dosage fr finals
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
what is hard gelatin made out of ?
gelatin + water + sugar
hard gelatin moisture content
10-15%
hard gelatin
2 parts
large narrow - body
wider smaller - cap
what are soft gelatin capsules made out of?
gelatin + glycerin or sorbitol + preservatives + water
hermetically sealed
difficult to compound
types of gelatin
type A : pork skin
type B: animal bones
gelatin alternatives
polysaccharide (pullulan)
plant caps
water soluble
non-hydroscropic
cellulose derivatives (hypromellose)
Vcaps
coni-snap
tapered rims
indentations / dimples
locking grooves
coni-snap supro
smaller
makes seperating 2 parts more difficult
weight variation (gross weight)
± 10%
content uniformity (API strength)
± 5%
QA compendial requirements
content uniformity : 9/10 should have drug strength 85-115%
stability testing
moisture permeation test
disintegration test
dissolution test
tablet advantages
temper resistant
convenient to use
how to make tabs?
tab manufacture
compression
wet granulation
dry granulation
direct compression
wet granulation
drugs with low compressibility / weak physical strength
dry granulation
drugs unstable in water / heat
direct compression
drugs with high compressibility / flowability
no need for granules
microcrystalline cellulose
dibasic sodium calcium phosphate
compression aid
sodium starch glycolate
disintegrant
magnesium stearate
tableting lubricant
tablet defects
capping
lamination
chipping
cracking
mottling
sticking
picking
capping
upper or lower part of the tablet separates from the main body
not enough binder
didnt dry well

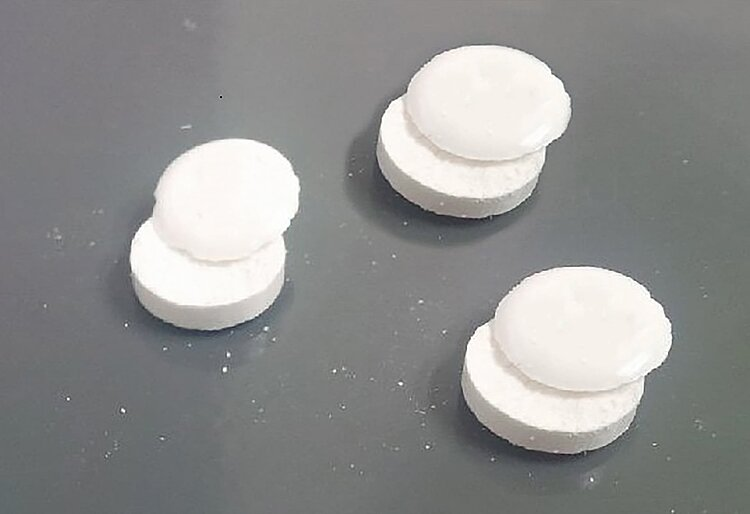
lamination
seperation of tab into 2 or more distinct layers
air entrapment
too oily

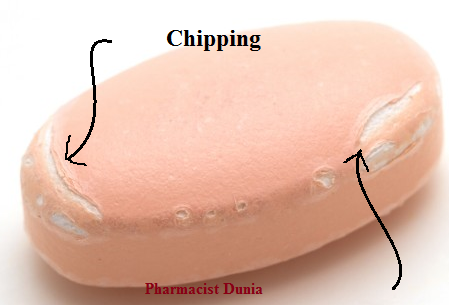
chipping
breaking of tablet edges while tablet leaves press
too dry
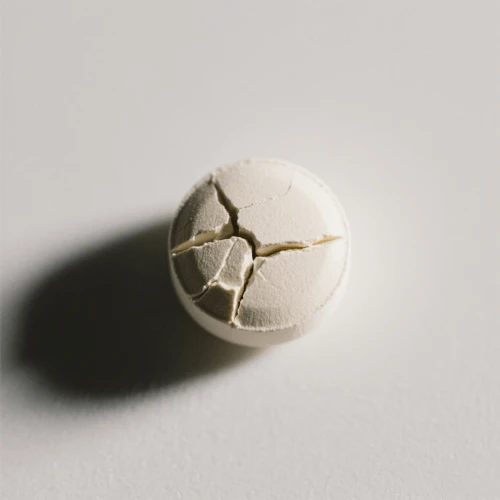
cracking
small fine cracks
granules too big/dry

mottlings
unequal distribution of tablet color

sticking
tablet material adhering to dye wall
sticks to other tabs

picking
adheres to the surface of the punches
letter may be too big
effervescent tablets
release CO2
rapdily dissolving tabs storage
very hydroscopic
if you leave outside = start dissolving
friability is an issue
if shake = break
individually packed
multiple compressed tabs
seperate incompatible drugs
deliver drugs @ different rates
film coated tabs IR
coat dissolves in stomach fluid
film coated tabs MR
coat does not dissolve in GI tract
dissolve in stomach
eudragit E
dissolve in small intestine
eudragit L or S
neutral in charge, insoluble in water, swll to release
eudragit NE or NM
insoluble in water, swell to release, high Tg
eudragit RS or RL
enteric coated tabs
polymors used
cellulose acetate phthalate
HPMC succinate
methcrylic acid co-polymers
shellac
types of ER release
gum-type
slow-release pellets, beads or granules
core tabs
microencapsulation
osmotically controlled release oral delivery system (OROS)
composition
trilayer surronded by semi-permeable membrane
2 drug layers → push compartment q
OROS
how does it work?
passes through semi-permeable membrane
control rate of passage into tablet membrane core
OROS
benefit
reduced fluctuation between drug peak and serum concentrations
binders
acacia
alginic acid
polyvinylpyrrolidone
microcrystalline cellulose
common excipients
binders
diluents
disintegrants
lubricants
glidants
antioxidants
when are lubricants usually added?
at the last step
glidants
tac
colloidal silicon dioxide
antioxidants
ascorbic acid
sodium ascorbate
sodium bisulfite
sodium metabisulfite
lubricants
metallic stearate
stearic acid
talc
4Ds
disintegration
deaggregation
dissolution
diffusion
which forms should not disintegrate slowly?
buccal
vaginal
sublingual
some film coated tabs
what does delay disintegration must occur with?
enteric coated tablets
diluents
fillers added to bulk up tab
hydroscopic
coming in contact with liquid → disintegrates
advantages of suppositories
avoids 1st past effect
how is drug absorbed in the rectum?
lining of rectum ampule and passes into circulation via hemorrhoidal veins
rectal circulation route
lower hemorrhodial veins
lymphatic circulation
rectal colonic contents
enema administered and allowed to at before suppository of a drug to be abs
rectal pHand lower buffer capacity
6.8-7.4 negligible buffer capacity
too alkaline will irritate the rectal area
rectal like dissolves like
lipo drug distributed in fatty suppository base in low concentrations = less tendency to escape to surrounding aqueous fluids
suppository bases
melt or dissolve
stable during storage
contact slightly on cooling to release from mold
do not melt at ambient temp
fatty base
melt to release 3-7 mins
1-4 days to return to stable form
stable fatty base temp
34.5C
examples of fatty base
beeswax
cetyl ester wax
fatty base
hydrogenated vegetable oils with emulsifers
fattibase
wecobee
witespol
fatty base advatages
innocuous
non-reactive
melt at body temp
fatty base disadvantage
melt in warm weather
leakage
water soluble/miscible bases
glycerinated gelatin
dissolve 30-40 mins
vaginal application
hydroscopic nature of gelatin
promotes laxation
water soluble/miscible bases
PEG
dissolve 30-50 mins
hydroscopic → irritating to body cavity tissues
drug release
from slow to rapid
lipophilic: fatty base
lipophilic: water base / water-miscible drug
hydrophilic drug: fatty base
vaginal pH
4-5
preparation of suppositories
hand molding
compression molding
fusion
intra-nasal drug delivery
epithelial lining
goblet cells
mucus layer
advantages of nasal delivery
targeted treatment
fast onset of action
minimize side effects
intranasal absorption
paracellular
tight junction
slow and passive
transcellular absorption
partitioning coefficient
physiochemical properties of intranasal
solubility
rapid dissolution of drug solids
ionization
non-ionized better
intranasal delivery
by pass BBB
delivery of large drug molecules
peptide drugs
across nasal endothlium
avoid degradation in GI
nasal vaccines
stimulate mocusal-nasal associated lymphoid tissue to produce secretory IgA / IgM and IgG
how are drugs intranasally?
nasal
spray
powders
> 10 um
nasal drops
solution formulation
deposit as film
disperse as drug
nasal spray
solution or susp
nebulized or aero
< 10um
droplets or larger particles
deposit in front part of nasal cavity
limited abs
variable bioavailability
nasal spray
squeeze bottle
solution → mist
metered-spray
spray pumped used
no propellent
accurate
atomization spray
more accurate
nasal solution enhanced by solvents
propylene gycol
alcohol
medium chain glycerides
nasal solution pH
4.5-6.5
intranasal
osmolarity/tonicity
isotonic solution PREFFERED
intranasal preservatives
benzalkonium chloride
enhancement of nasal absorption
increase viscosity
use of muco-adhesives
permeability enhancers
pulmonary drug delivery
systemic
anesthesisa
parkinson
diabetes
pulmonary advantages
avoid 1st pass
less amount of drug to treat therapeutic effect
reduce systemic side effects
pulmonary disadvantages
small portion of the dose can reach the lungs due to particle deposition in respiratory tract
complicated devices are needed
gas
can easily reach alveoli
penetration of droplets/particles depends on ?
delivery system
conditions of airways
particle size
aerodynamic particle size
diameter of spherical particle of standard denity → same terminal settling into velocity in air
factors affecting aerodynamic particles size
physiochemical properties
humidity and tonicity
surface active agents
effect of particle size
depth of particle penetration depends on aerodynamic particle size
smaller particles can pen deeper
mode of particle deposition
inertial impacting
blocked by airways : large particles
mode of particle deposition
sedimentation particles
fall out of air flow, epithelium of airways