lab 5: energy transformations in cells
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what indicator was used to monitor pH levels?
bromothymol blue
list the colours of bromothymol blue indicator
yellow = acidic (pH < 7)
green = neutral (pH = 7)
blue = basic (pH > 7)
Flasks A and B both have 100mL of tap water, 0.5M NaOH and 5mL of bromothymol blue indicator in each flask. 10mL of tap water is added to Flask A, while a 10mL of pH 9 buffer is added to Flask B. Blowing CO2 to the flasks, why did they eventually turn yellow in colour?
The H2O in the flasks reacted with the CO2, producing carbonic acid (H2CO3), which can dissociate into H+ ions and decrease the pH level -- making it more acidic, to which bromothymol blue will turn yellow.
Flasks A and B both have 100mL of tap water, 0.5M NaOH and 5mL of bromothymol blue indicator in each flask. 10mL of tap water is added to Flask A, while a 10mL of pH 9 buffer is added to Flask B. Blowing CO2 to the flasks, which flask would require more breaths until it turned yellow? Explain.
B, because of the presence of the pH 9 buffer, it required more CO2 to react with water to produce enough carbonic acid (H2CO3) to eventually lower the pH from 9 to less than 7.
Flasks A and B both have 100mL of tap water, 0.5M NaOH and 5mL of bromothymol blue indicator in each flask. 10mL of tap water is added to Flask A, while a 10mL of pH 9 buffer is added to Flask B. Why was it necessary to add 10mL of water in Flask A?
Denature
loss of the secondary and tertiary structure of the protein
How can a protein denature?
change in pH
What is produced when CO2 reacts with H2O?
carbonic acid (H2CO3)
What does a finger pulse oximeter detect?
a person's oxygen saturation level (the percentage of hemoglobin in arterial red blood cells carrying O2)
What does the oximeter do?
sends 2 wavelengths of light
Describe what each wavelength of light from the oximeter does.
1 wavelength detects red blood cells w/ O2 bound to hemoglobin
1 wavelength detects red blood cells w/unbound hemoglobin
What is the normal value for O2 saturation?
95-100%
In a table with O2 saturation, pulse rate, ventilation rate with rest and exercise divisions, which measurements would show an increase in the exercise division? Why would they be higher (give an explanation for each measurement given)?
In a table with O2 saturation, pulse rate, ventilation rate with rest and exercise divisions, which measurements remained the same in both divisions? Why would they be the same (give an explanation for each measurement given)?
A germinating seed and a dormant seed have an initial temperature of 22C, will heat be generated in one or both seed/s. Explain the significance of your answer.
Seeds are plant tissue and plants can perform both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Which process is producing heat, and how do you know?
cellular respiration produces heat
What metabolic process can still transform energy in organic compounds to produce ATP in the absence of O2?
fermentation
What is an example of fermentation in humans?
lactic acid fermentation
What organism can perform alcoholic fermentation, and what do they produce?
Yeasts
Ethanol
Draw the summary equation of alcoholic fermentation.
What does CO2 form with Ca(OH)2 (limewater)?
calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
Flask A has yeast and sucrose, while Flask B only contains sucrose. Each of these flasks are attached to a flask of limewater (Ca(OH)2). The flask of limewater attached to Flask A has calcium carbonate (CaCO3) present, but not with Flask B. Is CO2 coming from the yeast culture? Explain your answer.
yes, cellular respiration?
Which reagents will react with ethanol to produce a distinct colour to indicate its presence?
potassium dichromate (K2CrO4) and sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
What is the purpose of a positive and negative control?
positive control demonstrates what the positive results look like, and negative control demonstrates what negative results look like and checks for contaminants
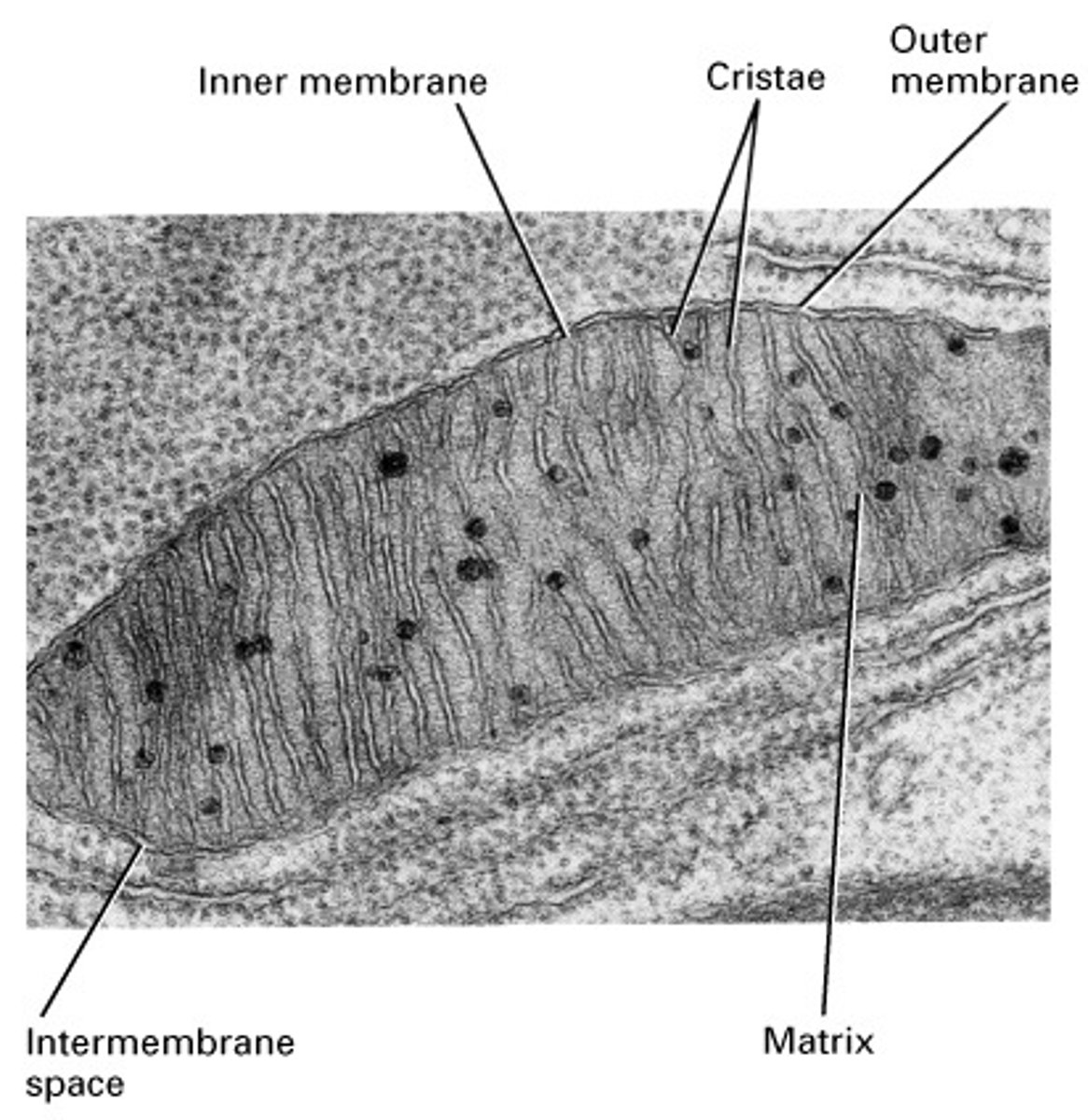
Name and label the organelle and the parts indicated.
Draw the cellular respiration reaction.
What are the stages of cellular respiration in order?