Bioenergetics: Energy Transformations and Thermodynamics
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Energy
Capacity to do work or produce change.
Joule (J)
SI unit of energy; equivalent to Nm or Ws.
Calorie (cal)
Energy to heat 1g water by 1°C.
1 cal
Equals 4.184 Joules.
Potential Energy
Stored energy in a specific form.
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion; harnessed potential energy.
Biologic Work
Energy used for cellular processes.
Mechanical Work
Energy for muscle contraction and cell division.
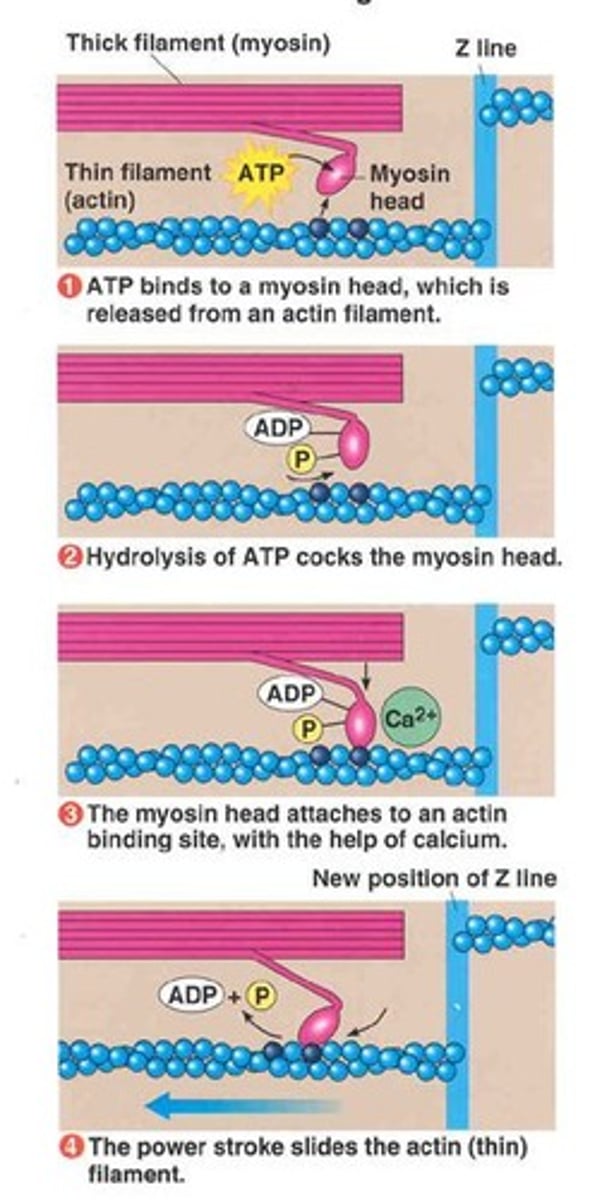
Chemical Work
Energy for synthesizing molecules.
Transport Work
Energy for moving substances across membranes.
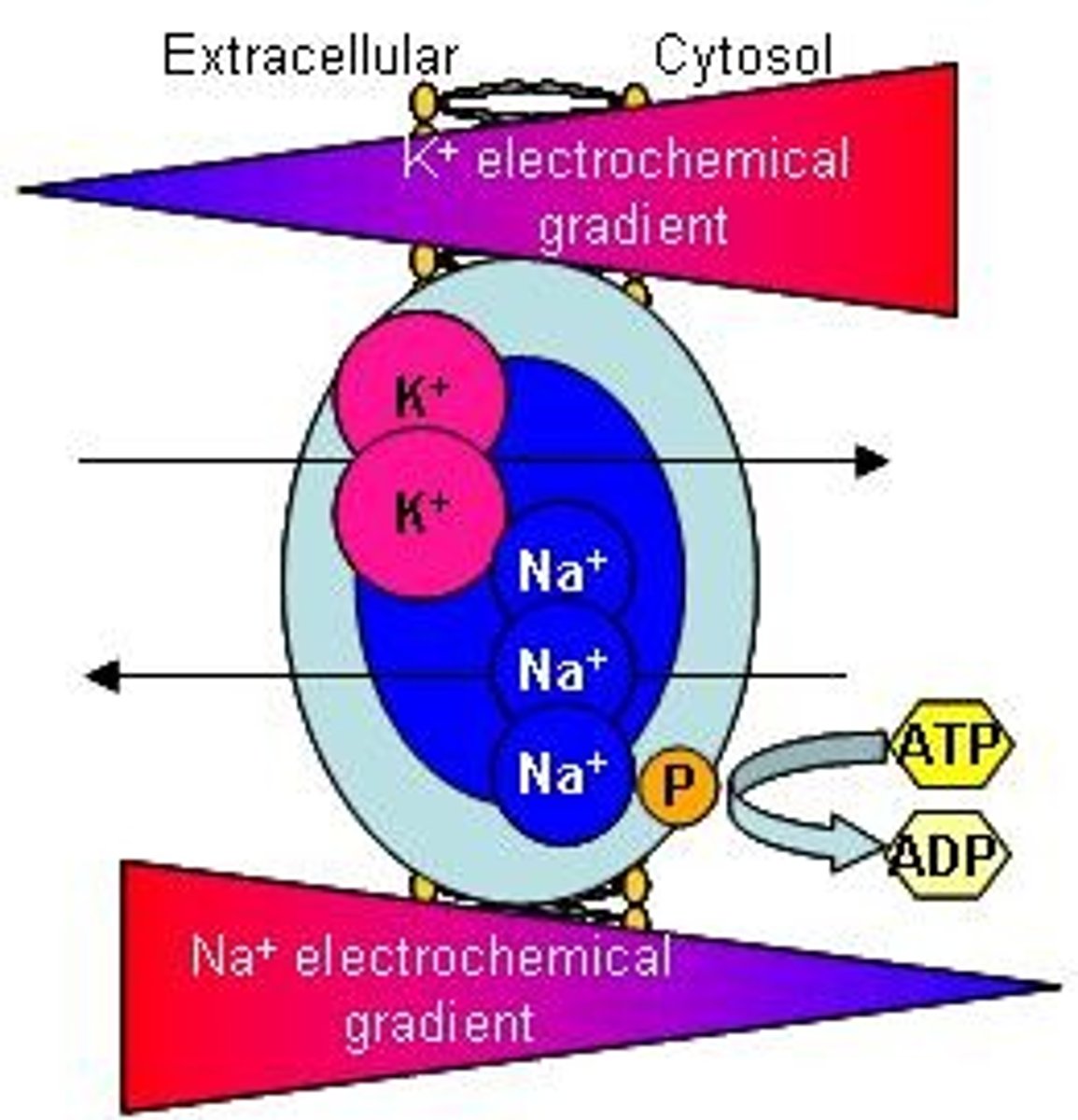
Electrical Work
Energy for transporting charged particles.
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
Conservation of Energy
Energy transforms without being depleted.
Entropy
Measure of disorder in a system.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Energy transformations increase universe's entropy.
Gibbs Free Energy (G)
Energy available to do work in a system.
Spontaneous Process
Occurs with a decrease in Gibbs Free Energy.
Equilibrium Constant (Keq)
Ratio of products to reactants at equilibrium.
Coupled Reactions
Linking reactions to drive non-spontaneous processes.
Dynamic Steady State
Balance between production and consumption in systems.
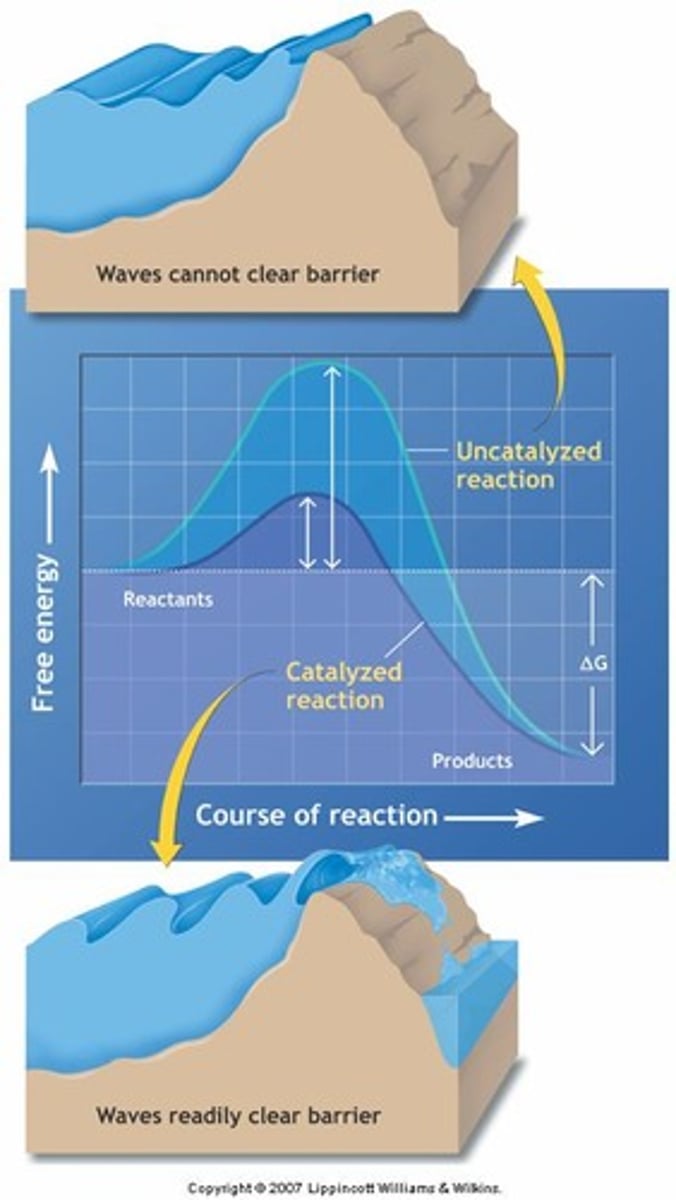
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up reactions.

Activation Energy
Energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
Lock and Key Mechanism
Enzyme specificity based on substrate shape.
Exergonic Reaction
Releases free energy; spontaneous process.
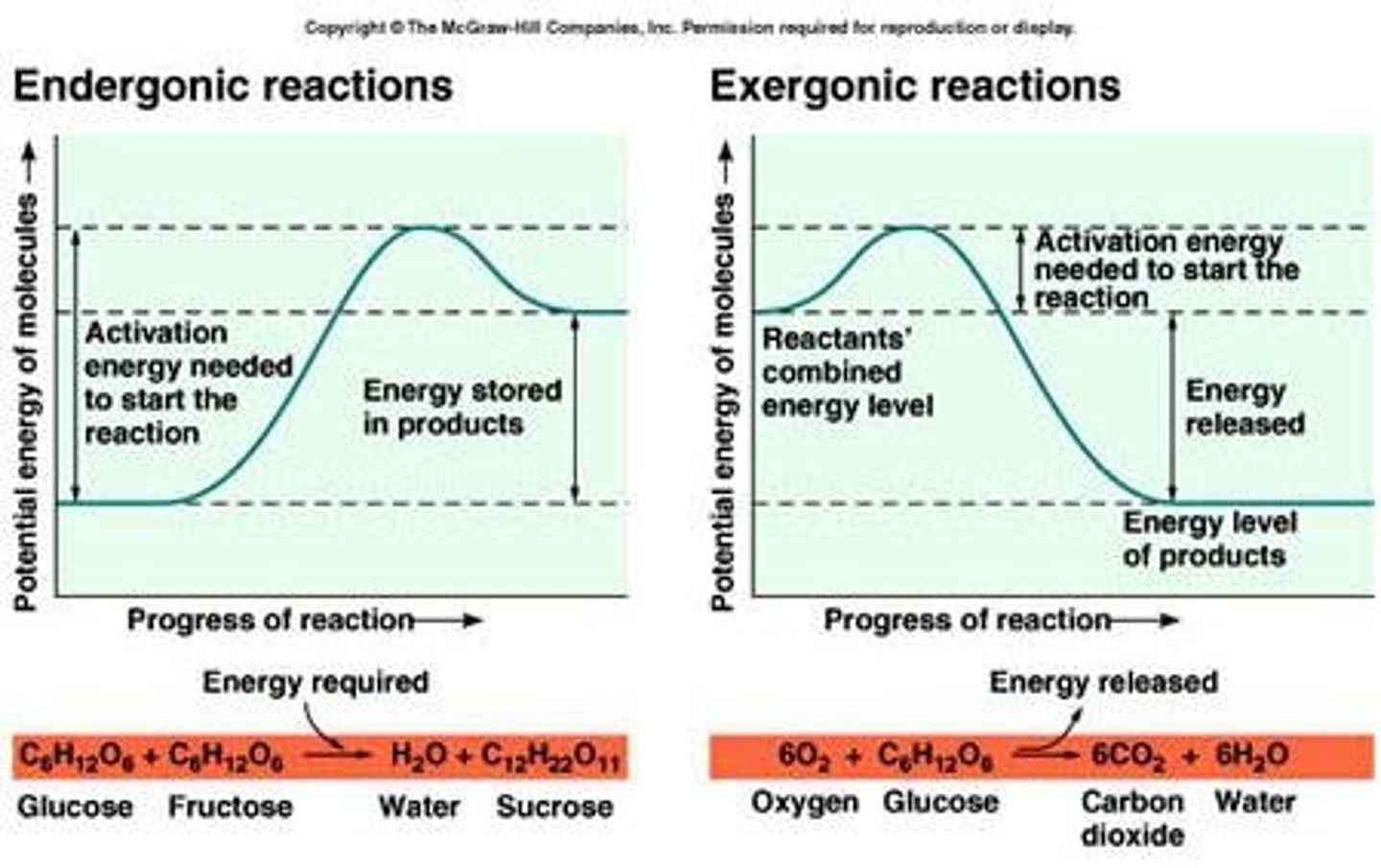
Endergonic Reaction
Requires energy input; non-spontaneous process.
Heat Loss
Energy dissipated as heat during transformations.
Biochemical Catalysis
Enzymes lower activation energy for reactions.
Non-equilibrium Thermodynamics
Living systems never reach equilibrium.
Thermodynamic Equilibrium
State where reactants and products are balanced.
High Enthalpy Food
Energy-rich food with low entropy.
Low Enthalpy Waste
Energy-poor waste with high entropy.