Science y10 yearly
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Sequences
Order of nucleotides in a gene.
Heredity
Passing traits from parent to offspring.
Dominant allele
One copy shows the trait.
Recessive allele
Needs two copies to show the trait.
Mutation
Changes in DNA.
Recombination
Gene shuffling during meiosis.
Allele
Variant form of a gene.
Genotype
The gene combination in an organism.
Phenotype
Observable traits.
Homozygous
Same alleles (AA or aa).
Heterozygous
Different alleles (Aa).
Chromosome
DNA structure with many genes.
Genome
Complete genetic material.
Mendelian genetics
Study of single-gene trait inheritance.
Describe the strcuture of Dna
A double helix twisted ladder with 2 strands of nucleotides.
Nucleotides
building block of DNA.
Cloning
Process of creating a genetically identical copy of an organism.
Therapeutic cloning
cells are cloned for medical purpose.
Reproductive cloning
entire organism is produced with the same genotype.
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF)
A medical procedure where an egg is fertilized by sperm outside the body in a lab.
Evolution
organisms changing over time.
Survival of the fittest
Process of inheritable traits that assist in survival becoming more common.
Haploid
a set of chromosomes
Diploid
2 sets of chromosomes in non-sex cells.
Natural selection
The process of favorable characteristics becoming more common through reproduction.
Comparative anatomy
comparing skelton of different organisms to find similarities.
Comparative embryology
compares embryo development to find common ancestors.
Comparative cytology
Our organelles are structural and functionally very similar suggesting that everything is related.
Comparative biochemistry
We all have different similar enzymes and proteins, so our DNA is similar.
Fossils
Shows different forms of species at different times. Through these fossils we compare their features. Carbon dating is used to estimate the age of organisms.
Energy transfer
carry energy
Superposition
overlap or combing leading to stuff like diffraction.
Reflection
bounce of surfaces
Refraction
Waves bend as they pass from one substance to another, measured in PAscals
Diffraction
Bending around obstacles.
Frequency
measured in Hertz, speed of the wave, controls pitch.
Wavelength
Distance between each compression, measured in meters
Amplitude
max displacement of particles caused by a wave; basically its strength. Controls sound. Measured in metres. Height of trough/crest
Pressure
measured in Pascals
Density
kilos per cubic meter
Longitudinal waves
displacement is parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
Mechanical wave
A wave that requires a medium to propagate.
Compression
High pressure regions, the higher area. Crest
Rarefraction
Low pressure region, the bottom area. Trough
Superposition
combine of waves. Calculate its amplitude by summing up the amplitude of the waves combined.
Acceleration formula
V = u + at | A = acceleration t = time u = initial speed v= final speed
Law of motion one
Objects in motion stay in motion and objects at rest stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. More mass means harder to change motion. There is always an unbalanced force acting upon an object.
Law of motion 2
Force (N) = mass(Kg) * acceleration. Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration of an object.
Law of motion 3
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Waves in the EM spectrum
radio waves, microwaves, infrared, light, Ultraviolet, X-rays, Gamma rays
Radio waves
Electromagnetic waves with longest wavelengths (1mm to 100km) and lowest frequencies (3Hz to 300MHz)
Radio wave properties
Low energy(weakest wave), non-ionizing, travel through wall and long distances.
Microwaves
Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths from 1mm to 1m + frequencies of 300MHz to 300GHz.
Microwave properties
2nd weakest wave, focused into beams, absorbed by water molecules to heat.
Infrared waves
Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths from 700nm to 1mm + frequencies from 300 GHz to 430 THz.
infrared properties
transfers heat, invisible to us, emitted by anything has heat.
Visible light
Only part of EM that is visible to our eyes, with wavelengths from 400 nm (violet) to 700 nm (red), frequencies range from 430THz to 750THz.
visible light properties
colours of light WE can see, carries some energy, uses reflection, refraction and absorption to interact with other particles.
UV radiation
Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths from 10 nm to 400 nm + frequencies from 750THz to 30PHz.
UV properties
3rd strongest, can cause chem reactions such as sunburns, partially ionizing.
X-rays
Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths from 0.01 nm to 10nm + frequencies from 30PHz to 30 EHz.
X-rays properties
2nd strongest, ionizing, can penetrate soft tissues but absorbed by denser materials like bones.
Gamma rays
Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths less than 0.01 nm + frequencies above 30EHz.
Gamma properties
most powerful, highly ionizing, can penetrate most materials, produced by radioactive decay or nuclear reactions.
uses for radio waves
broadcasting and wireless comms
uses for Microwaves
ovens, satelliite comms
uses for Infrared rad
thermal imaging, older remotes
uses for visible light
digital screens, light bulbs
uses of UV rad
sterilise surfaces, skin tanning,
uses of X-rays
medical imaging, security
uses of Gamma rays
cancer treatment, cleaning medical equipment
Atom
smallest unit of matter
Element
consist of one type of atom
Compound
bonded elements
Molecules
atoms of same type grouped together; not bonded
Properties of acids
hydrogen ions, sour taste, pH less than 7, turn litmus red, donates protons,
Properties of alkali
hydroxide ions, bitter taste, pH greater than 7, turn litmus blue, accepts protons.
Acid+ base gen equation (neutralisation)
Acid + base —> salt + water
Acid + metal gen equation
Acid + metal —> hydrogen + salt
Acid + carbonate gen equation
acid + carbonate —> salt + carbon dioxide + water
combustion gen equation
fuel + oxygen —> carbon dioxide + water + energy
Decomposition gen equation
AB —> A + B
Precipitation gen equation
AB + CD —> AC + BD
corrosion define
A chemical reaction where metal react with oxygen and start rusting
precipitation define
creation of insoluble solid through 2 liquids
Combustion define
Substances burns with oxygen to create energy, water and CO2
Collision theory
States atoms collide and create energy to react. Collision must be in correct order
how increasing temp speed up reaction
increasing temperature speeds up particles, so more collisions
how increasing concentration speed up reaction
more particles to collide with so more collisions
how increasing surface area speed up reaction
more particles exposed for collision
how catalyst speed up reaction
activation energy reduced so less collisions needed.
Endothermic
absorbs heat, temp decrease
Exothermic
releases heat, temp increase
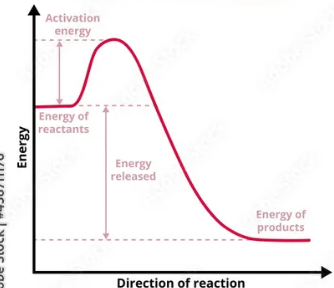
Exo or endo
Exothermic
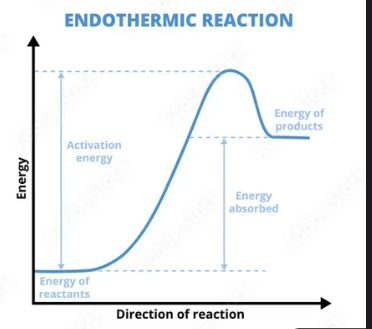
Exo or endo
Endothermic
NH₄⁺
Ammonium
OH⁻
Hydroxide
NO₃⁻
Nitrate
CO₃²⁻
Carbonate
SO₃²⁻
Sulfite