States of matter and mixtures
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
what are the 3 states of matter?
solid
liquid
gas
solid- arrangement of particles
regular pattern
solid- movement of particles
vibrate around a fixed position
solid- relative energy of particles
low energy
liquid- arrangement of particles
randomly arranged
liquid- movement of particles
move around each other
liquid- energy of particles
greater energy than solid
gas- arrangement of particles
randomly arranged
gas- movement of particles
move quicly in all directions
gas- energy of particles
highest energy
what type of change is a change in state?
physical change
what is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change?
physical change is reversible and doesn't change the chemical properties of the substance
unlike a chemical change
melting
solid to liquid
boiling
liquid to gas
freezing
liquid to solid
evaporation
liquid to gas
condensation
gas to liquid
sublimation
solid to gas
melting in terms of particles
heat energy increases particles' kinetic energy, allowing the particles to move
boiling in terms of particles
liquid particles gain so much kinetic energy that they escape
freezing in terms of particles
significant decrease in temperature= decrease in kinetic energy=particles lose so much energy that they become solid
evaporation in terms of particles
only occurs on the surface of liquids
where high energy particles can escape from the liquid's surface at low temperatures
condensation in terms of particles
When a gas is cooled its particles lose energy that when they bump into each other, they lack energy to bounce away again, instead grouping together to form a liquid
mixture definition
consists of 2 or more elements or compounds NOT chemically combined together
pure substance definition
a single element or compound, not mixed with any other substace
pure melting point data vs mixture melting point data
mixtures melt over a range of temperatures
whereas pure substances melt at specific/exact temperatures
this can be used to distinguish pure substances and mixtures
When should simple distillation be used?
used to separate a dissolved solvent from a solute (e.g. producing water from a salt solution)
Simple distillation works because the dissolved solute has a much higher boiling point than the solvent.
how to carry out simple distillation (trying to produce water from a salt solution)
1. The solution is heated, and pure water evaporates producing a vapour which rises through the neck of the round bottomed flask
2. The vapour passes through the condenser, where it cools and condenses, turning into the pure liquid that is collected in a beaker
3. After all the water is evaporated from the solution, only the solid solute will be left behind
when is fractional distillation used?
used to separate two or more liquids that are miscible with one another (e.g., ethanol and water from a mixture of the two)
how to carry out fractional distillation
1. The solution is heated to the temperature of the substance with the lowest boiling point
2. This substance will rise and evaporate first, and vapours will pass through a condenser, where they cool and condense, turning into a liquid that will be collected in a beaker
3. All of the substance is evaporated and collected, leaving behind the other components(s) of the mixture
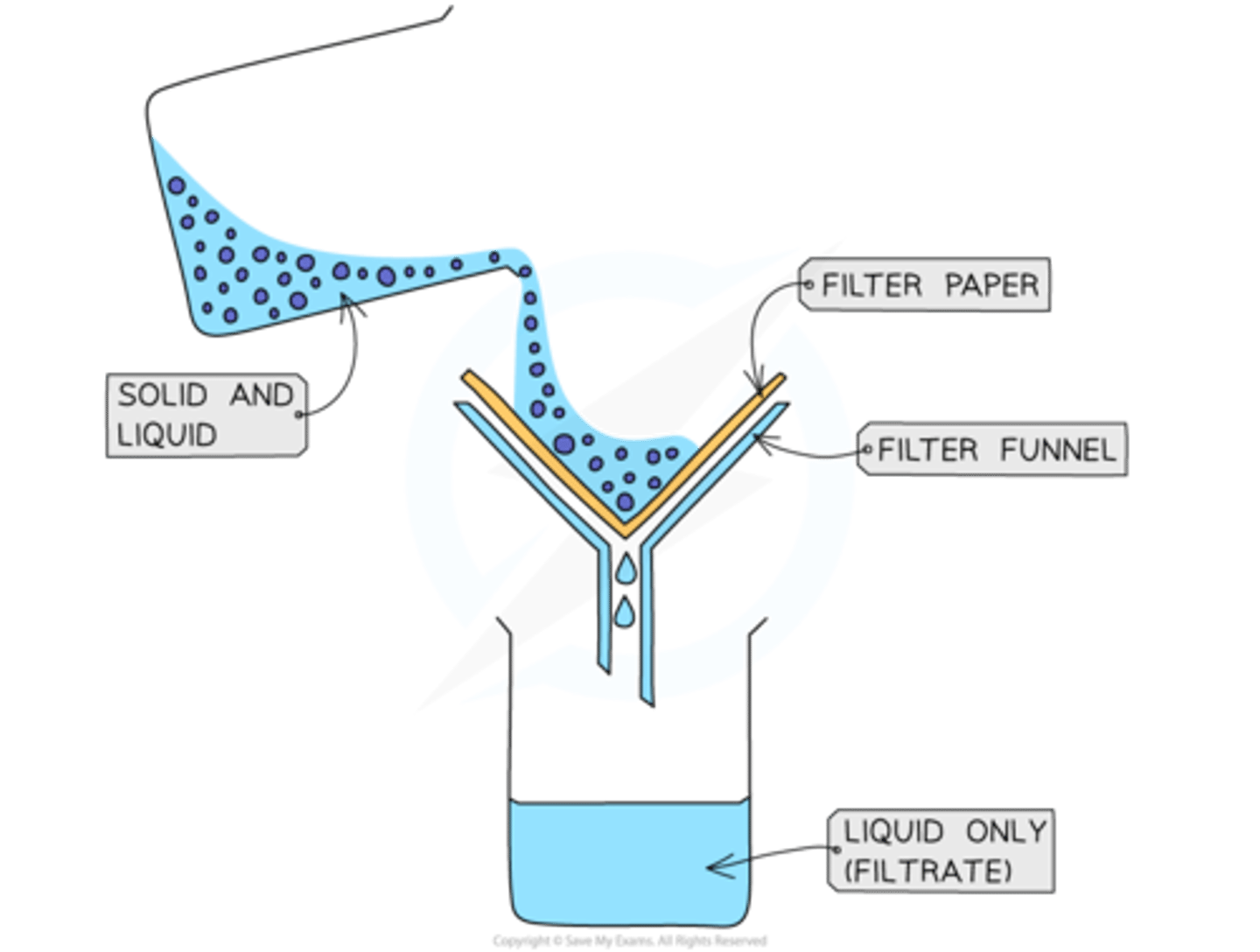
when is filtration used?
Used to separate an insoluble solid from a mixture of the solid and a liquid
e.g. sand from a mixture of sand and water
how to carry out filtration
1. A piece of filter paper is placed in a filter funnel above a beaker
2. A mixture of insoluble solid and liquid is poured into the filter funnel
3. The filter paper will only allow the liquid to pass through as filtrate
4. Solid particles are too large to pass through the filter paper so will stay behind as a residue
when should crystallisation be used?
Used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution (e.g. salt and water)
how to carry out crystallisation
1. The solution is heated, allowing the solvent to evaporate, leaving a saturated solution behind
2. Cool the saturated solution
3. Crystals will begin to grow as solids
4. The crystals are collected by filtering the solution, they are washed with cold distilled water to remove impurities and are then allowed to dry
when should paper chromotography be used?
used to separate substances that have different solubilities in a given solvent
e.g. different coloured inks that have been mixed to make black ink
how to carry out paper chromotography
1. A pencil line is drawn on chromatography paper and spots of the sample are placed on it.
2. The paper is then lowered into the solvent container, making sure that the pencil line sits above the level of the solvent
3. The solvent travels up the paper, taking some of the coloured substances with it
4. Different substances have different solubilities so will travel at different rates, causing the substances to spread apart
why is a pencil line drawn on the chromatogram?
Pencil is used for this as ink would run into the chromatogram along with the samples
why should the pencil line be above the solvent?
so the samples don't wash into the solvent container
how to distinguish between pure and impure substances on a chromatogram
- Pure substances will produce only one spot on the chromatogram
- An impure substance therefore will produce a chromatogram with more than one spot
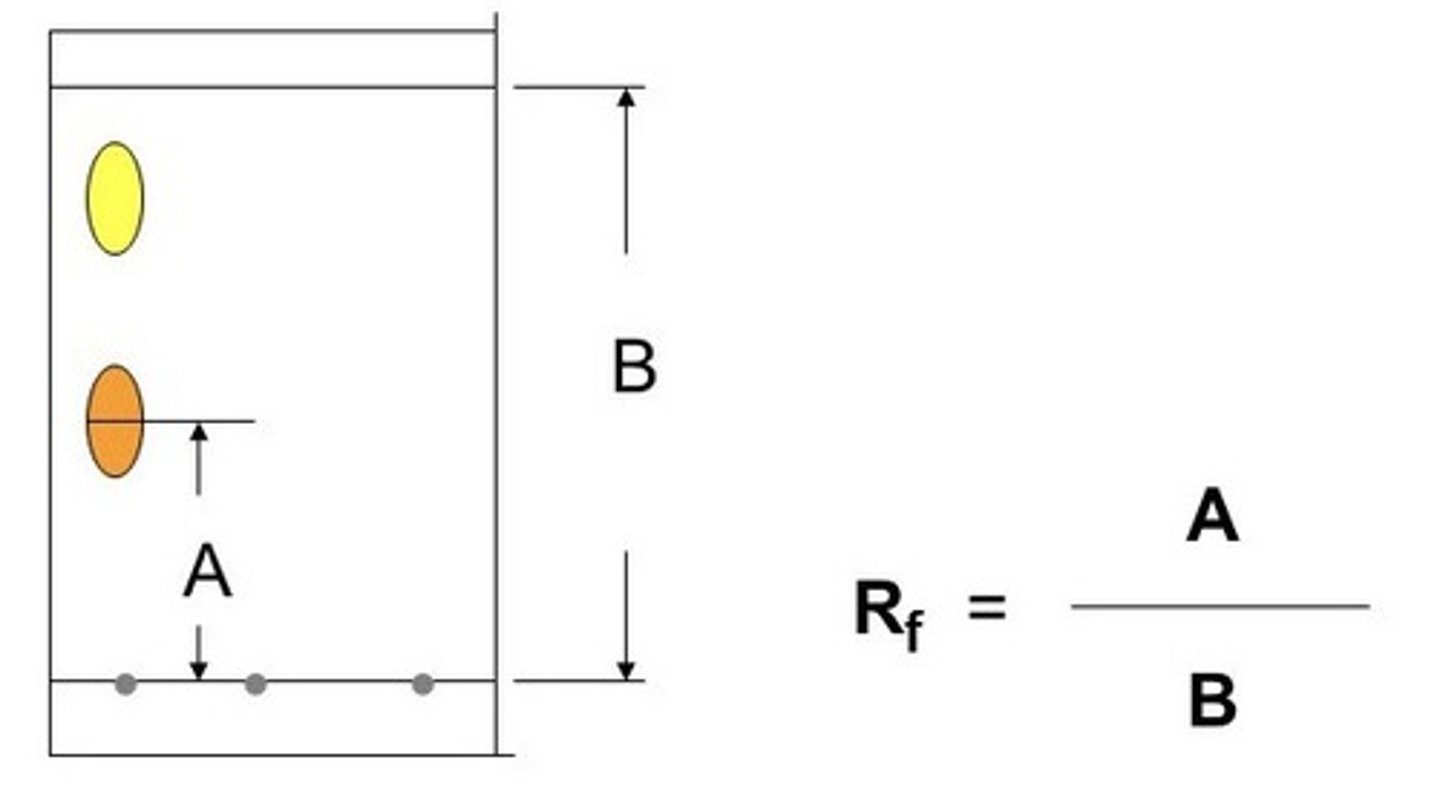
how to identify substances using Rf values
the same substance will have the same Rf value if dissolved in the same solvent
how to calculate the Rf value
(distance travelled by) SPOT / (distance travelled by) SOLVENT
how to identify substances by comparison with known substances
If two or more substances are the same, they will produce identical chromatograms
stationary phase
the paper
mobile phase
the solvent running through the paper
potable water
potable water: it is suitable for drinking so must have:
- low levels of microbes
- low levels of contaminating substances
NOT the same as pure water
what are the 3 steps to make waste and ground water potable
1. sedimentation
2. filtration
3. chlorination
sedimentation
large insoluble particles will sink to the bottom of the water
filtration
water is filtered through beds of sand which removes small insoluble particles
chlorination
chlorine gas is put through water to kill microbes
how to make sea water potable
distillation
distillation when making seawater potable
1. filter the seawater
2. boil it
3. water vapour is cooled and condensed
why must water used in anaylsis be pure?
must be pure because any dissolved salts could react with the substances you are analysing, leaving you with a false result