Lesson 01 - MSM
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
who proposed the multi-store model
Atkinson and Shiffrin
when was the multi-store model proposed
1968
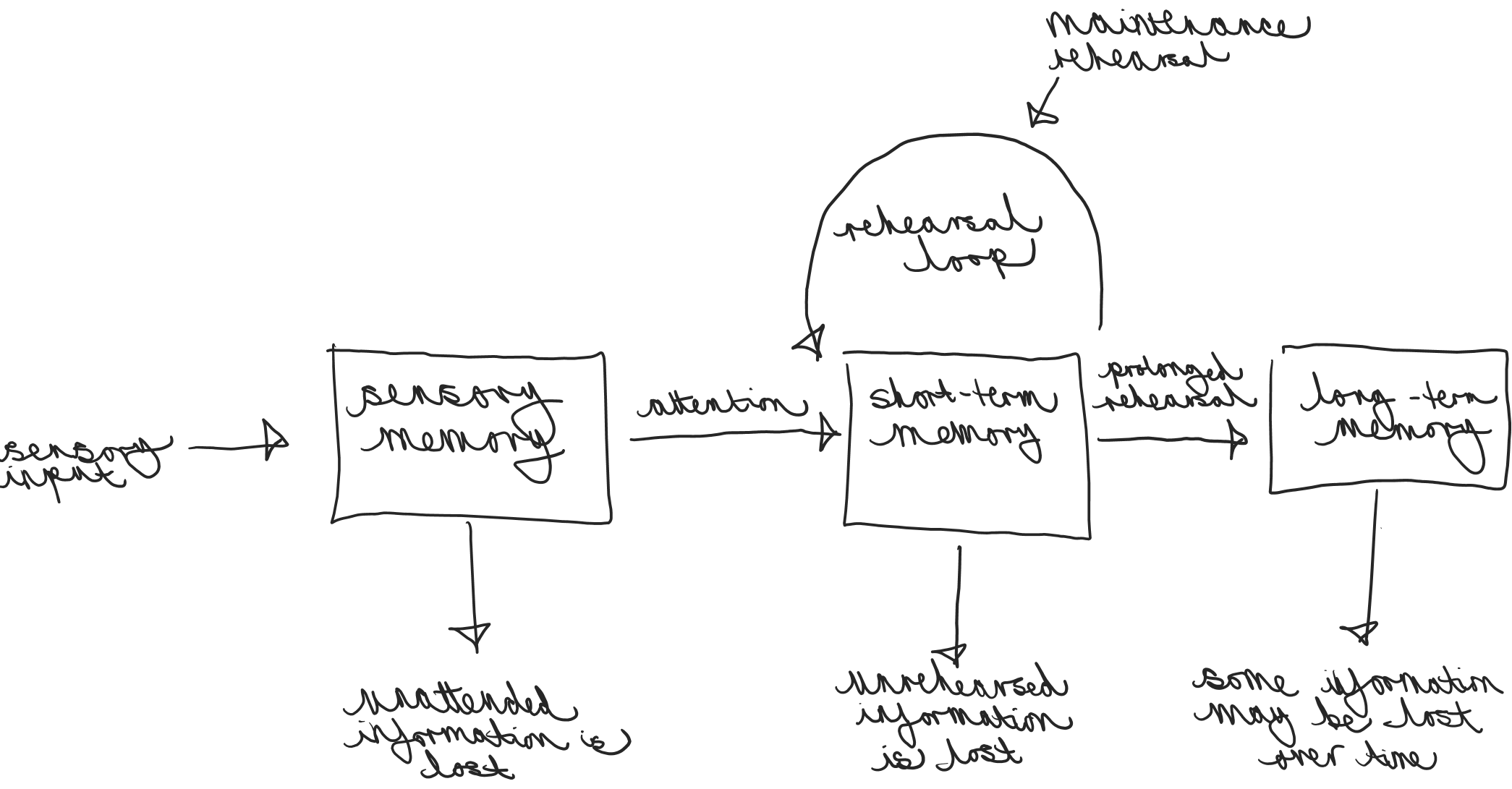
describe the MSM structure
memory is structured in 3 stores:
sensory register
short term memory
long term memory
describe how information travels through the MSM
enters the sensory register
moves to the STM if attended to
transferred to the LTM through rehearsal.
describe the serial position experiment
a list of words are read to a group at constant intervals. the group has a set period of time to record the words they can recall. record how many people recalled which words and plot a line graph portraying this
describe the general trend of results of the serial position experiment
a U-shaped curve showing better recall for the first (primacy effect) and last (recency effect) items compared to those in the middle
explain the results of the serial position experiment
the primacy effect occurs because early items are rehearsed and transferred to long-term memory
the recency effect is due to items at the end remaining in short-term memory for recall
define coding
the initial stage of forming memories, where the brain converts information from the senses (like sights, sounds, and feelings) into a form that can be stored and organised in the brain for later storage and retrieval
define storage
holding information in the memory system
define retrieval
the mental process of accessing information stored in long-term memory and bringing it into conscious awareness
define capacity
the maximum amount of information that can be stored or held at a given time
describe the procedure of Jacob’s 1887 study on the STM capacity
get participant to read back a list of 3 digits. if they do this without making a mistake, continue onto a list of numbers 1 digit longer. repeat until they make a mistake
count how many digits they could recall correctly – this indicates the individual’s digit span
findings of Jacob’s 1887 study on the STM capacity
mean digit length - 9.1
mean letter length - 7.3