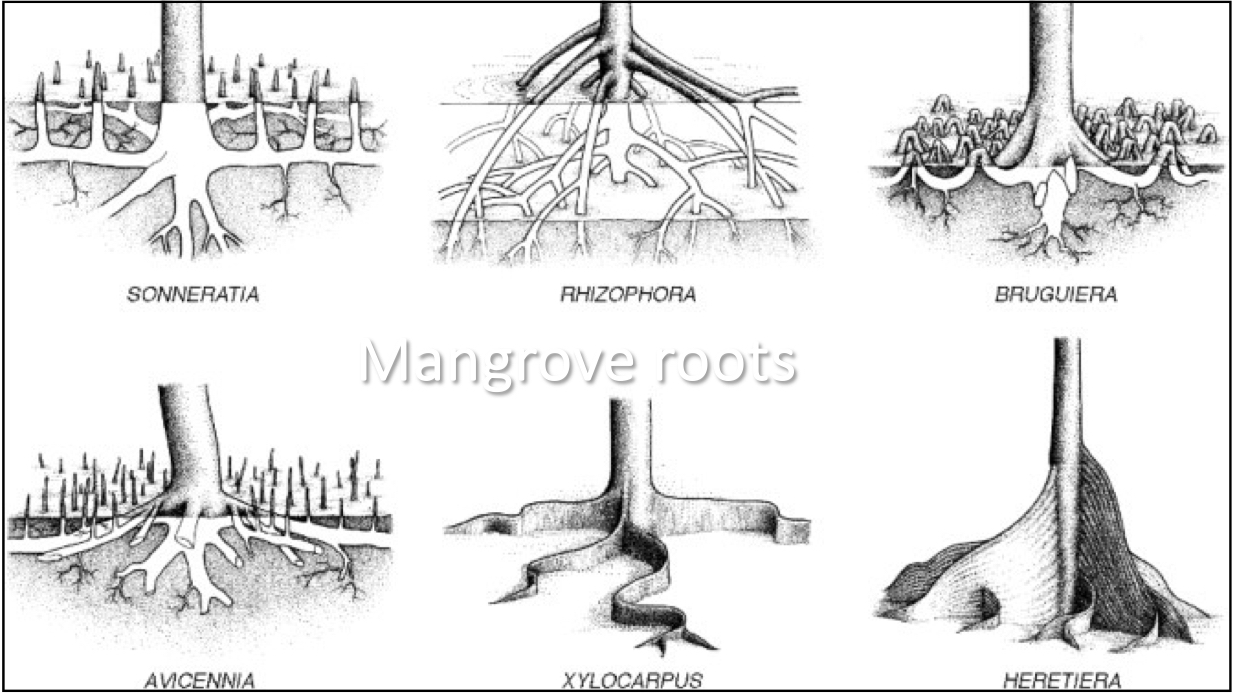
Types of mangrove roots
How are sponges beneficial to mangroves?
Nitrogen: sponges provide nitrogen to mangroves, essential for growth
Carbon: mangroves provide CO2 to sponges through photosynthesis
Protection: sponges protect mangrove roots from isopods that burrow into roots
Growth: mangroves grow 2-4 times faster when sponges grow on their roots
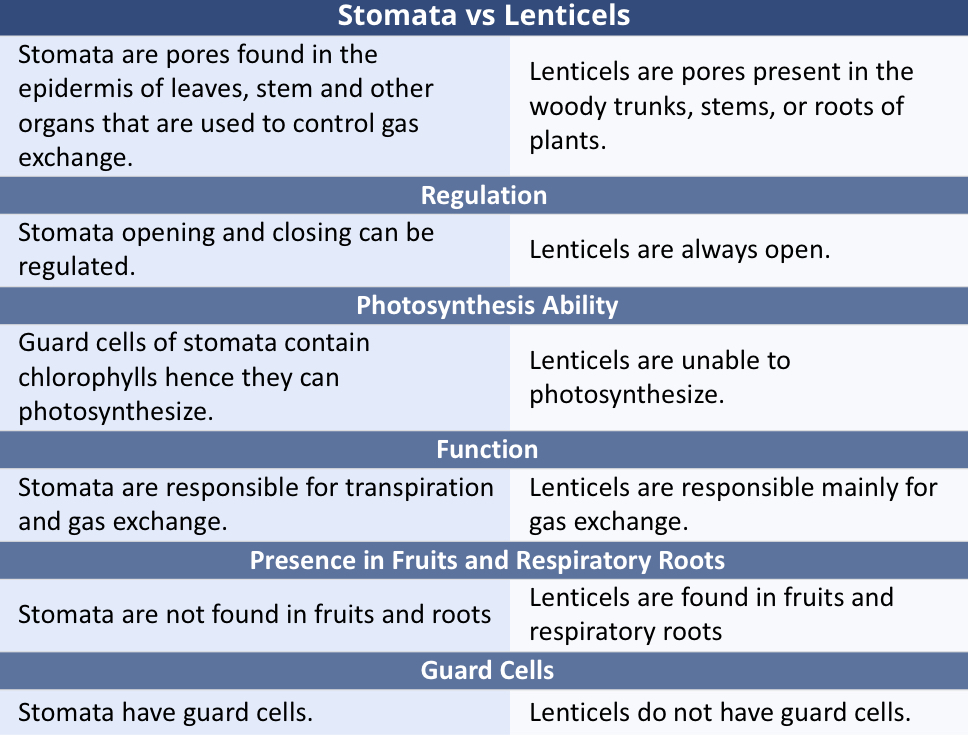
What is gas exchange?
Occurs through specialized pore in plants
Stomata: pores in the epidermis of leaves
Lenticels: pores found in the trunk or roots of the tree
Adaptations for salinity
Mangroves have aerial and salt-filtering roots and salt-excreting leaves which enable them to occupy the saline wetlands
Exclusion of salt (prevention)
From root and leaves
Transport systems with low affinity to Na+ and Cl- uptake
Secretion of salt (expelling excess)
In bark of stems or roots
In leaves (salt glands)
Conserving water
Succulent leaves with waxy cuticle on top
High water use efficiency
Smaller leaves
Leaves at an angle to the sun (adaptation to light)
How do mangroves reproduce?
By flowering with pollination
Wind - Rhizophora
Produce lots of light, powdery pollen
No nectar
Animals
Bats
Bees
Birds
Hawk moths
What are mangrove propagules?
Seed-like structures that allow mangrove trees to reproduce (“seedlings”)
All mangroves disperse offspring by water
Produce large propagules
Vivipary: growing embryo remains on parent tree before departing as a seedling
Parent supplies water, nutrients, carbohydrates
Controlled by hormones
Threats to mangroves
Over ½ of the world’s mangrove forests have been destroyed during the last 50 years (80 million acres)
Coastal developments, shrimp aquaculture, agriculture expansion, and unsustainable tourism
Natural habitat migration vs coastal squeeze
Natural habitat migration: mangrove forests migrate landwards
Sea level rise causes erosion of mangrove at seaward edge
Coastal squeeze
Area is being ‘squeezed’ as mangrove forest cannot migrate landward due to a sea wall
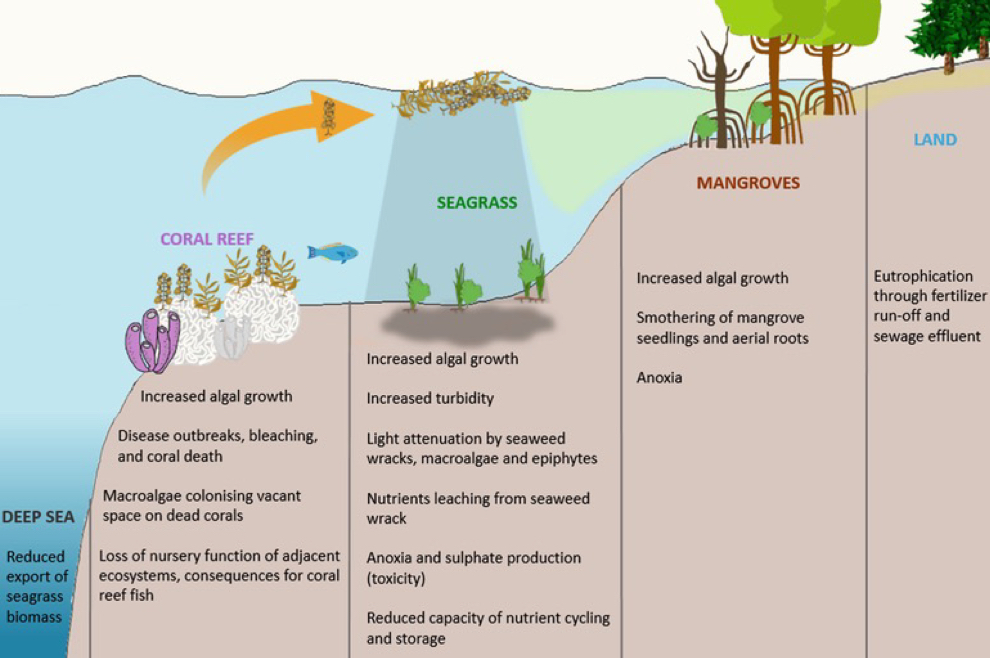
What are the impacts of eutrophication on mangroves?
What are mangrove cultivating pots?
Rough texture
Made with concrete that disintegrates within a few years
Pot hold soil and reef safe slow fertilizers
Anchor to hold in position
Helps keep waves and floating debris from knocking over
Wrack protector (pop off as tree grows)
What are problems with mangrove restoration?
Mostly happening with red mangrove propagules
Single species creates monoculture that are not resilient to storms and surges
Planting is often done where mangroves do not naturally grow
Other ecosystems (seagrass beds) are trampled on by volunteers
Seedlings are planted in areas that are submerged for too many hours or where wave impact is too strong
Restored mangrove belts do not often extend for more than 100 meters
What is the mangrove zonation?
Caused from varying salinity tolerances
Red mangroves with prop roots are closest to the water, followed by black mangroves with pneumatophores, and white mangroves closest to land