Histology of Skin and Accessory Structures of the Skin (APR)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:42 AM on 5/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
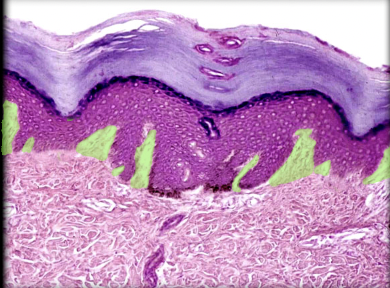
Derman papilla
Location:
* Interface between dermis and epidermis
Description:
* Projection of papillary (external) layer of dermis
* Forms core of epidermal ridge
* Numerous and often branched
* Contains capillary loops
Function:
* Provides nourishment to avascular epidermis
* Provides fingerprints for grasping objects
* Interface between dermis and epidermis
Description:
* Projection of papillary (external) layer of dermis
* Forms core of epidermal ridge
* Numerous and often branched
* Contains capillary loops
Function:
* Provides nourishment to avascular epidermis
* Provides fingerprints for grasping objects
2
New cards
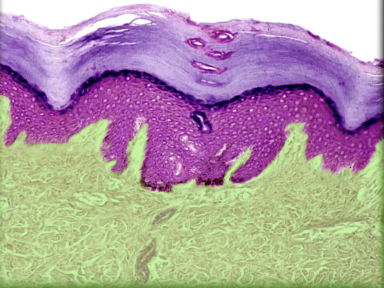
Dermis
Location:
* Skin (between epidermis and hypodermis)
Description:
* Two layers: papillary (superficial), composed of areolar connective tissue; and reticular (deep), composed of dense irregular connective tissue
* Contains appendages of skin: hair follicles and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
* Contains sensory nerve endings and dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels
* Includes part of hair follicle (which develops as invagination from epidermis)
Function:
* Supports epidermis
* Dense concentration of collagen and elastin gives skin strength
* Receives general sensory stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) via nerve endings and specialized receptors
* Regulates body temperature
Comment:
* Muscles of facial expression insert on dermis
* Skin (between epidermis and hypodermis)
Description:
* Two layers: papillary (superficial), composed of areolar connective tissue; and reticular (deep), composed of dense irregular connective tissue
* Contains appendages of skin: hair follicles and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
* Contains sensory nerve endings and dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels
* Includes part of hair follicle (which develops as invagination from epidermis)
Function:
* Supports epidermis
* Dense concentration of collagen and elastin gives skin strength
* Receives general sensory stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) via nerve endings and specialized receptors
* Regulates body temperature
Comment:
* Muscles of facial expression insert on dermis
3
New cards
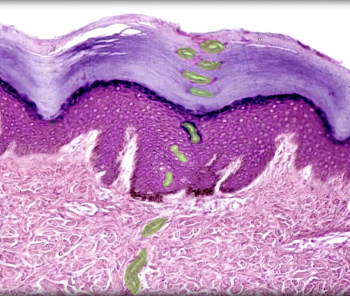
Duct of merocrine sweat gland
Location:
* Dermis and epidermis of skin
Description:
* Lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium
* Has spiral course through dermis and epidermis from secretory part of gland
* Cells of duct epithelium are smaller and duct has a smaller lumen than secretory part of gland
Comment:
* Sweat from merocrine gland is a nonviscous, hypotonic watery secretion
* Dermis and epidermis of skin
Description:
* Lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium
* Has spiral course through dermis and epidermis from secretory part of gland
* Cells of duct epithelium are smaller and duct has a smaller lumen than secretory part of gland
Comment:
* Sweat from merocrine gland is a nonviscous, hypotonic watery secretion
4
New cards
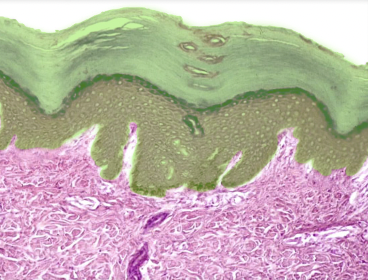
Epidermis
Location:
* Skin (superficial to dermis)
Description:
* Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of variable thickness
* Avascular
* Major cell type is keratinocyte
* Thick skin has five layers (superficial to deep): stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
* Thin skin has four layers (stratum lucidum is missing)
* Cells of stratum lucidum and stratum corneum lack nuclei
Function:
* Physical barrier
* Protection of underlying structures
Comment:
* Also contains stem cells, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and dendritic cells
* Depends on underlying dermis for nutrients (i.e., vascular supply)
* Skin (superficial to dermis)
Description:
* Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of variable thickness
* Avascular
* Major cell type is keratinocyte
* Thick skin has five layers (superficial to deep): stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
* Thin skin has four layers (stratum lucidum is missing)
* Cells of stratum lucidum and stratum corneum lack nuclei
Function:
* Physical barrier
* Protection of underlying structures
Comment:
* Also contains stem cells, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and dendritic cells
* Depends on underlying dermis for nutrients (i.e., vascular supply)
5
New cards
Stratum basale
Location:
* Skin
* Deepest layer of epidermis
Description:
* Single layer of columnar or high cuboidal cells resting on basement membrane
* Keratinocyte is predominant cell
* Also contains melanocytes, Merkel cells (touch receptors), and stem cells
Function:
* Keratinocytes undergo mitosis, producing stem cells and cells that migrate into stratum spinosum
Also known as:
* Basal layer or stratum germinativum
Comment:
* Cells in stratum basale and stratum spinosum responsible for turnover of epidermal keratinocytes
* Melanocytes of this layer produce melanin, a natural sunscreen
* Skin
* Deepest layer of epidermis
Description:
* Single layer of columnar or high cuboidal cells resting on basement membrane
* Keratinocyte is predominant cell
* Also contains melanocytes, Merkel cells (touch receptors), and stem cells
Function:
* Keratinocytes undergo mitosis, producing stem cells and cells that migrate into stratum spinosum
Also known as:
* Basal layer or stratum germinativum
Comment:
* Cells in stratum basale and stratum spinosum responsible for turnover of epidermal keratinocytes
* Melanocytes of this layer produce melanin, a natural sunscreen
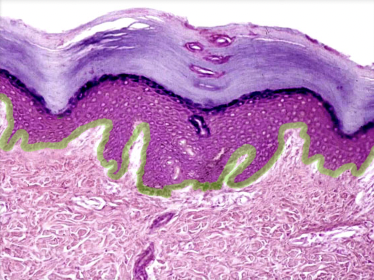
6
New cards
Stratum corneum
Location:
* Skin
* Outermost layer of epidermis
Description:
* Up to 30 layers of cornified, dead cells
* Dead cells contain keratin
Function:
* Creates barrier to fluids
Also known as:
* Keratin layer
Comment:
* Cells sloughed (shed) from surface and continually replaced from deeper layers
* Sloughed cells form major component of household "dust"
* Latin: cornu = horn
* Skin
* Outermost layer of epidermis
Description:
* Up to 30 layers of cornified, dead cells
* Dead cells contain keratin
Function:
* Creates barrier to fluids
Also known as:
* Keratin layer
Comment:
* Cells sloughed (shed) from surface and continually replaced from deeper layers
* Sloughed cells form major component of household "dust"
* Latin: cornu = horn
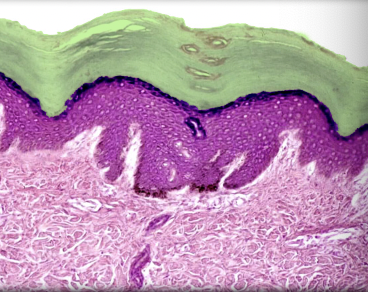
7
New cards
Stratum granulosum
Location:
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum spinosum and stratum lucidum
Description:
* Three to five layers of flattened keratinocytes
* Keratinocytes contain dark staining keratohyalin granules (precursor of keratin)
* Nuclei of keratinocytes in various stages of degeneration
Function:
* Protection for deeper layers
Also known as:
* Granular layer
Comment:
* Not a distinct layer in thin skin
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum spinosum and stratum lucidum
Description:
* Three to five layers of flattened keratinocytes
* Keratinocytes contain dark staining keratohyalin granules (precursor of keratin)
* Nuclei of keratinocytes in various stages of degeneration
Function:
* Protection for deeper layers
Also known as:
* Granular layer
Comment:
* Not a distinct layer in thin skin
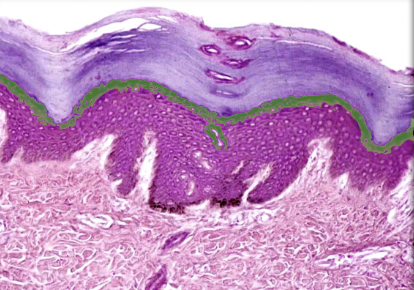
8
New cards
Stratum lucidum
Location:
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum granulosum and stratum corneum
Description:
* Thin translucent layer composed of three to five layers of keratinocytes without nuclei or organelles
* Keratinocytes contain eleidin (an intermediate in keratin production)
Comment:
* Present only in skin of palm (hand) and sole (foot)
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum granulosum and stratum corneum
Description:
* Thin translucent layer composed of three to five layers of keratinocytes without nuclei or organelles
* Keratinocytes contain eleidin (an intermediate in keratin production)
Comment:
* Present only in skin of palm (hand) and sole (foot)
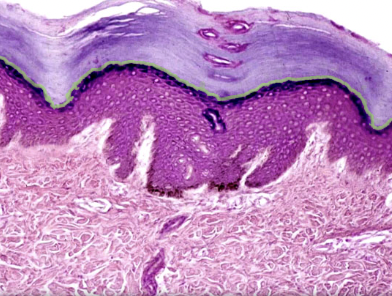
9
New cards
Stratum spinosum
Location:
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum basale and stratum granulosum
Description:
* Many layers of keratinocytes
* Deepest cells can divide
* Cells firmly attached to each other by desmosomes (cell junctions)
* Also contains dendritic (Langerhans) cells
Function:
* Helps maintain physical strength of epidermis
* Helps maintain barrier to infectious agents and harmful substances
Also known as:
* Prickle cell layer
Comment:
* Cells in stratum basale and stratum spinosum responsible for turnover of epidermal keratinocytes
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum basale and stratum granulosum
Description:
* Many layers of keratinocytes
* Deepest cells can divide
* Cells firmly attached to each other by desmosomes (cell junctions)
* Also contains dendritic (Langerhans) cells
Function:
* Helps maintain physical strength of epidermis
* Helps maintain barrier to infectious agents and harmful substances
Also known as:
* Prickle cell layer
Comment:
* Cells in stratum basale and stratum spinosum responsible for turnover of epidermal keratinocytes
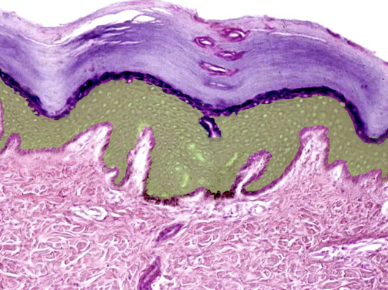
10
New cards
Dermis
Location:
* Skin (between epidermis and hypodermis)
Description:
* Two layers: papillary (superficial), composed of areolar connective tissue; and reticular (deep), composed of dense irregular connective tissue
* Contains appendages of skin: hair follicles and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
* Contains sensory nerve endings and dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels
* Includes part of hair follicle (which develops as invagination from epidermis)
Function:
* Supports epidermis
* Dense concentration of collagen and elastin gives skin strength
* Receives general sensory stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) via nerve endings and specialized receptors
* Regulates body temperature
Comment:
* Muscles of facial expression insert on dermis
* Skin (between epidermis and hypodermis)
Description:
* Two layers: papillary (superficial), composed of areolar connective tissue; and reticular (deep), composed of dense irregular connective tissue
* Contains appendages of skin: hair follicles and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
* Contains sensory nerve endings and dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels
* Includes part of hair follicle (which develops as invagination from epidermis)
Function:
* Supports epidermis
* Dense concentration of collagen and elastin gives skin strength
* Receives general sensory stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) via nerve endings and specialized receptors
* Regulates body temperature
Comment:
* Muscles of facial expression insert on dermis
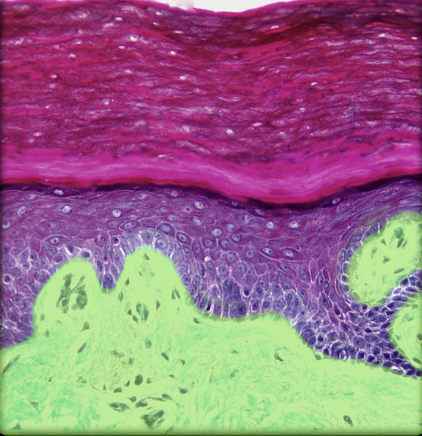
11
New cards
Epidermis
Location:
* Skin (superficial to dermis)
Description:
* Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of variable thickness
* Avascular
* Major cell type is keratinocyte
* Thick skin has five layers (superficial to deep): stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
* Thin skin has four layers (stratum lucidum is missing)
* Cells of stratum lucidum and stratum corneum lack nuclei
Function:
* Physical barrier
* Protection of underlying structures
Comment:
* Also contains stem cells, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and dendritic cells
* Depends on underlying dermis for nutrients (i.e., vascular supply)
* Skin (superficial to dermis)
Description:
* Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of variable thickness
* Avascular
* Major cell type is keratinocyte
* Thick skin has five layers (superficial to deep): stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
* Thin skin has four layers (stratum lucidum is missing)
* Cells of stratum lucidum and stratum corneum lack nuclei
Function:
* Physical barrier
* Protection of underlying structures
Comment:
* Also contains stem cells, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and dendritic cells
* Depends on underlying dermis for nutrients (i.e., vascular supply)
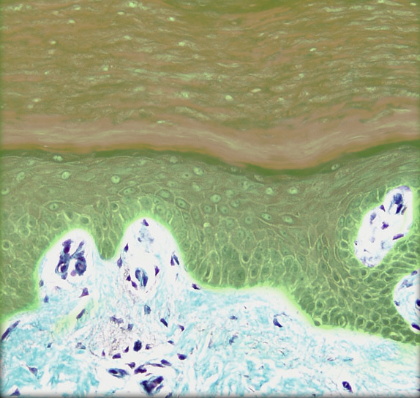
12
New cards
Stratum basale
Location:
* Skin
* Deepest layer of epidermis
Description:
* Single layer of columnar or high cuboidal cells resting on basement membrane
* Keratinocyte is predominant cell
* Also contains melanocytes, Merkel cells (touch receptors), and stem cells
Function:
* Keratinocytes undergo mitosis, producing stem cells and cells that migrate into stratum spinosum
Also known as:
* Basal layer or stratum germinativum
Comment:
* Cells in stratum basale and stratum spinosum responsible for turnover of epidermal keratinocytes
* Melanocytes of this layer produce melanin, a natural sunscreen
* Skin
* Deepest layer of epidermis
Description:
* Single layer of columnar or high cuboidal cells resting on basement membrane
* Keratinocyte is predominant cell
* Also contains melanocytes, Merkel cells (touch receptors), and stem cells
Function:
* Keratinocytes undergo mitosis, producing stem cells and cells that migrate into stratum spinosum
Also known as:
* Basal layer or stratum germinativum
Comment:
* Cells in stratum basale and stratum spinosum responsible for turnover of epidermal keratinocytes
* Melanocytes of this layer produce melanin, a natural sunscreen
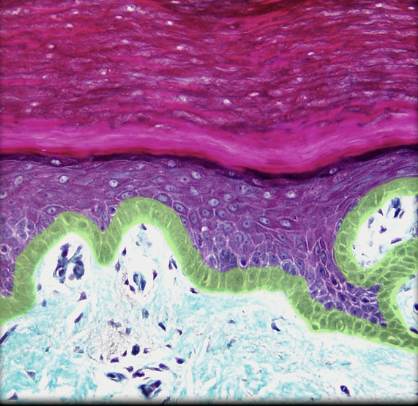
13
New cards
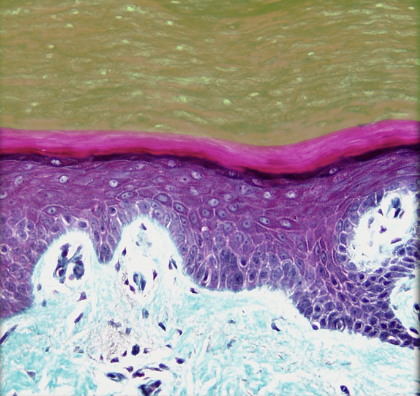
Stratum corneum
Location:
* Skin
* Outermost layer of epidermis
Description:
* Up to 30 layers of cornified, dead cells
* Dead cells contain keratin
Function:
* Creates barrier to fluids
Also known as:
* Keratin layer
Comment:
* Cells sloughed (shed) from surface and continually replaced from deeper layers
* Sloughed cells form major component of household "dust"
* Latin: cornu = horn
* Skin
* Outermost layer of epidermis
Description:
* Up to 30 layers of cornified, dead cells
* Dead cells contain keratin
Function:
* Creates barrier to fluids
Also known as:
* Keratin layer
Comment:
* Cells sloughed (shed) from surface and continually replaced from deeper layers
* Sloughed cells form major component of household "dust"
* Latin: cornu = horn
14
New cards
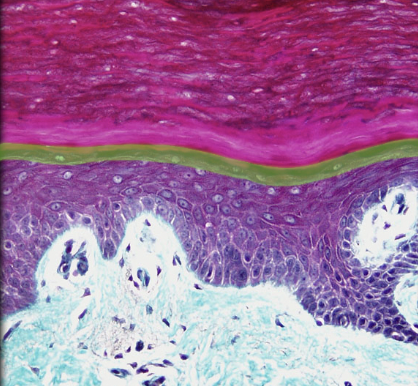
Stratum granulosum
Location:
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum spinosum and stratum lucidum
Description:
* Three to five layers of flattened keratinocytes
* Keratinocytes contain dark staining keratohyalin granules (precursor of keratin)
* Nuclei of keratinocytes in various stages of degeneration
Function:
* Protection for deeper layers
Also known as:
* Granular layer
Comment:
* Not a distinct layer in thin skin
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum spinosum and stratum lucidum
Description:
* Three to five layers of flattened keratinocytes
* Keratinocytes contain dark staining keratohyalin granules (precursor of keratin)
* Nuclei of keratinocytes in various stages of degeneration
Function:
* Protection for deeper layers
Also known as:
* Granular layer
Comment:
* Not a distinct layer in thin skin
15
New cards
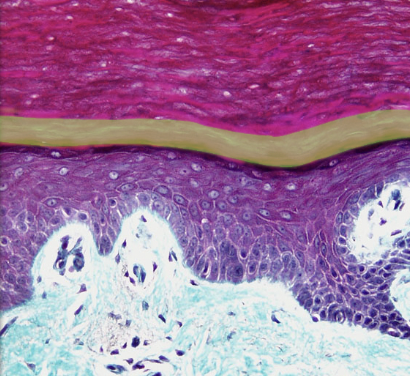
Stratum lucidum
Location:
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum granulosum and stratum corneum
Description:
* Thin translucent layer composed of three to five layers of keratinocytes without nuclei or organelles
* Keratinocytes contain eleidin (an intermediate in keratin production)
Comment:
* Present only in skin of palm (hand) and sole (foot)
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum granulosum and stratum corneum
Description:
* Thin translucent layer composed of three to five layers of keratinocytes without nuclei or organelles
* Keratinocytes contain eleidin (an intermediate in keratin production)
Comment:
* Present only in skin of palm (hand) and sole (foot)
16
New cards
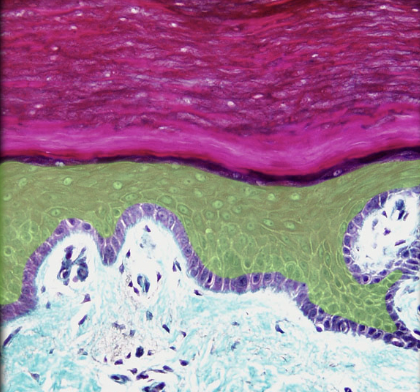
Stratum spinosum
Location:
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum basale and stratum granulosum
Description:
* Many layers of keratinocytes
* Deepest cells can divide
* Cells firmly attached to each other by desmosomes (cell junctions)
* Also contains dendritic (Langerhans) cells
Function:
* Helps maintain physical strength of epidermis
* Helps maintain barrier to infectious agents and harmful substances
Also known as:
* Prickle cell layer
Comment:
* Cells in stratum basale and stratum spinosum responsible for turnover of epidermal keratinocytes
* Skin
* Epidermis, between stratum basale and stratum granulosum
Description:
* Many layers of keratinocytes
* Deepest cells can divide
* Cells firmly attached to each other by desmosomes (cell junctions)
* Also contains dendritic (Langerhans) cells
Function:
* Helps maintain physical strength of epidermis
* Helps maintain barrier to infectious agents and harmful substances
Also known as:
* Prickle cell layer
Comment:
* Cells in stratum basale and stratum spinosum responsible for turnover of epidermal keratinocytes
17
New cards
Dermis
Location:
* Skin (between epidermis and hypodermis)
Description:
* Two layers: papillary (superficial), composed of areolar connective tissue; and reticular (deep), composed of dense irregular connective tissue
* Contains appendages of skin: hair follicles and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
* Contains sensory nerve endings and dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels
* Includes part of hair follicle (which develops as invagination from epidermis)
Function:
* Supports epidermis
* Dense concentration of collagen and elastin gives skin strength
* Receives general sensory stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) via nerve endings and specialized receptors
* Regulates body temperature
Comment:
* Muscles of facial expression insert on dermis
* Skin (between epidermis and hypodermis)
Description:
* Two layers: papillary (superficial), composed of areolar connective tissue; and reticular (deep), composed of dense irregular connective tissue
* Contains appendages of skin: hair follicles and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
* Contains sensory nerve endings and dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels
* Includes part of hair follicle (which develops as invagination from epidermis)
Function:
* Supports epidermis
* Dense concentration of collagen and elastin gives skin strength
* Receives general sensory stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) via nerve endings and specialized receptors
* Regulates body temperature
Comment:
* Muscles of facial expression insert on dermis
18
New cards
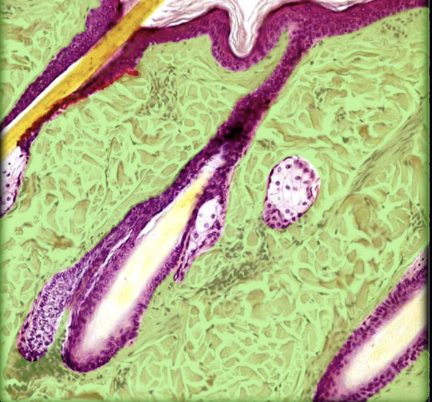
Duct of sebaceous gland
Location:
* Dermis and epidermis of thin skin
Description:
* Short passage between secretory part of gland and hair follicle
* Lined by stratified squamous epithelium that is continuous with external root sheath of hair
* Most frequently opens into upper portion of hair follicle
* May open directly on skin surface of glans penis, clitoris, and lips
Function:
* Release of sebum into hair follicle or onto skin surface
Comment:
* Sebum is oily substance produced by sebaceous glands
* Dermis and epidermis of thin skin
Description:
* Short passage between secretory part of gland and hair follicle
* Lined by stratified squamous epithelium that is continuous with external root sheath of hair
* Most frequently opens into upper portion of hair follicle
* May open directly on skin surface of glans penis, clitoris, and lips
Function:
* Release of sebum into hair follicle or onto skin surface
Comment:
* Sebum is oily substance produced by sebaceous glands
19
New cards
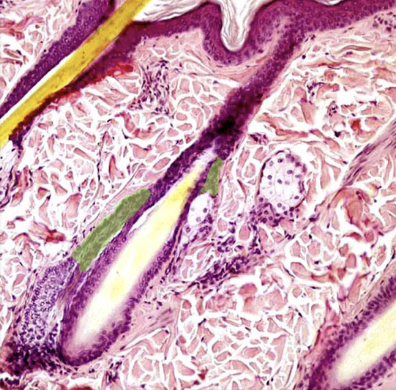
Epidermis
Location:
* Skin (superficial to dermis)
Description:
* Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of variable thickness
* Avascular
* Major cell type is keratinocyte
* Thick skin has five layers (superficial to deep): stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
* Thin skin has four layers (stratum lucidum is missing)
* Cells of stratum lucidum and stratum corneum lack nuclei
Function:
* Physical barrier
* Protection of underlying structures
Comment:
* Also contains stem cells, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and dendritic cells
* Depends on underlying dermis for nutrients (i.e., vascular supply)
* Skin (superficial to dermis)
Description:
* Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium of variable thickness
* Avascular
* Major cell type is keratinocyte
* Thick skin has five layers (superficial to deep): stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, and stratum basale
* Thin skin has four layers (stratum lucidum is missing)
* Cells of stratum lucidum and stratum corneum lack nuclei
Function:
* Physical barrier
* Protection of underlying structures
Comment:
* Also contains stem cells, melanocytes, Merkel cells, and dendritic cells
* Depends on underlying dermis for nutrients (i.e., vascular supply)
20
New cards
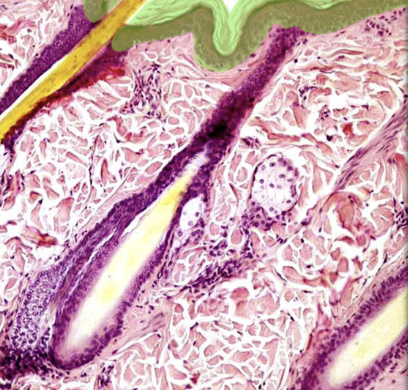
Hair
Location:
* Thin skin
Description:
* Accessory organ of skin
* Fine, keratinized filament
* Grows from oblique tube in skin called hair follicle
* Each hair has three zones: bulb, root, and shaft
* Projects from epidermal surface (length varies by body region)
* Usually pigmented (hair color due to melanin pigment granules in hair cortex)
Function:
* Protection (e.g., from sunburn)
* Heat retention (esp. on scalp)
* Cutaneous sensation
* Dispersion of chemical signals
* Facial recognition/visual identification
Comment:
* Hair not found in thick skin of palms (hands) or soles (feet)
* Genetic and hormonal factors determine body hair distribution
* Single hair also known as pilus (plural, pili)
* Thin skin
Description:
* Accessory organ of skin
* Fine, keratinized filament
* Grows from oblique tube in skin called hair follicle
* Each hair has three zones: bulb, root, and shaft
* Projects from epidermal surface (length varies by body region)
* Usually pigmented (hair color due to melanin pigment granules in hair cortex)
Function:
* Protection (e.g., from sunburn)
* Heat retention (esp. on scalp)
* Cutaneous sensation
* Dispersion of chemical signals
* Facial recognition/visual identification
Comment:
* Hair not found in thick skin of palms (hands) or soles (feet)
* Genetic and hormonal factors determine body hair distribution
* Single hair also known as pilus (plural, pili)
21
New cards
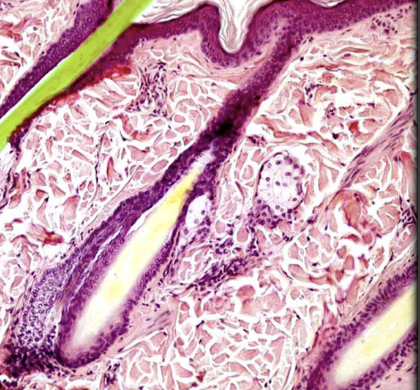
Hair follicle
Location:
* Dermis
* May extend into hypodermis
Description:
* Tube that surrounds hair root
* Courses obliquely through dermis
* Two coats: epidermic (inner) and dermic (outer)
* Characteristic parts include: dermal papilla bulb, hair shaft, cuticle layer, internal follicular sheath, and external follicular sheath
* Associated with hair receptors and arrector muscle of the hair
Function:
* Hair formation and growth
Comment:
* Hair follicle develops as invagination from epidermis
* Follicle associated with a sebaceous gland, an arrector muscle of the hair, and an apocrine gland (in axilla and anogenital regions)
* Apocrine glands release part of apical cytoplasm with secretion
* Arrector muscle of the hair also known as arrector pili (piloerector) muscle
* Dermis
* May extend into hypodermis
Description:
* Tube that surrounds hair root
* Courses obliquely through dermis
* Two coats: epidermic (inner) and dermic (outer)
* Characteristic parts include: dermal papilla bulb, hair shaft, cuticle layer, internal follicular sheath, and external follicular sheath
* Associated with hair receptors and arrector muscle of the hair
Function:
* Hair formation and growth
Comment:
* Hair follicle develops as invagination from epidermis
* Follicle associated with a sebaceous gland, an arrector muscle of the hair, and an apocrine gland (in axilla and anogenital regions)
* Apocrine glands release part of apical cytoplasm with secretion
* Arrector muscle of the hair also known as arrector pili (piloerector) muscle
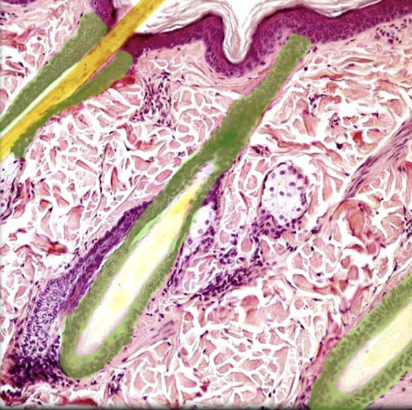
22
New cards
Sebaceous gland
Location:
* Skin
Description:
* Simple, saccular holocrine gland
* Secretory part lies in dermis
* Duct opens into hair follicle or onto skin surface
Function:
* Secrete sebum (oily substance)
* Lubricate and waterproof hair shaft
Comment:
* Not found in skin of palms (hands) or soles (feet)
* Holocrine glands produce secretion through fatty degeneration of cells in secretory part of gland
* Skin
Description:
* Simple, saccular holocrine gland
* Secretory part lies in dermis
* Duct opens into hair follicle or onto skin surface
Function:
* Secrete sebum (oily substance)
* Lubricate and waterproof hair shaft
Comment:
* Not found in skin of palms (hands) or soles (feet)
* Holocrine glands produce secretion through fatty degeneration of cells in secretory part of gland
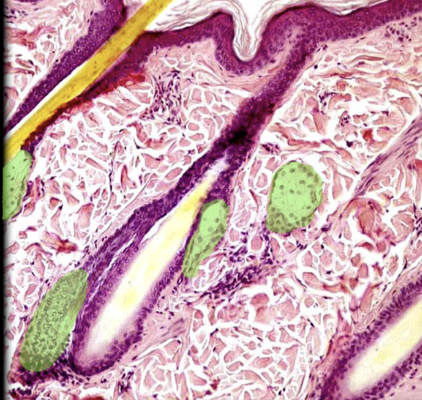
23
New cards
Dermis
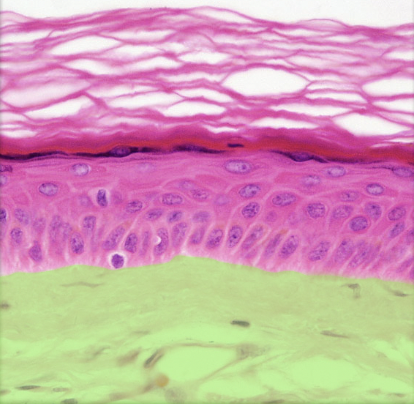
24
New cards
Epidermis
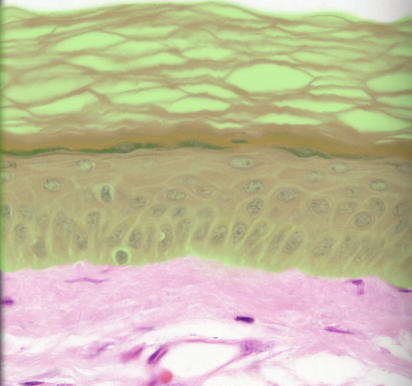
25
New cards
Stratum basale
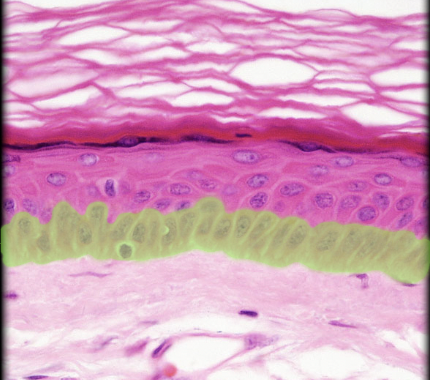
26
New cards
Stratum corneum
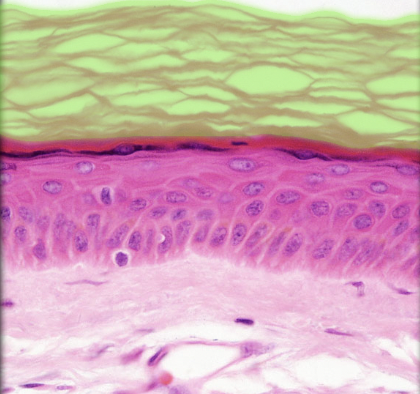
27
New cards
Stratum granulosum
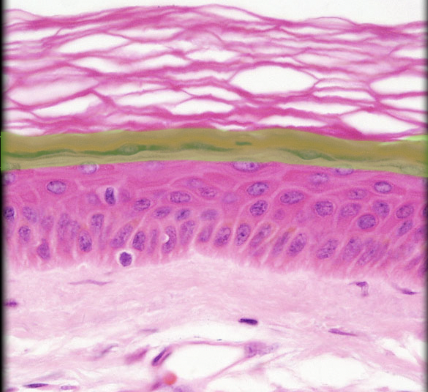
28
New cards
Stratum spinosum
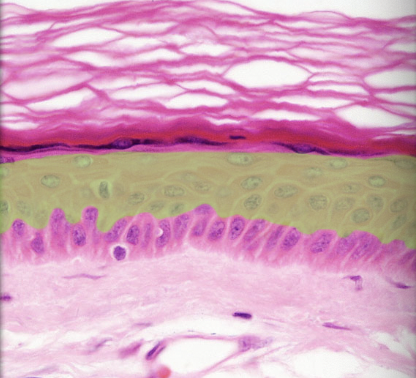
29
New cards
Hair shaft
Location:
* Surface of epidermis
Description:
* Filamentous, pigmented, keratinized structure
* Projects from epidermal surface, i.e., extends beyond skin surface (length varies by body region)
Function:
* Protection (e.g., from sunburn)
* Heat retention (esp. on scalp)
* Cutaneous sensation
* Dispersion of chemical signals
* Facial recognition/visual identification
* Surface of epidermis
Description:
* Filamentous, pigmented, keratinized structure
* Projects from epidermal surface, i.e., extends beyond skin surface (length varies by body region)
Function:
* Protection (e.g., from sunburn)
* Heat retention (esp. on scalp)
* Cutaneous sensation
* Dispersion of chemical signals
* Facial recognition/visual identification
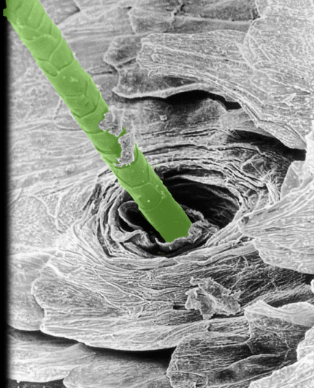
30
New cards
Keratinocyte
Location:
* Skin
Description:
* Predominant cell of epidermis
* Originates in basal layer of epidermis and differentiates as they migrate toward surface of skin
* Fully differentiated keratinocyte composed of 85% keratin
Function:
* Helps form epidermal barrier to water and dehydration
Comment:
* Epidermis arranged in five layers (deep to superficial): stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum
* Individual keratinocytes in epidermis for approximately 1 month: they move from stratum basale to stratum corneum in approximately 2 weeks and then remain on the surface for an additional 2 weeks
* Keratin is major structural protein of epidermis
* Skin
Description:
* Predominant cell of epidermis
* Originates in basal layer of epidermis and differentiates as they migrate toward surface of skin
* Fully differentiated keratinocyte composed of 85% keratin
Function:
* Helps form epidermal barrier to water and dehydration
Comment:
* Epidermis arranged in five layers (deep to superficial): stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, and stratum corneum
* Individual keratinocytes in epidermis for approximately 1 month: they move from stratum basale to stratum corneum in approximately 2 weeks and then remain on the surface for an additional 2 weeks
* Keratin is major structural protein of epidermis
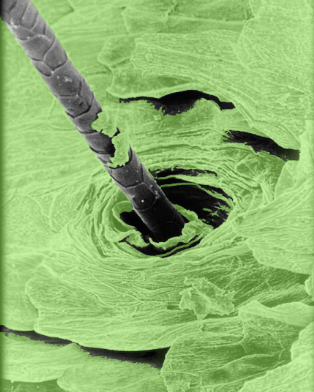
31
New cards
External root sheath
Location:
* Hair follicle
Description:
* Downgrowth of epidermis that forms external layer of hair follicle
* At skin surface composed of all layers of epidermis
* Thinner at dermal papilla, where it is composed only of cells corresponding to stratum basale of epidermis
Function:
* Support for hair production and growth
* Hair follicle
Description:
* Downgrowth of epidermis that forms external layer of hair follicle
* At skin surface composed of all layers of epidermis
* Thinner at dermal papilla, where it is composed only of cells corresponding to stratum basale of epidermis
Function:
* Support for hair production and growth
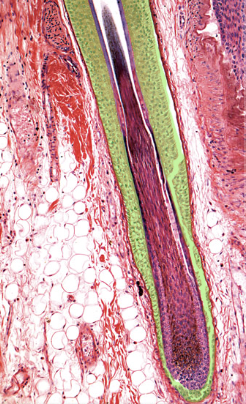
32
New cards
Hair matrix
Location:
* Hair bulb
Description:
* Surrounds dermal papilla of hair bulb
* Scattered melanocytes present in matrix
Function:
* Zone of dividing cells that give rise to all layers of hair and hair follicle
* Division and proliferation of cells in matrix account for hair growth
Comment:
* Hair color determined by amount of melanin pigment synthesized by melanocytes in hair matrix
* Hair bulb
Description:
* Surrounds dermal papilla of hair bulb
* Scattered melanocytes present in matrix
Function:
* Zone of dividing cells that give rise to all layers of hair and hair follicle
* Division and proliferation of cells in matrix account for hair growth
Comment:
* Hair color determined by amount of melanin pigment synthesized by melanocytes in hair matrix
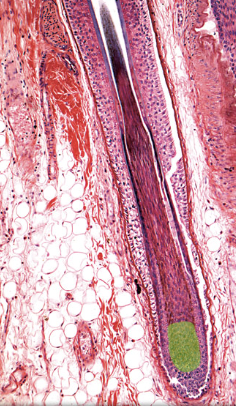
33
New cards
Internal root sheath
Location:
* Hair follicle
Description:
* Multicellular sheath that surrounds hair
* Extends around inferior part of hair
* Separates hair from external root sheath
* Comprised of soft keratin
Function:
* Support for hair production and growth
* Hair follicle
Description:
* Multicellular sheath that surrounds hair
* Extends around inferior part of hair
* Separates hair from external root sheath
* Comprised of soft keratin
Function:
* Support for hair production and growth
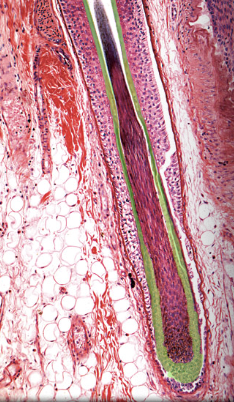
34
New cards
Dermal papilla of hair bulb
Location:
* Inferior part of hair follicle (base of hair bulb)
Description:
* Invagination of loose connective tissue
* Contains capillary network
Function:
* Blood supply for hair follicle
Comment:
* Damage to dermal papilla results in death of hair follicle
* Inferior part of hair follicle (base of hair bulb)
Description:
* Invagination of loose connective tissue
* Contains capillary network
Function:
* Blood supply for hair follicle
Comment:
* Damage to dermal papilla results in death of hair follicle
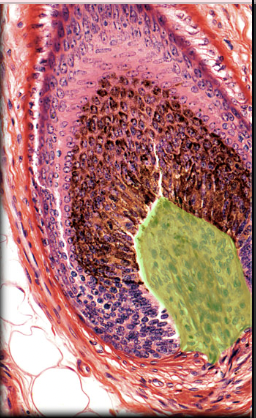
35
New cards
Dermis
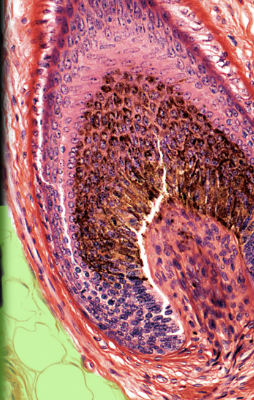
36
New cards
External root sheath
Location:
* Hair follicle
Description:
* Downgrowth of epidermis that forms external layer of hair follicle
* At skin surface composed of all layers of epidermis
* Thinner at dermal papilla, where it is composed only of cells corresponding to stratum basale of epidermis
Function:
* Support for hair production and growth
* Hair follicle
Description:
* Downgrowth of epidermis that forms external layer of hair follicle
* At skin surface composed of all layers of epidermis
* Thinner at dermal papilla, where it is composed only of cells corresponding to stratum basale of epidermis
Function:
* Support for hair production and growth
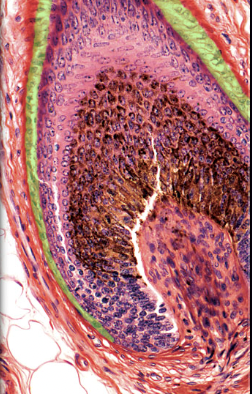
37
New cards
Hair matrix
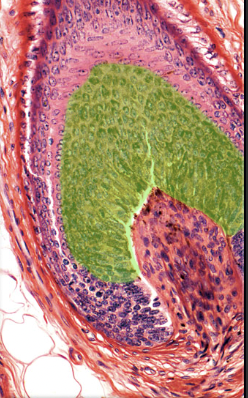
38
New cards
Internal root sheath
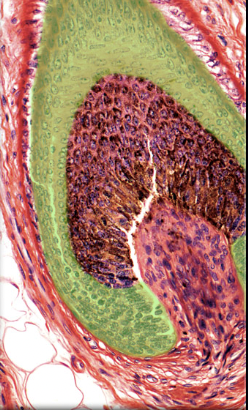
39
New cards
Duct of sebaceous gland
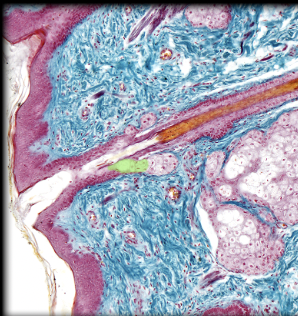
40
New cards
Epidermis
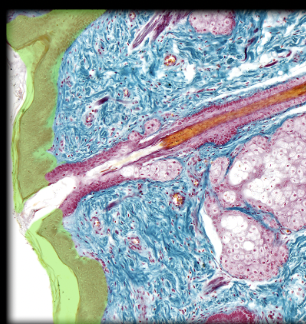
41
New cards
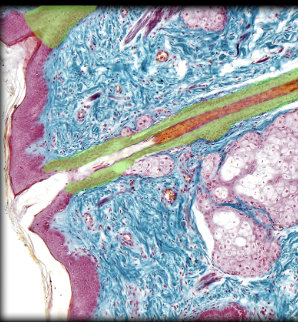
Hair follicle
42
New cards
Sebaceous gland
43
New cards
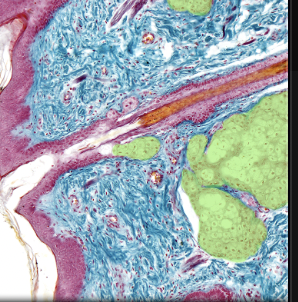
Duct of sebaceous gland
44
New cards
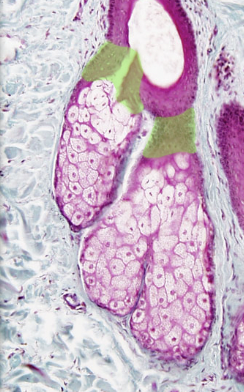
Hair follicle
45
New cards
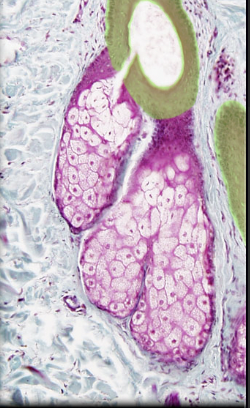
Sebaceous gland
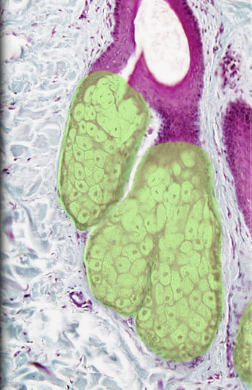
46
New cards
Dermis
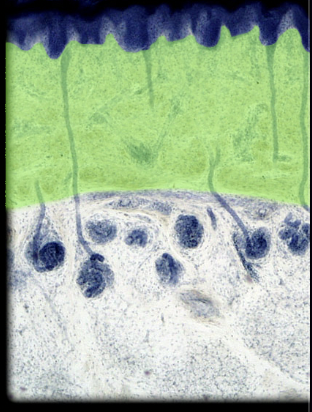
47
New cards
Duct of merocrine sweat gland
Location:
* Dermis and epidermis of skin
Description:
* Lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium
* Has spiral course through dermis and epidermis from secretory part of gland
* Cells of duct epithelium are smaller and duct has a smaller lumen than secretory part of gland
Comment:
* Sweat from merocrine gland is a nonviscous, hypotonic watery secretion
* Dermis and epidermis of skin
Description:
* Lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium
* Has spiral course through dermis and epidermis from secretory part of gland
* Cells of duct epithelium are smaller and duct has a smaller lumen than secretory part of gland
Comment:
* Sweat from merocrine gland is a nonviscous, hypotonic watery secretion
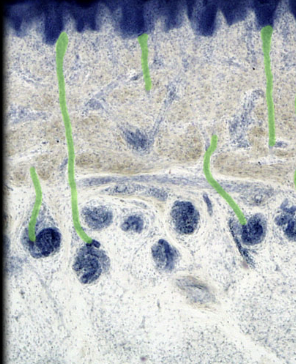
48
New cards
Epidermis
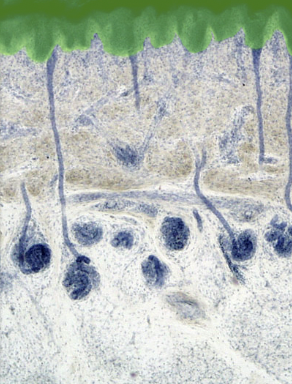
49
New cards
Hypodermis
Location:
* Deep to skin
Description:
* Layer of loose areolar connective and adipose tissue
* Contains cutaneous nerves and blood vessels, and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
* Contains lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscle (pressure receptor)
* Contains portions of hair follicles associated with thin skin
Function:
* Fat storage
* Thermal regulation
* Permits movement of skin
Also known as:
* Subcutaneous tissue or superficial fascia
* Deep to skin
Description:
* Layer of loose areolar connective and adipose tissue
* Contains cutaneous nerves and blood vessels, and glands (sweat and sebaceous)
* Contains lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscle (pressure receptor)
* Contains portions of hair follicles associated with thin skin
Function:
* Fat storage
* Thermal regulation
* Permits movement of skin
Also known as:
* Subcutaneous tissue or superficial fascia
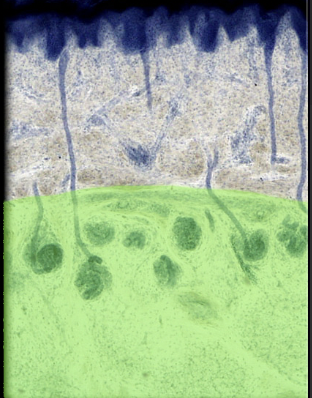
50
New cards
Merocrine of sweat gland
Location:
* Dermis and hypodermis of skin
Description:
* Simple, coiled, tubular gland
* Secretory part of gland composed of simple cuboidal epithelium
* Duct opens directly on surface of skin at sweat pore
* Innervated by cholinergic nerve fibers
Function:
* Production and release of non-viscous, hypotonic, watery secretion known as sweat
* Plays a major role in temperature regulation through cooling that results from evaporation of sweat from body surface
Comment:
* Most numerous and widely distributed sweat glands in the body
* Palms, soles, and forehead have highest number of glands per square centimeter
* Some merocrine glands also called eccrine glands
* Dermis and hypodermis of skin
Description:
* Simple, coiled, tubular gland
* Secretory part of gland composed of simple cuboidal epithelium
* Duct opens directly on surface of skin at sweat pore
* Innervated by cholinergic nerve fibers
Function:
* Production and release of non-viscous, hypotonic, watery secretion known as sweat
* Plays a major role in temperature regulation through cooling that results from evaporation of sweat from body surface
Comment:
* Most numerous and widely distributed sweat glands in the body
* Palms, soles, and forehead have highest number of glands per square centimeter
* Some merocrine glands also called eccrine glands
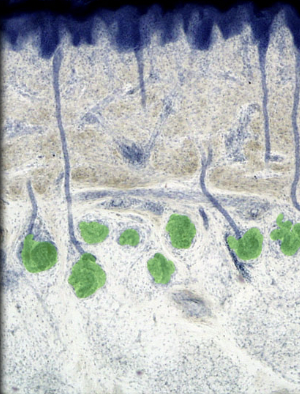
51
New cards
Dermis
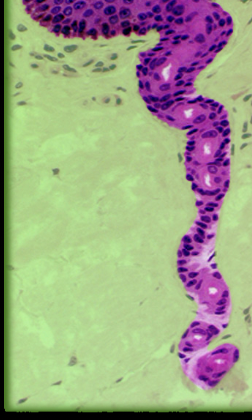
52
New cards
Duct of sweat gland
Location:
* Dermis and epidermis
Description:
* Lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium
* Has spiral course through dermis and epidermis from secretory part of gland
* Cells are smaller and duct has a smaller lumen than secretory part of gland
Function:
* Passage for release of sweat onto body surface
* Dermis and epidermis
Description:
* Lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium
* Has spiral course through dermis and epidermis from secretory part of gland
* Cells are smaller and duct has a smaller lumen than secretory part of gland
Function:
* Passage for release of sweat onto body surface
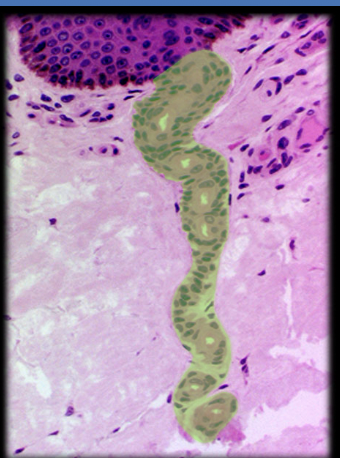
53
New cards
Epidermis
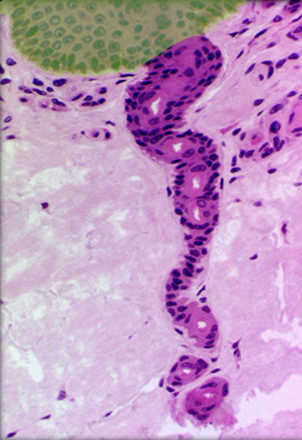
54
New cards
Epithelium of apocrine sweat gland
Location:
* Secretory part of apocrine sweat gland
Description:
* Simple cuboidal cells form secretory part of apocrine sweat gland
* Myoepithelial cells underlie cuboidal cells and line basement membrane of gland
Function:
* Production of viscous secretion (sweat) released into hair follicles in axilla, around areola of nipple, and anal region
Comment:
* Secretory products are odorless when released but when metabolized by bacteria on skin creates distinctive odor
* Secretory part of apocrine sweat gland
Description:
* Simple cuboidal cells form secretory part of apocrine sweat gland
* Myoepithelial cells underlie cuboidal cells and line basement membrane of gland
Function:
* Production of viscous secretion (sweat) released into hair follicles in axilla, around areola of nipple, and anal region
Comment:
* Secretory products are odorless when released but when metabolized by bacteria on skin creates distinctive odor
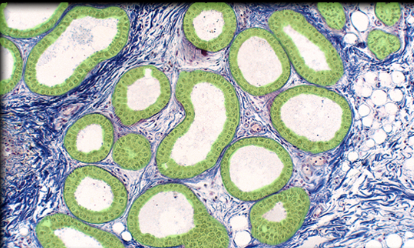
55
New cards
Lumen of apocrine sweat gland
Location:
* Apocrine sweat gland
Description:
* Central opening in secretory part of gland
* Surrounded by secretory epithelial cells
Function:
* Receives secretions from epithelial cells of apocrine sweat
* Storage of apocrine secretion prior to release
Comment:
* Sweat from apocrine glands contains protein, carbohydrate, ammonia, lipid, and other organic substances
* Apocrine sweat gland
Description:
* Central opening in secretory part of gland
* Surrounded by secretory epithelial cells
Function:
* Receives secretions from epithelial cells of apocrine sweat
* Storage of apocrine secretion prior to release
Comment:
* Sweat from apocrine glands contains protein, carbohydrate, ammonia, lipid, and other organic substances
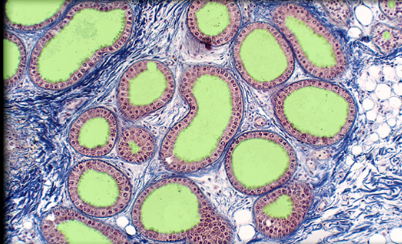
56
New cards
Dermis
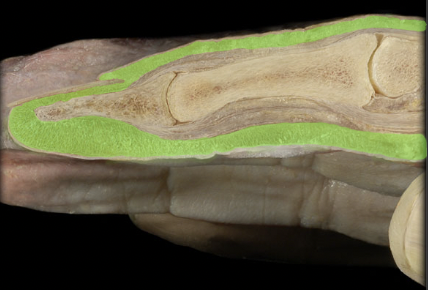
57
New cards
Epidermis
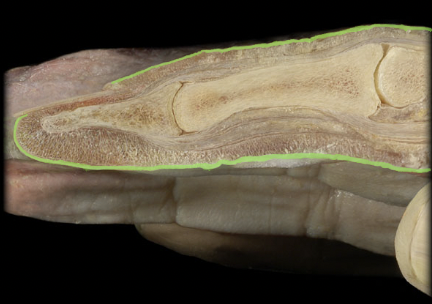
58
New cards
Eponychium
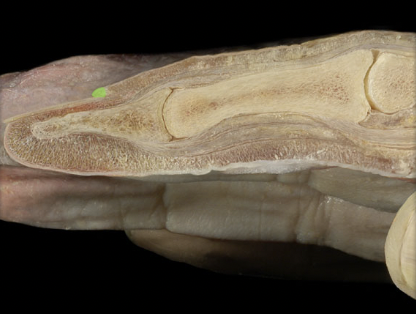
59
New cards
Free edge of nail
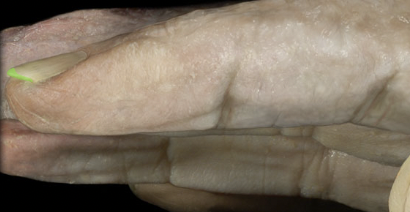
60
New cards
Lateral nail fold
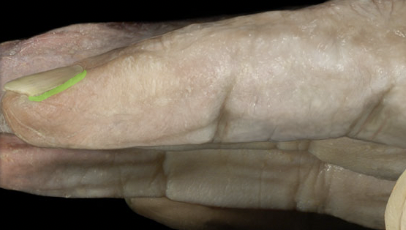
61
New cards
Nail bed
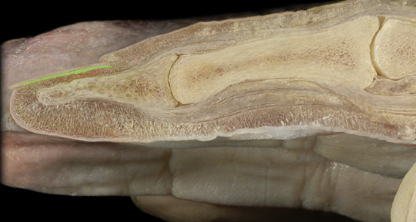
62
New cards
Nail body
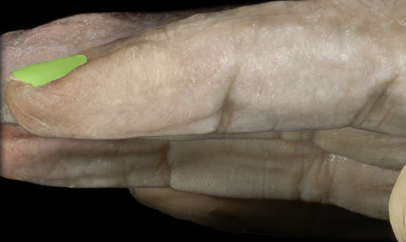
63
New cards
Nail matrix
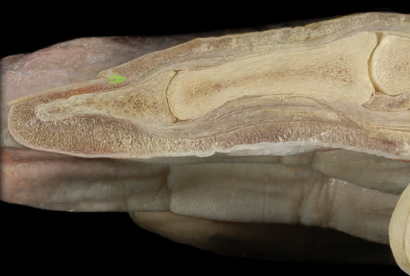
64
New cards
Nail root