Chapter 1 - Plate Tectonic
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Pangaea - definition
Large landmass of connected continents over 250 million years ago
Continental drift - meaning
Continents breaking apart and moving
Plate - definition
Large slab of earth’s crust
Plate boundary - definition
Where plates meet
Crust - definition
Thin outer layer of earth, made of solid rock
Mantle - definition
Magma found under the crust that moves in convection currents
Magma - definition
Hot molten and semi-molten rock
Outer core - definition
Molten and composed of nickel and iron
Inner core
Solid centre of earth with temperatures up to 6000 C
Continental crust - definition
Plates with land on top
Oceanic crust - definition
Crust with ocean on top
Convection currents - definition
Circular motion of magma within the mantle

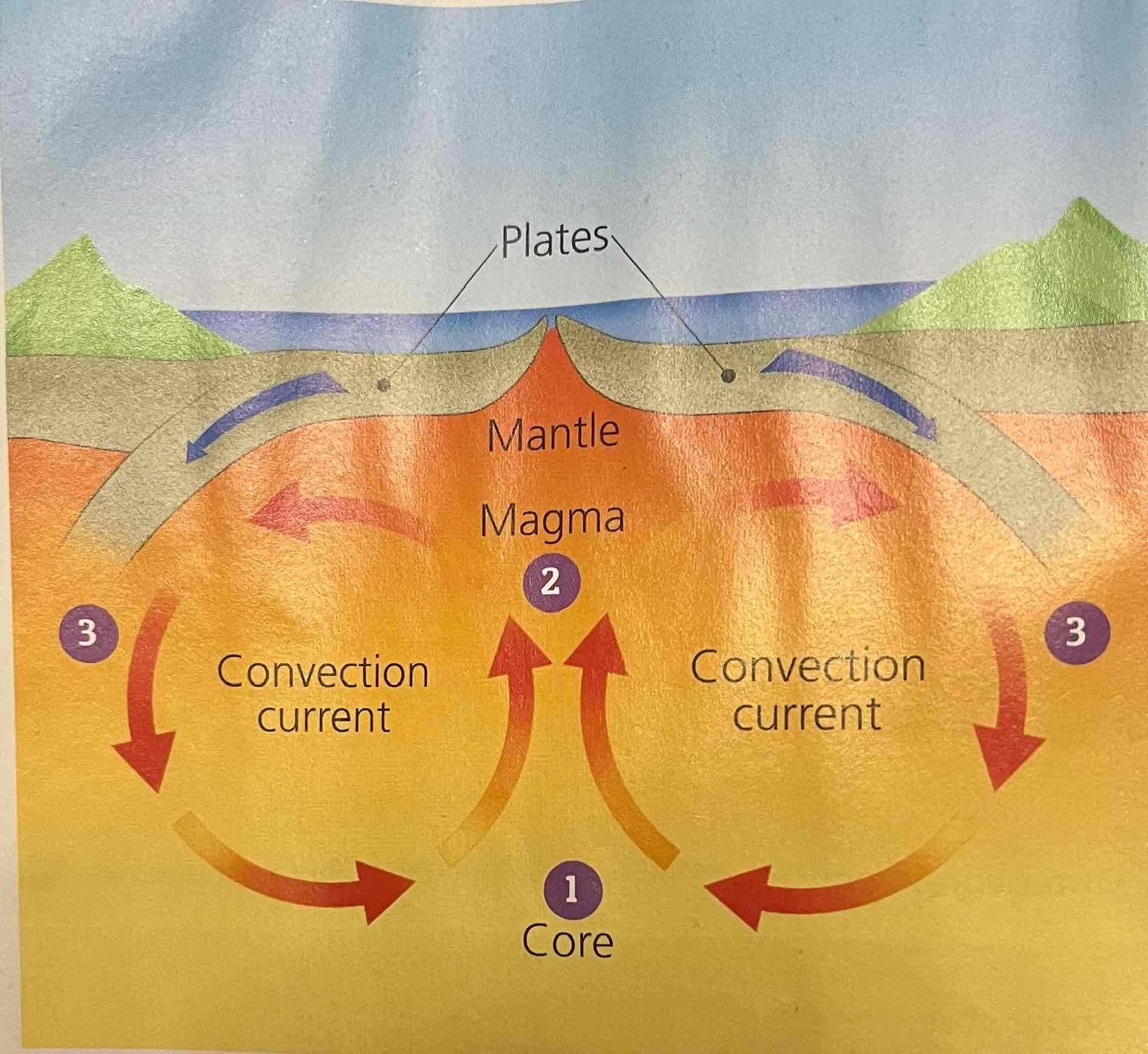
How do convection currents work
Core heats magma above. Rises slowly towards crust
Magma rises, starts cooling
Cooled magma heavier sinks back towards core
Cycle repeats and causes convection currents
Causes slow colliding, separation and sliding movement of plates
Sliding boundaries - example
Transform boundary: Pacific and North American
Separating plates - example
Divergent - Eurasian and North American
Colliding Boundaries- example
Convergent boundaries - Eurasian and African
What happens when plates separate
Magma wells up to fill space between. Magma cools and forms new crust. Volcanic islands and mountains, mid ocean ridges formed
What happens when plates collide
Crust destroyed. Oceanic plate collides with continental, heavier oceanic forces under lighter continental into hot mantle. Part of oceanic melt and part of continental buckles. Forms fold and volcanic mountains
What happens when to plates slide
Edges sometimes lock together. Pressure builds up, an edge may snap/jolt suddenly. Great waves of energy released, causing trembling of earth as earthquake