Unit 5: Heredity
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Genetics
The scientific study of heredity
Allele
Refers to the different versions of a gene.
Genotype
genetic makeup.
Use letters (alleles).
Phenotype
physical trait.
Not always visible (e.g. enzymes).
Recessive
must inherit 2 copies to produce phenotype.
lower case
Dominant
will produce a phenotype over other alleles
Homozygous
means same
Heredity
the passing on of genetic characteristics
Gene
segment of DNA that codes for a protein/trait.
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes, but not necessarily the same versions, or alleles, of those genes.
Wild Type
references which trait is most common in the population
Typically non-mutant alleles (common)
Genome
collection of ALL of an organism’s genes.
Heterozygous/hybrid
Means different; two different alleles are inherited
Why do two alleles get inherited for each gene?
The offspring inherits one allele from each parents, resulting in 2 of either the same, or one of each.
Law of Dominance
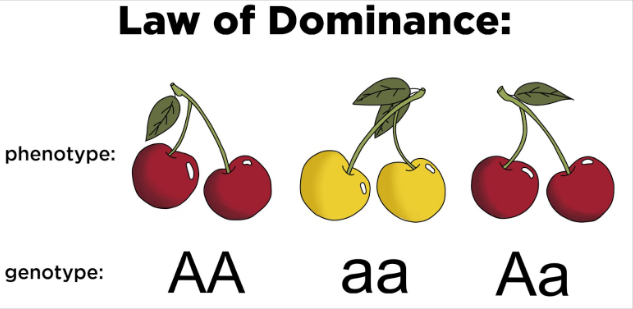
Law of Independent Assortment
Alleles of genes on homologous chromosomes assort independently during gamete formation
Law of Segregation
The two alleles for each gene separate during gamete formation
Monohybrid P generation genotype
parent generation
Homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive are crossed
Monohybrid F1 generation genotype
100% are heterozygous
Monohybrid F2 generation genotype
homozygous dominant
heterozygous
homozygous recessive
Monohybrid P generation phenotype (single trait)
# 1 : # 1
Phenotypic ratio
a way to report the resulting phenotypes of a cross
# dominant : # recessive
Monohybrid F1 generation phenotype
4:0 (1:0)
Monohybrid F2 generation phenotype
3:1
The testcross
Organism with dominant phenotype x organism with recessive must use this to discover the truth about its genotype
Recessive offspring = unknown was heterozygous
Only dominant offspring = inconclusive
Two Trait Phenotypic Ratio
#1: Dom/Dom
#2: Dom/Rec
#3: Rec/Dom
#4: Rec/Rec
Dihybrid P generation genotype
One Dom/Dom allele
One Rec/Rec allele
Dihybrid F1 generation genotype
heterozygous- Dom; Rec/ Dom; Rec
Dihybrid F2 generation genotype
#1: Dom/Dom
#2: Dom/Rec
#3: Rec/Dom
#4: Rec/Rec
Incomplete Dominance
No true dominant/recessive trait
The result: BOTH SHOW UP (blended) in a heterozygote
Codominance
No true dominant/recessive trait.
In heterozygotes, two phenotypes appear (pattern).
No mixed/blended phenotype results
Multiple Alleles
More than 2 alleles for a gene exist in a population
Polygenic
A single trait is determined by many genes
Number of genes involved in Codominance, Incomplete dominance, and Multiple Alleles
1
Number of traits involved in Codominance, Incomplete dominance, and Multiple Alleles
1 (t)
Number of alleles involved in Codominance and Incomplete Dominance
2
Number of alleles involved in Multiple Alleles
3 or MORE
Number of traits in Polygenic Inheritance
2+ genes
Polygenic Inheritance special characteristics
Bell curve characteristic of polygenic traits
Continuous range of variation
Most fall within the intermediate phenotypes
Human examples of polygenic inheritance
Height (more than 400 gene regions)
Skin tone (many)
Hair color (many - 2 main genes, possibly over 20)
Eye color (2 main, at least 50! others***)
Y Chromosome
Few genes
Sex-determining region (SRY) gene
Helps form testes which trigger testosterone release
X Chromosome
~900+ genes
Mutations could result in:
Hemophilia (blood disorder)
Muscular dystrophy
Color-blindness
Disorders linked to the X chromosome are called
X-linked
More than 60 disorders are X-linked
Genotypes for X-Linked Recessive
Affected XX = hom rec;
Affected XY = one rec allele.
Unaffected XX = heterozygous (carriers) or hom dom;
Unaffected XY = one dom allele.
Which sex is more likely to be affected by X-Linked Recessive Disorders?
XY = have a higher chance of inheritance.
Only have one X chromosome
Genotypes for X-Linked Dominant
Affected XX = heterozygous or hom. dom;
Affected XY = one dom allele.
Unaffected XX = hom rec;
Unaffected XY = one rec allele.
Who is affected by X-linked dominant disorders?
XX have a higher chance of being affected
Inherit two X-chromosomes - higher chance of getting the allele.
Y Linked Disorders
Exclusively affect individuals with a Y chromosome