the mind's machine ch. 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:23 AM on 2/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
1
New cards
glia/glial cells
non neuronal brain cells, provide structural and nutritional support and process information
2
New cards
input zone
dendrites, collect and process information from the environment and other neurons
3
New cards
integration zone
cell body and axon hillock. where the decision to produce neural signal is made
4
New cards
conduction zone
axon. information is electrically transmitted
5
New cards
output zone
axon terminals/terminal buttons. where information is transferred to other cells.
6
New cards
golgi staining
staining that reveals a few cells in their entirety. guy who made it thought neurons were connected like a continuous matric
7
New cards
cajal
drew golgi’s stained neurons. believed neurons to be individual units
8
New cards
motor neurons
long, long neurons, stimulate muscles
9
New cards
sensory neurons
various shapes, responds to environmental stimuli (can be internal or external)
10
New cards
interneurons
small axons, analyze input from one set of neurons and communicate with others. tell neurons what other neurons are around them
11
New cards
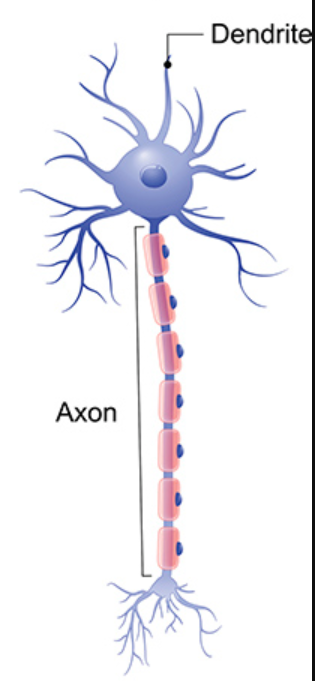
what kind?
multipolar
12
New cards
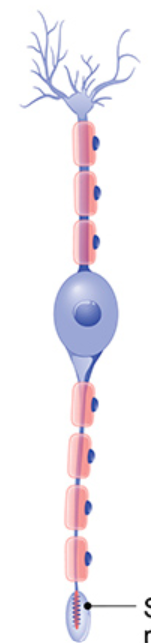
what kind?
bipolar
13
New cards
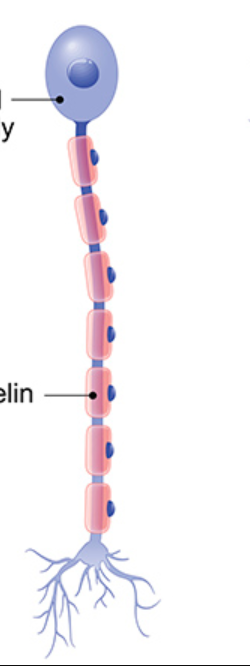
what kind?
unipolar
14
New cards
presynaptic membrane
on the axon terminal of the presynaptic cell. the vesicles fuse with the membrane and release their neurotransmitters into synaptic cleft
15
New cards
synaptic cleft
the gap that separates pre and post synaptic membranes
16
New cards
postsynaptic membrane
on the post synaptic cell. had neurotransmitter receptors
17
New cards
synaptic vesicles
a bag like enclosure in the presynaptic neuron that holds neurotransmitters
18
New cards
neurotransmitter recepts
specialized proteins. react to transmitter molecules
19
New cards
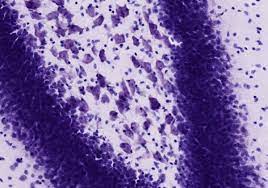
nissl stain
see all cells but not detailed
20
New cards
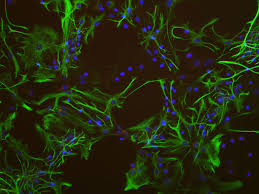
c-fos staining
looks at functionality of a particular location
21
New cards
tract tracing
see populations of cells and look at patterns of activation
22
New cards
axon hillock
cylindrical area at base of bell body. if threshold reached it starts first Action Potential that travel down axon. makes sense of chemical inputs to make electrical outputs
23
New cards
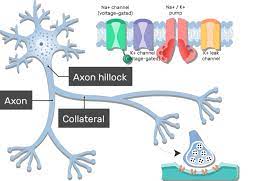
axon collateral
when the axon branches
24
New cards
schwann cells
a type of glial cell. provides myelin sheath to neurons outside the brain and spinal cord. only wraps around one bit of axon and one schwann cell makes one ‘balloon’ of myelin
25
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
a type of glial cell. provides myelin sheath to neurons in brain and spinal cord. myelinates multiple sections of multiple neurons.
26
New cards
astrocytes
star shaped glial cell. stretch around and between neurons and blood vessels providing a structure. secrete chemicals and help form outer membrane around brain.
27
New cards
micro glial
type of glial cells. tiny, mobile cells that remove debris and dead/injured cells
28
New cards
nodes of ranvier
gaps between myelin sheaths where axon is exposed
29
New cards
saltatory conduction
special type of conduction in which action potential ‘jumps’ between nodes of ranvier
30
New cards
schwann cell death
when we hurt ourselves and tear through neurons because it’s schwann cells in our PNS we only kill one little part of the axon, not a cell attatched to multiple axons.
31
New cards
oligodendrocytes cell death
when oligodendrocytes die they take a bunch of neurons with them and don’t grow back. create a dead zone in the brain that can never be recovered
32
New cards
PNS bundle of axons
nerve
33
New cards
motor nerves
transfer information from CNS to muscles and glands
34
New cards
sensory nerves
transfer information from body to CNS
35
New cards
autonomic NS
has two parts, sympathetic and parasympathetic
36
New cards
sympathetic NS
preps the body for action, responsible for fight or flight response, expends a lot of energy (turns off some processes to divert energy to more important muscles)
37
New cards
parasympathetic NS
helps the body relax and recuperate (digest). in use most often, more stable, energy conserving
38
New cards
gyri
ridges on the cortex
39
New cards
sulci
valleys in the cortex
40
New cards
cerebrum
the hemispheres of the brain, **not** including the cerebellum
41
New cards
frontal lobe
executive function (in humans), motor and movement systems
42
New cards
parietal lobe
somato sensations (body awareness)
43
New cards
occipetal lobe
visual processing
44
New cards
temporal lobe
auditory processing
45
New cards
central sulcis
divides frontal and parietal regions of brain. had a pre-central gyrus and a post-central gyrus
46
New cards
sylvian fissure
horizontal sulci
47
New cards
cerebellum
‘little brain’, involved in learning, motor skills, storing unconscious memory, balance, muscles moving in tandem
48
New cards
gray matter
more cell bodies and dendrites, closer to outside of cortex
49
New cards
white matter
more axons and myelin, towards center of brain
50
New cards
hindbrain
cerebellum, ponds, medulla
51
New cards
brainstem
midbrain, pond, medulla
52
New cards
embryotic development
a fluid filled neural tube. develops bumps (vesicles) that turn into specific part of the brain
53
New cards
pons
‘bridge’, connects cerebellum to rest of CNS, separates out information for cerebellum or cortex
54
New cards
cortex layers
the cerebral cortex has 6 layers. each layer has different processes and these processes communicate
55
New cards
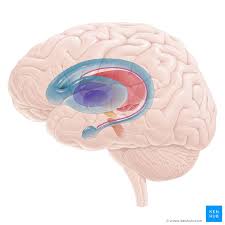
Forebrain
limbic system (amygdala, hippocampus, fornix, cingulate gyrus, olfactory bulb, thalamus, hypothalamus) and basal ganglia (caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra)
56
New cards
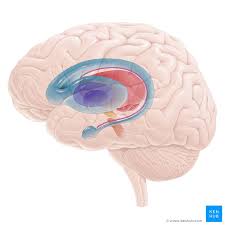
caudate nucleus
light blue part of pic. looks like a horse tail.
57
New cards
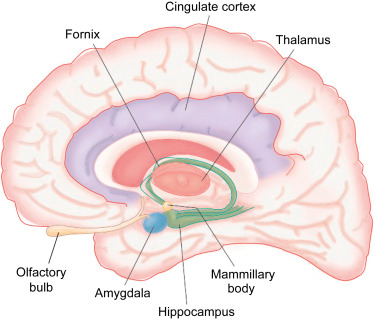
amygdala
emotional regulation. small blue dot
58
New cards
basal ganlia
motor control
59
New cards
limbic system
emotion and learning
60
New cards
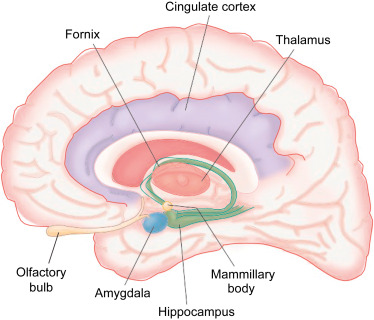
hippocampus and fornix
learning and memory coding. green
61
New cards
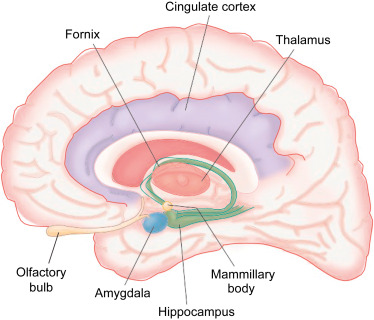
cingulate gyrus
attention. purple
62
New cards
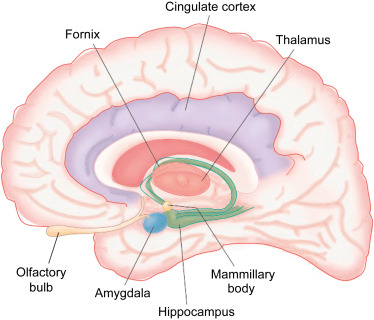
thalamus
center of rain, cluder of nuclei, relay sensory information (except small) to rest of cortex. like a post office. light pink
63
New cards
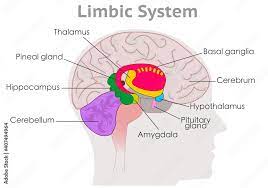
hypothalamus
controls pituitary gland (endocrine system), regulates rhythms (circadian). blue
64
New cards
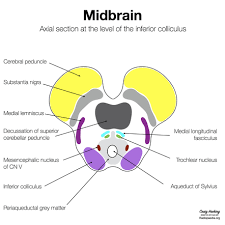
midbrain
sensory system of the tectum
65
New cards
superior colliculi
visual processing. handles sudden, unintended incursions into your visual world
66
New cards
inferior colliculi
auditory processing, handles sudden, unintended incursions into your auditory world
67
New cards
substrantia nigra
part of basal ganglia, movement control
68
New cards
reticular formation
involved with sleep and arousal
69
New cards
periaqueductal gray
pain perception
70
New cards
medulla
basic living functions, heart beat, breathing, reflexes (sneezing, blinking)
71
New cards
meninges
three protective layers around the brain and spinal cord
1. dura mater-tough, outermost layer. flexible but not stretch
2. arachnoid membrane-middle layer, filled with cerebral spinal fluid, looks like a spider wed
3. pia mater- delicate innermost layer
1. dura mater-tough, outermost layer. flexible but not stretch
2. arachnoid membrane-middle layer, filled with cerebral spinal fluid, looks like a spider wed
3. pia mater- delicate innermost layer
72
New cards
meningitis- infection of the meninges
meningiomas- tumors in the meninges
meningiomas- tumors in the meninges
73
New cards
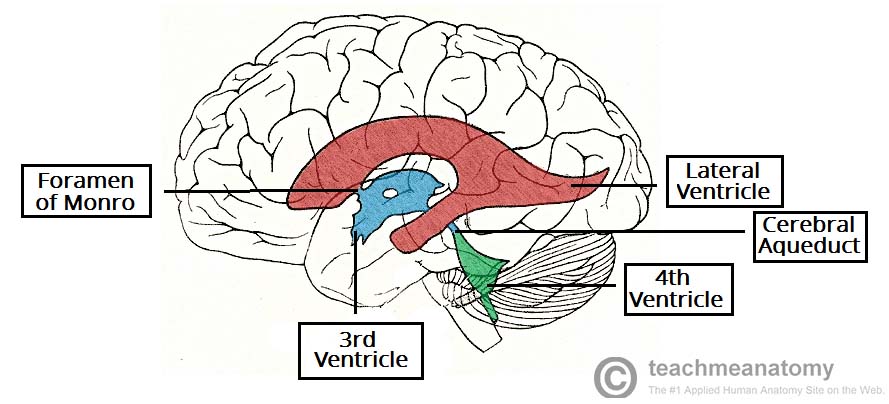
ventricular system
series of chambers filled with CSF
\-2 lateral ventricles, one in each hemisphere
\-3rd ventricle, between thalamus on each side has a hole in the middle to allow the two axons to connect
\-4th ventricle, runs down spinal cord
CSF runs through system, down spine, then back up to the meninges
\-2 lateral ventricles, one in each hemisphere
\-3rd ventricle, between thalamus on each side has a hole in the middle to allow the two axons to connect
\-4th ventricle, runs down spinal cord
CSF runs through system, down spine, then back up to the meninges
74
New cards
cranial nerves
12 pairs, connect to brain in order they occur from back to from of head (i.e. nose, eyes, face, neck, tongue, etc.)
75
New cards
spinal cord sections
cervical-thoracic-lumbar-sacral-coccyx
76
New cards
spinal cord
has gray matter **inside** white matter
77
New cards
dorsal root nerves
spinal cord, sensory nerves, sends info in
78
New cards
ventral root nerves
spinal cord, motor nerves, sends info out