BIO 330 Unit 1 Elmhurst University
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Monophyletic group
a group of organisms that includes a common ancestor and all of its descendants
synapomorphies
a characteristic present in an ancestral species and shared exclusively (in more or less modified form) by its evolutionary descendants.
paraphyletic group
a collection of organisms that includes a single common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants
Polyphyletic group
a collection of organisms that do not share a single common ancestor but instead have multiple, independent evolutionary origins
contains various organisms with no recent common ancestor.
homologous traits
inherited from a common ancestor
Vertebral column
analogous traits
not inherited from common ancestor
Result of convergent evolution
Wings
A phylogenetic tree is a…
hypothesis of evolutionary relationships
Deuterostomes
echinoderms, hemichordates, and chordates belong to this group
Monophyletic group
Share a type of larval form
How an organism develops is an indicator of…
evolutionary relationships
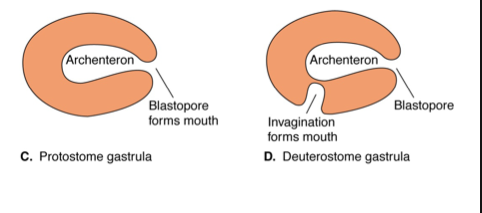
blastopore
forms early in development
Becomes the anus in deuterostomes
Becomes the mouth in in protostome
Echinodermata
Includes: Sea lilies, brittle and basket stars, sea cucumbers, sea urchins, and star fishes, along with many extinct taxa
Marine
Monophyletic
2 synamorphies
Water vascular system and tube feet
Hemichordata
two clades
Pterobranchs
Enteropneusts
Marine
1 snyapmorphy
Tripartite body
Proboscis, collar, and turnk
Pharyngotremata
hemi chordata + chordata
Pharyngotremateshave
1) A pharyngeal
skeleton
2) Ciliated pharyngeal
slits
Chordata
Monophyletic group Bios
5 synapomorphies
Pharyngeal pouches
Grow laterally from the pharynx and often open to the surface as pores or gill slits
Endostyle
Turns in to Thyroid gland
Notochord
A stiff, longitudinal rod of turgid cells along the dorsal part of the body
Dorsal nerve cord
A single, tubular nerve cord that is located dorsal to the notochord
Postanal tail
Somitochordata
cephalochordata + craniata
Synapomorphies
Somites
Retention of larval features as adults
Specifically notochord, neural tube, and tail
Cephalochordata
lancelets or amphioxus
Animals are pointed at each end
Have shorts, postanal tails, and distinct anterior ends, but no well developed head
Somites - segmented muscles in development
Craniata
Includes all animals having a skull (or cranium, hence their name), be it cartilaginous or bony
Craniata
The evolution of many characteristics of craniates is correlated with their relatively high level of activity and large sizes.
• Craniates are cephalized, and have a head, trunk and tail.
• Head houses the mouth and gill slits
• Head also contains well developed, paired sense organs- nose, lateral eyes and ears
Neurogenic placodes
Nose and ears develop embryologically from neurogenic placodes
• Neurogenic placodes are unique to craniates and invaginate to form sensory receptor cells and sensory neurons
The end of the dorsal nerve cord in cranaites becomes…
The rest of the dorsal chorse becomes the…
The Brain
Spinal cord
Craniata synapomorphies
Earliest somitichordates may have been derived from such an ancestor by Paedomorphic retention of three larval features
What are these 3 larval features?
Notochord
Neural tube
Elongate postanal tail
Fertilization
Union of haploid sperm and haploid egg to form a zygote
Different methods of cleavage
Diff methods (flash card broke)
Tissues
Group of cells working together to perform a particular function
Tissues unite to form…
Organs, organs are bunch of tissues working together
Ectoderm, mesodermal, endoderm
EME (flash card broke)
Modes of neural crest formation
Modes of neural (flash card broke)
Anterior neural tube
3 primary vesicles
prosencephalon
Mesencephalon
Rhombencephalon
Endoskeleton
deeper part of skeleton
Forms from Endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification
cartilage → Endochondral bone
(Post cranial skeleton)
intramembranous ossification
connective tissue → bone
(Skull bones, clavicle)
dermal skeleton
the pattern and from of bones derived from intramembranous ossification Endochondral ossification
Develop as membrane bones or just beneath the skin
Chondocranium
Cranial skeleton that includes endoskeletal elements that encase and protect much of the brain, nose and inner ear
Function is protection
Most of it arises from neural crest cells
dermatocranium
dermal elements that surround other parts
solid, hard
Superficial dermal bones nearly completely cover the chondrocranium, splanchnocranium, jaw muscles, and eyeball
Splanchonocranium
endoskeletal visceral arches
Support’s marine life pharynx and gills
Structure supports respiration and feeding
Consists of a series of arches of cartilage or Endochondral bone
For humans, we lose them, gradually reduce over time
Arches in Splanchnocranium
mandibular arch
Part of jaw
Dorsal palatoquadrate cartilage
Lower mandibular cartilage
Hyoid arch
Helps to suspend the jaw
Support throat
Hyomandibula
Bronchial or gill arches
Nearly all jawed fishes have 5 brachial arches
Parts of dermatocranium
dermal roof - covers top and sides of head
Palatal series - develops in roof of the mouth
Lower jaw series
Opercular series
Gulag series
Epithelial tissue
covers body surfaces and lines hollow organs, body cavities, duct, and forms glands
connective tissues
protects, supports and binds organs
Stores energy as fat and provides immunity msu
muscular tissue
generates the physical force needed to make body structures move and generate body heat
nervous tissue
detect changes in body and responds by generating nerve impulses
Adductor mandibulae
mouth closing muscle for vertebrates
Cranium synapomorphies
Lose post temporal gene star
Zygomatic arch
3 middle ear ossicles
Dentary/squamosal jaw joint
Dentary is single element of lower jaw
Trends for cranial
Cranial complex expands relative to body size and facial complex
The appendicular skeleton consists of
paired pectoral appendages
Pectoral girdle
Paired pelvic appendages
Pelvic girdle
Benthic fish
move/live a long the surface of the ocean
Hypothesis of origin of appendicular skeleton
Fin Fold Hypothesis
early vertebrates had a continuous fin fold on the lateral side of the body
Paired fins evolved by loss of an intermediate parts of the fin fold
Chondrichthyans
has narrow fin base
Pectoral fine has 3 basal pterygiophores
Pelvic fin has 2…(claspers??)
Actinopterygians
ray finned fishes
Narrow based, fan shaped paired fins
Triassic fin composed of 3 basal pterygiophores to which many radials attach
Distinct scapula and coracoid form
Sarcopterygians
pectoral girdle resembles that of actinopterygians except for presence of inter clavicle
Pelvic girdle contains pubic, ischiadic, and iliac portions
More robust and larger
Could be used for weight bearing activities
Tiktaalik
a fish capable of coming on to land temporarily
Five digit Kim cheiropterygium, has what 3 distinct regions
proximal stylopodium
Middle zeugopodium
Distal autopodium
Proximal stylopodium
brachium (humerus)
Thigh (femur)
Middle zeugopodium
antebrachium (radius and ulna)
Crus (tibia and fibula)
D
distal autopodium
manus (carpals and metacarpals)
Pes (tarsals and metatarsals)
Phalanges