Biol 226 (A&P II) Lab Exercise 6 - Heart Rate, Electrocardiogram, and Volume Pulse
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
P wave
This waveform on an ECG tracing represents atrial depolarization
QRS complex
This waveform on an ECG tracing represents atrial repolarization plus ventricular depolarization
T wave
This waveform on an ECG tracing represents ventricular repolarization
P-Q interval
This portion of an ECG is the time between depolarization of the S-A node and depolarization of the A-V node. It represents the time it takes for the signal to travel throughout the atria.
Duration of the QRS complex
This portion of an ECG is the time necessary for complete depolarization of ventricular fibers, the signal travels down the A-V bundle and out through Purkinje fibers
Q-T interval
This portion of an ECG represents the complete depolarization and repolarization of the ventricles
R-R interval
This portion of an ECG represents the time required for one complete cardiac cycle
The number of cardiac cycles (beats) per minute can be calculated by:
(1 beat/R-R interval in seconds) x (60 sec/1 min) = beats/min
How do you calculate heart rate from an ECG tracing using the R-R interval?
Volume pulse
The peak of this measurement represents the maximum pressure in the vessel when the left ventricle ejects blood into the systemic circulation
The elapsed time between the electrical depolarization of the ventricles and the physical contraction of the ventricles
What does the time between the R wave and the peak volume pulse represent?
A lengthened Q-T interval can increase the risks of ventricular tachyarrhythmia and sudden death. This could be caused by hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia. Long Q-T syndrome is a condition associated with delayed repolarization of the ventricles. This is caused by an inherited gene that regulates K+ channels in the heart.
What is the significance of an abnormally long Q-T interval?
Low blood calcium would cause premature depolarization. Calcium blocks sodium channels, so a decrease in calcium means more sodium channels are open, leading to increased excitability
How could hypocalcemia cause an increase in the Q-T interval?
High blood calcium would delay repolarization by prolonging the plateau phase
How could hyercalcemia cause an increase in the Q-T interval?
Repolarization is due to the efflux of potassium ions. If these channels fail to open in a timely fashion, repolarization will be delayed
Why would abnormal activity of potassium channels in the heart cause delayed repolarization of the ventricles in regards to Long QT syndrome?
Mass of tissue involved (more tissue mass = greater amplitude); fluid in pericardial cavity (more fluid = less amplitude)
What factors might lead to differences in the relative magnitudes of waveforms?
Yes. Any two wave forms may be used as long as you measure from the same point in two successive wave forms
Could you calculate heart rate from an ECG tracing using other waveforms?
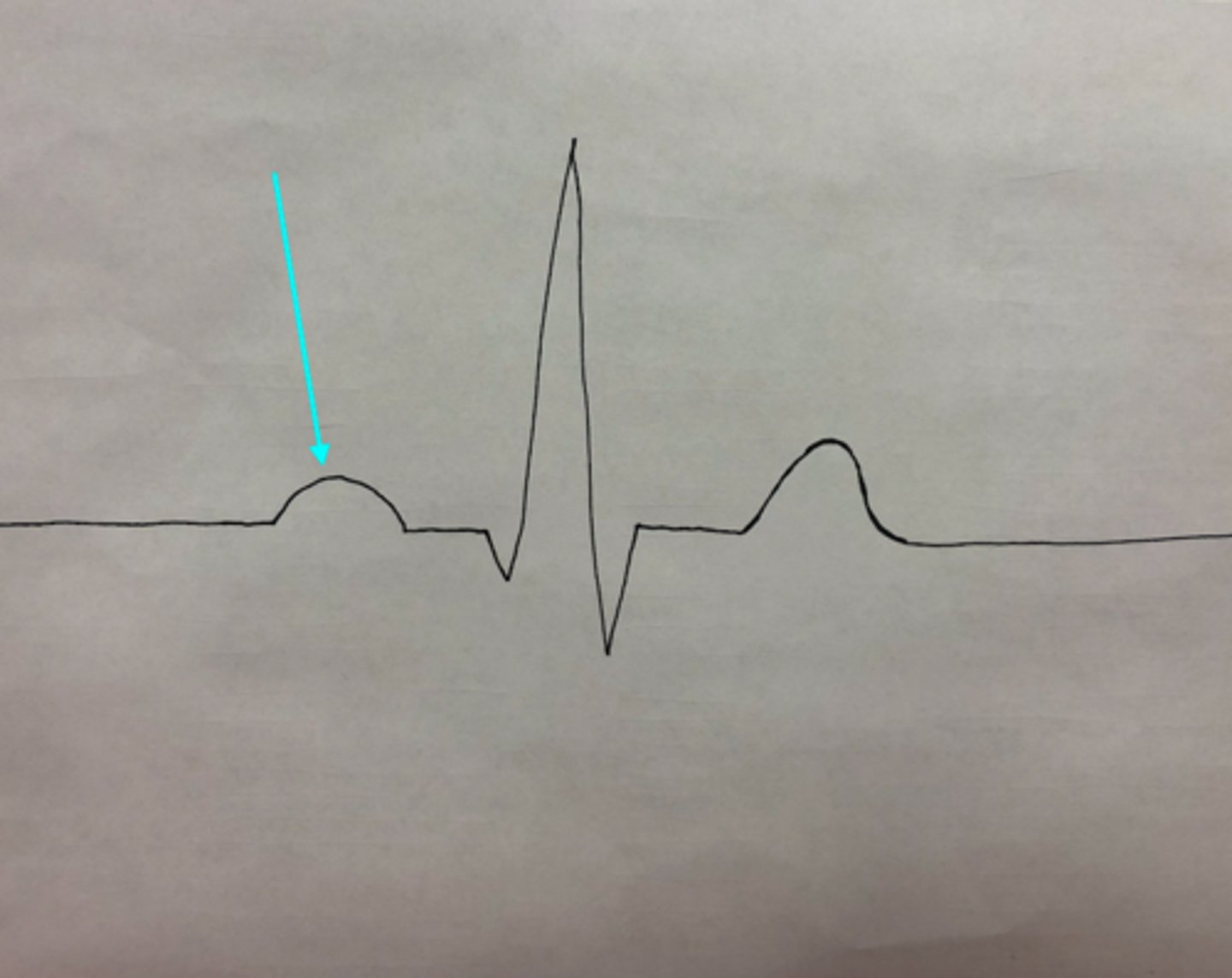
P wave
What feature of an ECG is the blue arrow pointing at?
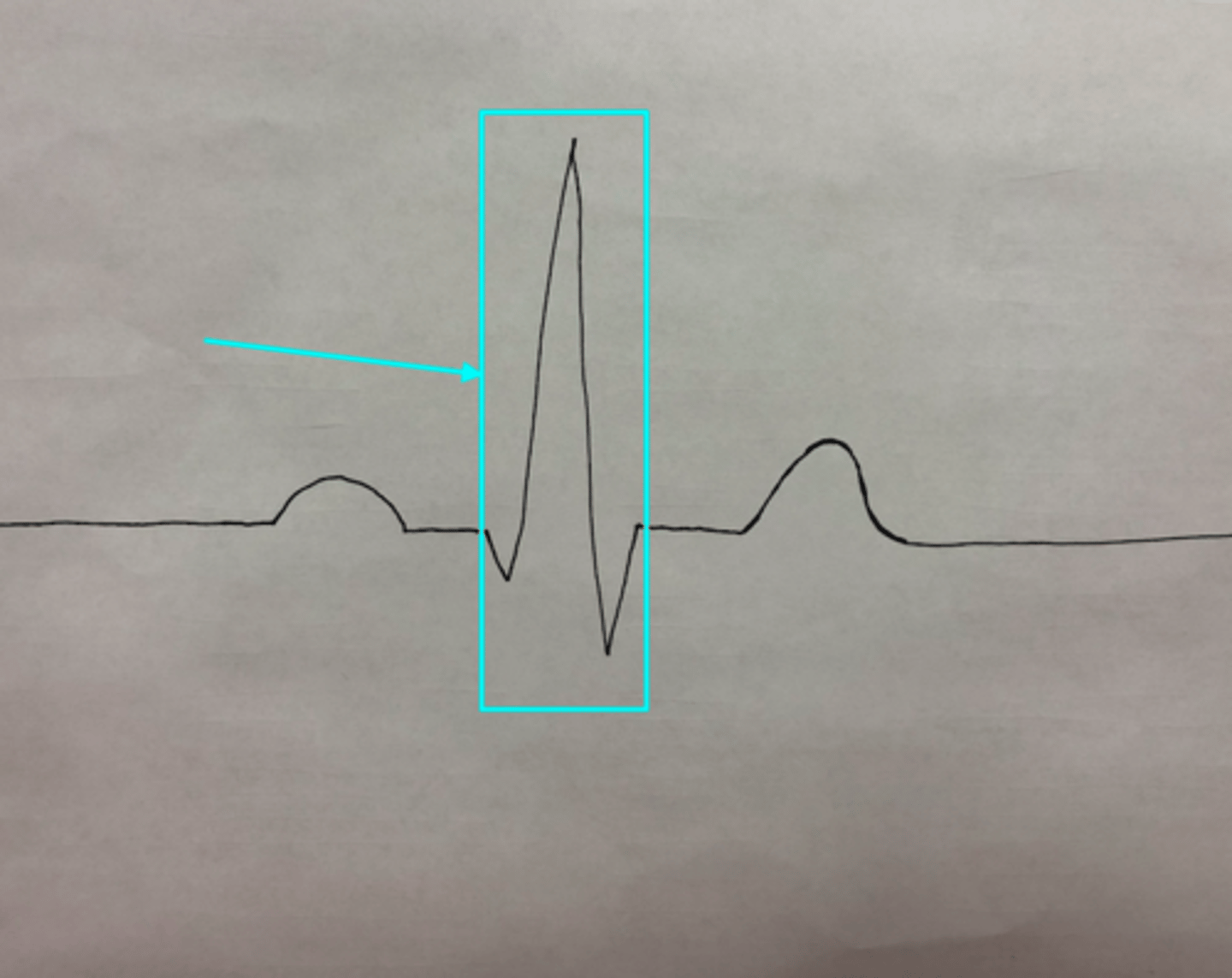
QRS Complex
What feature of an ECG is the blue arrow pointing at?
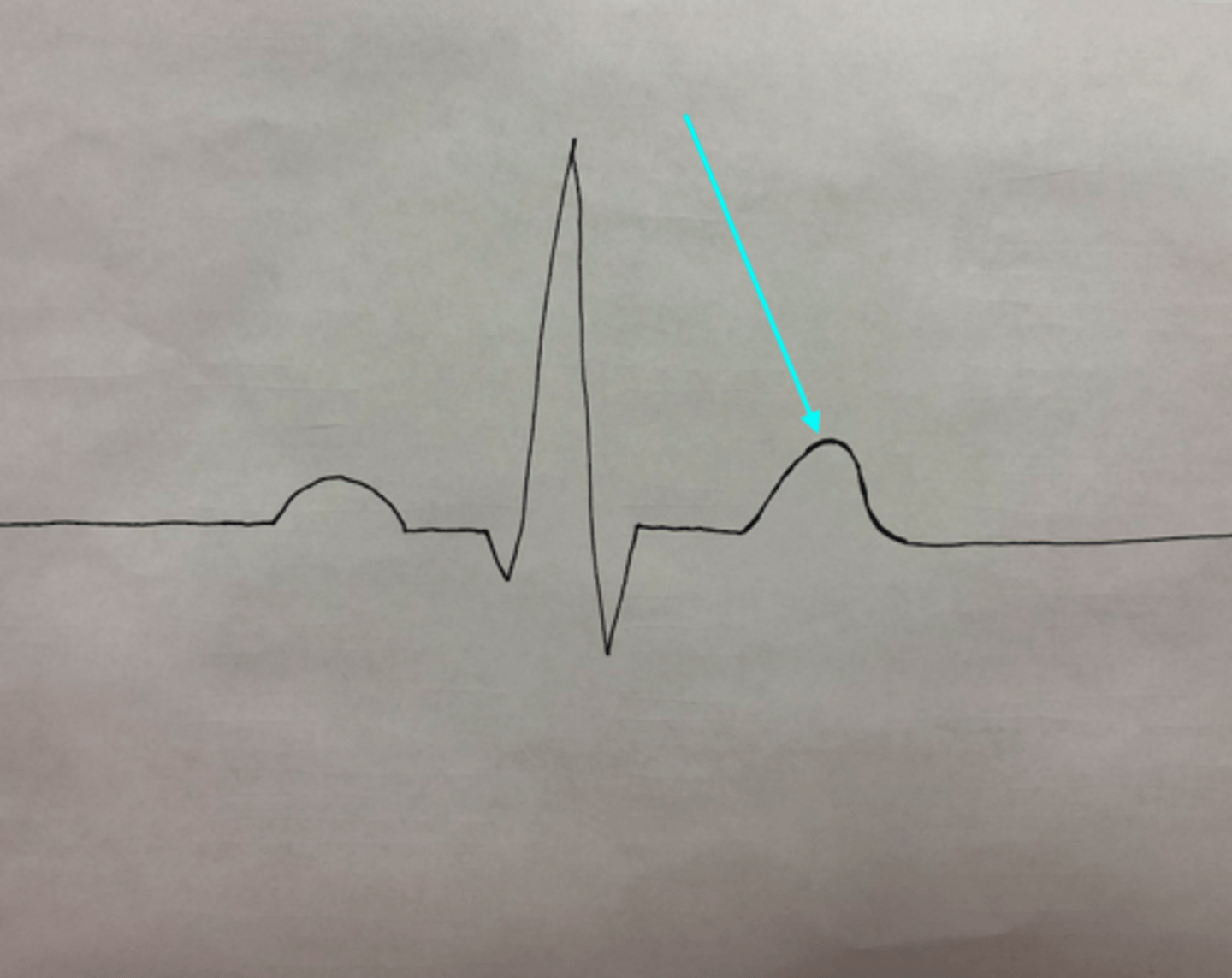
T wave
What feature of an ECG is the blue arrow pointing at?
P-Q interval (also known as PR interval)
What feature of an ECG is the blue arrow pointing at?
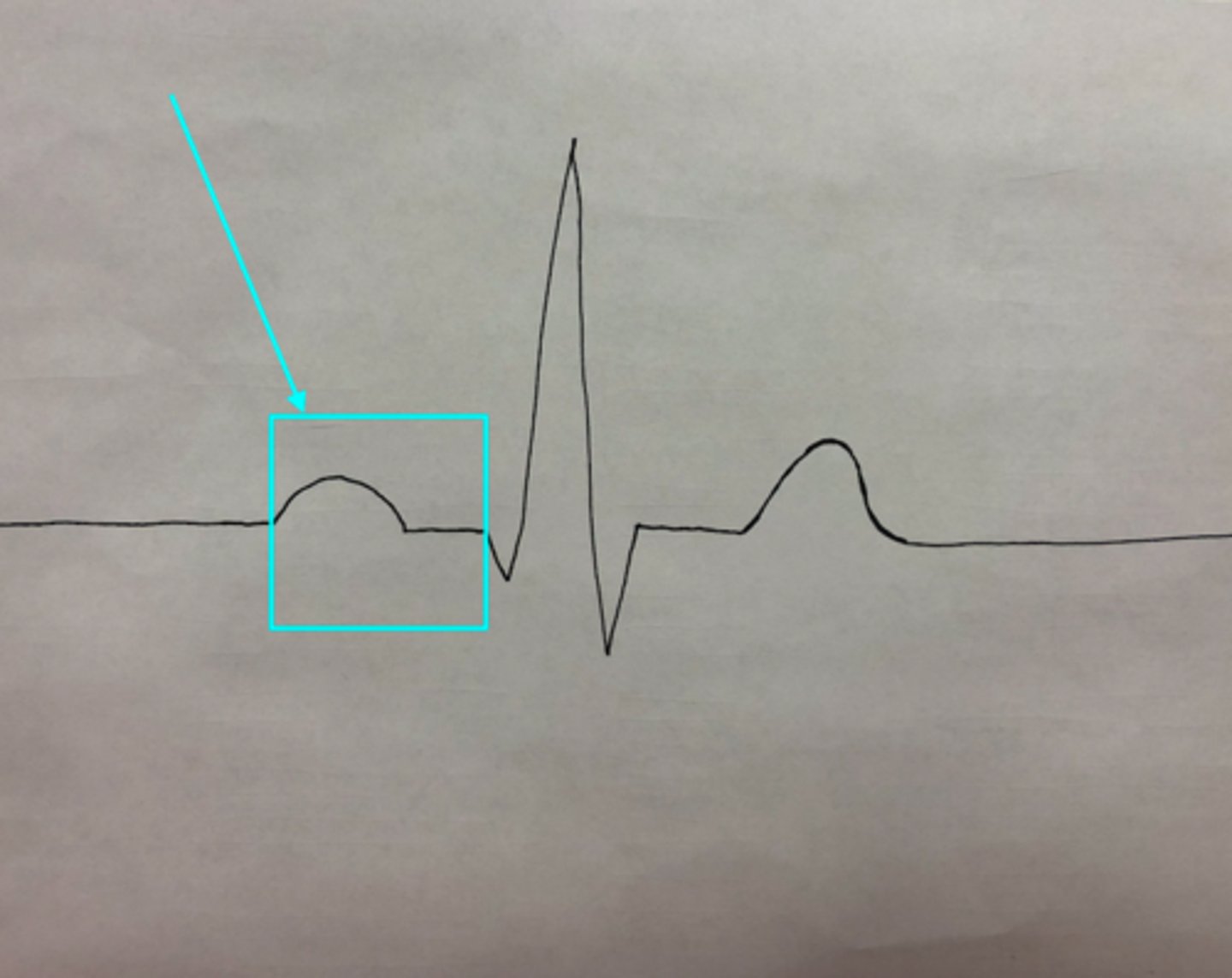
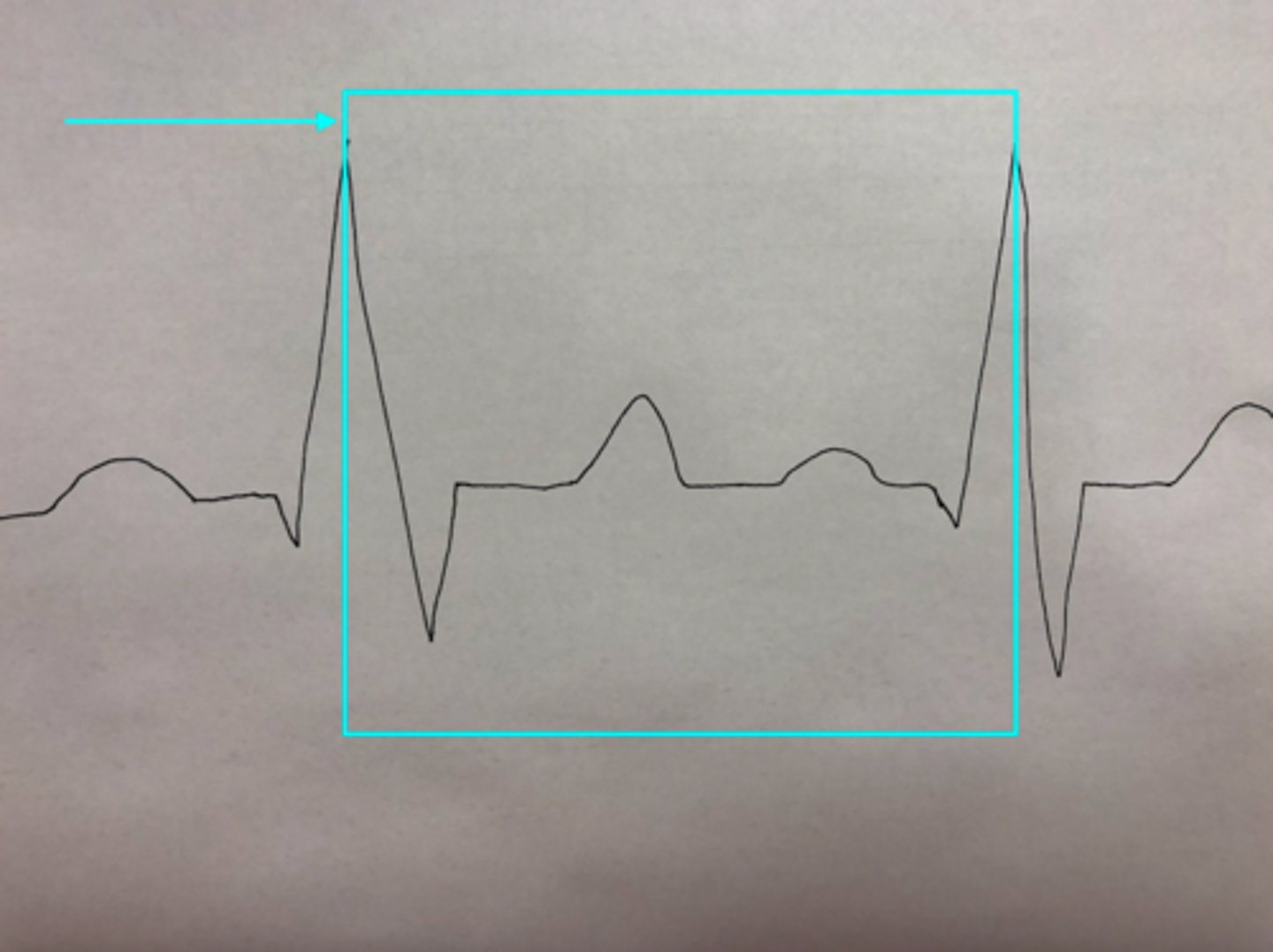
Q-T Interval
What feature of an ECG is the blue arrow pointing at?
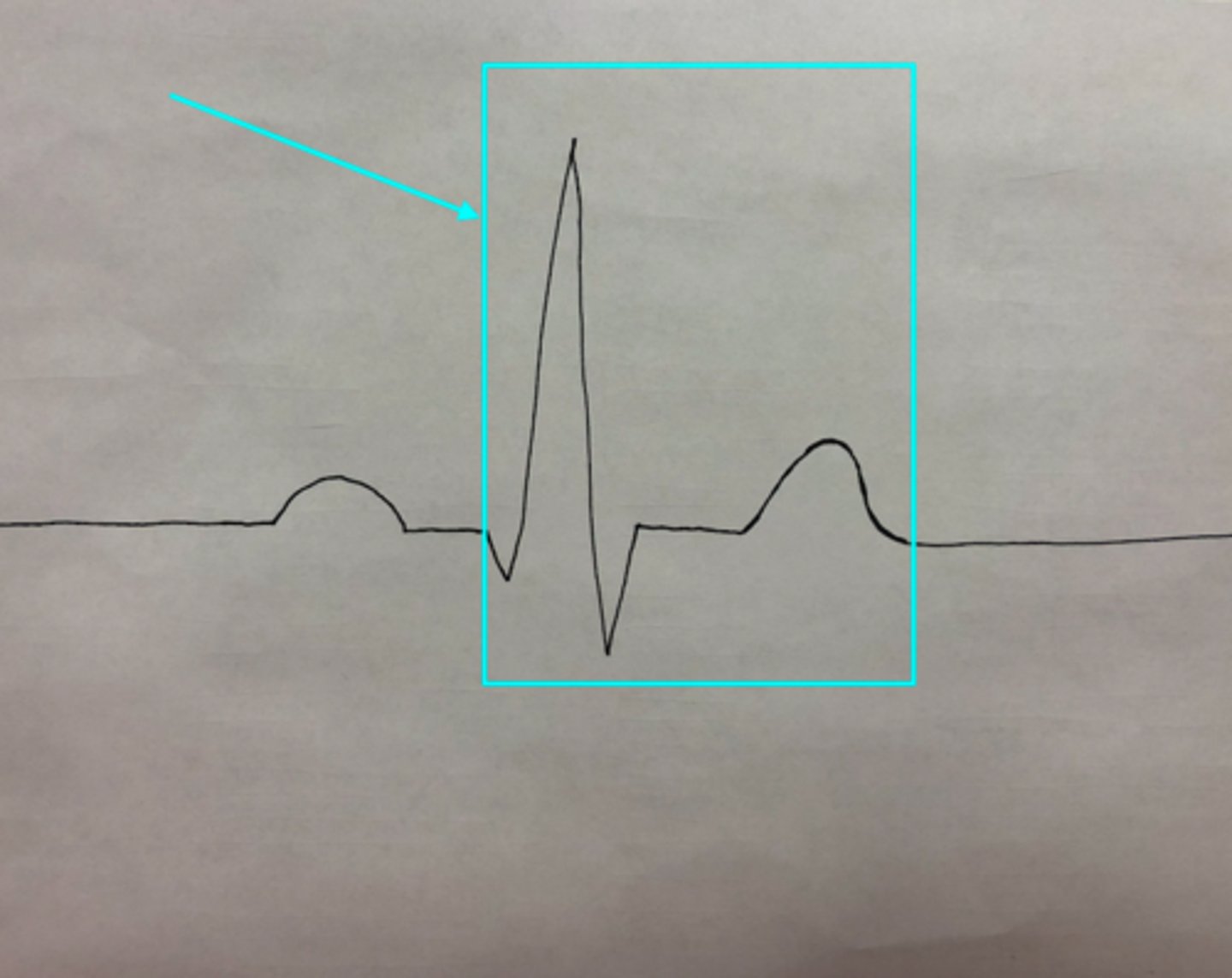
R-R Interval
What feature of an ECG is the blue arrow pointing at?