neonatal infant spine and hips
1/268
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
269 Terms
US has equaled MRI in quality for detecting certain ______ anomalies.
Spine
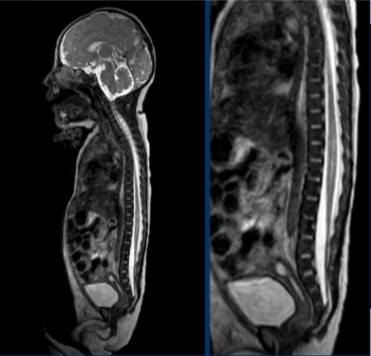
Which imaging modality was used for this scan?
MRI
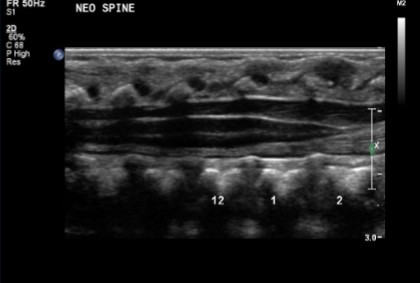
Which imaging modality was used for this scan?
US
The neural tube and spinal cord arise from __________ cells.
Ectodermal
Defects in the spine will typically occur in the first __ weeks of life.
8 ½
What are the 3 fetal spine separations?
Incomplete
Premature
Failure
The incomplete separation of the (1)_________ occurs from the (2)________.
Neural tube
Ectoderm
The incomplete separation of the neural tube could result in what 3 pathologies?
Cord tethering
Dermal sinus
Other spinal defects
The premature separation of the (1)________ from the (2)__________.
Ectoderm
Neural tube
Premature separation of the ectoderm can result in abnormal (1)________ elements, such as (2)_______ forming between the (3)_________ and the (4)_____.
Mesenchymal
Lipomas
Neural tube
Skin
If the neural tube fails to (1)____ and (2)____ in the midline, defects such as (3)___________ occur.
Fold
Fuse
Myelomeningocele
What are the 3 indications for a neonatal spinal US?
Congenital anomalies
Suspicious sacral dimple
Soft tissue mass suspected of being spina bifida occulta
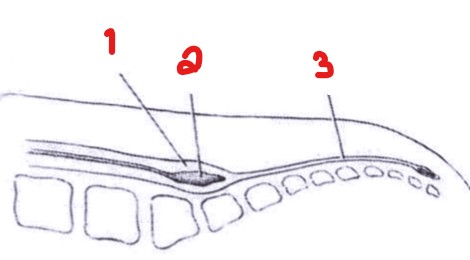
A defect on the lower midline back will be suspected for what pathology?
Sacral dimple
A sacral dimple will lie above the…
Gluteal crease
A sacral dimple has a possibility of being…
Drained
A sacral dimple can go through skin changes, which includes having a (1)___________ or (2)___________.
Hairy patch
Skin tag
Tethered cords have an association with neonates with…
Imperforate anus
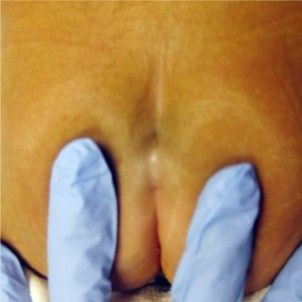
What is the pathology seen here?
Sacral dimple
What are some additional indications that are not as common for a neonatal spine US?
Lipomas
Hydromyelia
Myelomeningocele
Myeloschisis
Lipomas are (1)______ tumors composed of (2)____ cells.
Benign
Fat
Hydromyelia is the (1)_______ of the central canal of the…(2)
Dilation
Spinal cord
Myelomeningocele is seen in patients with (1)___________ with a portion of the (2)__________ and (3)__________ protruding through the defect.
Spina bifida
Spinal cord
Membranes
Myeloschisis is a (1)______ spinal cord resulting from failure of the (2)____________ to close.
Cleft
Neural tube
The vertebral column extends from the (1)_____________ to the (2)____________.
Base of the skull
Tip of the coccyx
The vertebral column extends along the ________ surface of the body.
Posterior
Within the vertebral cavity, there are what 3 things?
Spinal cord
Roots of spinal nerve
Covering meninges
The vertebral column consists of __ vertebrae.
33
The vertebral column consists of…
__ cervical
__ thoracic
__ lumbar
__ sacral
__ coccygeal
7
12
5
5
4
The sacral vertebrae fuses to form the…
Sacrum
The coccygeal vertebrae fuses to form the…
Coccyx
In neonates, problems typically occur in the lower back of the (1)_____________ and (2)______.
Lumbar vertebrae
Sacrum
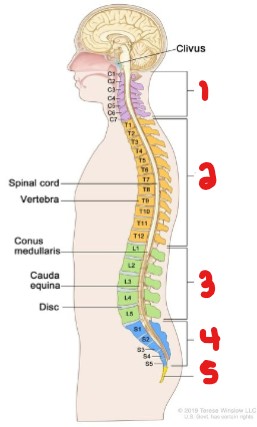
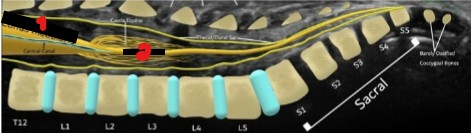
Label the sections of the vertebral column.
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Coccyx
Each vertebrae consists of a (1)____________ anteriorly and a vertebral (2)_______ posteriorly.
Rounded body
Arch
The vertebrae encloses a space called the…
Vertebral foramen
The vertebral foramen protects the (1)___________ and its (2)___________.
Spinal cord
Coverings
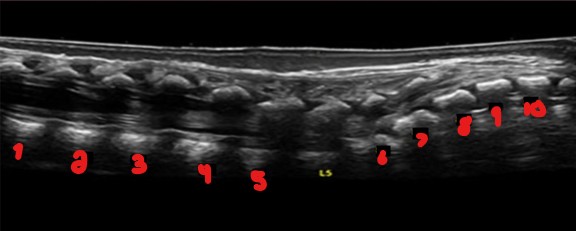
‘L5’ is the only vertebrae labeled on this image. Label the empty numbered space vertebrae.
T12
L1
L2
L3
L4
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
To know all the bones consisted in the sacrum on an US scan, you would count backwards from…
S5
On a neonatal spine US, why is the vertebrae labeled?
For the doctor
All sacral vertebrae are…
Curved
The coccyx will be mostly or completely (1)_________ and (2)________.
Unossified
Hypoechoic
On a neonatal spine US, the coccyx is typically…
Not seen
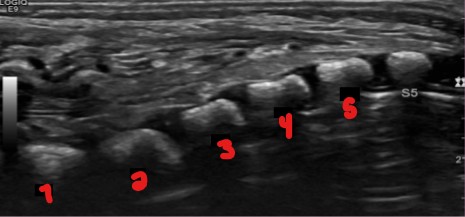
Label the vertebrae if ‘S5’ is the only one still labeled here.
L5
S1
S2
S3
S4
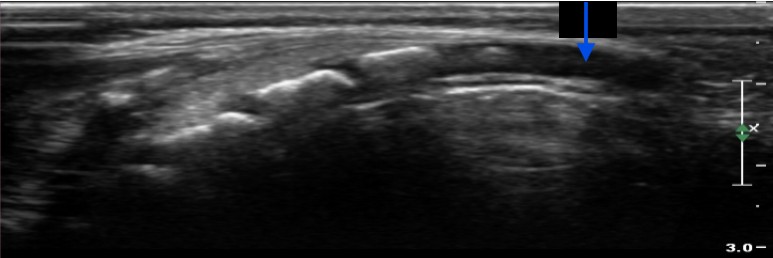
What structure is pointed at by this blue arrow?
Coccyx
The size and shape of the spinal cord varies along its…
Length
The spinal cord is narrowest in what region?
Midthoracic
The filum terminale is a ____, ________ connective tissue.
Thin, echogenic
The filum terminale extends inferiorly from the (1)______________ to the (2)_______.
Conus medullaris
Sacrum
The filum terminale should measure less than…
2 mm
Inferiorly, the spinal cord tapers off into the…
Conus medullaris
What fluid surrounds the spinal cord?
Cerebrospinal fluid
Describe how the spinal cord appears sonographically.
Hypoechoic
Echogenic borders
Echogenic line extends longitudinally along midline
Label the parts of this scan that are crossed out.
Conus medullaris
Filum terminale
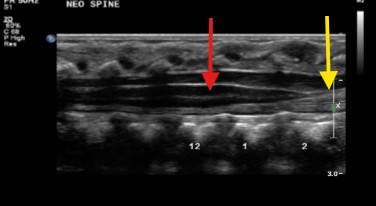
What structure is seen at the red arrow?
Yellow arrow?
Spinal cord
Filum terminale
The echogenic border of the spinal cord is referred to as the…
Thecal sac
The thecal sac is the (1)______________ that covers the (2)__________.
Protective membrane
Spinal cord
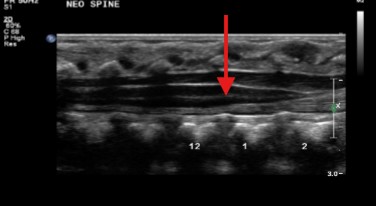
The central echogenic complex in the spinal cord represents what?
Cord’s central canal
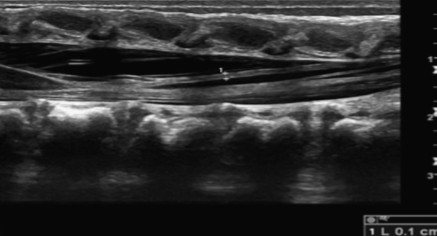
Looking at this image of the filum terminale, would this be normal or abnormal?
Normal, based on sonographic appearance and measurement
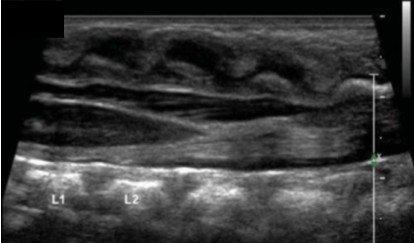
Looking at this image of the filum terminale, would this be normal or abnormal?
Abnormal, filum terminale looks thick and spinal cord appears tethered
The ventriculus terminalis is a slight (1)__________ or (2)__________ of the central canal at the (3)______ end of the cord.
Prominence
Widening
Caudal
The ventriculus terminalis is a ________ finding in neonates.
Common
The ventriculus terminalis is a _________ variant.
Anatomical
What are some other terms for ventriculus terminalis?
Terminal ventricle
5th ventricle
Since ventriculus terminalis is a normal variant, when can it typically disappear?
Within the first few months of life
Ventriculus terminalis is typically positioned at the transition of the tip of the (1)______________ to the origin of the (2)________________.
Conus medullaris
Filum terminale
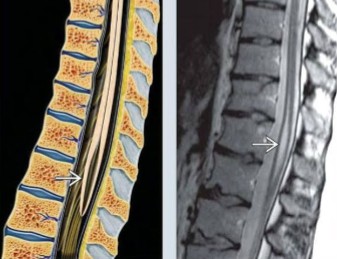
Label the image seen here.
Conus medullaris
Ventriculus terminalis
Filum terminale
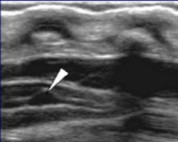
The tip of the arrow points to a normal variant. What can be assumed here?
Ventriculus terminalis
The tip of the arrow points to a normal variant. What can be assumed here?
Ventriculus terminalis
What is another term for transient dilation of the central canal?
Syrinx
Transient dilation of the central canal is a slight ________ in newborns.
Enlargement
Transient dilation of the central canal usually disappears when?
Within the first few weeks of life
What are the differences and similarities between ventriculus terminalis and transient dilation of the central canal?
Differences: Transient dilation of the central canal will have a slightly larger dilation than ventriculus terminalis
Similarities: Both resolve on their own
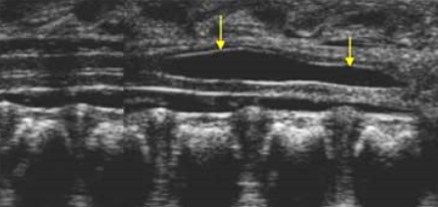
The pathology seen here was found on a recently birthed newborn. What can be assumed here?
Transient dilation of the central canal
A filar cyst is a _______ variant.
Normal
A filar cyst is a (1)_________ cyst like-structure that is usually an (2)________ finding.
Elongated
Incidental
Filar cysts tend to be located in the…
Filum terminalis
Between the ventriculus terminalis, transient dilation of the central canal, and filar cysts; which is the most common?
Filar cyst
This cyst like structure was found in the filum terminale. What can be assumed here?
Filar cyst
The lower nerve roots together are called…
Cauda equina
The spinal nerve roots unite to form a…
Spinal nerve
__ pairs of spinal nerves are attached along the length of the spinal cord.
31
The cauda equina descends from the (1)___________, below the (2)_____________.
Spinal cord
Conus medullaris
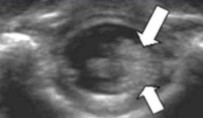
What plane was this image taken in?
What are the arrows pointing to?
Why does it appear this way?
Transverse
Clumping of nerve roots on the left
LLD
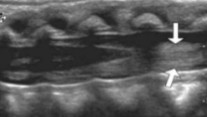
What plane was this image taken in?
What are the arrows pointing to?
Longitudinal
Mass-like appearance of nerve roots
The spinal cord should lay (1)___ to (2)___ towards the (3)_________ vertebrae in the spinal cord.
1/3
Half way
Anterior (ventral)
The spinal cord position allows it to be (1)_________________ and (2)______________.
Gravity dependent
Free floating
The spinal cord position will have a _________ pulsatile movement.
Normal
To prove the pulsatile movements of the spinal cord, what can be done?
Use M-Mode
Cine loops
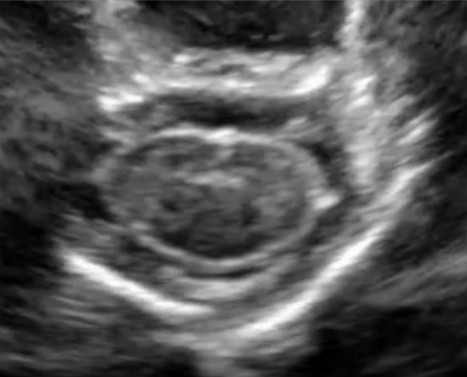
Is this transverse image normal or abnormal?
Normal
Why are spine USs performable on infants but not adults?
Due to the incomplete ossification of the spine
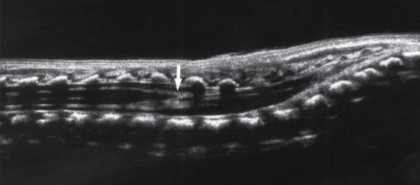
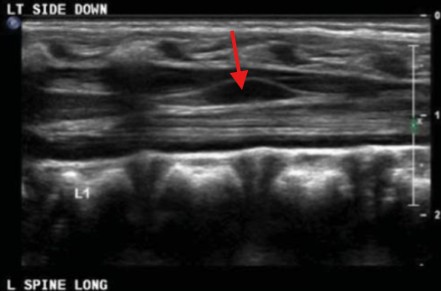
What plane was this image taken in?
The arrow points to the end of the conus medullaris, is this a normal location for it to end?
Longitudinal
Yes, ends between L1 and L2
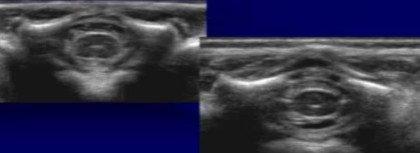
What plane were these images taken in?
Transverse
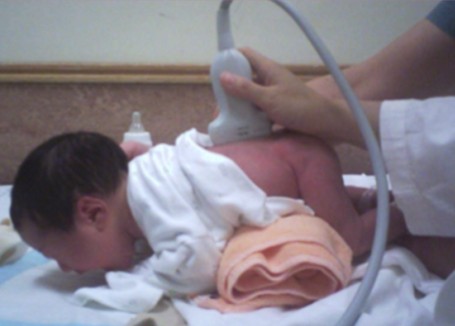
What exam is being performed here?
How is the fetus positioned for this exam?
Neonatal spine
Prone or LLD
How is the fetus positioned for a neonatal spine US?
Prone
LLD
The transducer is placed from a __________ viewpoint.
Posterior
The prone position for a neonatal spine US will have the spine (1)________ to separate the (2)________ spinal elements. The slight (3)___________ to the upper body to distend the (4)_________ aspect of the spine.
Flexed
Posterior
Elevation
Caudal
What kind of transducer should be used for a neonatal spine US?
Highest frequency linear transducer
Smaller neonates will require higher frequencies (15 MHz)
Larger neonates will require lower frequencies (8-12 MHz)
Neonatal spinal US are performed at (1)__________ for sagittal images and in (2)______ planes for transverse.
Midline
Axial
What is one of the most common reasons for an ordered neonatal spine US?
To view the level of the tip of the tapered conus medullaris
The conus medullaris will most commonly terminate at…
L1 and L2
The lumbar vertebral may be determined on an US in several different ways. List two ways.
Counting back from S5
Seeing where the vertebrae starts to curve (indicates S1)