FINAL Questions: Exam 2
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Pressure that develops within a living cell as a result of water entering the cell is called _______
A. turgor
B. osmosis
C. plasmolysis
D. transpiration
E. water potential
A. turgor
Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion in which water molecules _______
A. move across a selectively permeable membrane
B. move from a region of low H2O concentration to a region of higher H2O concentration
C. exhibit random kinetic motion
D. move through suberin
E. both A & B are correct
A. move across a selectively permeable membrane
The energy "currency" of the cell occurs in the form of ______
A. NAD-
B. water
C. FADH2
D. ATP
E. glucose
D. ATP
Which of the following is involved in guard cell regulation of stomata opening?
A. transport of K+
B. photosynthetic rates
C. osmosis
D. turgor pressure
E. all of these
E. all of these
Holding all other environmental variables constant, as relative humidity in the outside air increases, ______
A. transpiration rates increase
B. transpiration rates decrease
C. transpiration only occurs at night
D. leaves close stomata
E.transpiration rates remain uaffected
B. transpiration rates decrease
The oxygen liberated by green plants during photosynthesis comes from _______
A. the breakdown of carbon dioxide
B. the breakdown of food in living cells
C. ATP
D. the glucose formed in the Calvin Cycle
E. the breakdown of water molecules
E. the breakdown of water molecules
What is contained in each photosynthetic unit of photosystem 1?
A. one P700 molecule
B. one P680 molecule
C. approximately 200 or more molecules of chlorophyll a
D. both A & C
E. both B & C
D. both A & C
Approximately how much water typically leaves the plant by transpiration?
A. 75%
B. 25% or less
C. 90% or more
D. 65%
E. 50%
C. 90% or more
Which nutrient is considered to be most "limiting" to plant growth on the global scale?
A. potassium
B. phosphorus
C. carbon
D. nitrogen
D. nitrogen
Glycolysis takes place in the _______
A. mitochondria
B. chloroplast
C. nucleus
D. cytoplasm
E. ER
D. cytoplasm
Which group takes the products of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
A. glucose and oxygen
B. carbon dioxide and water
C. NADPH, ATP, and oxygen
D. ethanol and carbon dioxide
E. glucose
C. NADPH, ATP and oxygen
The Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) takes place in the ______
A. dictyosome
B. chloroplast
C. nucleus
D. cytoplasm
E. mitochondria
E. mitochondria
The longest wavelengths of light useful in photosynthesis are those of
A. ultraviolet
B. red light
C. blue light
D. infrared
E. green llight
B. red light
_________ is defined as an irreversible increase in mass due to the division and enlargement of cells
A. development
B. differentiation
C. determination
D. growth
E. change
D. growth
The citric acid cycle __________
A. may occur in cells where photosynthesis is also taking place
B. takes place as a part of the light independent reactions of photosynthesis
C. involves the breakdown of glucose into a simpler compound
D. is the final step of the respiration process
E. takes place primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum
A. may occur in cells where photosynthesis is also taking place
The aerobic respiration of 1 molecule of glucose produces approximately how many ATP molecules?
A. 46
B. 36
C. 26
D. 2
E. 6
B. 36
The response of plants growing toward light is most closely associated with the hormone group _______
A. gibberellin
B. auxin
C. cytokinin
D. ethylene
E. abscisic acid
B. auxin
In which phase of meiosis does crossing-over occur?
A. Prophase 1
B. Prophase 2
C. Metaphase 1
D. Metaphase 2
E. Anaphase 2
A. Prophase 1
Which of the following pertaining to auxins is true?
A. involved in cell enlargement
B. movement is polar
C. movement requires the expenditure of energy stored in ATP molecules
D. tend to delay leaf and fruit abscission
E. all of these answers are correct
E. all of these answers are correct
Two important actions of cytokinins are the influence on ________
A. cell division and enlargement
B. stomatal opening
C. cell death
D. flowering
E. dormancy
A. cell division and enlargement
Abscisic acid is associated with maintaining _______ in seeds
A. turgor pressure
B. fertility
C. dormancy
D. growth and development
E. steady rates of cell division
C. dormancy
The fruit ripening process releases large quantities of _______
A. auxin
B. cytokinin
C. ethylene
D. abscisic acid
E. gibberellin
C. ethylene
If the haploid number of chromosomes in a diploid plant is 20, the number of chromosomes in root, stem, and leaf cells would be ______
A. 10
B. 20
C. 30
D. 40
E. 60
D. 40
The change from a _________ occurs as a result of meiosis
A. zygote to sporophyte
B. gametophyte to sporophyte
C. sporophyte to gametophyte
D. gametophyte to gamete
E. gamete to zygote
C. sporophyte to gameophyte
Which of the following statements pertaining to sexual reproduction is true?
A. the first cell of a sporophyte generation is normally a gamete
B. the change from a gametophyte generation to a sporophyte generation occurs immediately after meiosis
C. the first cell of a gametophyte generation is normally a spore
D. asexual cells fuse in pairs
E. the offspring are nearly always identical to the parents
C. the first cell of a gametophyte generation is normally a spore
Alternate forms of a gene (eg: red flowers vs. white flowers) are called ________
A. gene factors
B. homologous traits
C. alleles
D. centromeres
E. chromosome traits
C. alleles
Consider the trait seed color (yellow seed dominant vs. green seed recessive). If a paretn heterzygous fr seed color were crossed with a green seeded parent, the F1 generation (offspring) would produce:
A. 100% yellow seeds
B. 50% yellow seeds, 50% green seeds
C. 75% yellow seeds, 25% green seeds
D. 75% green seeds, 25% yellow seeds
E. not enough information given
50% yellow seeds, 50% green seeds
Genetic diversity in the parental populations of cultivated plant species is critically important to plant breeders because ________
A. crop seeds should be variable
B. variability is the source of disease and pest resistance that can be bred into new crop varieties
C. modern agriculture relies on low diversity in crop varieties
D. they are searching for new crop species to develop
E. approximately one new crop species has been domesticated every year since 1900
C. variability is the source of disease and pest resistance that can be bred into new crop varieties
The part of North America that contains the USA is the point of origin for __________
A. tobacco
B. corn
C. squash
D. sunflower
E. rice
D. sunflower
A plant that will no flower if days are too short or too long is a _______ plant
A. short-day
B. long-day
C. intermediate-day
D. day-neutral
C. intermediate-day
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 12H2O + light ->->-> C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
What is the equation for aerobic respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ->->-> 6CO2 +6H2O +36ATP
List the 18 elements essential for plant growth
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Phosphorus
Potassium
Nitrogen
Sulfur
Magnesium
Manganese
Molybdenum
Calcium
Iron
Cobalt
Sodium
Zinc
Boron
Copper
Chlorine
What is the major difference between C4 plants and CAM plants in how they conduct photosynthesis?
CAM plants absorb CO2 at night and utilize it for photosynthesis during the day, while C4 absorb CO2 in the daytime
How many carbons are needed to make one molecule of Glucose in the Calvin cycle?
Where do the carbons come from?
6 Carbons
From Carbon dioxide
What 14 plant species supply the vast majority of the calories consumed by humans worldwide?
Wheat
Rice
Corn
Potato
Sweet potato
Cassava
Bean
Soybean
Sorghum
Barley
Sugarcane
Sugar beet
Banana
Coconut
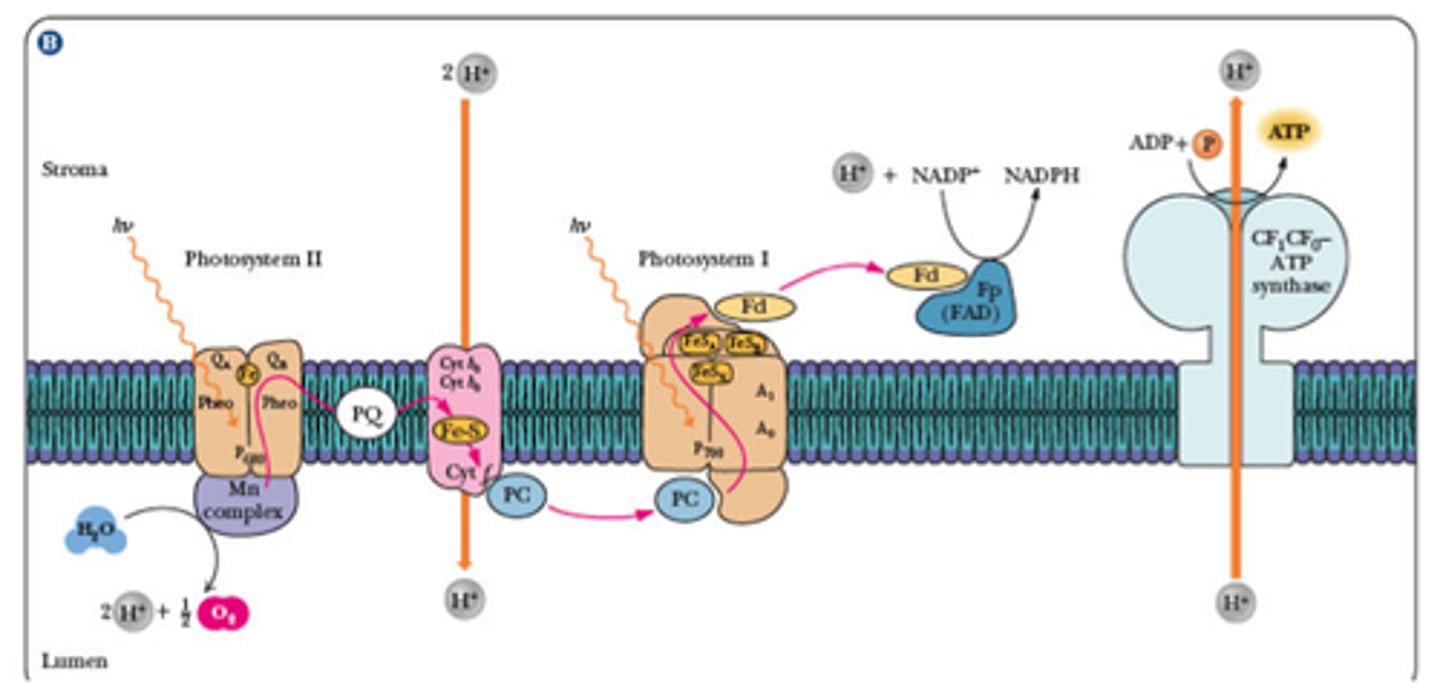
Draw the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis, and label using all of the following terms
Sunlight, O2, H2O, ATP, ADP, Photosystem I, Photosystem II, NADPH, NADP, Chloroplast, Granum, Stroma, Thylakoid Membrane, Thylakoid Lumen, P680, P700, H+, e-, Electron Transport Chain, ATP Synthase