Organic Chemistry
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
State the name of a family of compounds related in a certain way
Homologous series
Ethanol is a good solvent. Explain how ethanol could dissolve both polar and non-polar substances.
Ethanol has a polar -OH group that attracts polar molecules and a small hydrocarbon chain that attracts non-polar molecules.
State the function of yeasts in fermentation.
Function is that yeast is a micro-organism that releases the enzyme zymase that is used in the fermentation process.
State the colour of acidified potassium dichromate.
orange
Primary alcohols
Only one hydrocarbon chain (R) is attached to the carbon containing
the hydroxyl group
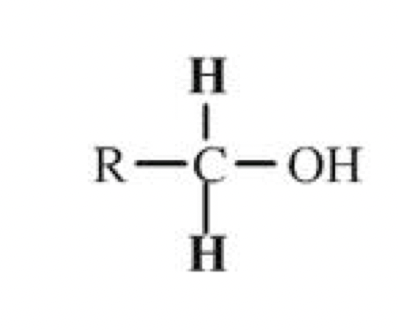
Secondary Alcohols
Two hydrocarbon chains (R and R’) are attached to the carbon
containing the hydroxyl group
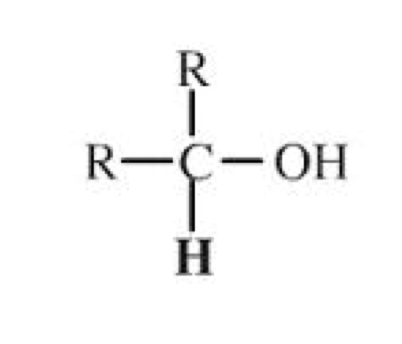
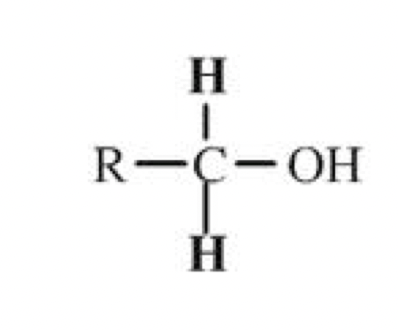
Tertiary alcohols
Three hydrocarbon chains (R, R’ and R’’) are attached to the carbon
containing the hydroxyl group
what colour change indicates that a primary alcohol is present with acidified dichromate
orange to green
Name the organic technique used to obtain a more concentrated solution of ethanol.
Distillation
State one other condition, other than a warm temperature, that is required for fermentation to take place.
Anaerobic conditions
why does some stuff react with HBr
due to the C-C bond in the substance which allows addition reactions. Therefore it is likely that Her will add across the double bond the same as hydrogen
what is the carboxyl group
COOH
What are amines
Amines contain a carbon bonded to a basic nitrogen with a lone pair
Polarity of amines
Both N–C and N–H bonds in amino functional groups are polar. However, because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen, the magnitude of the partial charges in amines is considerably less than in functional groups which contain oxygen.
Why do amines act as bases
The lone pair on the nitrogen can accept H+ to form a protonated amine. ]
How do amines react in water
they form a protonated amine and hydroxide ion
How do amines react with acids
they react to form ionic salts which are water soluble
Why do many pharmaceutical drugs contain amino groups but are also large molecules with many non-polar components
these amine salts can form strong ion-dipole interactions with polar water molecules. Ion-dipole interactions are stronger than hydrogen bonds; hence, the drugs dissolve more easily in bodily fluids.
How are esters produced
An ester can be prepared by reacting a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. It is a condensation reaction, as a water molecule is produced.
What is the ester functional group
COO
How are esters named
alcohol component then carboxylate component
\
What type of reaction is involved in forming a polyester
This is a condensation reaction, as one water molecule is produced for each ester group.
What type of intermolecular forces do esters experience
dipole-dipole secondary interactions. This is because the carbon atom with a ∂+ charge is surrounded by other bulky atoms and cannot be accessed by ∂– atoms in other molecules.
are unsaturated hydrocarbon triglycerides more likely to be solid or liquid at room temperature
substance is likely to be a liquid at 25oC because unsaturated substances have poorer packing and hence weaker secondary interactions (dispersion forces) caused by the greater distances between molecules. This leads to lower MPs.
systematic name for glycerol
propan-1,2,3-triol
what is a carbonyl group
C=O c double bonded to O
Monosaccharides are the simplest of the carbohydrates . name examples
Glucose and fructose
What are Disaccharides
Disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharide molecules that have combined in a condensation reaction.
What are polysaccharides
The complex carbohydrates are condensation polymers of monosaccharides
What does complete hydrolysis of polysaccharides produce
Produces monosaccharides such as glucose while Partial hydrolysis may produce di- or trisaccharides.
Why does the cyclic form of glucose not contain aldehyde or ketone groups
The cyclic form does not contain the aldehyde or ketone groups because they are joined with an O-H on another part of the molecule to complete the ring. The sugars still act as aldehydes or ketones because there are enough straight chain molecules left.
where do saturated molecules come from
animals
where to unsaturated molecules come from
plants
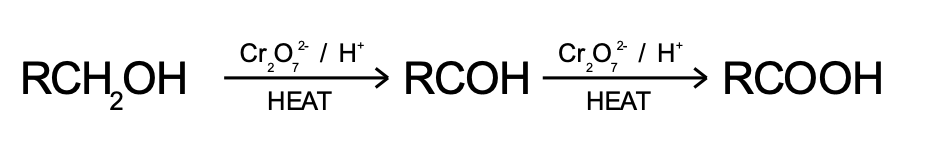
How are carboxylic acids produced
Produced by oxidation of aldehydes or primary alcohols with excess acidified dichromate solution.
Carboxylic acids are weak acids therefore
Weak acids. Only ionize to a small extent to produce the carboxylate ion

Are potassium and sodium carboxylates soluble in water
Potassium and sodium carboxylates are soluble in water because of the strong ion – dipole bonds that form between the negatively charged carboxylate ion and the water molecules.
Are amines soluble in water
Some of the smaller primary amines are soluble in water because of the polar N-H bonds but as the molecule increase in size, their solubility decreases.
are salts of amines (protonated amines) soluble in water
The salts of amines (protonated amines) are soluble in water because of the ion – dipole attraction between the ions and water. This forms stronger bonds with water than the polar N-H groups found in amines.When insoluble amines react with acids they appear to dissolve because of the formation of the water soluble salts produced.
How are esters prepared
Esters are prepared by reacting an alcohol with a carboxylic acid in the presence of conc. sulfuric acid under reflux. This is a condensation reaction(water is produced). The reaction is slow and low yielding.
What is the reverse of preparing an ester
Hydrolyisis
products of alkaline hydrolysis of an ester
carboxylate anion and the alcohol.
systematic name of glycerol
propane-1,2,3-triol
what is it called if more than one C = C bond exists in a tryglericeride
polyunsaturated
what naturally occurring substances contain the amine link / peptide link
proteins
How to draw carboxylic acid in anionic form
get rid of H on OH and add - charge on O
how do u draw zwitterion
draw the molecule with both the cation and anion features/ acidic and alkaline conditions
what makes some proteins susceptible to oxidation
lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom
name the reaction that converts sucrose into glucose and fructose
hydrolysis
what type of bonds does the less polar ester group form with itself
dipole-dipole interactions. they are weaker than hydrogen bonds
products of acidic amide hydrolysis
original carboxylic acid and protonated amine
products of alkaline amide hydrolysis
carboxylate anion and amine
products of acidic hydrolysis of an ester
original carboxylic acid and alcohol
products of alkaline hydrolysis of an ester
carboxylate anion and alcohol
what happens when an amine is protonated upon reaction with water (ONLY THING THAT HAPPENS TO AMINE)
Each N has + charge and gains a h
Type of reaction in which polysaccharides are converted into di or monosaccharides
hydrolysis
conditions needed for formation of ester
high temperature, concentrated catalyst eg sulphuric acid
what are isomers
isomers have the same molecular formula but a different structure formula
) State an observation likely to be made during the reflux process making an ester
sweet fruity odour
why is the reflux process needed to make esters
Esterification is a slow reaction
Heating under reflux allows the reaction to occur at its
boiling point (increasing the rate) without losing any of the
reagents
(3)
why proteins are sensitive to changes in pH.
pH affects ionic bonding between NH3+ and COO – side groups
causing disruption of the bonds that hold the structures in shape
what is primary structure
The sequence in which the amino acids are linked together
What is secondary structure
this refers to In aqueous solution, protein chains fold and coil in specific ways. The secondary structure is determined by the hydrogen bonding between non-adjacent amide functional groups.
What is tertiary structure
The folding that occurs between the twisted and folded chains (like a
coiled spring twisting in on itself) because of interactions between
distant amino acids.
Interactions may be due to:
Covalent bonding (ie disulphide bridges)
Hydrogen bonding between polar groups on a side chain
Ionic bonds may form between -NH3
+ and –COO- groups
Hydrophobic interactions where the non-polar groups exclude the polar regions
Tertiary structure gives proteins 3D shape
QUATERNARY STRUCTURE
The 3D arrangement of the packing together of a multi chain protein
Separate polypeptide chains can interact together to give a more
complex structure