B11 Gas exchange
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is the breathing system?
The organ system that allows the body to obtain oxygen for aerobic respiration and to remove carbon dioxide as a waste product
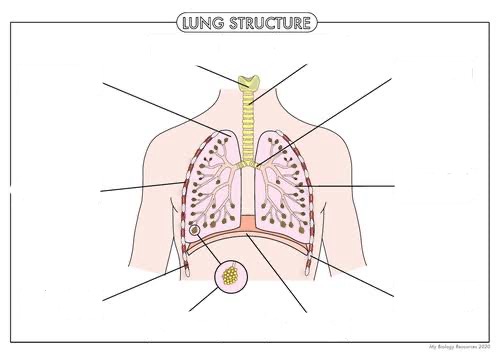
Label this diagram
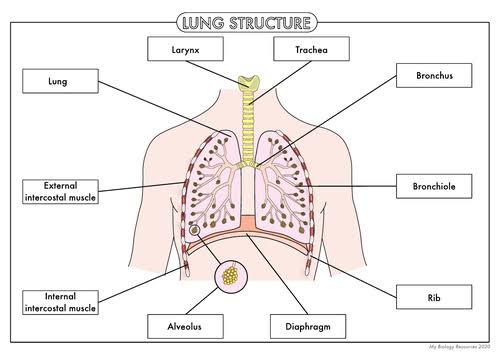
When you breathe what is the pathway the air takes?
nose/mouth → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
Lungs explanation
the main organs in the respiratory system, containing the surfaces where gas exchange takes place
Ribs and intercostal muscles explanation
Intercostal muscles are found between the ribs.
Internal and external intercostal muscles work antagonistically in pairs to expand and contract the rib cage during breathing.
The ribs also protect the lungs and heart from physical damage.
Larynx explanation
contains the vocal cords.
Trachea explanation
connects the throat to the bronchi. C-shaped cartilage rings are present to provide structural strength, keeping the trachea open so that air can pass through it.
Bronchi explanation
hollow tubes composed of cartilage rings that carry air from the trachea to the lungs. The bronchi splits into two tubes to enter the left and right lung, before branching further inside the lungs.
Bronchiles explanation
Smaller tubes which branch off from the bronchi in the lungs, leading to the alveoli.
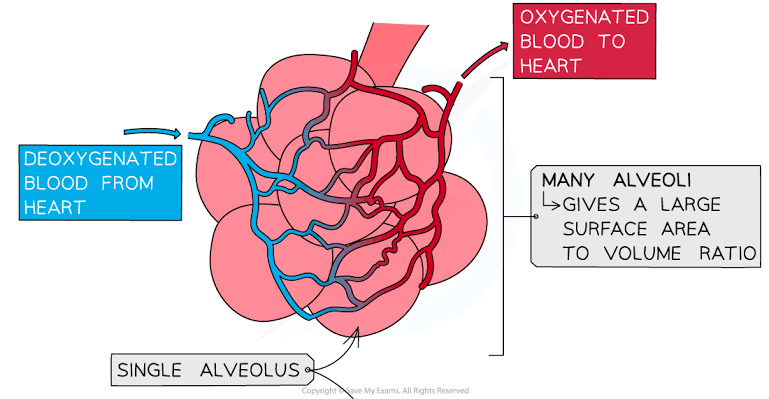
Alveoli explanation
Where gas exchange occurs
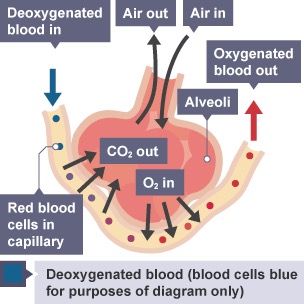
How does gas exchange happen?
Happens at the surface of the alveoli. Oxygen diffuses across the wall of the alveoli from the air into the blood in the capillaries.
Carbon dioxide diffuses across the wall of the alveoli from the blood capillaries into the air
How are alveoli adapted for gas exchange?
large surface area- more efficient diffusion as more gas can diffuse at once
thin surface- short diffusion distance
good blood supply- maintains concentration gradient
good ventilation with air- that waste gases can diffuse out of the blood into the air in the lungs whilst oxygen diffuses into the blood.
What is breathing/ventilation?
the act of moving air into and out of the lungs to allow gas exchange to occur
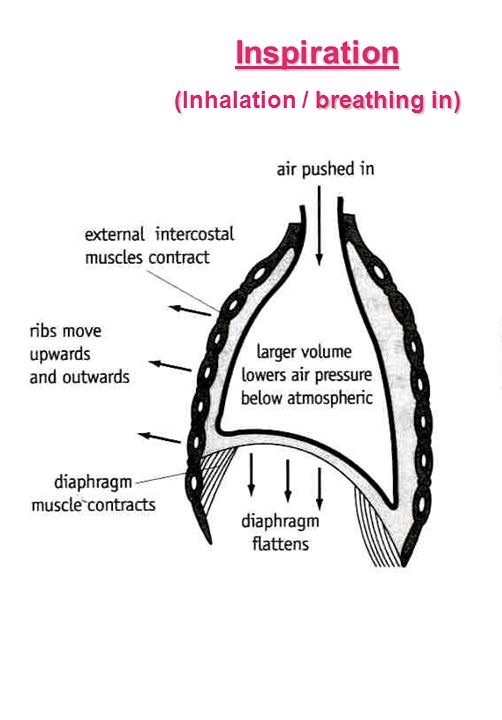
How does breathing in/inhaling happen?
internal intercostal muscles relax
external intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribs up and out
the diaphragm flattens/contracts down which causes the volume in the thorax to increase
as the volume of the thorax increases, the pressure inside it decreases
air enters the lungs from the atmosphere to equalise
-there is a lower concentration of air inside the lungs compared to outside, thus air diffuses in
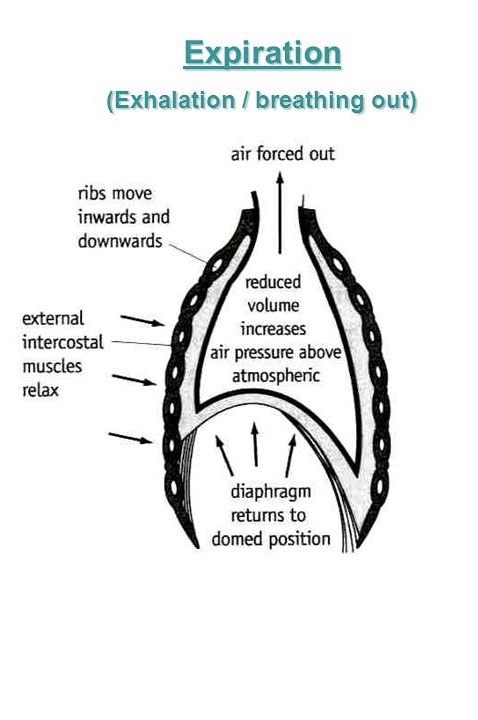
How does breathing in/inhaling happen?
external intercostal muscles relax
internal intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribs down and in
the diaphragm relaxes upwards which causes the volume in the thorax to decrease
as the volume of the thorax decrease, the pressure inside it increases
air leaves the lungs as it is forced out by the increasing pressure to equalise
What is inspired air?
the air you breathe in from the atmosphere
What is expired air?
the fire you breathe out after it has been processed by the lungs
Fill in this table
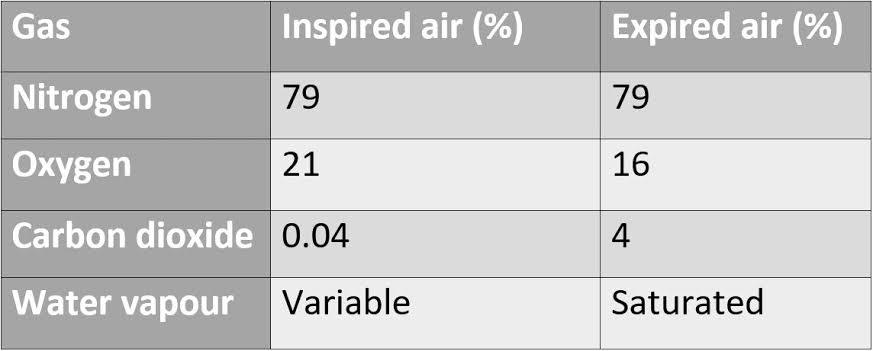
Explain the differences in inspired and expired air for oxygen
Inspired air contains more oxygen because it comes directly from the atmosphere
Expired air contains less oxygen because
Explain the differences in inspired and expired air for carbon dioxide
Inspired air contains little co2 as atmosphere co2 levels are naturally low
Expired air contains more co2 because it is as a waste product of respiration that you body breathes out
Explain the differences in inspired and expired air for nitrogen
Both inspired and expired air have the same amount of nitrogen because it is not used or produced during respiration
Explain the differences in inspired and expired air for water vapour
Inspired air has variable water vapour levels depending on the surrounding humidity
Expired air is always saturated with water vapour because water evaporates from the moist linings of lungs
Explain the differences in inspired and expired air for temperature
Inspired air has variable temperature because it depends on surroundings
Expired air is warmer because air is heated to body temp as it passes through respiratory system
What is the effects of physical activity on the rate and depth of breathing?
Exercise causes an increase in heart rate and greater depth of breathing
Explain the effects of physical activity on the rate and depth of breathing
This is because muscles contract more frequently which requires more energy. Energy is released during respiration so more oxygen and glucose is needed. In response, the heart beats faster to deliver oxygenated blood to the muscles and remove carbon dioxide more efficently.