HCI Final Exam Review
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Prototyping Theory
Principles and practices of creating prototypes during the design and development of interactive systems. Involves building systems to explore, test, and refine design ideas before committing to full-scale development
Low-Fidelity
Just enough details to communicate the idea (layout/structure…)
Focuses on the solution/idea not the visuals
Done quickly and in high amounts
Medium-Fidelity
Iterating on the low-fidelity, focusing on how the idea could be implemented. Incorporates basic visuals such as color (not many), typography and graphics.
High-Fidelity
Feature polished design that emulates the look and feel of the final product.
Used for demonstrating to stakeholder, usability testing, gathering feedback on designs and interactions.
Role Prototypes
Focuses on everything surrounding the idea itself. Looks at the benefits the user will experience, how the concept would function in the user’s life and the context it exists in (slice of life)
Includes: Storyboarding, journey mapping, concept videos
Look & Feel Prototypes
Defines the sensory experience of interacting with the idea (the sensory experience)
Includes: Wireframing, moodboards, interactive demos
Implementation Prototypes
How the idea will be produced and delivered as a solution. Focuses on the logistics of making the idea real (nuts and bolts)
Low fidelity: pseudocode, state machine diagram, flowcharts
Medium fidelity: test cases, benchmarks
Integration Prototypes
Built to represent the complete user experience. Bringing together role, look and feel, and implementation
Hierarchy of Saliency
Levels of ‘attention’ (saliency = attention). Things like color, thickness, size, tone, etc., can play a role in drawing more attention to certain design aspects
Serif
A small decorative flourish on the end of the strokes that make up letters and symbols
Used: Where legibility matters, high resolution displays, paragraphs
Sans Serif
No flourishes on the end of the stroke of letters and symbols
Used: Where readability matters, low resolution displays, headings and titles
Mono
Fonts where characters each occupy the same amount of horizontal space
Used: Where alignment matters (code editors)
Hue (HSV)
Represents the pure color
Saturation (HSV)
Represents the intensity of the color
Value (HSV)
Represents the brightness or lightness. Determine how light or dark a color appears
Slips
Occurs when the goal is correct, but the required actions are not done properly (task understood, bad execution)
Mistakes
Occurs when the goal or plan is wrong (task misunderstood)
Mental Models
An internal representation or understanding that a user develops about a system after interacting with it
Metaphors
Used to map an existing mental model to the actions and feedback of a target interaction
Gulf of Execution
The gap between the user’s goals or intentions and the actions they need to take
Plan, Specify, Perform
Gulf of Evaluation
The gap between the system’s output and the user’s understanding or interpretation of the state
Perceive, Interpret, Compare
Murray’s Four Affordances
Participatory Affordances
Encyclopedic Affordances
Procedural Affordances
Spatial Affordances
Cognitive Affordances
Aligning with user’s existing mental model and expectations
Participatory Affordances
Design features or characteristics of an interface that encourages and enables users to actively engage, contribute and collaborate in the interaction process
(Empowers users to play an active role in shaping their experience)
Creating the feeling of agency
From Content-Consumer to Producer
Spatial Affordances
Design features and characteristics of an environment that provide cues and signals to users about how to interact with and navigate through that space
Repetition: Power Law of Practice/Flow
Encyclopedic Affordances
How information is organized within an interface
The Medium is the Message
The nature of the medium (where or how the content is presented) can be just as or even more influential than the actual message itself
Empathy Maps
A way to structure how we can empathize with our users
Personas
A depiction of a user group (not a single person) that is used to mitigate egocentric fallacy (designing for yourself)
Helps subvert stereotypes
Pre-attentive Cues
Visual Stimulus that can be perceived and processed in the sensory memory without requiring conscious attention (detected automatically, often within 200-250 milliseconds)
Use preattentive cue to reduce the cognitive load on the user
Working Memory
A part of short-term memory responsible for temporary storage
Capacity: 7 ± 2 chunks
Chunking
Decompose complex information into chunks, making it easier for working memory and cognitive process
3 chunks (sweet spot)
LTM (Long-term Memory)
A part of our memory system responsible for storage and retrieval of information over long periods of time
STM (Short-term Memory)
Responsible for temporarily storing and managing information required for completing complex tasks.
Auditory Stores
Audio half-life: 1500ms
Visual Stores
Visual half-life: 200ms
Medium Props
The physical or conceptual tools and elements that are used to convey messages through various media
useState
A React Hook that allows you to add state to functional components in order to manage and update dynamic data within the component.
const [plants, setPlants] = useState([‘Rose’, ‘Lily’]);
Flexbox
A CSS Layout model that is direction-agnostic. (can layout items horizontal/vertical)
display: flex
flex-direction: horizontal
align-items: flex-start
KLM (Keystroke Level Model)
K - Keystroke - 80ms(best)/200ms(avg)/750ms(bad)
P - Pointing - 1100ms
H - Homing - 40ms
M - Mental Prep - 1350ms
Typing (‘hello world’) = M (mental prep) + 11K (keys)
Fitts’ Law
Movement time calculation for moving mouse to target
MT - Average Movement Time
a - empirical constant, device specific
b - empirical constant, device specific (smaller b = faster input)
D - distance from starting point to the center of the target
W - width of the target measured along the axis of motion (error tolerance)
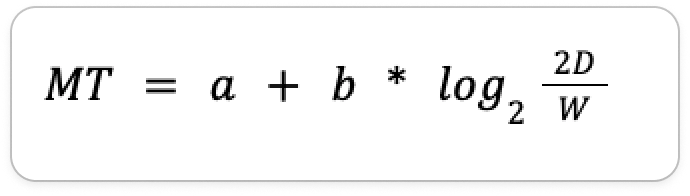
Hicks’ Law
The time it takes to make a decision increases with the number of choices given
RT - reaction time
a - empirical constant, device dependent
b - empirical constant, user dependent
n - number of choices
+ 1 = null decision (choice of not acting)
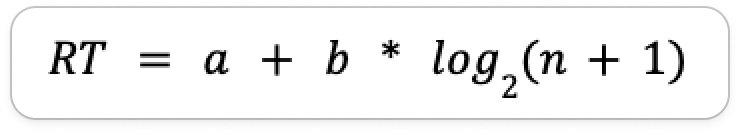
Touch vs. Screen Interactions
Affordances of touch interactions: Gestures (swipe, pinch)
Representational Strategies (PA)
Gather > Props > Expose > Evaluate
Places and Waypoints
Affective Design
LTM (SA)
Likert Scales
Semantic Differentials
Accessibility
Participatory Models
Machine Model
Tool Model
Companion Model
Game Model
Organization (EA)
Taxonomy
Typology
Ontology
Schemas
Encouraging Participation (PA)
fetch
useEffect
Semantic UI
Prototyping Encyclopedic Affordances