Acids,bases + salts
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Acid
A species that is a proton donor
PH less than
7
Strong acids
Acids that fully dissociate in water
Examples of strong acids
H2SO4, HCl, HNO3
H2SO4
Suluric acid
HNO3
Nitric acid
Weak acids
Acids that only partially dissociate in water
Examples of weak acids
C6H8O7, HCOOH + other carboxylic acids, CH3COOH
C6H8O7
Citric acid
HCOOH
Methanoic acids
CH3COOH
Ethanoic acid
Ion released when acids split up not component ions
H+
Examples f mono basic acid
HCl
Example of dibasic acid
H2SO4
Example of tribasic acid
H3PO4
When does dissociation not occur
When reactions are reversible
Bases
Species that are proton acceptors
What do bases tend to have
Species with lone pairs
Common bases
Metal oxides and hydroxides
Examples of metal oxides
MgO, CuO
Examples of metal hydroxides
NaOH, Mg(OH)2
What are all amines
Bases eg CH3NH2
What can b Sid about the relationship between alkalis and bases
Al alkalis are bases but not all bases are alkalis
Alkalis
A type of base that dissolve in water to form a hydroxide ion
Alkalis have a pH greater than
7
Alkalis have a pH greater than
7
Common alkalis
So idus hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), ammonia (NH3)
Easy way to tell is acids or alkalis are strong or weak
Strong are irreversible reactions, weak have double headed arrow= reversible reaction
Is ammonia a strong or weak alkali
Weak
What can amino acids be described as being and why
A substance that can behave as both and acid and as a base
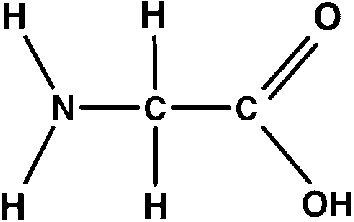
Show how amino acids are amphoteric
H-N-H is the amine group which is a base, OH-C—O is a carboxyl group which is acidic
Salts
An ionic compound formed from an acid when the H+ ion has been replaced by a metal ion or other positive ion eg NH4+
Features of salts
Positive cation in a salt is usually a metal ion or an ammonium ion, negative ion is derived from the acid
Sulfuric acid goes to what salt
Sulfate salts- NaOH + H2SO4→ Na2SO4
Hydrochloride acid goes to what salt
Chloride salts eg HCl→ NaCl
Nitric acid goes to what salt
Nitrate salts eg HNO3→ Ca(NO3)2
Acid + base/alkali=
Salt + water
Acid + metal carbonate→
Salt + carbon dioxide + water
Acid + metal→
Salt + hydrogen
Example of MASH
2Na + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H2
Example of acid + base
2HCl + MgO → MgCl2 + H2O
Example of metal carbonate + acid
2HCl + CaCO3 → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O