CMS II: GI - EXAM #2 (TEST QS) (quizlet)
1/262
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
263 Terms
Lymphoid tissue in the gut is responsible for:
immune responses
Two components of GALT:
1. Organized GALT (Peyer's patches)
2. Diffuse GALT
Immune response that is induced by antigens (food proteins) unresponsiveness
Oral tolerance
Inflammatory Bowel Disease has ________ incidence
bimodal (first peak its between 20-30 and second peak is between 60-70)
**lifelong w/ remissions and relapse
What is the possible pathogenesis of IBD?
hyperactivity or loss of oral tolerance (no longer able to withstand bacteria in the gut), causing a dis-regulated immune response
_____ has a thin, superficial layer or inflammation, and ________ has transmural inflammation
UC; Crohn's
A chronic, recurrent disease characterized by transmural inflammation (skip lesions) anywhere along the GI tract (except the rectum)
Crohn's disease
Where is Crohn's disease usually located?
terminal ileum or cecum
**RLQ tenderness often (because it is commonly in terminal ileum and cecum)
3 patterns of ____________:
1. inflammatory
2. stricturing
3. perforating
**inflammation can lead to fibrosis and strictures
Crohn's disease
Initial lesions of ______________: apthoid ulcers and focal crypt abscesses
Crohn's disease
What creates the "cobblestoning" appearance in ___________
Stellate ulcerations fuse longitudinally & transversely, demarcating normal islands of mucosa
Crohn's disease
Patient presents with crampy pain in the RLQ and diarrhea (w/o blood). When looking at labs, you see he has thrombocytosis, DEC serum albumin, INC ESR, and a (+) ASCA. What is the most likely diagnosis?
(Biopsy via colonoscopy to confirm!)
Crohn's disease
A panel of 7 tests combines serologic, genetic, and inflammatory markers to help differentiate IBD vs non-IBD & CD from UC
Prometheus IBD Serology 7
You order a UGI series with SBFT and note irregular caliber, poor distensibility, cobblestoning, areas of narrowing, & aphthous ulcers. What's your Dx?
Crohn's disease
Characteristic findings of ___________ on a CT enterography section:
Two inflammatory small bowel strictures separated by a segment of normal distended small bowel
Crohn's disease
CT enterogrphic findings of luminal narrowing and proximal dilatation are indicative of ___________.
obstruction
Hepatobiliary complications of Crohn's:
Dermatologic complications of Crohns:
Oral complications of Crohns:
Ocular complications of Crohns:
MS complications of Crohns:
HB: gallstones, primary sclerosing cholangitis (more common in UC), cholangiocarcinoma
Derm: erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum
Oral: aphthous ulcers
Ocular: uveitis, iritis, episcleritis
MS: sacroilitis, arthropathy, AS, osteopenia
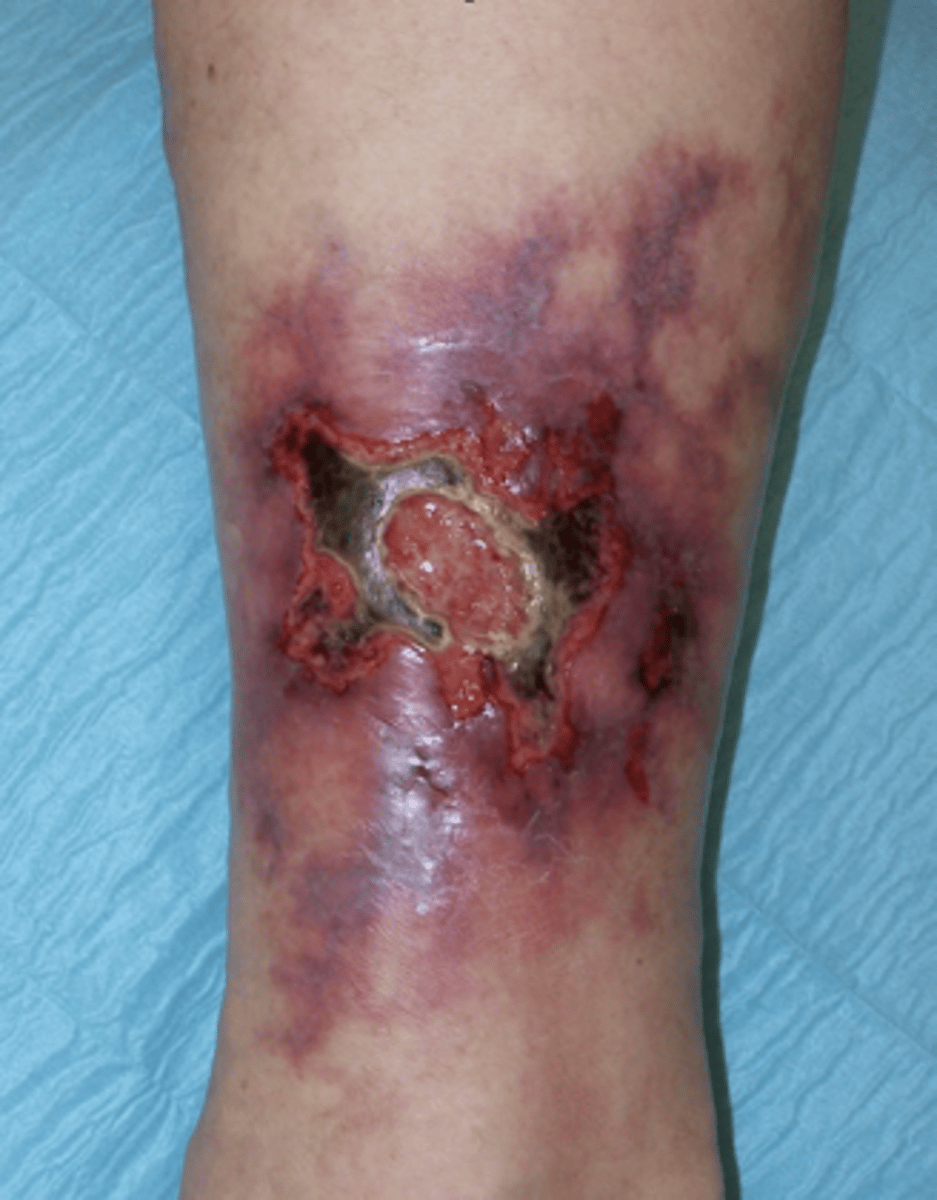
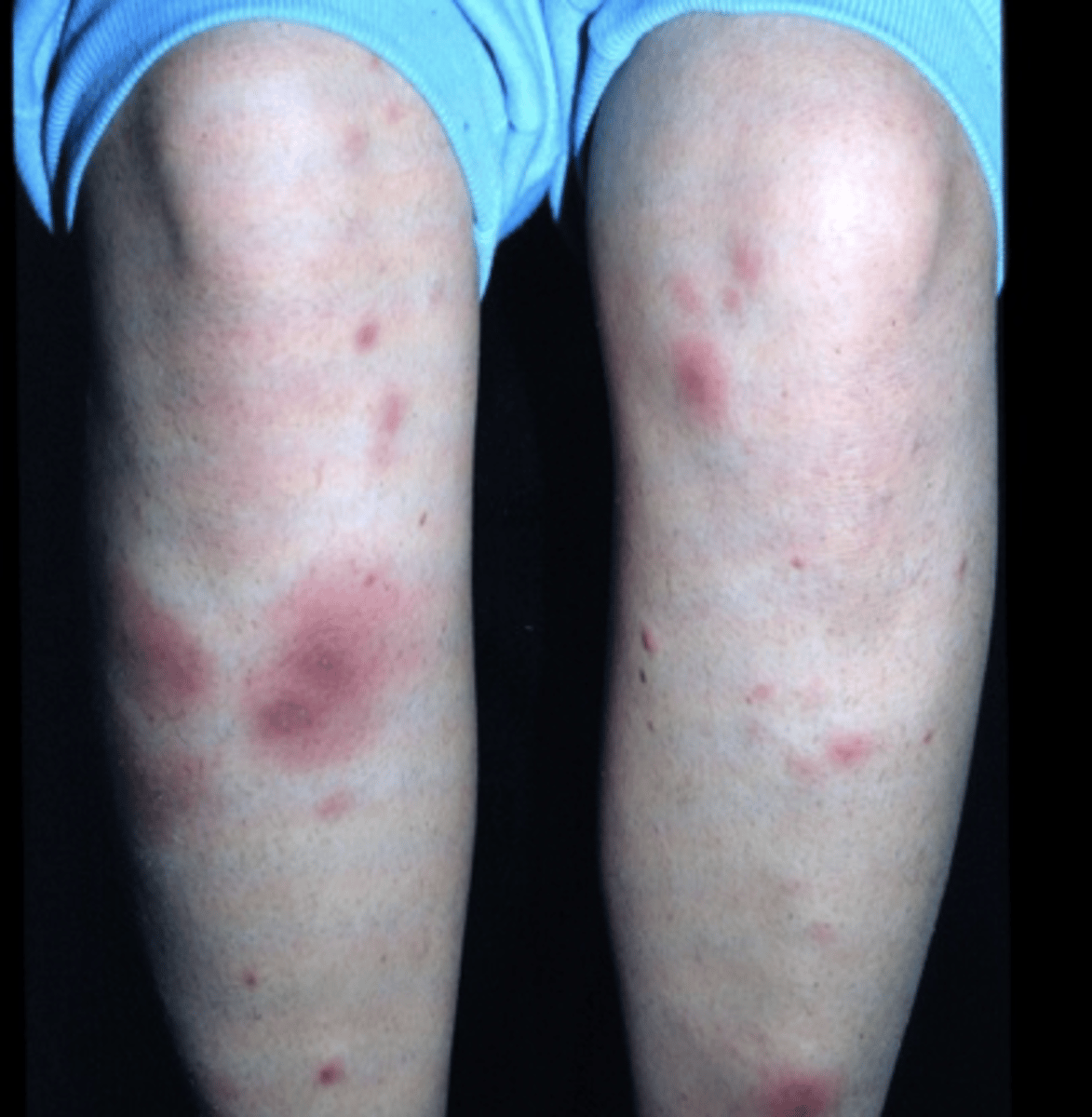
tender red nodules on the shins common in ___________ (and other inflammatory dz) = erythema nodosum
Crohn's disease
Common findings of ____________ on endoscopy:
punched out ulcers
edema to mucosa
cobblestoning
linear ulcers
Crohn's disease
What are some complications of Crohn's?
abscesses/fistulas, perianal dz, malabsorption, intestinal narrowing
Screening colonoscopy is recommended ________ after being diagnosed with Crohn's disease
8 years (increased risk of colon carcinoma), and yearly after that
Inflammatory disease that is limited to the mucosal layer of the colon and commonly begins in the rectum.
Ulcerative Colitis
UC that only involves rectum: __________
UC that involves sigmoid and rectum: __________
UC that only involves left side of colon: __________
UC that involves entire colon: __________
UC that involves distal ileum: __________
proctitis
proctosigmoiditis
distal colitis
pancolitis
backwash ileitis
What is the pathophysiology of __________:
Crypt architecture is distorted causing vascular congestion w/ edema (causing crypt abscesses)
Ulcerative Colitis
Patient comes in with bloody diarrhea and tenesmus. They have lower abdominal cramps. They have an INC ESR, hypoalbuminemia, and a (+) ANCA. What is most likely Dx?
Ulcerative Colitis
If a person w/ UC comes to ER w/ severe ABD pain, fever, hypotension, and tachycardia - what may be the cause?
fulminant colitis or toxic megacolon
**can also have altered mental status
Which diagnostic procedure is not very useful in Ulcerative Colitis and may precipitate toxic megacolon?
barium enemas
_________________ is CONTRAINDICATED with severe acute UC because of the risk of perforation & toxic megacolon
Colonoscopy
What are considerations in sexually active pts w/ proctitis
gonorrhea, chlamydia, herpes, and syphillis
What are some complications with Ulcerative Colitis?
colorectal cancer
Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy that impairs folate absorption and induces remission in both forms of IBD (but is better in UC)?
Sulfalsalazine
**watch for sulfa allergy - rash, fever, hepatitis, pancreatitis
Sulfa-free ASA preps (5-ASA agents)
control the site of delivery to bowel & limit systemic toxicity
**usually used in UC
Sulfa-free ASA preps (5-ASA agents)
__________ - released into ileum (remission in CD and UC)
__________ - small intestine (distal colon)
________________ - for proctitis (retention enema)
Asacol - released into ileum (remission in CD and UC)
Pentasa - small intestine (distal colon)
Masalamine supp (Rowasa) - for proctitis (retention enema)
What can be used for acute treatment of Ulcerative Colitis when it is unresponsive to 5-ASA therapy or in the treatment of mod/severe Crohn's?
Glucocorticoids (ex. prenisone)
Typical SE from ___________________: striae, fluid retention, hyperglycemia, osteonecrosis
Glucocorticoids (ex. prenisone)
Immunosuppressive agents for glucocorticoid-dependent IBD? What is the most common side effect?
Purine analogues (Azathioprine & 6-mercaptopurine)
leukopenia (also may cause pancreatitis or hepatitis)
Folate antimetabolite that impairs DNA synthesis and can be used weekly (injections) for IBD?
Methotrexate
Which drugs are very effective against Crohn's?
Anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody (anti-TNF) drugs
ex. Cimzia, Humira, Remicade
What is the M/C continence-preserving operation for UC?
IPPA (ileoanal pullthrough, ileal pouch-anal anastomosis)
**rectal mucosa is dissected to dentate line and a pouch is created from the ileum to the neorectum
What is the difference between gastritis and gastroenteritis
gastritis is inflammation of the stomach only, and gastroenteritis includes the stomach and intestines
**both considered food poisoning
What is the difference between preformed toxins and microbes that produce toxins after ingestion?
Preformed toxins - bacteria makes toxins in food before consumption, vomiting usually involves (ex. S. aureus and B. cereus)
Toxins after ingestion - bacteria makes toxins in the GI tract, less vomiting (ex. C. perfringens)
Mild vs. severe diarrhea
mild = < 3 stools a day
severe = 4+ stools a day w/ systemic sx (fever, chills, dehydration)
Inflammatory diarrhea vs. non-inflammatory diarrhea
inflammatory: blood, small volume, invasion of colon, fever/tenesmus
non-inflammatory: non-bloody, water, large volume
Common pathogens involved in non-inflammatory diarrhea?
Viruses, enterotoxin producing E.coli, giardia, cryptosporidia, vibriones
Profuse watery diarrhea that is prolonged but self-limited (1 - 2 weeks) d/t food or water consumption - think: ____________
Acute Infectious Diarrhea
Patient with diarrhea and a recent hospitalization or abx use, think: ______________
C. difficile
Patient with diarrhea and recent foreign travel, think: ______________
Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, E. coli, V. cholerae
Patient with diarrhea that consumed undercooked hamburger, think: ______________
E. coli 0157:H7
Patient with diarrhea that lives in long term care facility, attends school, or was on a cruise ship, think: ______________
Norovirus
Patient with consumption of fried rice, think:
B. cereus
For Sx of acute infectious diarrhea lasting beyond >1 week, initial onset of fever or bloody stools, &/or with immunocompromised pts, what should you order?
Stool culture
**WBC, O&P
Antibiotic Rx may be helpful with _______ or ________ infections
A. Norovirus; HSV
B. Shigella; Campylobacter
Shigella; Campylobacter
T/F Routine antibiotic use is NOT recommended for acute infectious diarrhea, as the disease is usually self-limiting.
TRUE
Abx if given w/ E.coli 0157:H7
Abx if given w/ C. diff
E.coli 0157:H7 - risk of HUS
C. diff - prolong dz
Patient comes in with diarrhea in June. They report drinking unpasteurized milk earlier in the week. What may be the cause?
Salmonella
**large numbers of Salmonella must be ingested to produce illness
Patient just got back from a trip overseas. They have developed diarrhea. Which highly virulent bacteria could be causing this?
shigella
Patient has diarrhea and vomiting after eating some raw veggies earlier this week. What could be the cause? What may be a complication?
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli Serotype 0157:H7
Complication: HUS due to the cytotoxin (causing endothelial damage --> renal dz)
Should you give abx for E.coli 0157:H7 infection?
NO - contraindicated
**Blood diarrhea or HUS should always be tested for this bacteria
Patient presents w/ diarrhea and vomiting. She was eating a lot of protein-rich meals last week. What may be the cause?
S. aureus (due to enterotoxin forming strain in food before ingestion)
What are the three types of botulism?
food, infant, wound
**grows in anaerobic acidic environments
What is the treatment for C. botulinum infection?
IV polyvalent antitoxin (and mainstay airway/breathing)
Main causes of _________________:
Enterotoxigenic E. coli
Shigella species
Campylobacter jejuni
traveler's diarrhea
Someone w/ traveler's diarrhea may have an increased risk of developing: ______
IBS
What is the mainstay treatment for Traveler's diarrhea?
Azithromycin 1g (single dose)
What pathogen causes of Pseudomembranous Colitis? What type of bacteria is this?
Clostridium difficile
gram-positive spore-forming bacilli
Which Abx may cause Pseudomembranous Colitis? ("FACT")
FQs
Ampicillin
Clindamycin
Third (3rd) Gen Cephalosporins
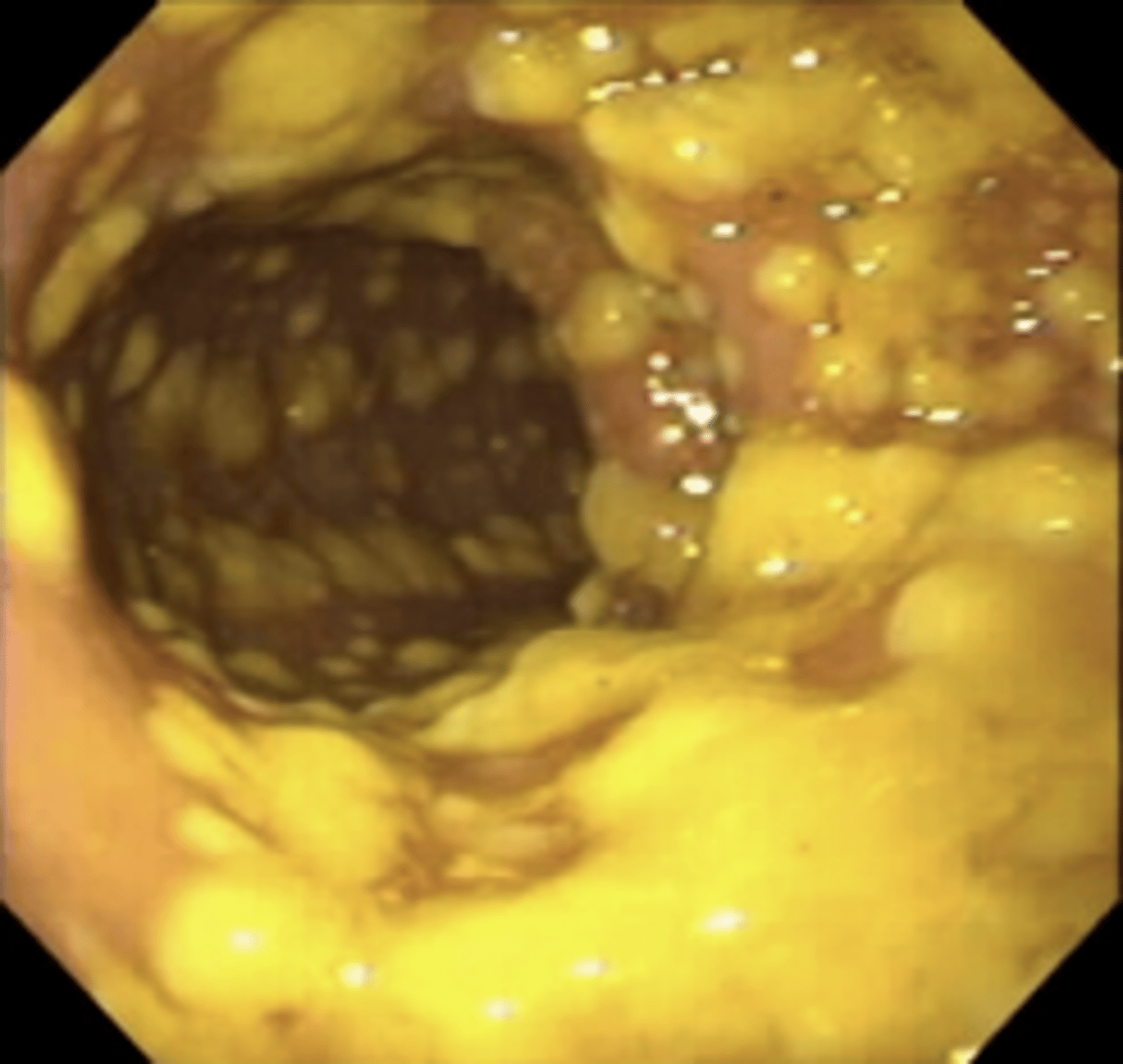
What do the toxins in Pseudomembranous Colitis do?
Destroy colonic mucosa (cannot absorb anything) and create yellowish-white plaques on the mucosa
Patient presents with greenish, foul-smelling watery diarrhea. They have mucus in the stool but NO BLOOD. They have LLQ tenderness. They were taking Clindamycin last week for an infection. What may be the cause?
Pseudomembranous Colitis (PMC) caused by Clostridium difficile
What is the rapid test for Pseudomembranous Colitis (PMC)? What is the definitive test?
Rapid: PCR assay
Definitive: Cytotoxicity assay
How do you treat Pseudomembranous Colitis (PMC)?
d/c offending abx, give oral vanco (or fidaxomicin), and avoid anti-motility agents or narcotics
Consider: fecal microbiota transplantation
What can untreated Pseudomembranous Colitis (PMC) lead to?
weight loss, protein losing enteropathy (or can progress to fulminant dz, such as megacolon)
Why is relapse common with Pseudomembranous Colitis (PMC)?
re-infection or failure to eradicate organism; or spores re-create the dz
Diarrheal disease in infants in winter months, think: __________
Rotavirus
**fecal-oral
Diarrheal disease in school-age children that went on a cruise, think: __________
Norwalk virus
M/C protozoan causing GI infection, caused by drinking from stream water w/o filtering: ______________
Giardia lamblia
("aka beaver fever")
Patient presents with pale, explosive diarrhea two weeks after a camping trip. She reports drinking water out of the lake near her campsite without filtering. What is the treatment?
Metronidazol (Flagyl) or Tinidazole
**Giardia most likely
**Tx close contacts and report to Board of health
___________: hepatic artery, portal vein, bile duct
Portal triad
__________: wide, leaky ‘capillaries’ without basement membrane empty into central vein.
Sinusoids
___________: hepatic portal vein -->
liver sinusoids -->
central vein -->
hepatic vein -->
IVC -->
right atrium
Hepatic blood flow
Where is the blood supply for the liver?
hepatic artery & portal vein (dual blood supply)
Water-soluble or Lipid-soluble?
Direct (conjugated) bilirubin is _____ soluble
Indirect (unconjuated) bilirubin is _______ soluble
Water-soluble (Direct); Lipid-soluble (Indirect)
What is the function of bile?
emulsifies fats so they can be absorbed
**made by liver, stored in GB
________ secretion pathway
bile ducts -->
R/L hepatic ducts -->
common hepatic duct, which joints cystic duct -->
common bile duct, which joints w/ pancreatic duct -->
Ampulla of Vater
Bile
Fatty acids, amino acids in duodenum stimulate _______ causing gall bladder to contract and empty
CCK
**also relaxes Sphincter of Oddi
Acidic chyme stimulates __________ which causes bile secretion
secretin
LFT pattern in:
Hepatocellular dz: ________________
Cholestatic dz: ________________
A. INC AST, ALT (Hepatocellular dz)
B. Retention of bile in liver, INC ALP (Cholestatic dz)
INC AST, ALT (Hepatocellular dz)
Retention of bile in liver, INC ALP (Cholestatic dz)
When will ALT be 2x the AST (both elevated)?
Acute Viral Hepatitis
When will both AST and ALT be over 1,000?
Acute Acetaminophen Toxicity or Ischemic Hepatitis
Liver function tests are:
bilirubin, albumin, PT/INR
What will you order when you suspect Wilson's dz? What will you order if patient is also having anemia?
Ceruloplasmin
Fe/TIBC
Gold standard to stage liver fibrosis
liver biopsy
**can have small sampling error, and is expensive (w/ risks of pain and bleeding)
New non-invasive test to measure the velocity of sound waves passing through the liver to determine liver stiffness
fibroscan
A hereditary condition whereby the conjugation of bilirubin by glucuronide is impaired due to a mild decrease in uridine phosphate (or glycuronyl transferase)
Gilbert's syndrome
What will you see in labs w/ Gilbert's syndrome?
persistent elevation of unconjugated bilirubin (w/ illness, fasting, or drugs)
**does not require tx
Loss of hepatocellular function or interrupted blood flow through the liver is called?
Hepatocellular failure
______ of the liver must be destroyed before life is threatened
80%
In hepatocellular failure, ↓ production of clotting factors & hypoalbuminemia → generalized _________
Edema
In hepatocellular failure, fluid and electrolyte shift due to lack of proteins - change in osmolality --> _________
Ascites
What will cause impaired absorption of vitamins A, D, E, and K from the GI tract?
decreased production of bile salts
Impaired processing of endogenous steroid hormones in hepatocellular failure cause in men? Women?
men: gynecomastia, impotence, testicular atrophy
women: irreg menses, palmar erythema, spider telangiectasia