Chapter 18 Nematodes (come around eat spongebob houuuse)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Nematode Characteristics
-Cylindrical body tapered at both ends
- Eutely: same # of cells
- Covered by a nonliving cuticle that is secreted by hypodermis & shed during growth and development
- Complete digestive system
- Many parasitic nematodes derive energy from glycolysis (anaerobic metabolism), but free living are aerobic
- No specialized circulatory or respiratory systems
- Excretion via diffusion across the body wall or using poorly understood excretory canals
-Found everywhere
- Nervous system consists of a ring-shaped brain and nerve cords (dorsal + ventral)
- Paired amphids function in chemoreception & mechanoreception
- Most are dioecious with males typically smaller than females
- Copulatory spicules in males allow for internal fertilization
Why is C. elegans a useful model system?
- Practical: can grow on petri dish at room temp & 10K can live on single dish
- Can be frozen and thawed
- Two forms: hermaphrodite & males
- Complete genome has been sequenced
- Neurons all mapped out; simple nervous system
- Short generation time
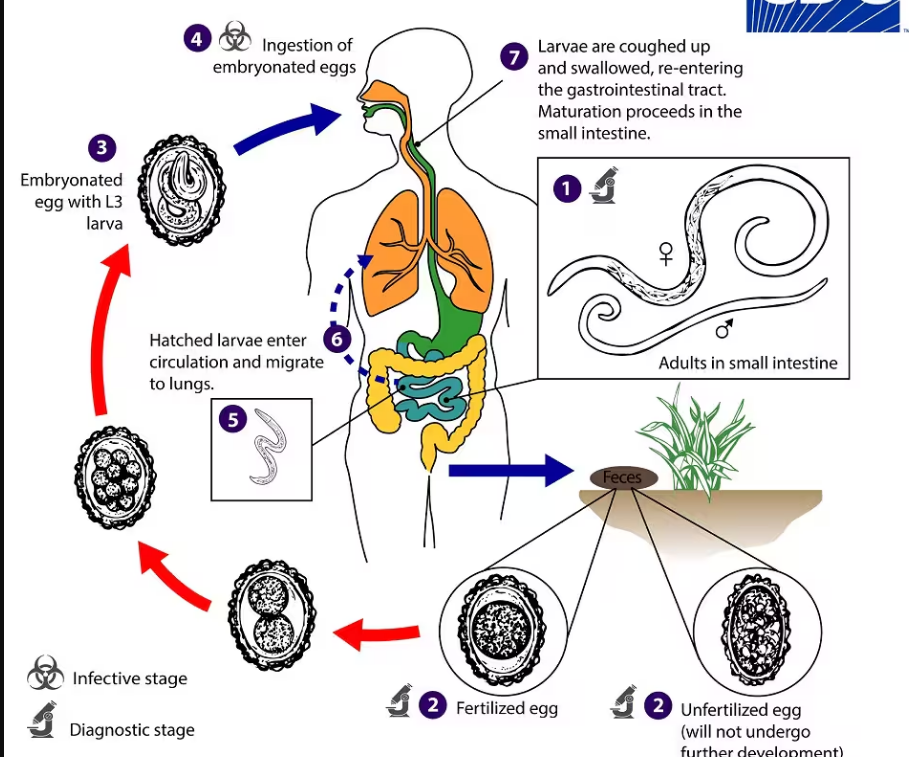
Ascaris lumbricoides
-one host
-juveniles eaten(infective stage) → feed on small intestine
content →travel to (blood→lymph→
→heart→lungs→trachea→pharynx) where they
are swallowed→back to stomach & intestine
to finalize dvpt→reproduce in intestine, eggs passed with feces (inactive stage, need warm, moist soil, can live there for years),
-light infection can include abdominal discomfort; heavy infection can cause intestinal blockage and impair growth in children
-tolerant to lack of O2, but killed by sun light and high temps
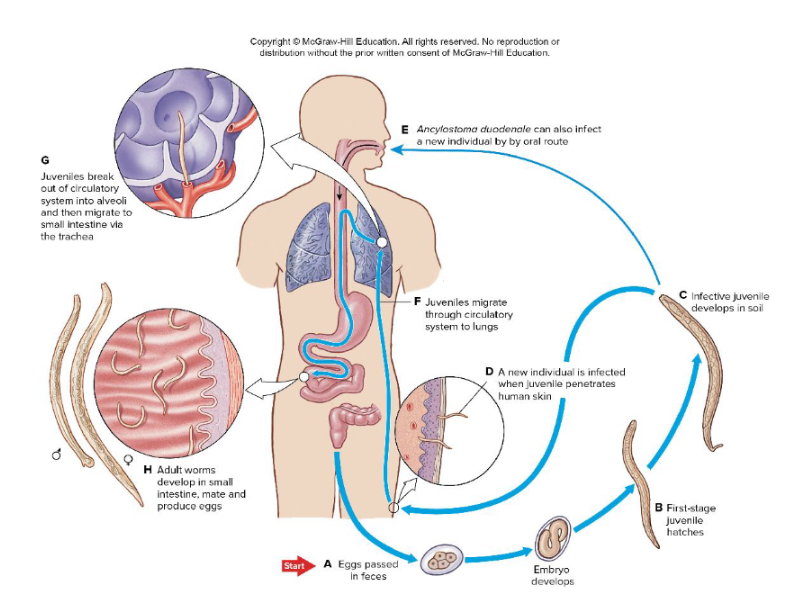
Hookworm
-one host
-Eggs pass in feces →juveniles hatch in soil where they live on bacteria → go through skin (can go orally but usually skin)→blood→lungs→intestine where they feed and reproduce
-In host intestine=suck blood (plates in their mouths) -> may cause anemia, in kids can lead to mental and physical developmental delay and deplete energy
-prevented by bettering sewer systems and sanitization
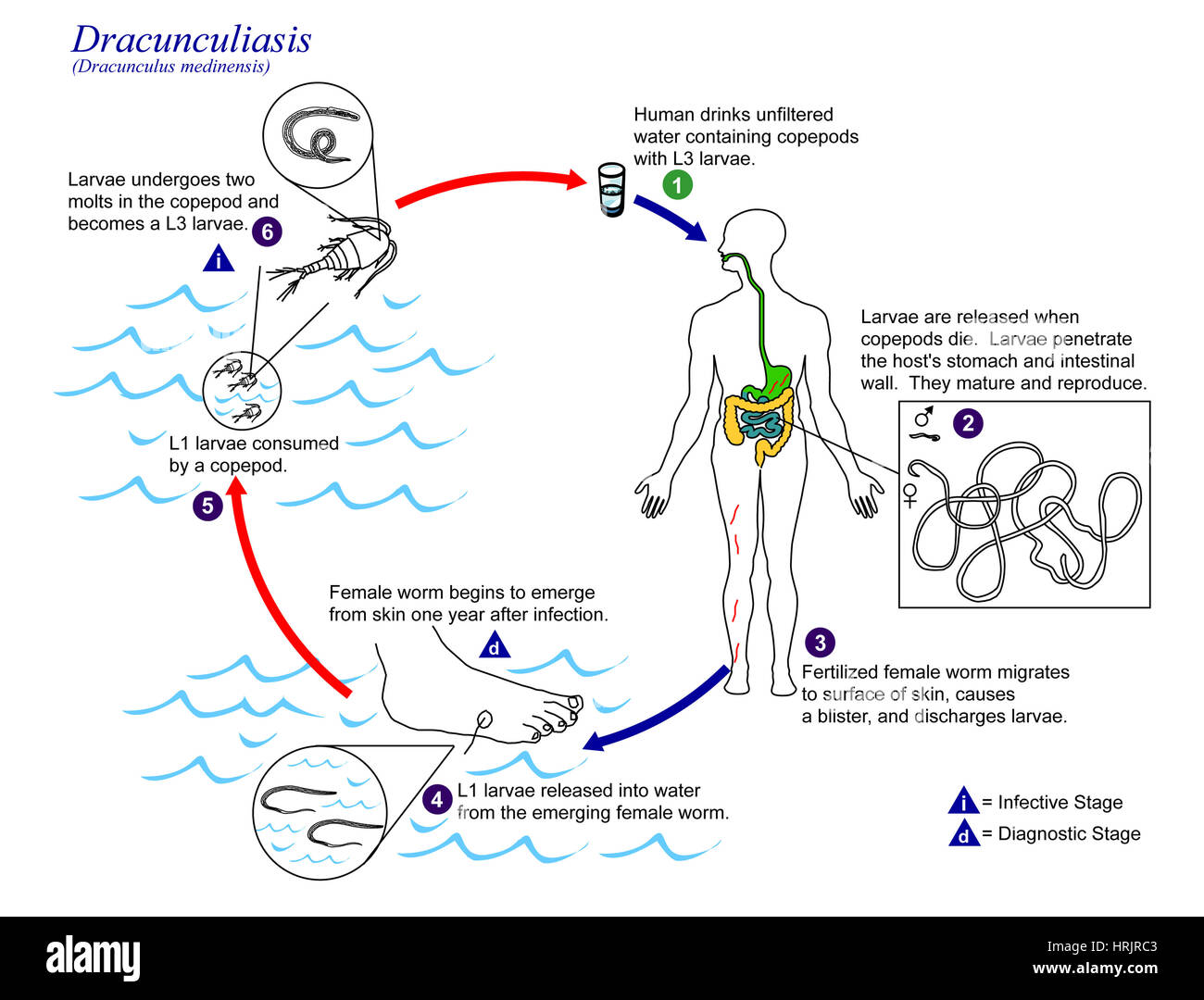
Guinea worm
-2 hosts, (primary= human, secondary=copepods, small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat)
-Humans drink water with infected copepods(infective stage)→ copepods die, release larvae→penetrate host stomach & intestinal wall and enter abdominal cavity →mature and reproduce, male dies and female moves into thin skin (foot usually)→~1yr after, female worm induces blister on skin, which ruptures. When this comes into contact with water, female worm emerges & releases larvae→larvae are eaten by copepod, develop into larvae inside
-treatment by extraction using stick (winded up), prevention is to clean water (boil/filter), close to eradication
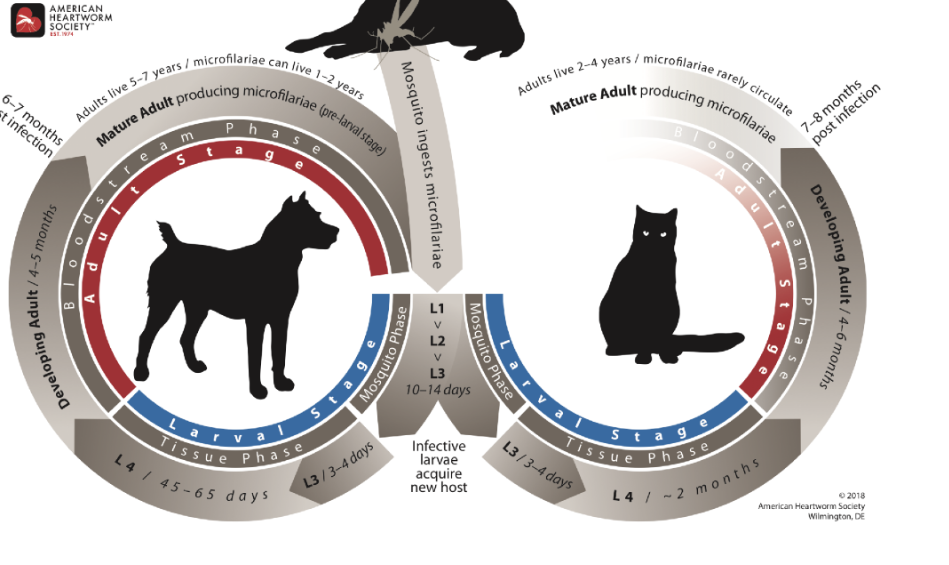
heartworm
-2 hosts, filarial worm (primary = dogs, cats, ferrets,
sea lions, occasionally humans, secondary= mosquitos)
-female mosquito bites infected dog & ingests microfilariae during→ microfilariae develop further for 10-30 days in mosquito's gut & then enter its mouthparts→ infective larvae go into another dog, blood→lungs→heart, mature in pulmonary artery
-Treatment involves injections (long, time consuming, difficult) while prevention is medicine
Eutely
the number of cells in adults is always the same
Ecdysis
shedding an old cuticle and making a new one
Locomotion
– Longitudinal muscles (ONLY, no circular) arranged
in 4 bands connected to nervous system via muscle arms (very unusual)
– the cuticle and high pressure in pseudocoel.
• Pseudocoelom with high hydrostatic pressure, functions
as an hydrostatic skeleton & aids in locomotion
reproduction
dioecious, male smaller than female and has copulatory spicule (just a guide/stabilization) that allows for internal fertilization
free living: direct development, parasitic: free-living juveniles stages, maybe intermediate hosts