Mutations and Mutagenesis: DNA Changes, Types, and Detection Methods
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is a mutation?
A permanent change in DNA structure that requires a round of replication to establish.
How often do mutations occur in cells?
About 6 nucleotide changes per cell yearly, with an overall frequency of ~10^-10.
What role does DNA polymerase III play in mutation prevention?
It is very stringent, removing about 10% of incorrect nucleotides during DNA replication.
What is the initial error rate of DNA polymerase III?
1 in 10,000, but only 1 in 1,000 errors remain, with 99.9% corrected later.
What are the two main types of point mutations?
Transitions (Pur → Pur, Pyr → Pyr) and Transversions (Pur → Pyr, Pyr → Pur).
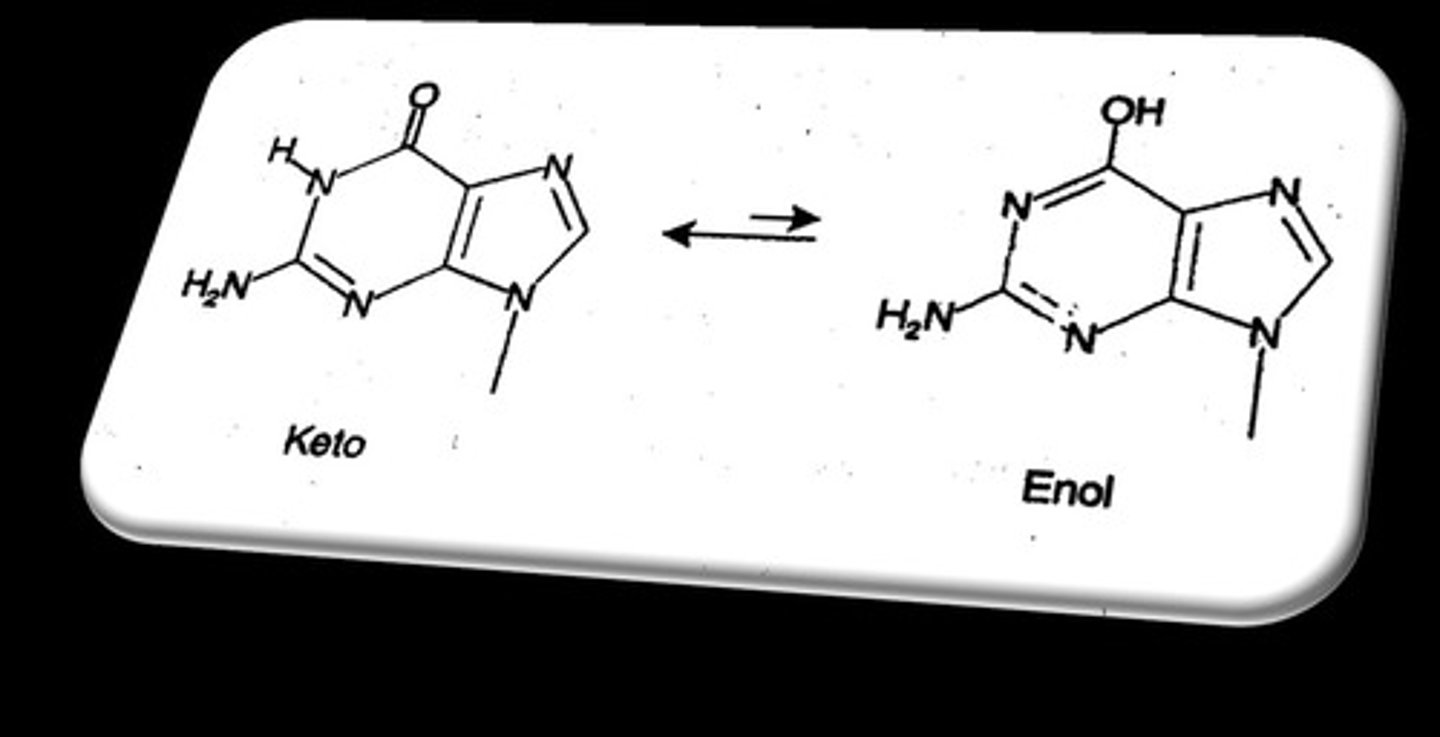
What is tautomerism in the context of mutations?
The shifting of electrons in a nitrogen base that can lead to mispairing during replication.
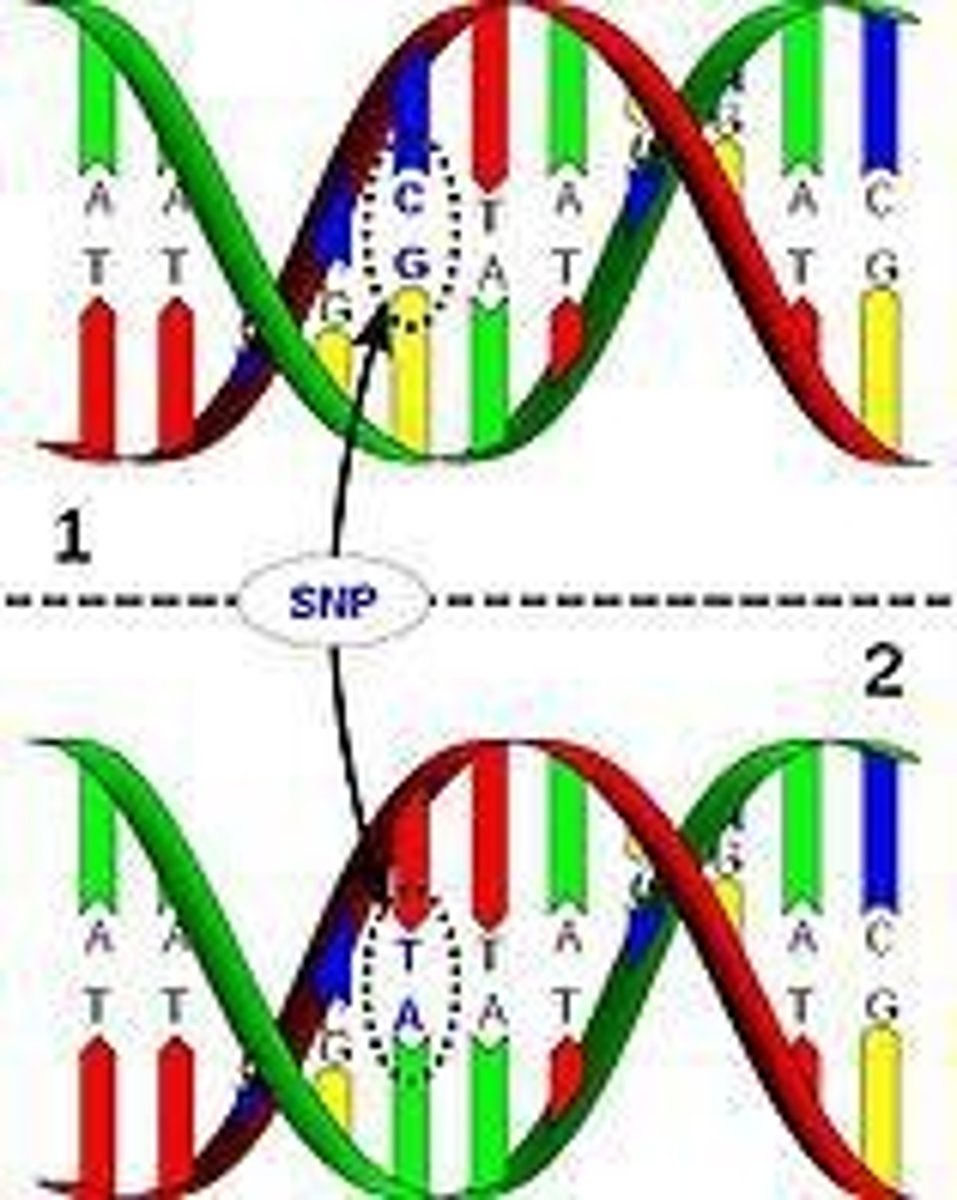
What percentage of DNA variation among humans is due to point mutations?
Approximately 0.1% of DNA varies among people, with 80% of that being SNPs from point mutations.
What happens when nucleotides are deleted in a mutation?
If the number deleted is not a multiple of 3, a frameshift occurs, potentially altering protein structure.
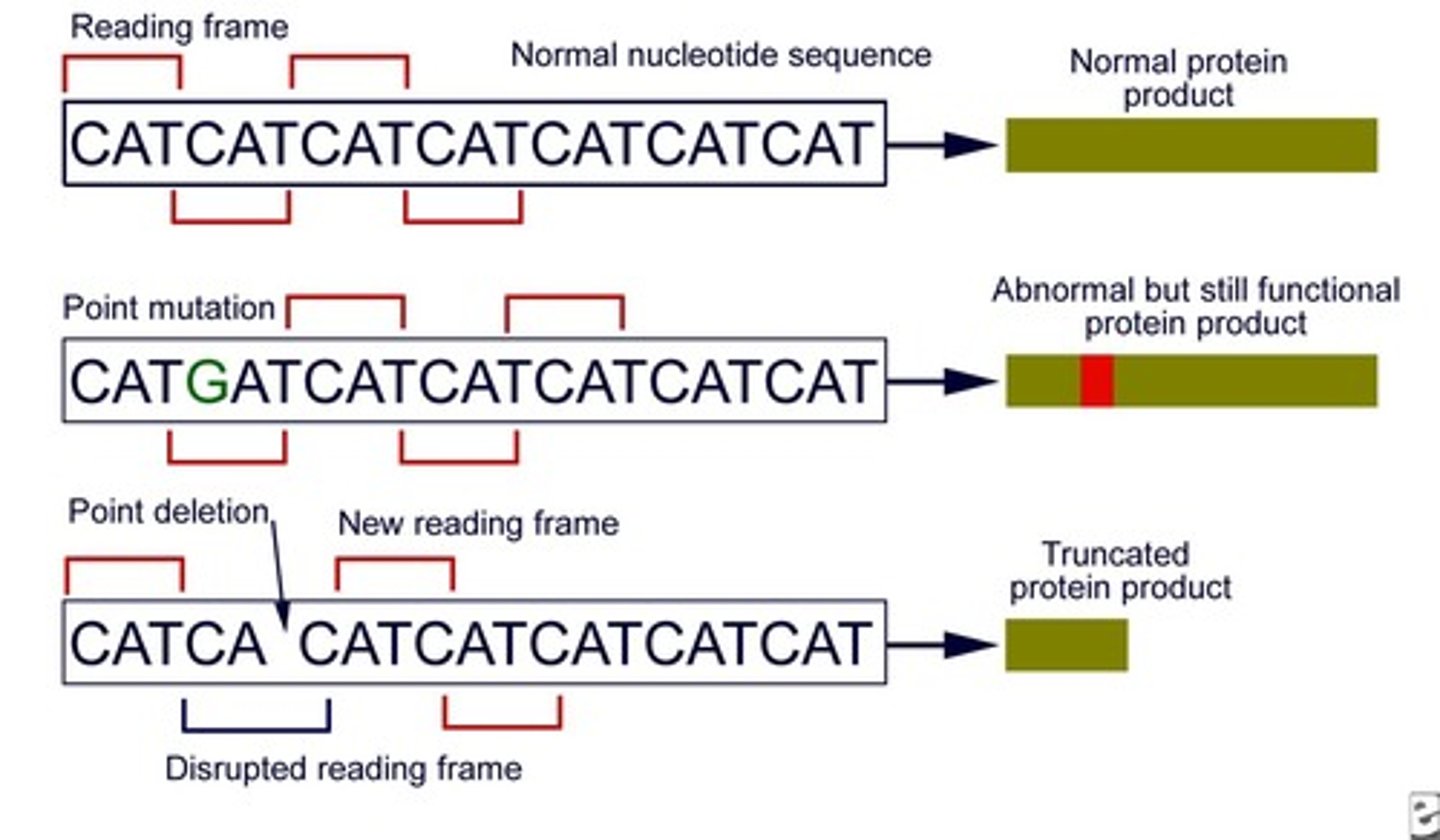
What is the effect of insertions in DNA mutations?
Insertions can also cause frameshifts if the number inserted is not a multiple of 3, leading to altered proteins.
What are suppressor mutations?
Second mutations that reduce the effects of an original mutation, often occurring in unrelated genes.
What are base analogs?
Chemical mutagens that resemble nitrogen bases and can be incorporated into DNA.
What is the role of alkylating agents in mutagenesis?
They cause about 10,000 alkylations per cell daily, with examples like benzopyrene found in cigarette smoke.
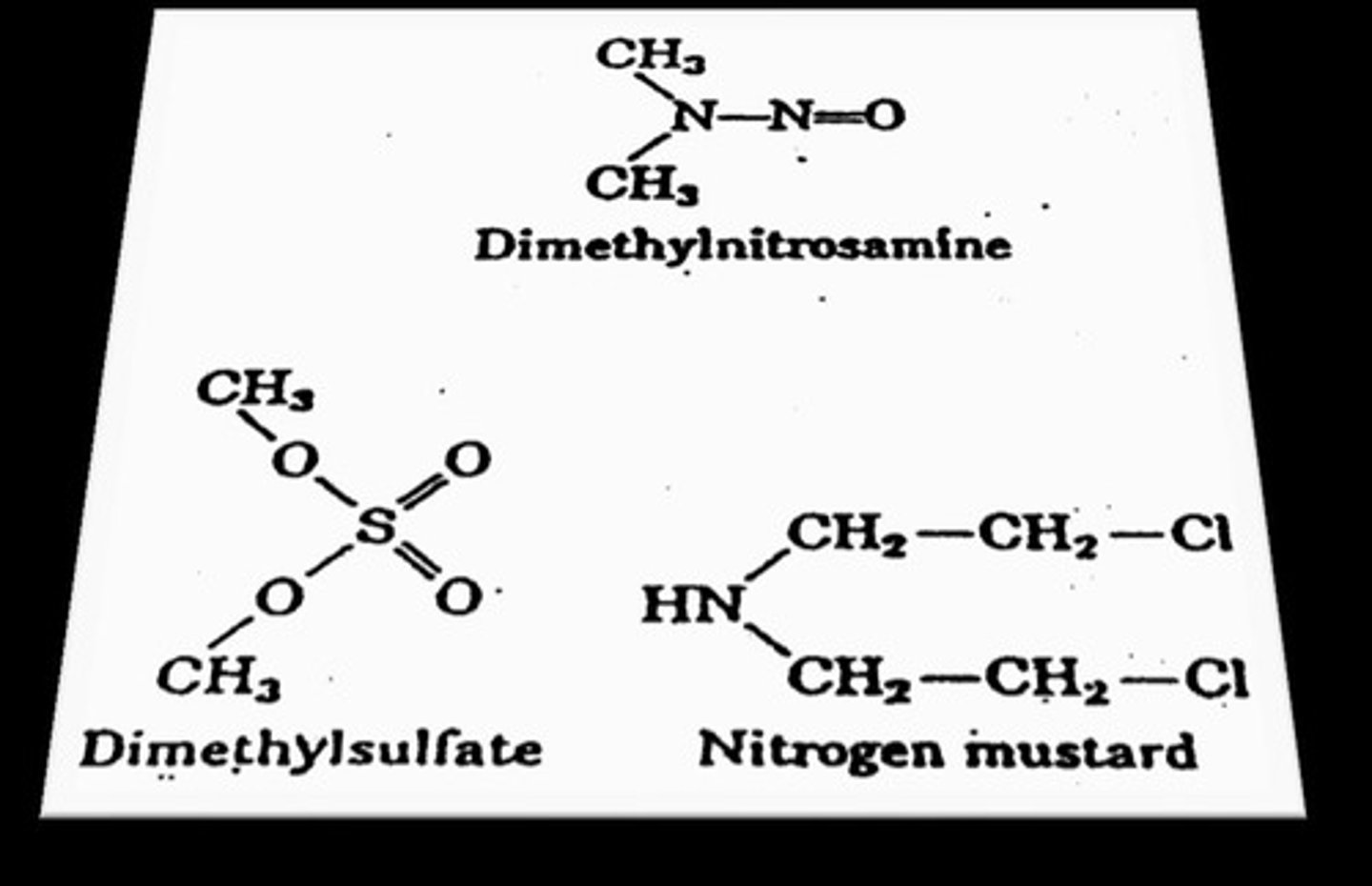
What do deaminating agents do?
They cause deamination, converting bases like cytosine into uracil, with examples including nitrous acid.
What are intercalating molecules?
Flat hydrophobic molecules that insert between DNA bases, altering DNA structure, such as acridine orange.
What is the Delaney Clause?
A regulation stating that if a chemical is shown to cause cancer in animals, it is banned for human consumption.
What are the main sources of cancer related to chemicals?
Heredity (10-30%), tobacco (1/5 of deaths), environment (70-90%), diet (1/3 of cancers), and occupational exposure (5-20%).
What is the effect of UV light as a physical mutagen?
UV light can covalently link thymines, forming cyclobutanes and 6-4 photoproducts.
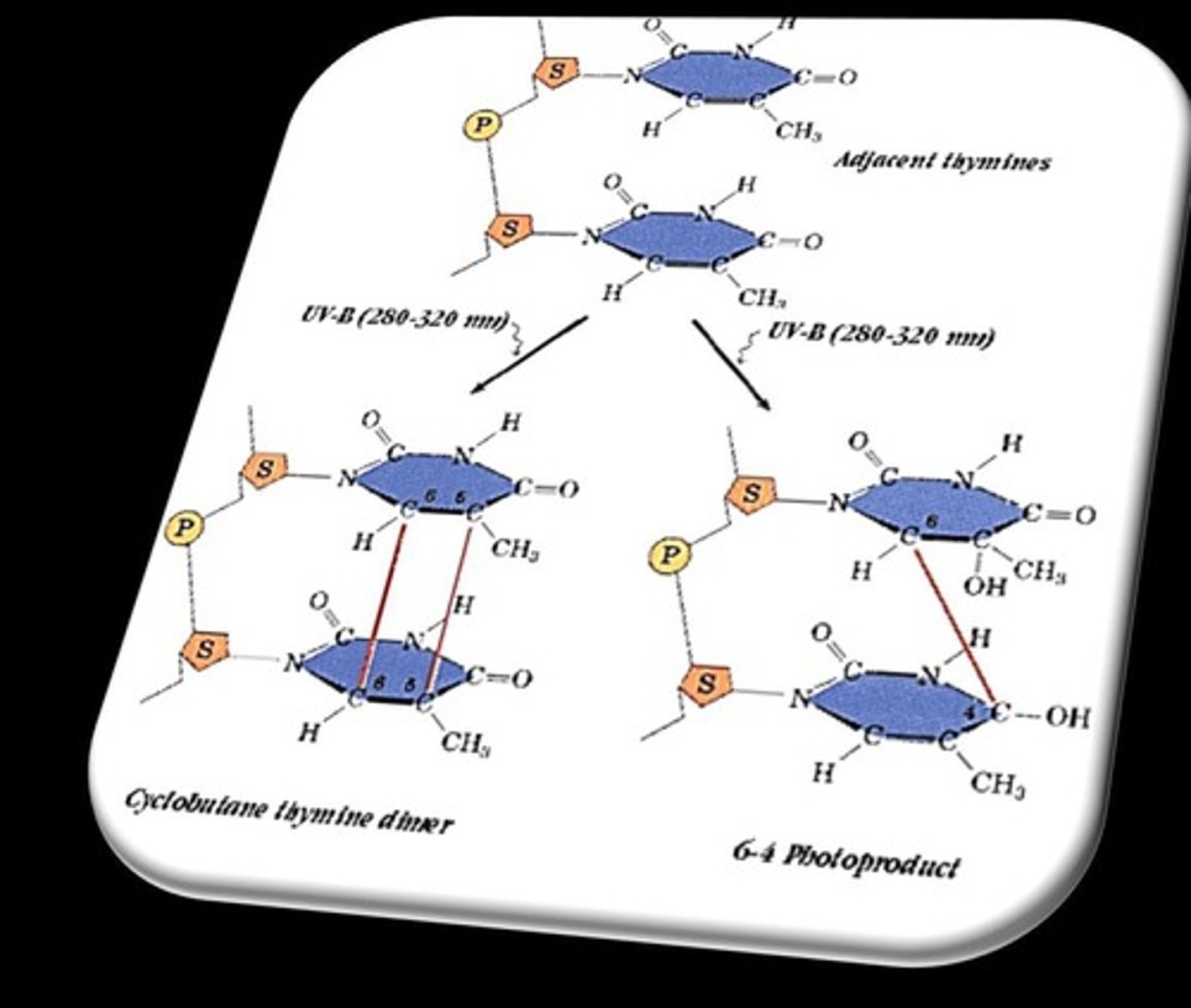
How does ionizing radiation cause DNA damage?
It produces free radicals that primarily cause strand breaks in DNA.
What is the average radiation exposure for a person in the US?
230 mrem, with 130 mrem from natural sources.
What are transposable elements and their impact on the genome?
They compose 1/3 of the genome but account for only 0.2% of mutations, with mechanisms to prevent harmful effects.
What is the Ames Test?
A microbiological test that detects mutagenicity by identifying mutations that revert a his- mutant strain of Salmonella.
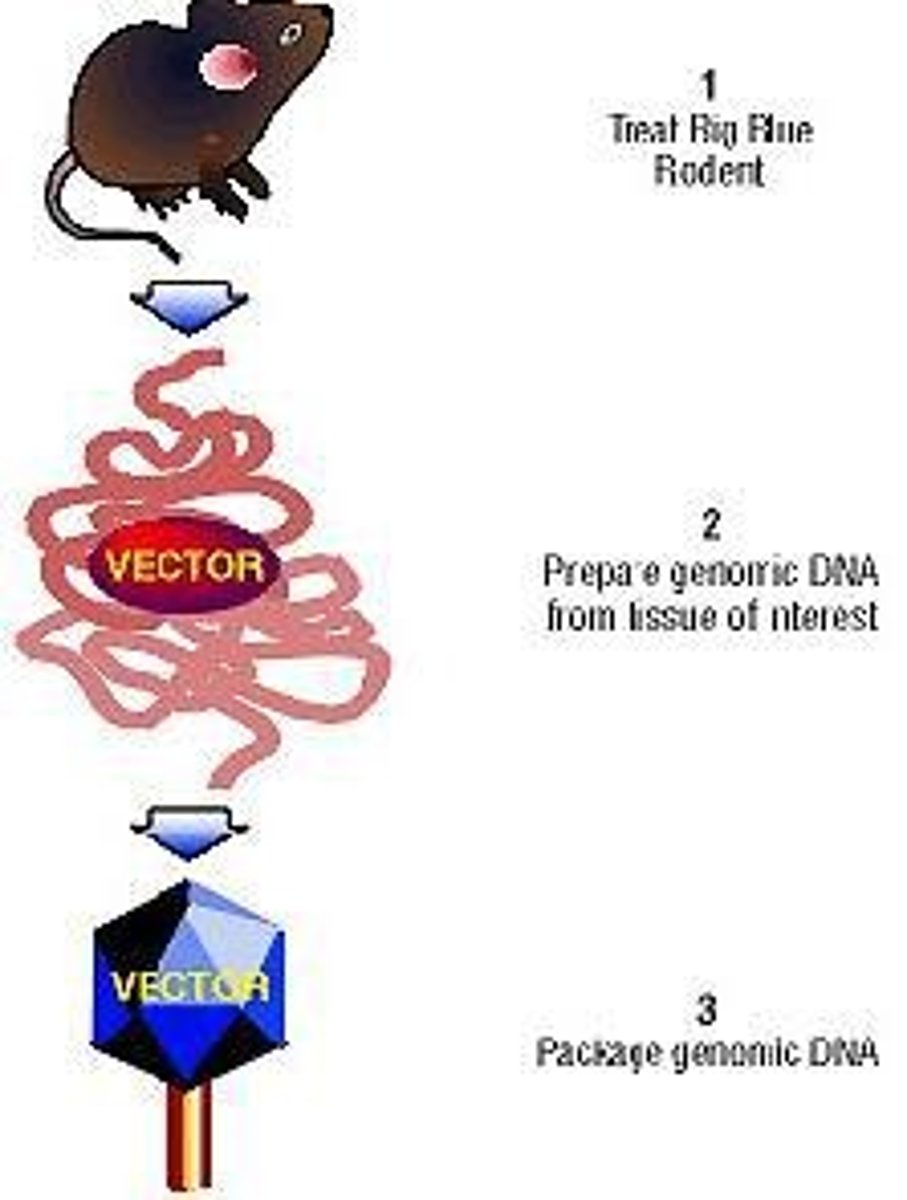
What is the significance of the Big Blue Mutagenicity Test?
It is a test for mutagenicity in mammals, assessing the effects of potential mutagens.