Exam 2: Jarvis Ch 4-11: Health History, Mental Assessment, Substance Abuse, Domestic Violence, Assessment Techniques, Vital Signs, Pain, & Nutrition
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
Purpose of the complete health history is...
to collect subjective data
Database
Combining subjective data with objective data from the physical examination and lab studies
For ill patients, the health history includes...
detailed chronological record of the health problem
For all patients, the health history...
is a screening tool for abnormal symptoms, health problems and concerns. It also records health promotion behaviors and coping skills
Health History
1. Biographical Data
2. Source of the history
3. Reason for seeking care
4. Present health or history of present illness + symptom analysis
5. Past health events
6. Family History
7. Review of symptoms
8. Functional Assessment
Biographical data
ex: patient's name, date of birth, occupation, primary language, communication needs...
Source of the history
this is usually the patient, but may be someone else, such as a relative or interpreter
Reason for seeking care
(formerly known as "chief complaint")
In the patient's own words, briefly describe the reason for the visit stating one or two symptoms or signs and their duration
Present health or history of present illness
For a well person, briefly note the general state of health. For a sick person, chronologically record the reason for seeking care. When a patient reports a symptom, perform a symptom analysis including location, character or quality, quantity or severity, timing, setting, aggravating or relieving factors, associated factors, and patient's perception.
OLDCART
O - Onset
L - Location
D - Duration
C - Characteristics
A - Aggravating Factors
R - Relieving Factors
T - Treatment

Past health events
ex: illnesses, injuries, hospitalizations, surgeries, allergies, current prescribed and herbal medicines
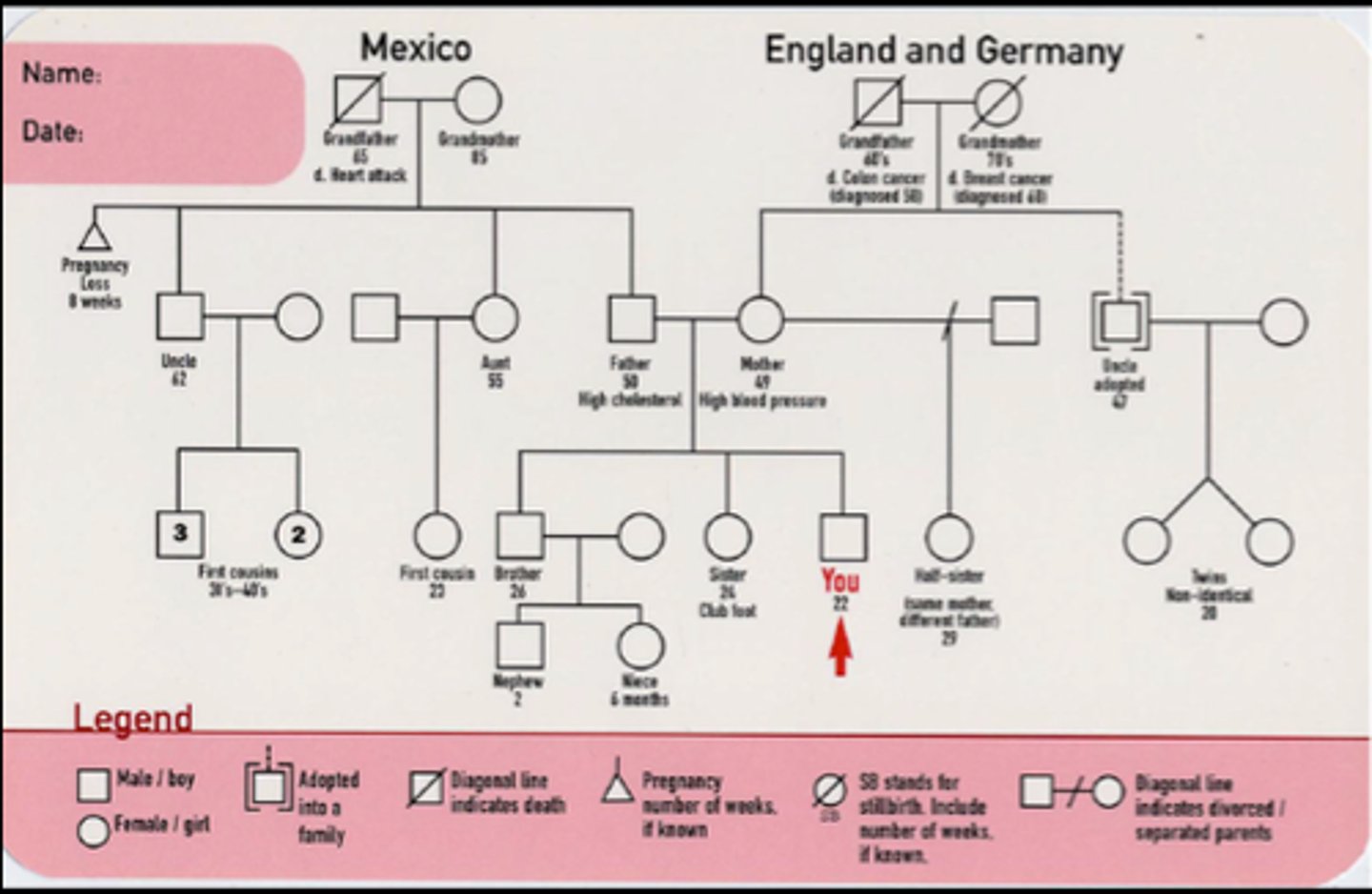
Family history
helps to detect health risks for the patient and assist with early screening and periodic surveillance
Review of systems
evaluate the past and present health of each body system, double-check for significant data that may have bee omitted, and assess health promotion practices
Functional assessment
activities of daily living + measuring a person's self-care ability
When obtaining a child's health history...
use the same structure you would use for an adult but make pertinent modifications or additions including:
*-a prenatal and perinatal history including the family unit
-the description of the present problem and who is providing the information
-any childhood illnesses or accidents
-immunizations
-a developmental overview
-a nutritional history*
Note: when assessing functional abilities, consider the child's environment and his/her function or role in the environment
When taking an older adult's health history...
ask additional questions such as exploring changes in activities of daily living that may result from the aging process or chronic illness. It is important to recognize positive health measures
Note: the impact/burden of a disease may be more important to an older adult than the actual disease diagnosis or pathology. Record the person's reason for seeking care, not your assumption about the problem
Mental Status
A person's emotional (feeling) and cognitive (knowing) function. Functioning related to ______________ is inferred by assessing the individual's consciousness, language, mood affect, orientation, attention, memory, abstract reasoning, thought process, thought content, and perceptions.
Mental disorders
apparent when a person's response is much greater than the expected reaction to a traumatic life event, including organic disorders and psychiatric mental disorders
The full mental status examination is a...
systematic check of emotional and cognitive functioning.
Its purpose is to determine mental health strengths and coping skills and to screen for dysfunction.
An initial brief screening suggests an anxiety disorder or depression. Family members express concern about a person's behavior, a patient has cerebral pathologic condition, aphasia is observed, emotional or cognitive changes are noted, or the symptoms of emotional problems are noted.
The 4 main components of the mental status assessment:
ABCT:
A - Appearance
B - Behavior
C - Cognitive Functions
T - Thought processes
When assessing appearance:
observe the patient's posture, body movements, dress, grooming, and hygiene

When assessing behavior:
evaluate level of consciousness, facial expression, speech and articulation, and mood and affect

When assessing cognitive functions:
check orientation, attention span, recent memory, remote memory, and new learning

When assessing thought processes:
ask questions to evaluate ____________, thought content, and perceptions. Also screen for anxiety disorders, depression, and suicidal thoughts

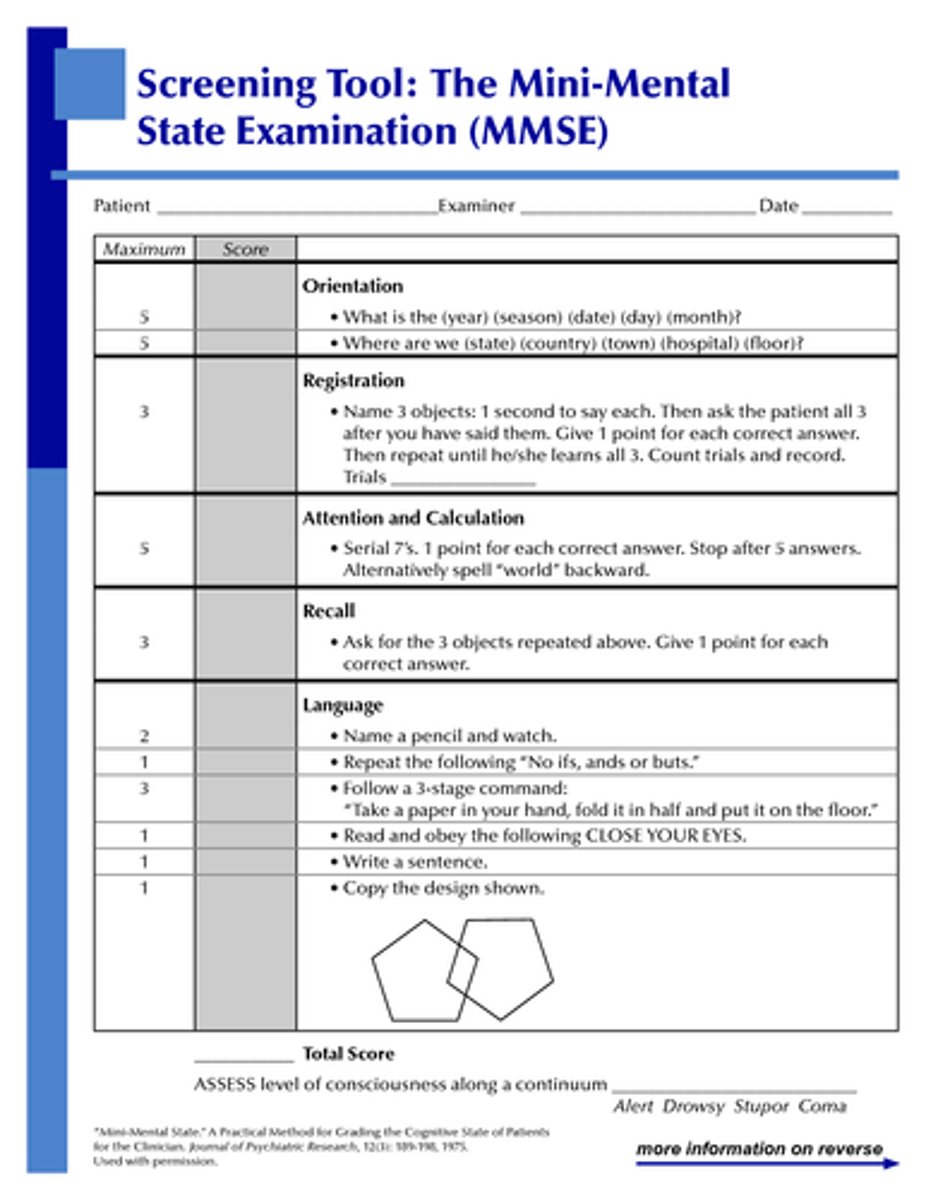
Mini-Mental State Examination
A simplified scored assessment of cognitive functions--not mood or thought processes. It includes a brief assessment of memory, orientation to time and place, naming, reading, copying or visual-space orientation, writing, and the ability to follow a 3-stage command. (Requires pencil and paper). Used to detect dementia and delirium and to differentiate these from psychiatric and mental illness
When examining an infant or child...
consider consciousness, language, attention span, and abstract thinking from a developmental perspective

For pediatric patients, the mental status assessment focuses on...
the child's behavioral, cognitive, and psychosocial development in coping with his/her environment
--Denver II screening tests allows direct interaction with the young child to assess the mental status
--the ABCT guidelines used for adults may be used for adolescents
Aging complications
Although mental status parameters remain mostly intact with aging, a slower response time may affect new learning. Also, age-related physical changes, such as vision or hearing deficits, may affect an older adult's mental status. (Before assessing an older adult's mental status, check sensory status and correct deficits, if possible.)
-Glasgow Coma Scale is useful for testing consciousness in aging adults
-Mini-Cog: a new, reliable, quick instrument to screen for cognitive impairment in otherwise healthy older adults

Alcohol
the most used and abused psychoactive drug

Excessive alcohol use
poses various risks that increase morbidity and mortality
-consumption of an average volume of _________ has a casual impact on many diseases including TB, cancer, diabetes mellitus, depression, heart disease, stroke, cirrhosis, and pneumonia
Alcohol dependence
a chronic progressive disease that is not curable but highly treatable. Excessive _______ use is often unrecognized until the patient develops serious complications
Illicit drug use and abuse...
remains a health problem

Illicit drug use
includes marijuana, cocaine, heroin, hallucinogens, and inhalants as well as nonmedical use of prescription pain relievers, tranquilizers, stimulants, and sedatives
Substance use and abuse is a _________________ concern
developmental
Here's WHY:
-Adolescents who use alcohol are at risk for decreased brain development and maturity levels
-Alcohol slips easily through the placenta to the fetus along with toxicity resulting in physical, learning, and behavioral problems in the child after birth
-Older adults have numerous characteristics that can increase the risk for alcohol use, such as decreased liver metabolism and kidney function and less muscle mass to which the alcohol can be distributed
To gather subjective data...
ask general screening questions r use an alcohol and drug abuse tool in a private, confidential, and nonconfrontational setting
--AUDIT
--CAGE
--TWEAK
--SMAST-G
AUDIT
a quantitative form with 10 questions that cover alcohol consumption, drinking behavior or dependence, and adverse consequences of alcohol
CAGE
uses the mnemonic _______ to ask 4 questions testing for lifetime alcohol abuse or dependence. It is less effective with women and minority groups
TWEAK
T - tolerance
W- worry
E - eye-opener
A - Amnesia
K - "kut" down
used for women with alcohol problems
SMAST-G
tool that can reveal an alcohol problem and a need for more in-depth assessment (used to assess older adults who report social or regular drinking)
To gather objective data...
consider the results of lab tests that may provide evidence of problem drinking:
-A significantly increased gamma glutamyltransferase (GGT) level suggests chronic heavy alcohol use
-An increase serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) level indicates months of chronic drinking
-An increased mean corpuscular volume (MCV) may identify heavy alcohol consumption for 4-8 weeks
-when the patient is intoxicated, a breath alcohol analysis can detect alcohol in exhaled air and correlates with the blood alcohol concentration
Prescription drug abuse
occurs when an individual takes a medication that was prescribed for someone else or takes a prescription in a manner or dosage other than what was prescribed
-the abuse of drugs normally prescribed for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is a growing problem, esp. among teens and young adults
Health care professionals must recognize, assess, and report [these problems], even if abuse or neglect is only suspected
intimate partner violence, child abuse, and elder abuse
4 types of intimate partner violence
1. Physical violence
2. Sexual violence
3. Threats of physical or sexual violence
4. Psychological or emotional abuse or coercion tactics
Child abuse and neglect includes:
-Neglect: the failure to provide for a child's basic needs
-physical abuse: nonaccidental physical injury
-sexual abuse: exploitation through prostitution or porn
-emotional abuse: any behavior pattern that harms a child's emotional development or sense of self-worth
Adolescent dating violence is...
physical, sexual, or psychological/emotional violence within a dating relationship and including stalking
Elder abuse
-physical abuse
-sexual abuse or abusive sexual contact
-psychological or emotional abuse including exposure to threats or coercive tactics
-financial abuse or exploitation
In all types of abuse, how much proof does the clinician need to report maltreatment to the appropriate authorities?
the clinician only needs a reasonable suspicion that the individual has been mistreated to make a report to the appropriate authorities
Abused women develop
more chronic health problems, such as neurologic, gastrointestinal, and gynecologic disorders and chronic pain. Abuse during pregnancy has serious consequences for both the mother and the fetus
Adolescents are at risk for adverse health outcomes...
similar to those of women, with adolescent relationship violence often becoming fatal
Older adults may experience...
complications from intentional injury ranging from minor pain and discomfort to life-threatening injuries. Abuse of older adults often is coupled with neglect
Children can develop...
long-term physical, psychological, emotional, social, and cognitive dysfunction due to abuse. There are various risk factors that may increase maltreatment from a caregiver, such as disabilities, poverty, substance abuse in the family, and community violence.
Routine, universal assessments for intimate partner violence involve...
asking every woman at every health care encounter if she has been abused by a husband, boyfriend, or other intimate partner or ex-partner
-can be screened with the Abuse Assessment Screen
The Abuse Assessment Screen
can be used to screen for intimate partner violence
-if a woman answers "yes" to any questions on the _____________________, carefully assess how recent and serious the abuse was. Convey a sense of concern, emphasize that the abuse is not the woman's fault, and state that help is available
How many screening tools are available to assess for adolescent relationship violence?
None
(it is important, however, to be aware of the factors that place adolescents at an increased risk for becoming victims)
For elderly patients, assessment of physical abuse or neglect in cognitively challenged patients is...
more complicated. Why?
red flags of abuse are physical findings that do not match the history
For children, when an injury is present or reported, an important part of the evaluation is to determine the...
child's age and developmental level
If a child is verbal, obtain a history...
away from caretakers.
Note: use open-ended questions or spontaneous statements
Be sure to assess the medical history and document...
prior to abuse, including intimate partner violence, childhood physical and sexual abuse, and prior rapes
Cumulative trauma
related to more severe mental and physical health problems
Physical examination of a known survivor of abuse includes...
a complete head-to-toe visual examination.
When your examination reveals physical findings, describe them using the correct basic medical forensic terminology. Describe bruising specifically and photograph it, if possible. Obtain specimens for baseline lab tests, if needed
Documentation of intimate partner violence, adolescent relationship violence, and elder abuse must include...
detailed, nonbiased progress notes, injury maps, and photographs. In written documentation, include verbatim statements by the victim that identify the reported perpetrator or severe threats of harm
For a woman who is suspected victim of intimate partner violence...
assess the risk of homicide, using the Danger Assessment, or a similar tool
If a woman denies intimate partner violence, but other indicators lead you to suspect abuse...
be persistent and thorough in the repeated assessment for domestic violence
Common barriers to treatments are:
societal stressors, legal status, lack of access to culturally responsive care, cultural values, and gender roles
Sequence of physical examination (according to Jarvis)
1. Inspection
2. Palpation
3. Percussion
4. Auscultation
Inspection
close, careful observation of the individual as a whole and then of each body system. Use the patient's body as the control and compare the right and left sides of the body to determine symmetry. _________ requires good lighting, adequate exposure, and sometimes the use of certain instruments, such as an otoscope or penlight
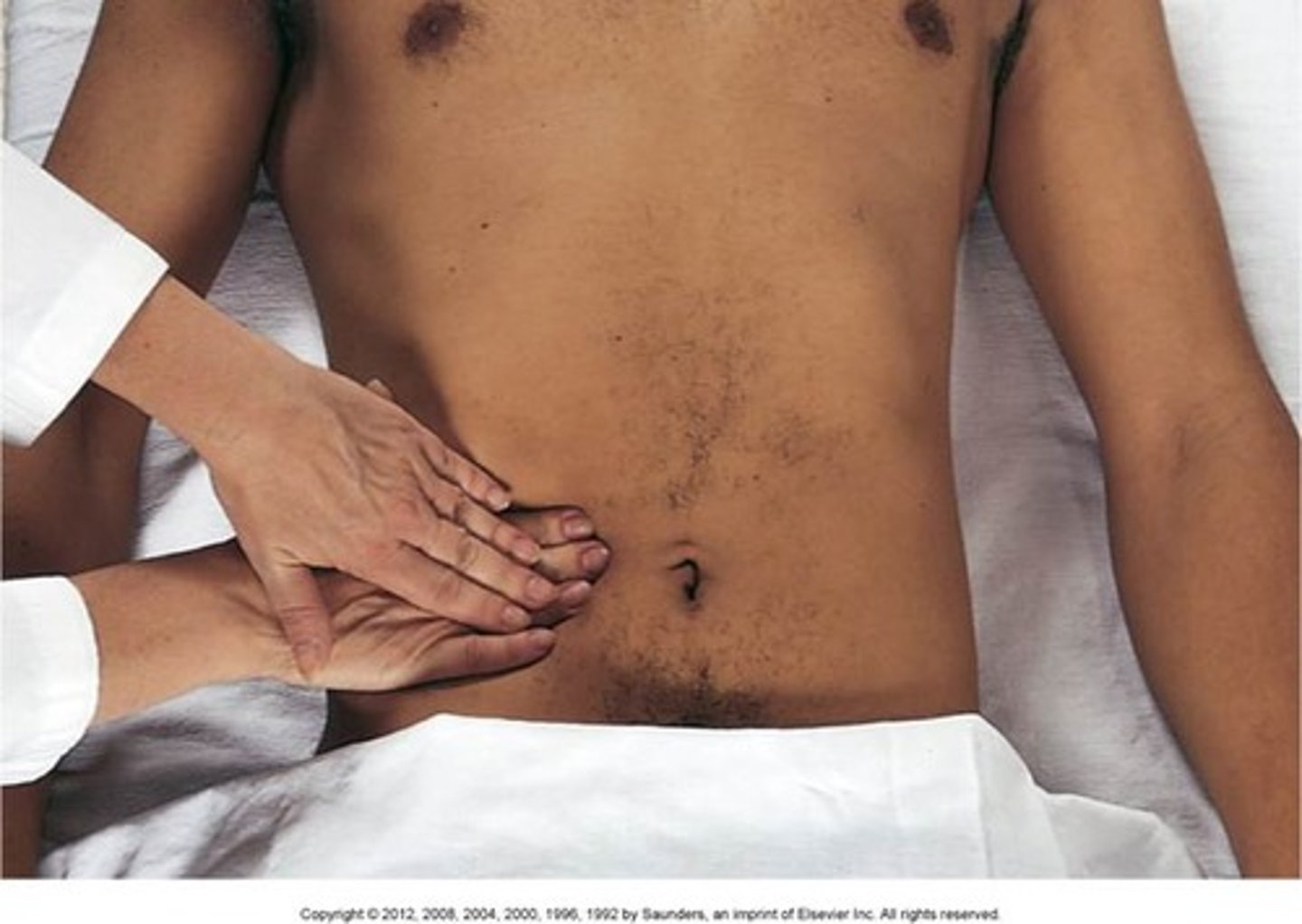
Palpation
the use of touch to assess texture, temperature, moisture, and organ location and size. This technique also helps identify swelling, vibration/pulsation, rigidity or spasticity, crepitation, lumps/masses, and tenderness or pain
The fingertips are best for...
fine tactile discrimination. Grasping with the fingers and thumb is ideal for detecting position, shape, and consistency of an organ or mass
The backs of the hands and fingers are good for...
determining temperature

The base of the fingers or ulnar surface of the hand is best for...
assessing vibration

Light palpation
detects surface characteristics and accustoms the person to being touched
Deep palpation
assess an organ or mass deeper in a body cavity
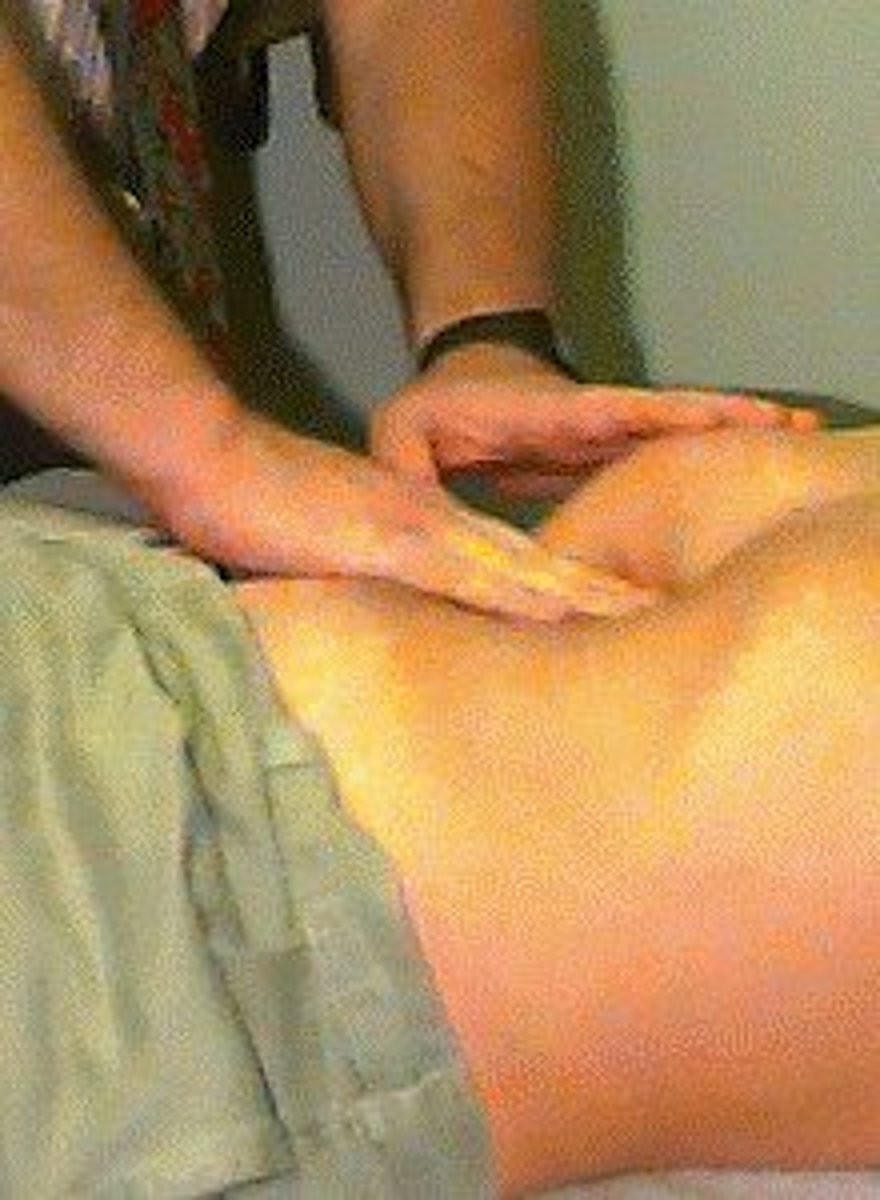
Bimanual palpation
requires the use of both hands to envelop or capture certain body parts or organs
Percussion
tapping the patient's skin with short, sharp strokes to assess underlying structures. This technique is used to assess the location, size, and density of an organ; detects a fairly superficial abnormal mass; or elicit a deep tendon reflex
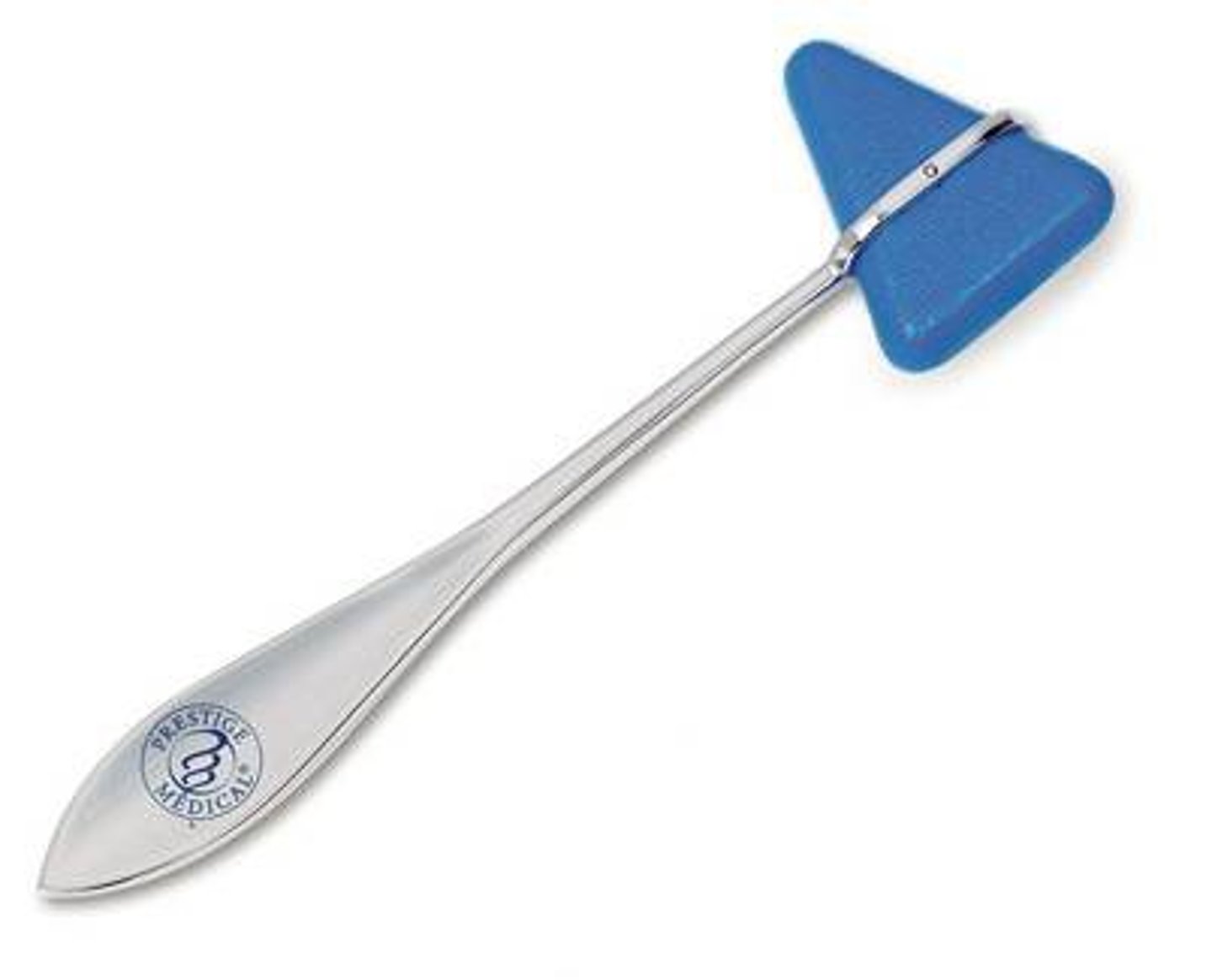

To perform percussion...
hyperextend the middle finger of our nondominant hand and place its distal joint and tip firmly against the person's skin. Then use the middle finger of your dominant hand to strike the stationary finger at a right angle. Deliver two even staccato (short) blows, using a quick wrist action
Each percussion sound has 4 components:
Amplitude- the sound's intensity, which may be loud or soft
Pitch- frequency describes the number of vibrations per second
Quality- (or timbre) is the subjective difference resulting from a sound's distinctive overtones
Duration- the length of time the note lingers
Auscultation
listening to sounds produced by the body, usually using a stethoscope. The heart, blood vessels, lungs, and abdomen are common areas
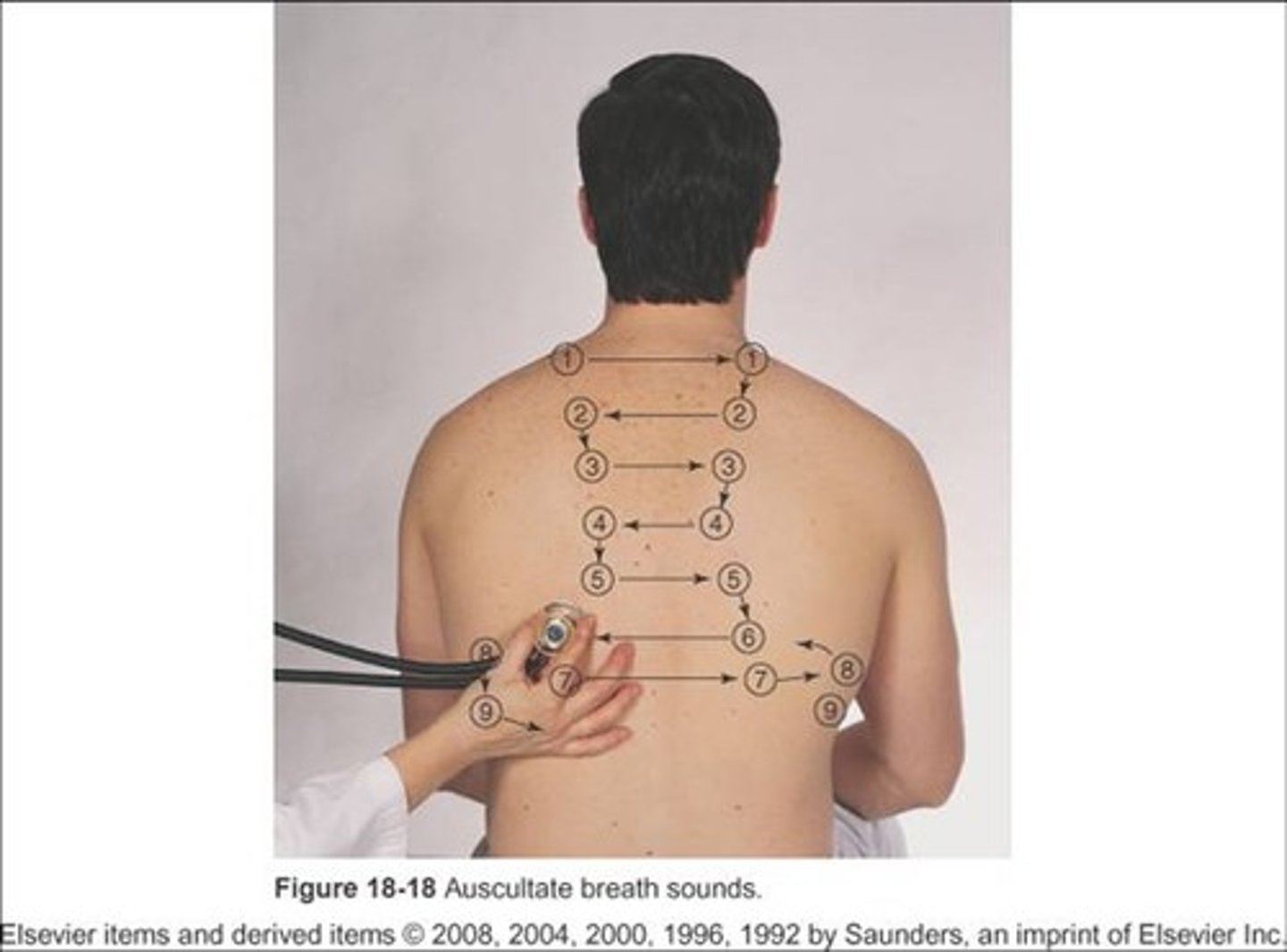
Use the stethoscope's diaphragm for...
high-pitched sounds (ex: breath, bowel, and normal heart sounds)

Use the stethoscope's bell for...
soft, low-pitched sounds (ex: extra heart sounds or murmurs)

To ensure accurate auscultation...
eliminate confusing artifacts (ex: making sure the room is quiet and warm and not listening through clothing)
The examination room should be...
warm, comfortable, quiet, private, and well lit
Before beginning the examination, ensure...
that all your equipment is within easy reach and laid out in an organized fasion
Observe infection control measures to...
prevent the spread of infection
What to do:
-maintain clean equipment and a clean field
-hand hygiene
-standard precautions
The most important step to decrease microorganism transmission is through...
handwashing or using and alcohol-based hand rub
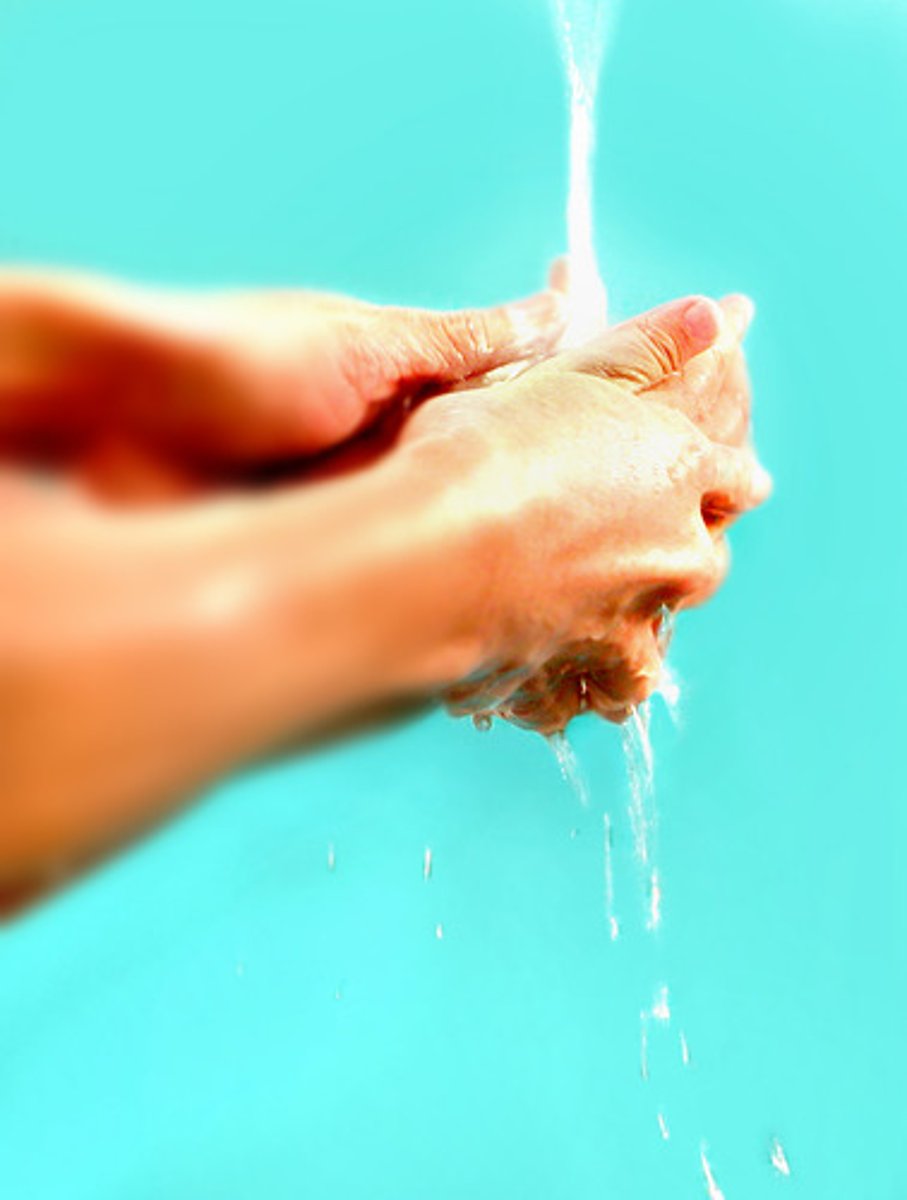

Perform hand hygiene...
before and after physical contact with each patient, after contact with body fluids or contaminated equipment, and after removing gloves
Use ________________ for all patients; use ______________________________ for patients with documented or suspected transmissible infections
1. standard precautions
2. transmission-based precautions
Reduce patient anxiety by...
beginning with familiar, non-threatening actions, such as measuring height, weight, and vital signs.
During the examination...
explain each step and how the patient can cooperate. Proceed systematically and offer brief teaching, as appropriate
When examining an aging adult...
adjust the position and preparation as needed. Pace the examination to match the older adult's pace, which may be slowed
When examining a patient in distressed, you may need...
to alter the position during the examination. First collect a min-database, and then complete the assessment after the initial distress is resolved
General survey
a study of the whole person, covering the general health state and any obvious physical characteristics. Covers:
1. Physical appearance
2. Body structure
3. Mobility
4. Behavior
Physical appearance
includes an assessment of the person's age, sex, level of consciousness, skin color, facial features, and overall appearance
Body structure
addresses stature, nutrition, symmetry, posture, position, body build or contour, and any obvious deformities
Mobility
is concerned with gait, range of motion, and the presence of involuntary movement
Behavior
considers facial expression, mood and affect, speech, dress, and personal hygiene
For a child, observe...
interactions with the accompanying adult. Unexpected behavior on the part of the adult or child may be clues to child abuse, mental illness, or a developmental disability or disorder
For an aging adult, be aware that...
posture, appearance, and mobility may change. By the 8th decade, spinal flexion may occur as well as an angulation of features and a redistribution of body proportions. The gait may have a wider base to compensate for changes in balance
To measure weight, you may use a...
standardized balance or electric standing scale. Instruct the person to remove heavy outer clothing and shoes before standing on the scale
To measure height, use a...
wall-mounted device or the measuring pole on the balance scale; have the shoeless person stand straight and look straight ahead. (note: variations with infants, children, and patients who can't stand)
Body Mass Index (BMI)
a practical marker of optimal healthy weight for height and indicator of obesity or malnutrition
(Roughly:)
<18 = underweight
18-24 = healthy
25-29 = overweight
29-39 = obese
>39 = extremely obese