GPs
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
custom
are GP lenses mass produced or custom made?
increase width
if you want to flatten a lens by changing the PC width, how should you modify it?
decrease width
if you want to steepen a lens by changing the PC width, how should you modify it?
smaller
a steeper curve radius is a ______ number
no real water content
describe the water content of a GP lens?
less
because GP lenses have no real water content, they are ____ likely to contain bacteria
more
because GP lenses have no real water content, they are _____ resistant to protein deposits
no
do GP lenses absorb liquids & gases?
more
for a GP, lens movement provides ____ oxygen to the cornea typically
GP
rigid
mask corneal astigmatism & irregularities
preferred for better quality optics
soft lenses
conform to the shape of the cornea
work better for individuals where the cornea is regular & the Rx is straightforward
sharp optics (especially for individuals with astigmatism or irregularities)
good corneal health due to tear exchange with blinking
wide variety of materials allows for individualization
durable
deposit resistant
good value
easy handling & care
what are the benefits of GP lenses?
initial comfort/adaptation
what is the disadvantage of GP lenses?
larger, smaller, bigger
GP lenses started ______ in size, got _______, and now are getting _____ again
cornea
corneal lenses fit to the _______
cornea & sclera
corneoscleral lenses fit to the __________
sclera, valuting the cornea
scleral lenses fit to the ________
spherical/regular GP lenses
spherical lens in optical area
use when corneal cyl is not too high (<2.50D)
scleral GP
larger GP lens for unhealthy eyes & irregular corneas, allows for more comfort & moisture chamber on cornea
front surface toric
used to correct cyl that is not corneal (lenticular cyl)
back/bitoric
used when corneal cyl is high (>2.50) so spherical GP is not stable on eye
toric back surface provides a more stable lens fit on a very toric cornea, front surface can be toric too to provide better correction
orthokeratology/corneal reshaping lens
corrects vision while sleeping so that no daytime lenses are required
bifocal/multifocal GP
multiple powers in one lens, better function than soft lenses due to lens movement/translation of powers
keeps its shape & delivers the lens power plus the power of the tear layer trapped b/t the lens & the eye
describe how a GP lens corrects vision
corneal cyl approximately equals the spectacle cyl
GP lens creates a new optical surface for the eye & corrects the cyl via the tear layer &/or lens power
what makes a good GP lens candidate?
WTR
horizontal cornea is flatter than vertical cornea
ATR
horizontal cornea is steeper than vertical cornea
overall diameter
OAD
optic zone diameter
OZD
base curve radius
BCR
peripheral curve widths
PCW
peripheral curve radii
PCR
optic zone diameter
what the patient sees through, must be over the visual axis when fitted or the pt cannot see
optic zone diameter, base curve radius
what makes up the optic zone on a GP?
cornea flattens
why does the lens need to flatten in the periphery?
flatten
secondary, intermediate, & peripheral curves ______ in a standard design to fit the corneal periphery
BC
which curve is the steepest on a standard GP?
flatter, steeper, flattens
the BC of a reverse geometry lens is typically ______, the secondary curve is ______, then the PC _____again
narrower
secondary, intermediate, & peripheral curves also tend to get ______ as they get closer to the edge in a standard GP
no
is the tear layer negligible with GP lenses?
plus, minus
if the lens is steeper than the cornea, we get a _____ powered tear layer, meaning the lens needs extra _____ to compensate
minus, plus
if the lens is flatter than the cornea, we get a ______ powered tear layer, meaning the lens needs extra _______ to compensate
steep
fluorescein pools in the middle but less in the periphery
Bull’s eye pattern
fluorescein patten that can result from a lens that fits too steep
fluorescein pools in center, dark in periphery, edge lift
tear film not exchanged b/t center & outside
becomes uncomfortable or is immediately uncomfortable
lens fits well & holds on over central cornea
top lid fails to pull the steep edge of the lens up
gravity pulls it down
center of gravity of the lens moves farther out in front of the lens the steeper it gets
why does a steep fitting lens usually center or drop?
flat
less or no fluorescein in the center, may be mechanically rubbing, more or excessive fluorescein at the edge of the lens
nasally & temporally
a flat fitting lens often decenters _______
flat
which fit has lots of edge clearance, a flat or steep fit?
high
a flat fitting lens oftne rides ______
lens often gets pulled up by the top lid since it does not fit to the cornea
why does flat fitting lens often ride high?
on K
closely contoured to corneal shape, diffuse fluorescein pattern
flattest
for a toric cornea, a GP rides on the _____ corneal meridian
flattest, steepest
for a toric cornea, fluorescein is less in the _____ meridian & pools in the _____ meridian
lid controlled
hangs off the upper lid, usually larger lens w/ slightly flat base curve
interpalpebral fit
initially centered & drops after blink; usually smaller lens w/ slightly steeper base curve
smaller or tighter lens, pt has higher upper lid position
what things make an interpalpebral fit more likely to occur?
smaller, steeper
if you want to achieve LESS lid control, getting a more interpalpebral fit, you should make the lens _______ or ______
more
the more the lens contours the cornea, the ______ it will stay with the cornea
larger or looser lens, pt has lower upper lid position
what things make a lid controlled fit more likely to occur?
larger or flatter
if you want to achieve MORE lid control, you should make the lens _______ or _____
more
the less the lens contours the cornea, the _____ it will ride with the lid
lid control
which fitting type is more comfortable?
lens movement is minimal & contact w/ lower lid is minimal
why is a lid control fit usually more comfortable?
move very little or not at all after the blink
describe how a lid controlled lens moves with a blink
moves up with the blink then drops to a centered location
describe how an interpalpebral fit lens moves with a blink
allow tear pumping under the lens & control lens position
what do peripheral curves do?
high
lenses with too much edge clearance ride _____
steepen
to make a lens have less lid control, _____ the edges
flatten
to make a lens have more lid control, _____ the edges
greater
the wider the PCW, the ______ the clearance
greater
the longer the PCR, the _____ the clearance
axial edge lift
z value, distance from the extension of the peripheral curve up to the edge of the lens
radial edge lift
distance from the extension of the base curve to the edge of the lens along the radius
flat

steep

on K
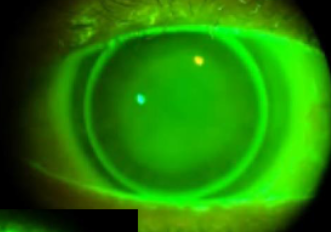
flat
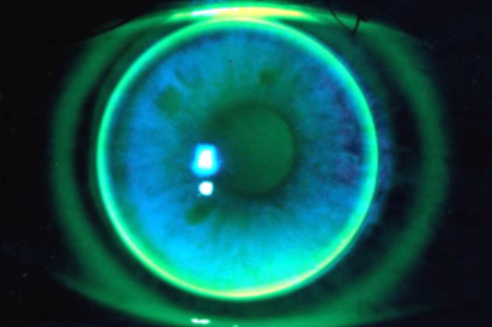
steep
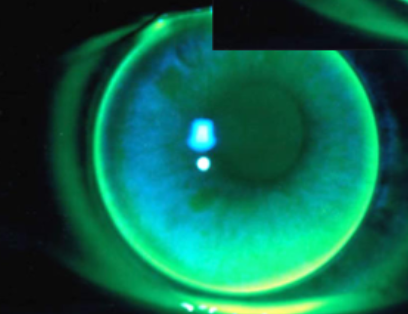
steep
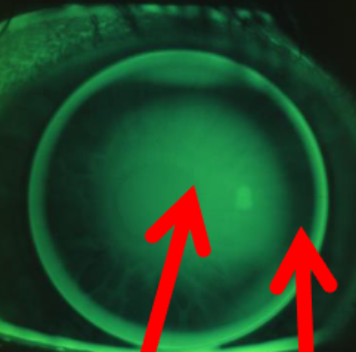
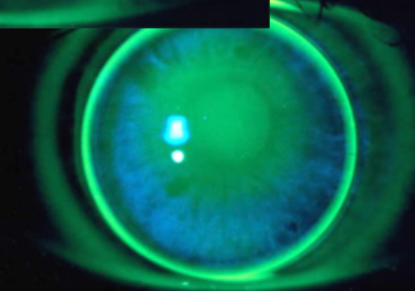
steep (bull’s eye pattern)

~0.50D steep
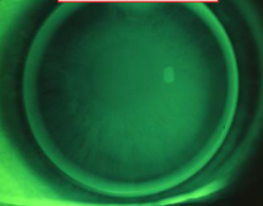
~1.00D steep
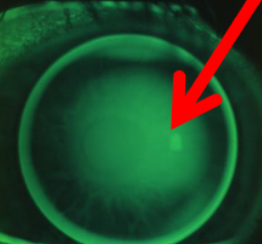
~2.50D steep
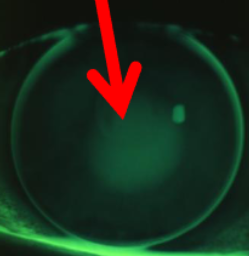
steep
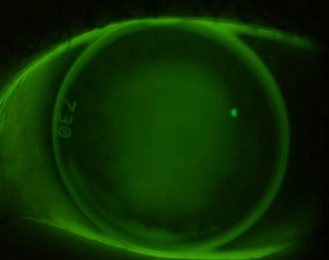
steep
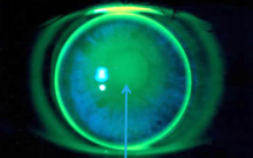
flat
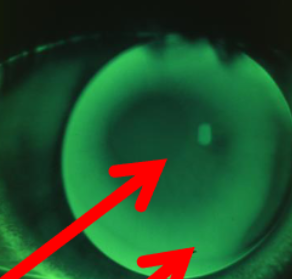
flat
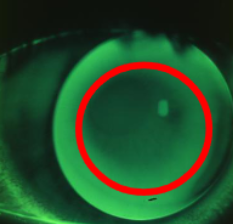
~0.50D flat
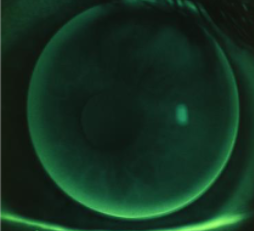
~1.00D flat
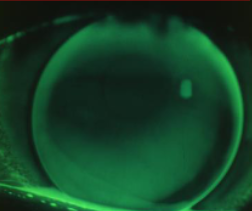
~1.50D flat
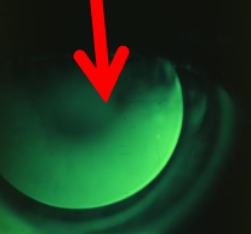
flat
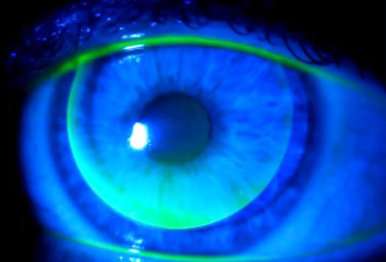
flat
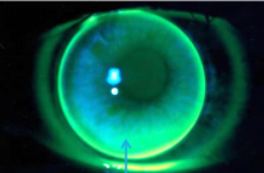
on K
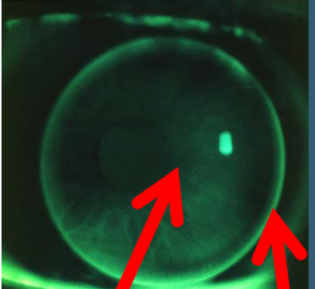
on K
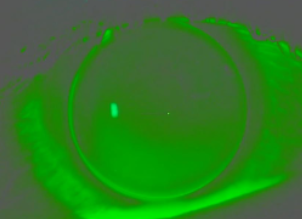
on K
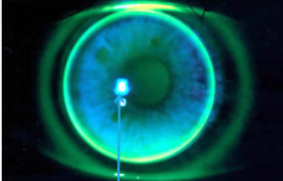
on K
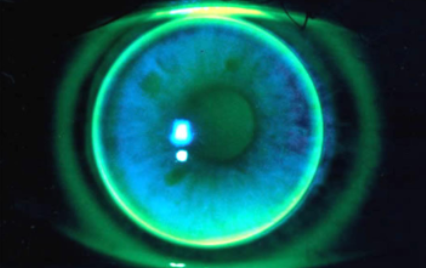
flat
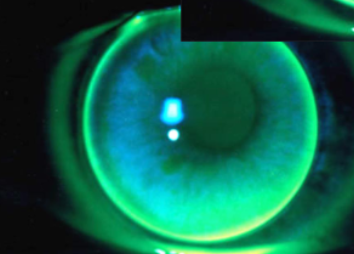
steep
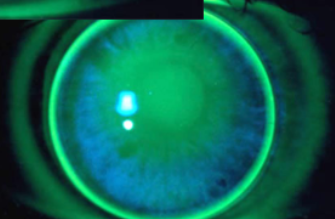
flat
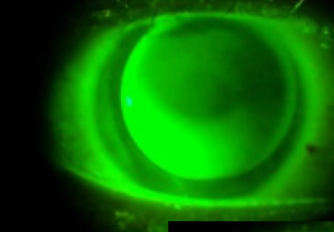
~0.75D steep