Quiz 6: Biomedical Sciences
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
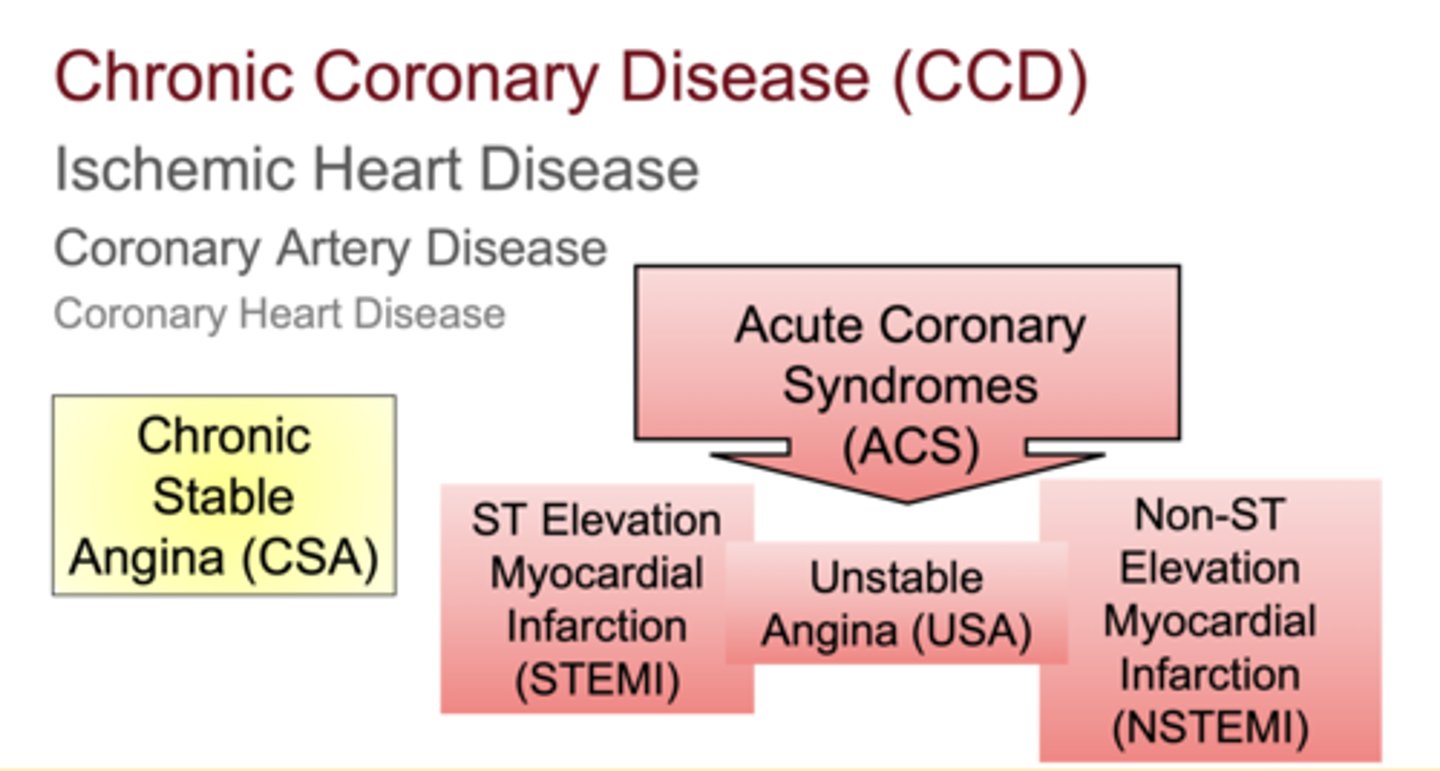
What major conditions fall under the umbrella of Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS)?
Unstable Angina (USA), NSTEMI, and STEMI
What causes ischemia and infarction?
reduced blood supply from a thrombus or embolus that limits oxygen delivery downstream
What is the difference between ischemia and infarction?
Ischemia = reduced oxygen and reversible damage
Infarction = cell death due to complete blockage
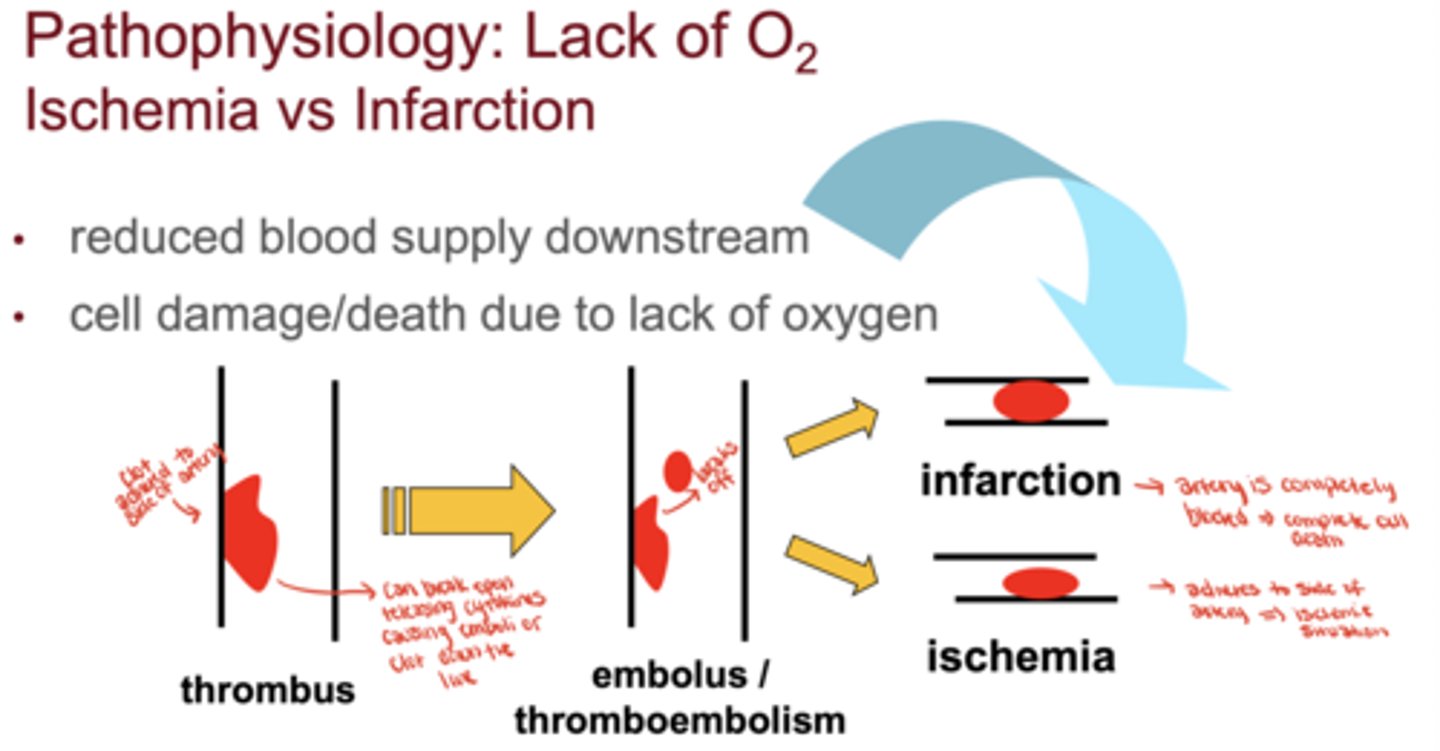
What happens when an artery becomes completely blocked?
it leads to infarction and irreversible myocardial cell death.
What is the most common symptom of ischemic heart disease?
chest pain (angina) or chest tightness often described as a heavy pressure or "rubber band" around the chest
Where can the chest pain radiate?
left arm or jawline
What other symptoms of IHD may occur?
shortness of breath, sweating, nausea/vomiting, tachycardia, and anxiety or sense of impending doom
What does chest pain (CP) indicate?
could be chronic stable angina, unstable angina, or myocardial infarction
**all are caused by lack of oxygen to heart muscle
What two main imbalances cause ischemia?
1. Inadequate oxygen supply from coronary arteries
2. Excessive oxygen demand from the myocardium
What are the three main types of angina?
Prinzmetal's Variant Angina. Chronic Stable Angina, and Unstable Angina
Cause of Prinzmetal's (Variant) Angina
Vasospasm → supply ischemia
Cause of Chronic Stable Angina (CSA)
Fixed stenosis/partial blockage → demand ischemia
Cause of Unstable Angina (UA)
Thrombus formation → supply ischemia
What is chronic stable angina (CSA)?
reversible ischemia without permanent muscle damage, causing predictable chest pain on exertion that resolves with rest
What defines "stable" in CSA?
no change in frequency or severity of chest pain over time
How can pharmacists monitor stability of patients with CSA?
track patient nitroglycerin refill frequency or reports of worsening angina
What proportion of CSA patients eventually experience an MI?
approximately 50%
How does CSA progress into ACS?
when an atherosclerotic plaque ruptures or a thrombus forms, causing complete or near-complete arterial occlusion
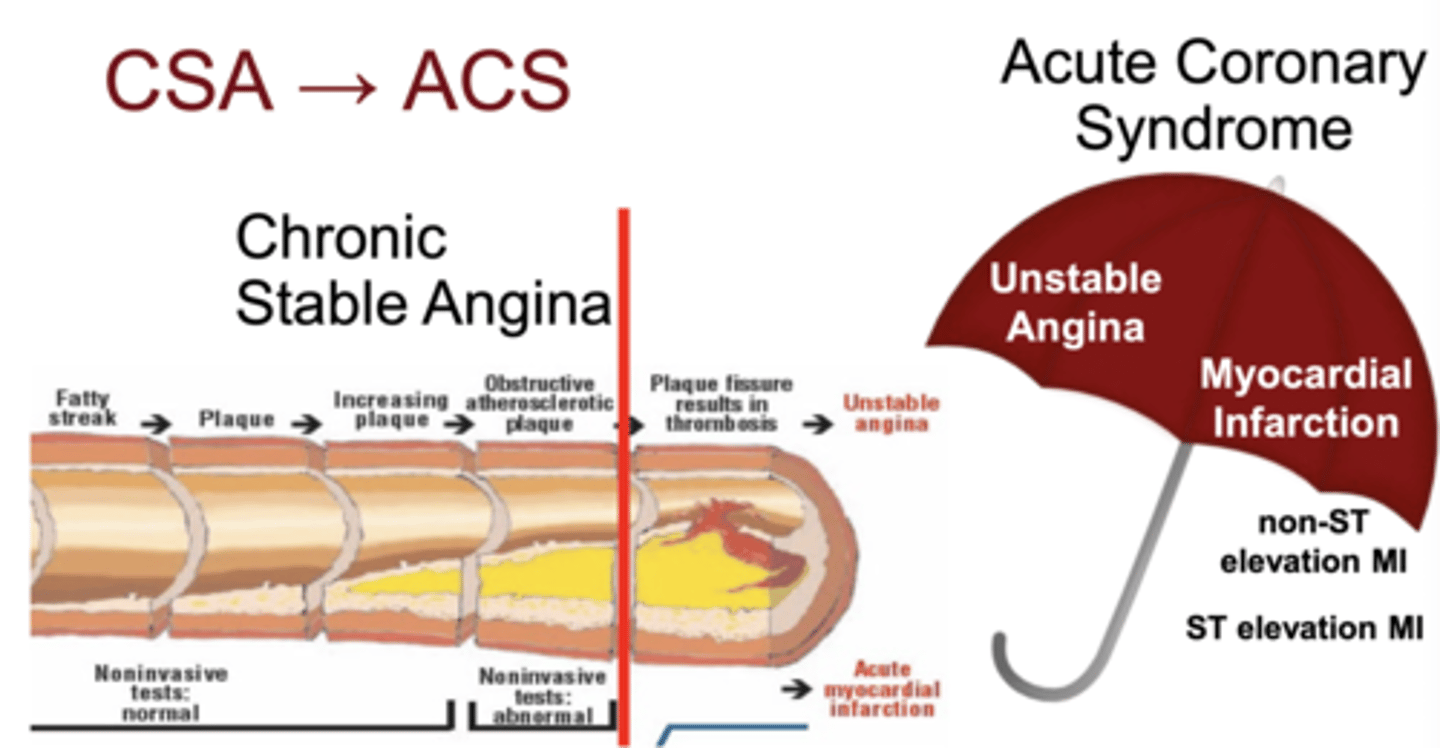
What conditions make up ACS?
Unstable Angina, NSTEMI, and STEMI
Why does the site of occlusion matter?
the affected coronary artery determines the location and severity of myocardial injury
What is the "widow-maker" infarction?
complete occlusion of the Left Anterior Descending (LAD) artery, often fatal
Which 2 drugs are first-line for ACS?
Aspirin and Heparin
3 multiple choice options
How is a STEMI identified?
ST elevation on ECG
How is a NSTEMI identified?
no ST elevation + positive/high cardiac enzymes
How is USA identified?
no ST elevation + negative cardiac enzymes (within normal limits)
What does cardiac enzyme testing confirm?
presence or absence of myocardial cell death
What causes STEMI?
complete thrombotic occlusion of a coronary artery causing myocardial cell death
What enzymes are elevated?
cardiac troponins (T or I)
What ECG finding is typical?
ST segment elevation and possibly new Q waves (transmural infarction)
What can a complete occlusion lead to?
sudden cardiac death
What causes unstable angina (USA)?
transient formation and dissolution of thrombi causing ischemia without infarction
Are cardiac enzymes elevated in USA?
No, enzymes are negative
What symptoms define USA?
new or sudden chest pain, pain at rest, increasing severity or frequency (crescendo angina)
Why is identifying USA clinically significant?
It can "herald" a future myocardial infarction
What causes NSTEMI?
thrombus formation causing partial occlusion and myocardial cell death
Which cardiac markers are positive?
troponin I or T
How does the ECG appear during an NSTEMI?
ST depression or no ST changes (no elevation)
How do NSTEMI symptoms compare to USA and STEMI?
they are similar; chest tightness, SOB, diaphoresis, etc
Which findings are definitive for myocardial infarction?
- detectable/elevated troponins (cardiac enzymes)
- ST elevation on ECG
Why is CK or chest pain alone not definitive of an MI?
CK can rise from non-cardiac causes, and chest pain isn't diagnostic on its own
What does "No ST Elevation" on ECG indicate?
could be NSTEMI or Unstable Angina
- need cardiac enzymes to distinguish
How long do cardiac enzymes take to result?
approximately 30-60 minutes
What do clinicians do in the meantime?
risk-stratify the patient using a validated score (e.g., TIMI)
What is the purpose of the TIMI risk score?
predicts risk of death or MI within 14 days in patients with NSTEMI or USA
What does the TIMI score influence?
whether a patient gets angiography, where they're admitted, and which medications are initiated
TIMI Score: 0-2
low risk
TIMI Score: 3-4
medium risk
TIMI Score: 5-7
high risk
Which TIMI scores indicate angiography?
medium- to high-risk (≥3 points)
What happens during angiography?
catheter is threaded to the aorta and dye is infused to visualize coronary arteries on X-ray
What three options does the interventionalist have after angiography?
no intervention, PCI (angioplasty/stent), or CABG surgery
What is PCI and how is it performed?
balloon angioplasty to dilate a narrowed coronary artery, often followed by stent deployment to maintain patency
What is the main difference between PCI and CABG?
PCI treats specific lesions via catheter; CABG reroutes blood flow around blockages surgically
When is CABG indicated?
for multi-vessel or high-risk disease not suitable for PCI
How is CABG performed?
vessel (from leg, chest, or arm) is grafted from the aorta to a point below the blockage to restore blood flow
What type of surgery is CABG?
open-heart surgery, typically planned 1-2 days after diagnosis
What are the two major electrical properties of the heart?
automaticity (self-generation of impulses)
conductivity (impulse transmission through the heart)
What does automaticity mean?
heart generates its own electrical impulses without input from the brain or nervous system
What does conductivity refer to?
heart's ability to conduct an electrical impulse from one region to another, coordinating contraction
Where does the electrical impulse originate in a healthy heart?
the sinoatrial (SA) node - the pacemaker of the heart
What is the purpose of the atrioventricular (AV) node delay?
to allow the atria to contract and fill the ventricles before ventricular contraction begins
What happens if the SA node fails?
AV node or other conduction tissues (Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers) can act as backup pacemakers
What causes arrhythmias?
impulses originating from abnormal areas of the heart instead of the SA node
Why do nodal cells have automaticity?
their resting membrane potential is unstable due to sodium leakage through hyperpolarization-activated (HCN) channels, creating a "funny current" (If
Why is the "funny current" named so?
because HCN channels are activated by hyperpolarization rather than depolarization (this is an unusual property)
Nodal Slow Action Potential (AP)
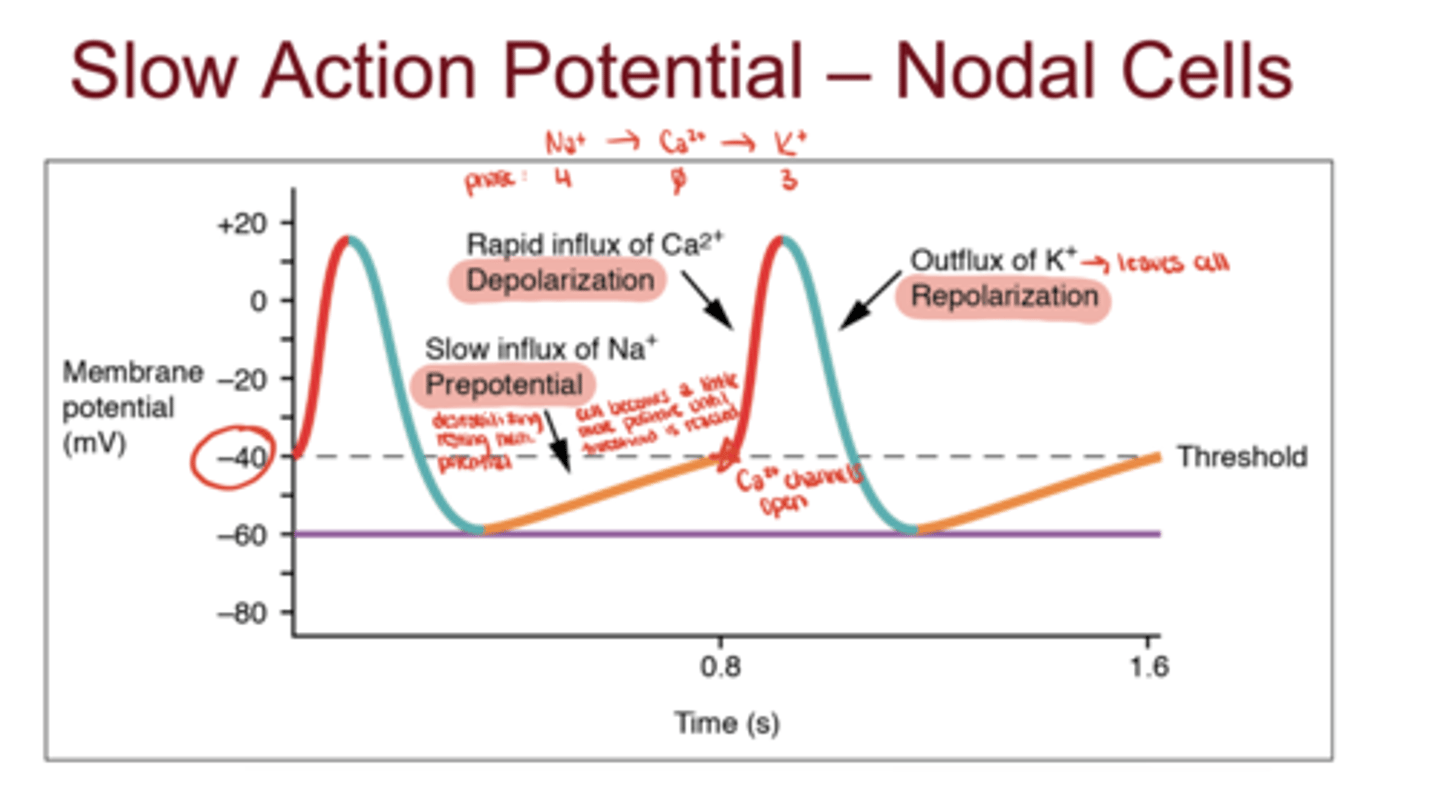
Nodal Slow AP - Phase 4
Na⁺ leak via HCN channels (funny current)
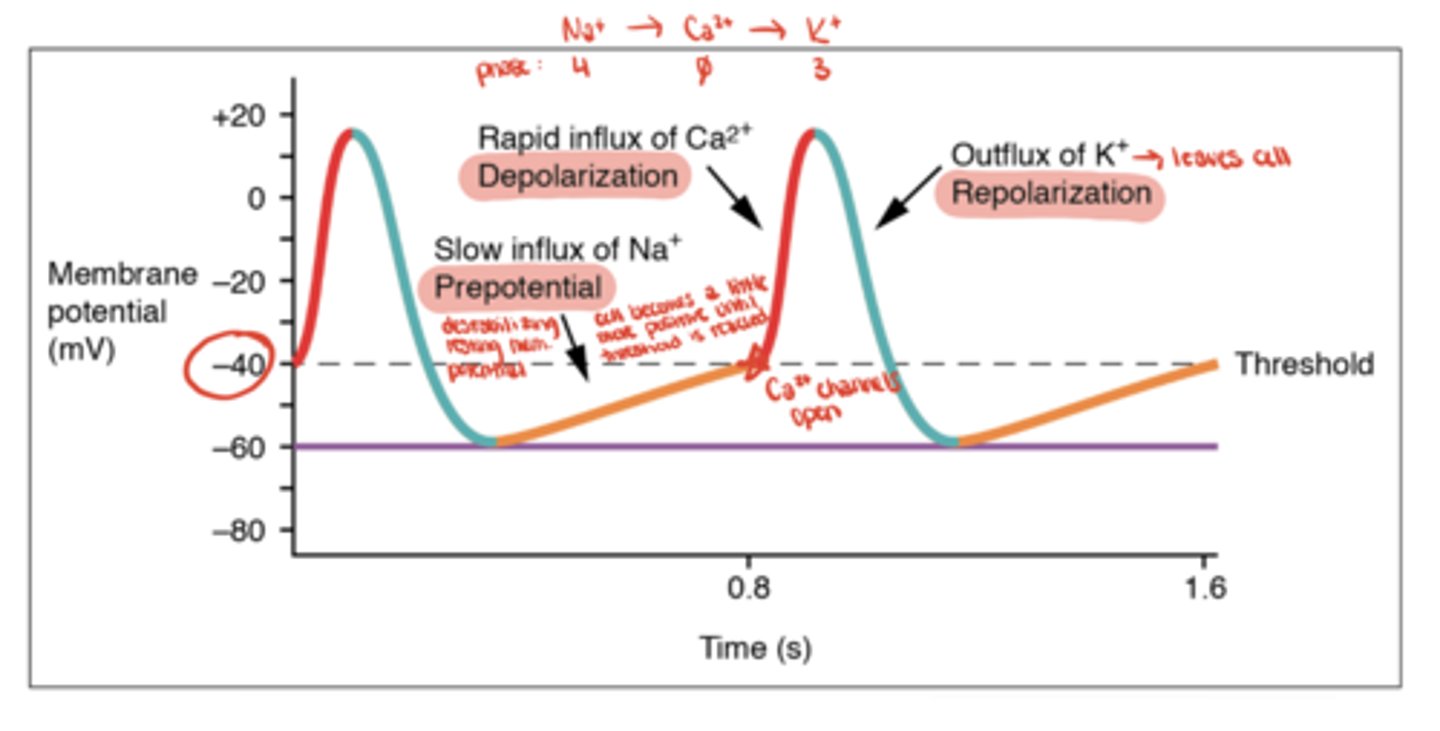
Nodal Slow AP - Phase 0
Ca²⁺ influx through L-type channels
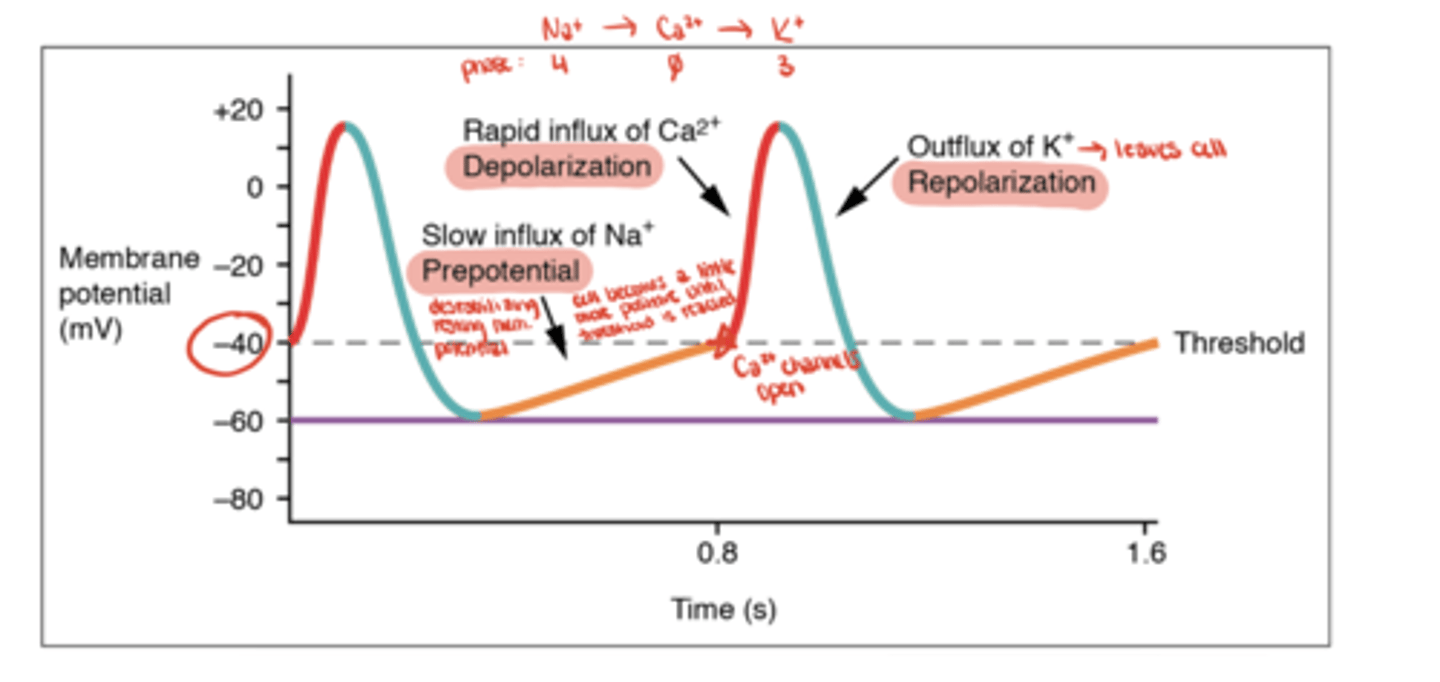
Nodal Slow AP - Phase 3
K⁺ efflux (repolarization)
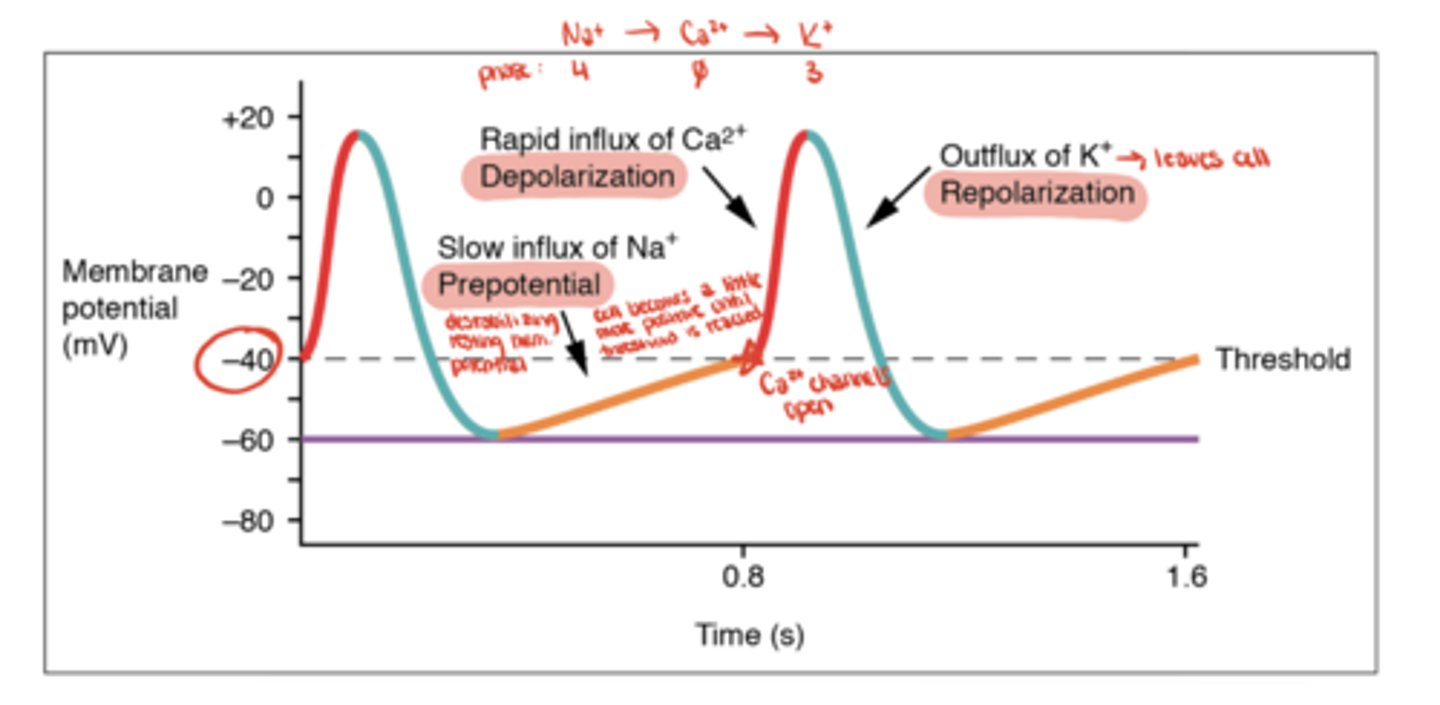
What is the resting potential of nodal cells?
about -60 mV and unstable (gradually drifts upward due to Na⁺ leak)
What determines heart rate in nodal cells?
The slope of Phase 4
- steeper slope means faster threshold reaching and faster heart rate
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect nodal activity?
increases slope of Phase 4 → faster Na⁺ leak → increased heart rate
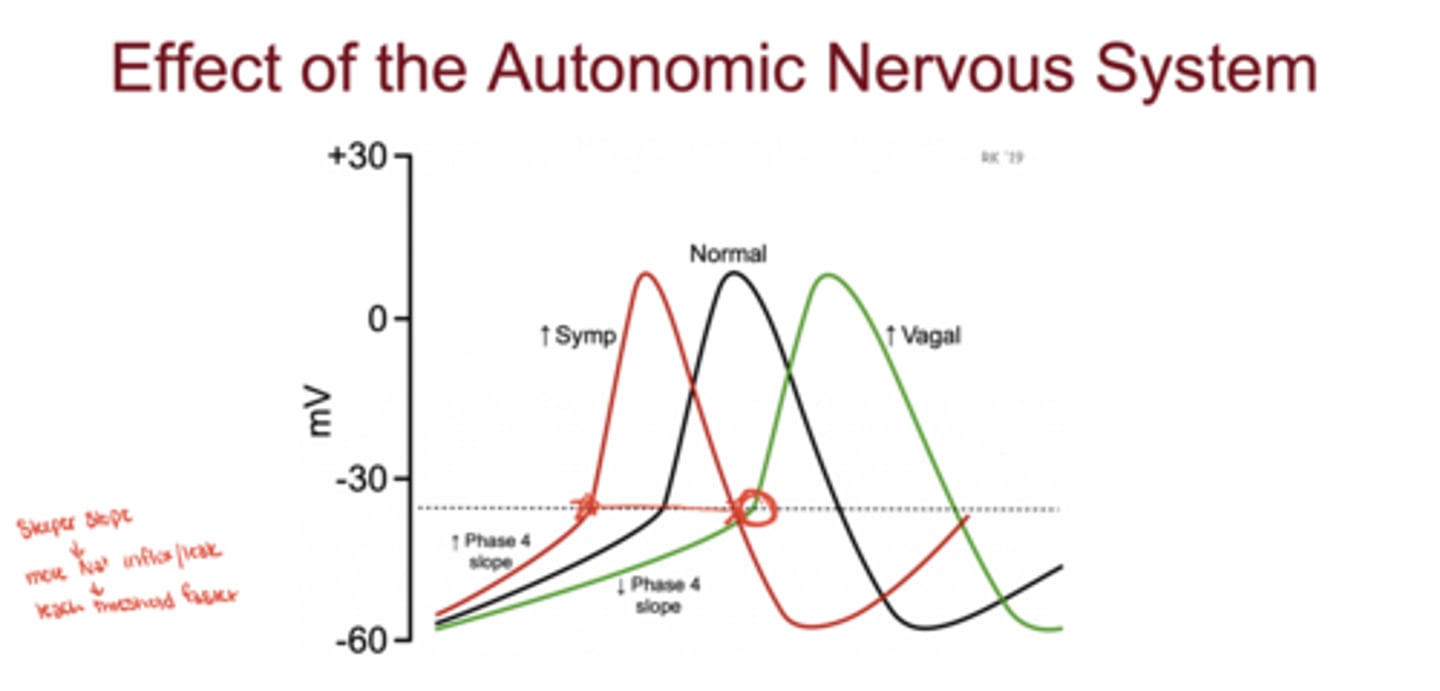
How does the parasympathetic nervous system affect nodal activity?
decreases slope of Phase 4 → slower Na⁺ leak → decreased heart rate
Which phase of the nodal AP is blocked by non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (e.g., verapamil)?
Phase 0 (Ca²⁺ influx)
3 multiple choice options
Where do fast action potentials occur?
in cardiomyocytes (contractile cells of the ventricles and atria)
Fast AP in cardiomyocytes
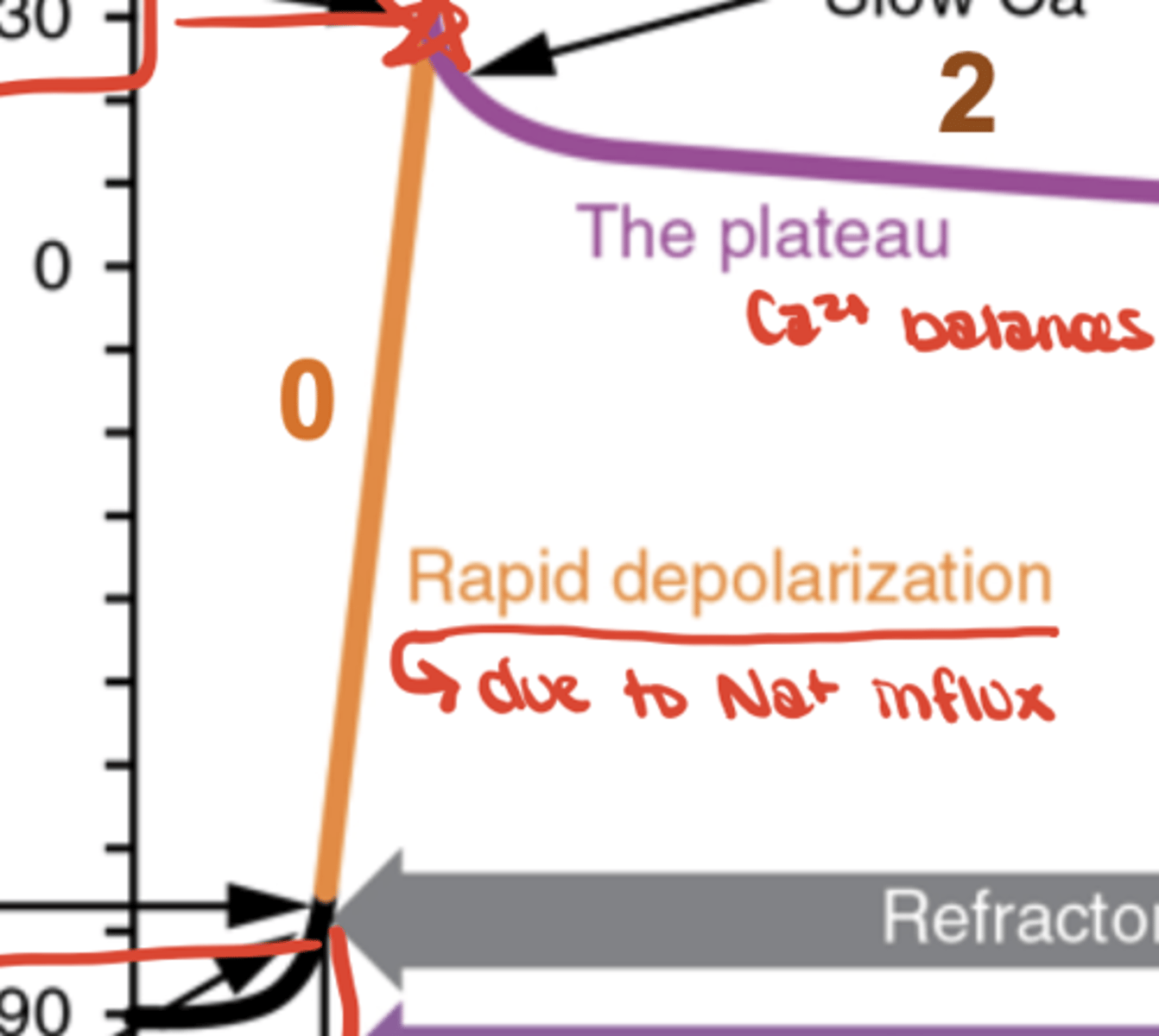
Fast AP - Phase 0
Na⁺ influx (depolarization)
Fast AP - Phase 1
K⁺ efflux (early repolarization)

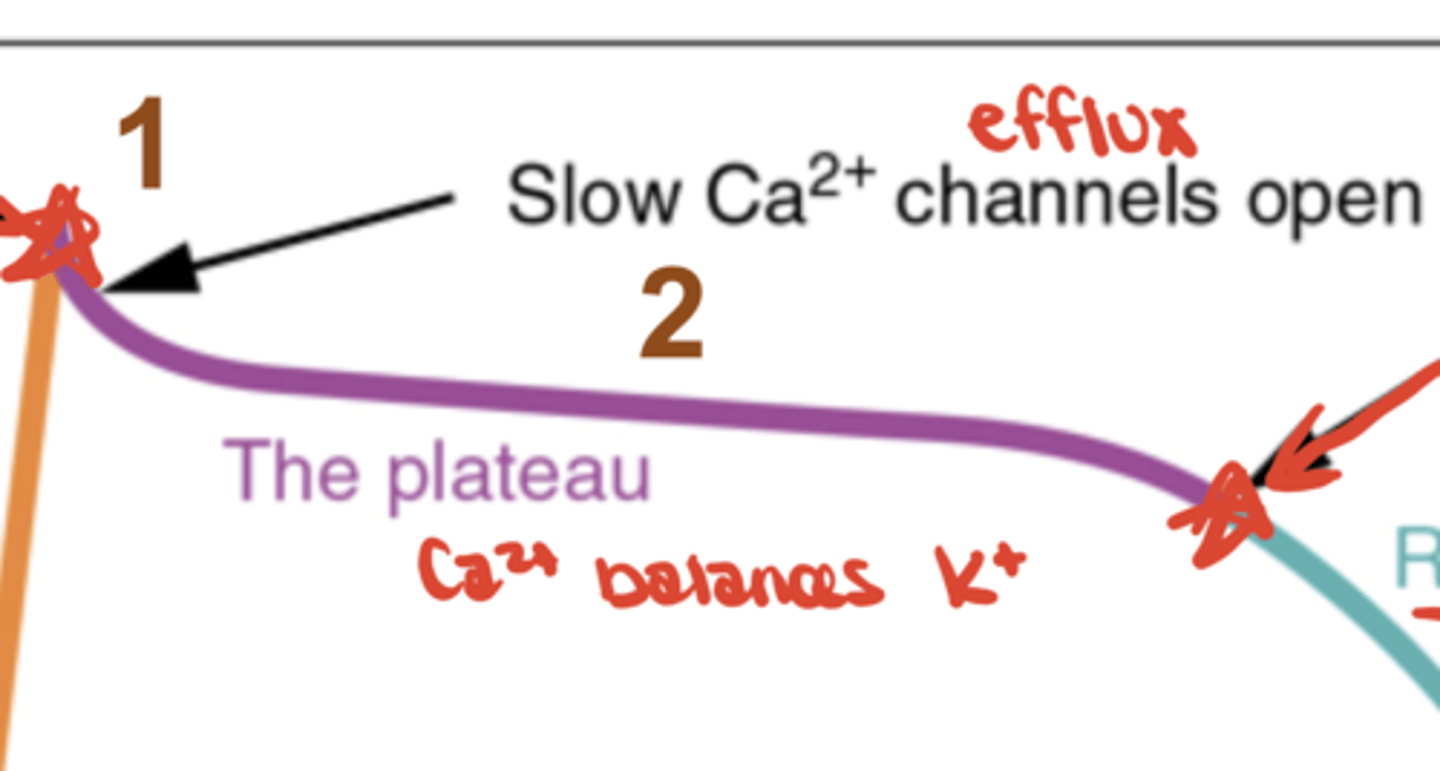
Fast AP - Phase 2
Ca²⁺ influx balances K⁺ efflux (plateau)
Fast AP - Phase 3
continued K⁺ efflux (repolarization)
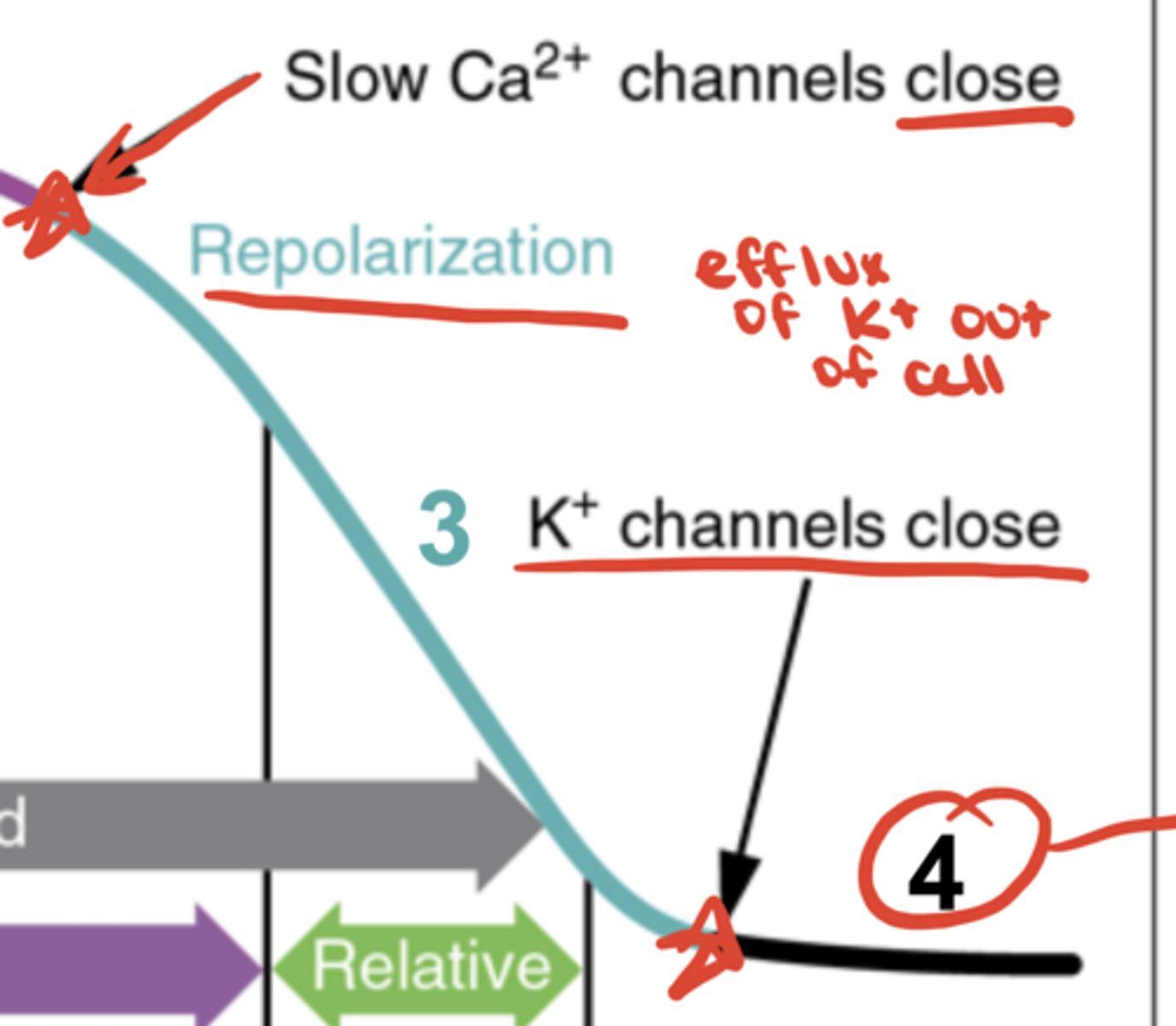
Fast Ap - Phase 4
Na⁺/K⁺ pump & Na⁺/Ca²⁺ exchanger restore gradients
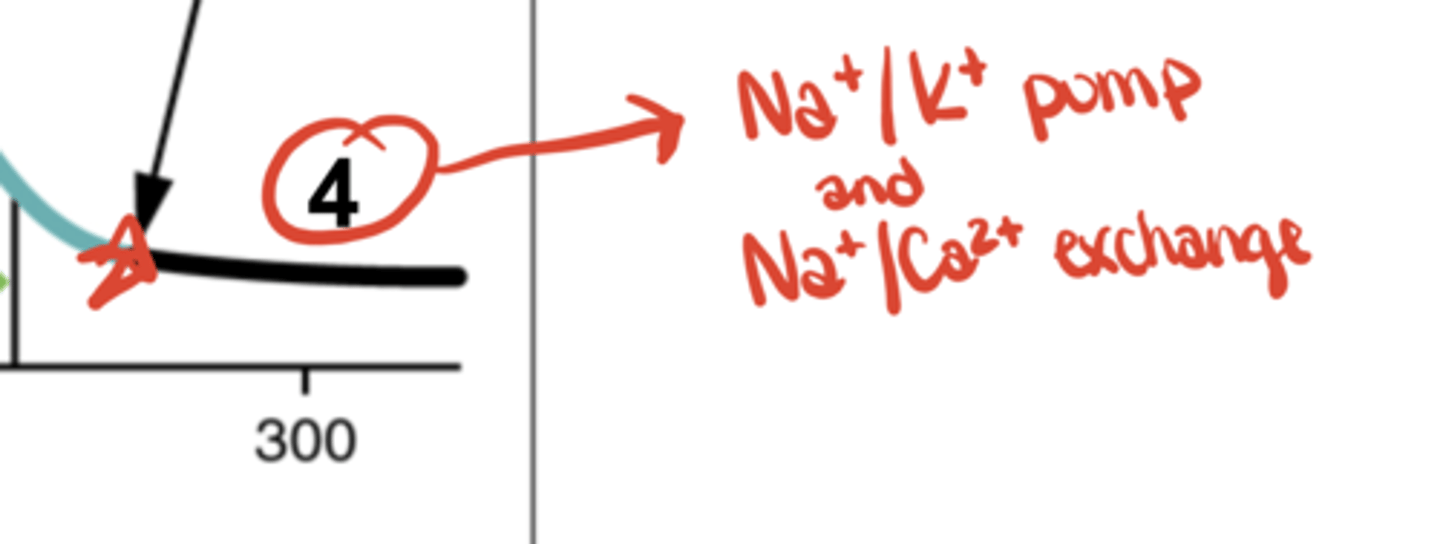
Why does Phase 2 (plateau) occur in fast APs?
Ca²⁺ influx balances K⁺ efflux, maintaining voltage; crucial for cardiac contraction
What is the resting potential of cardiomyocytes?
approximately -90 mV and stable (no Na⁺ leakage)
What is the refractory period?
time after depolarization during which the cell cannot be re-excited because ionic gradients are not yet restored
Compare slow vs fast AP depolarization phases.
Slow AP: Phase 0 caused by Ca²⁺ influx
Fast AP: Phase 0 caused by Na⁺ influx
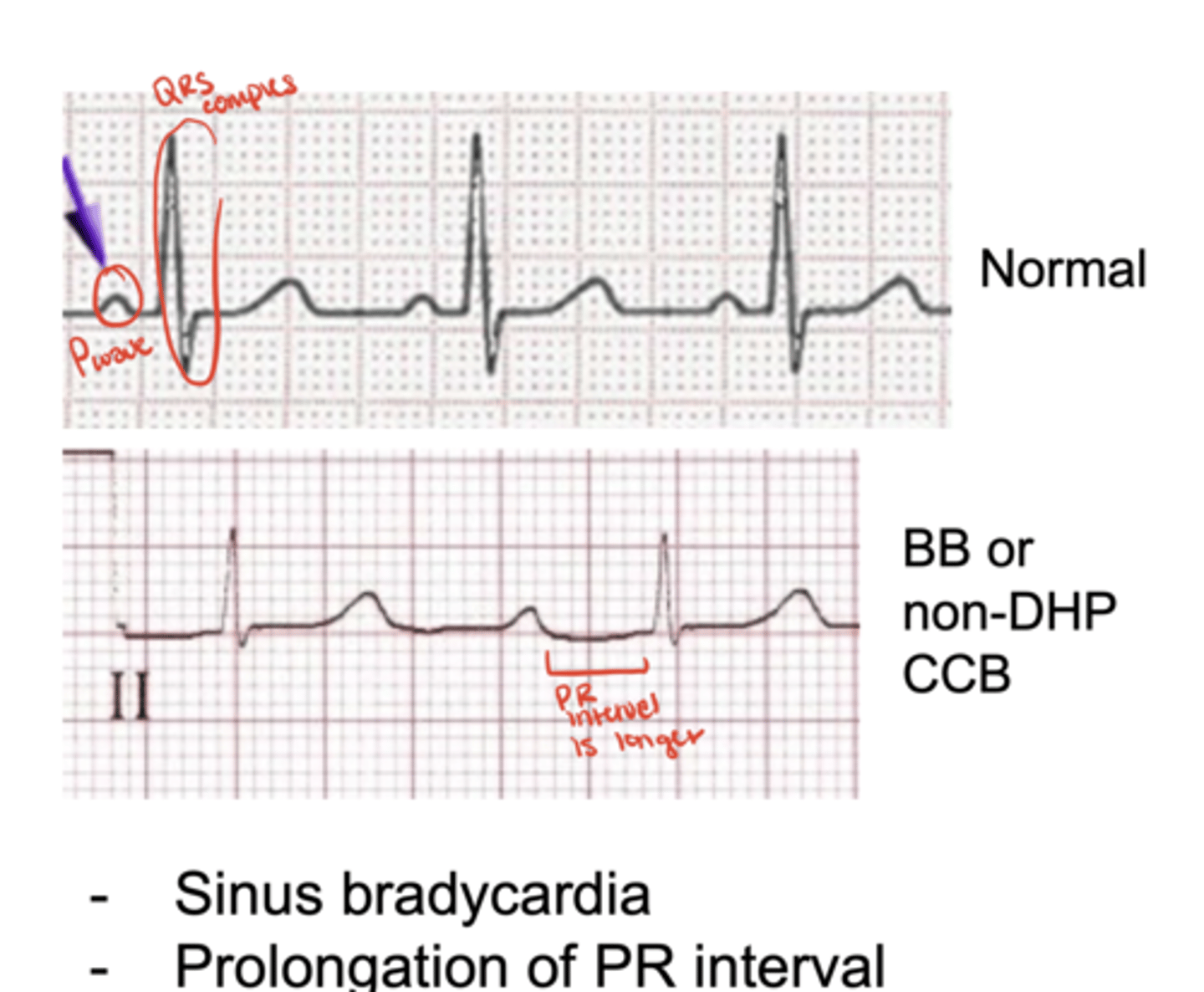
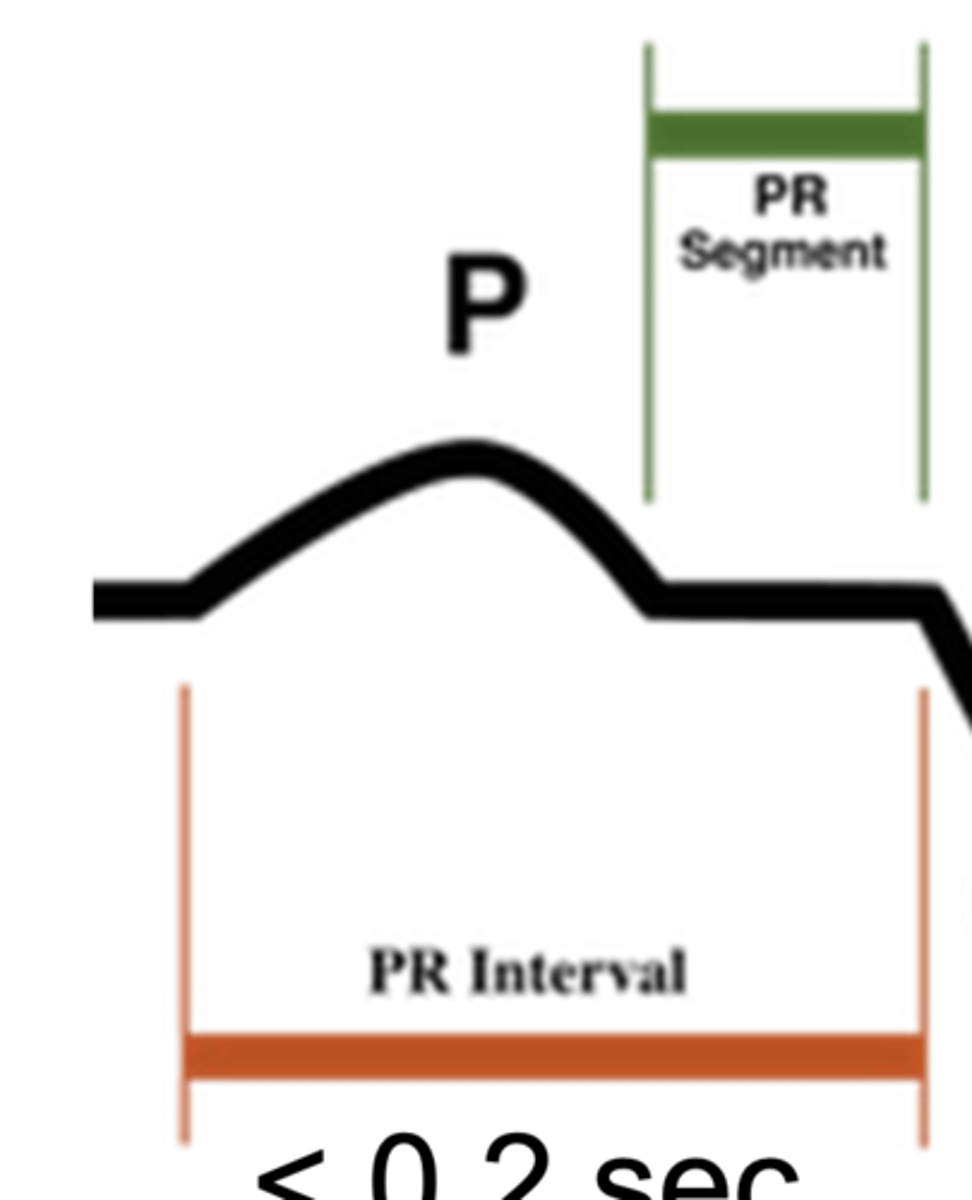
What does the P wave represent on ECG?
atrial depolarization
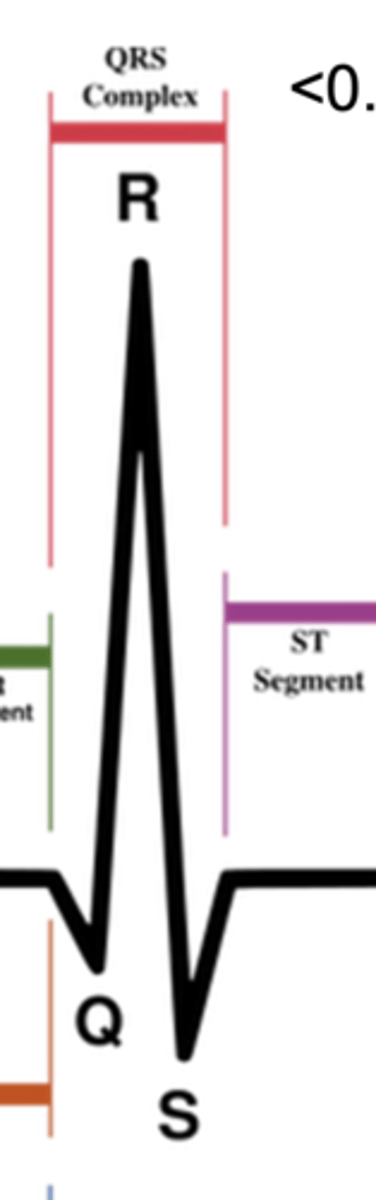
What does the QRS complex represent?
ventricular depolarization
What does the T wave represent?
ventricular repolarization
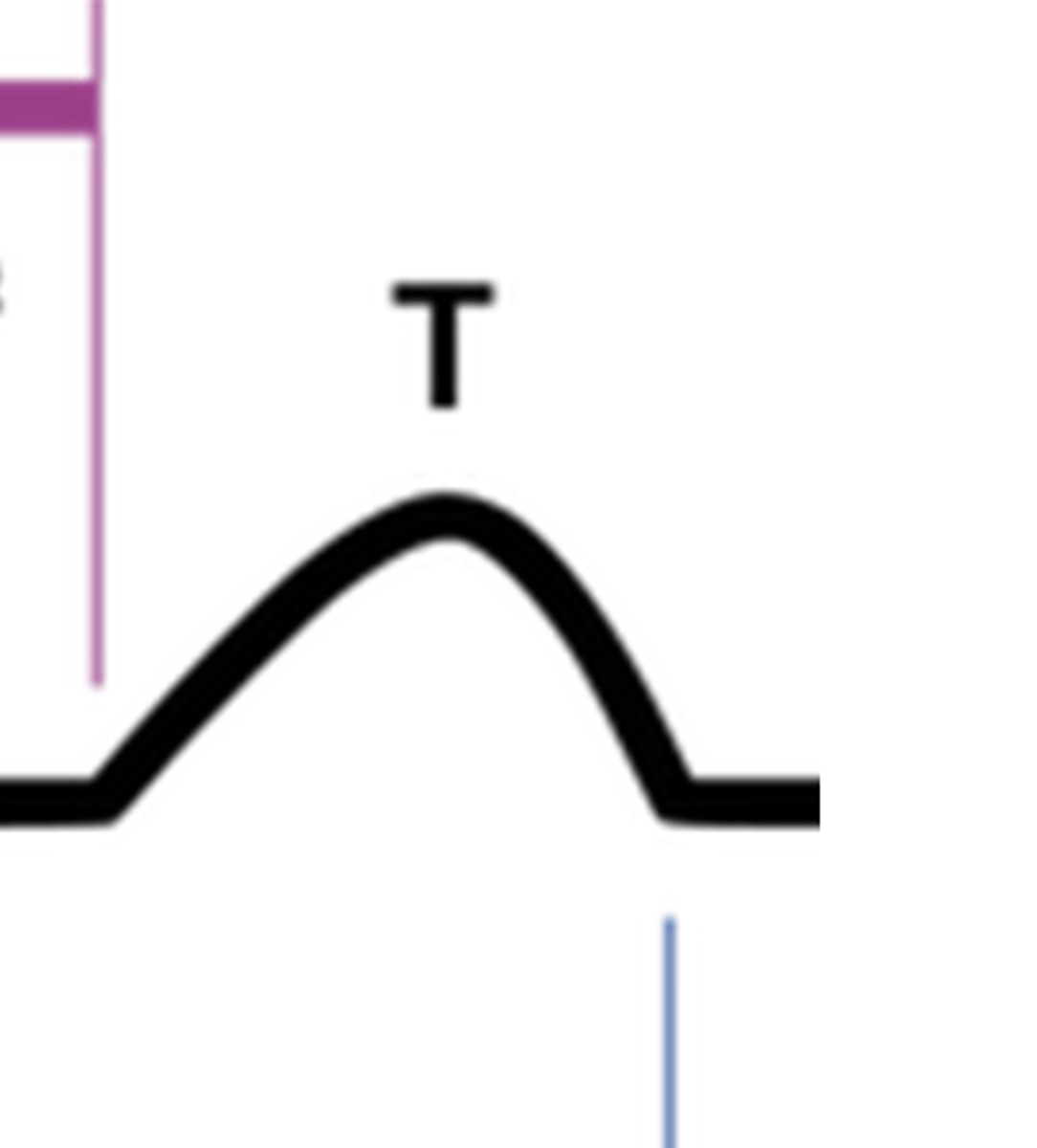
Why is atrial repolarization not seen on ECG?
It's masked by the stronger QRS complex signal
What does the PR segment represent?
AV nodal conduction (the delay between atrial and ventricular depolarization)
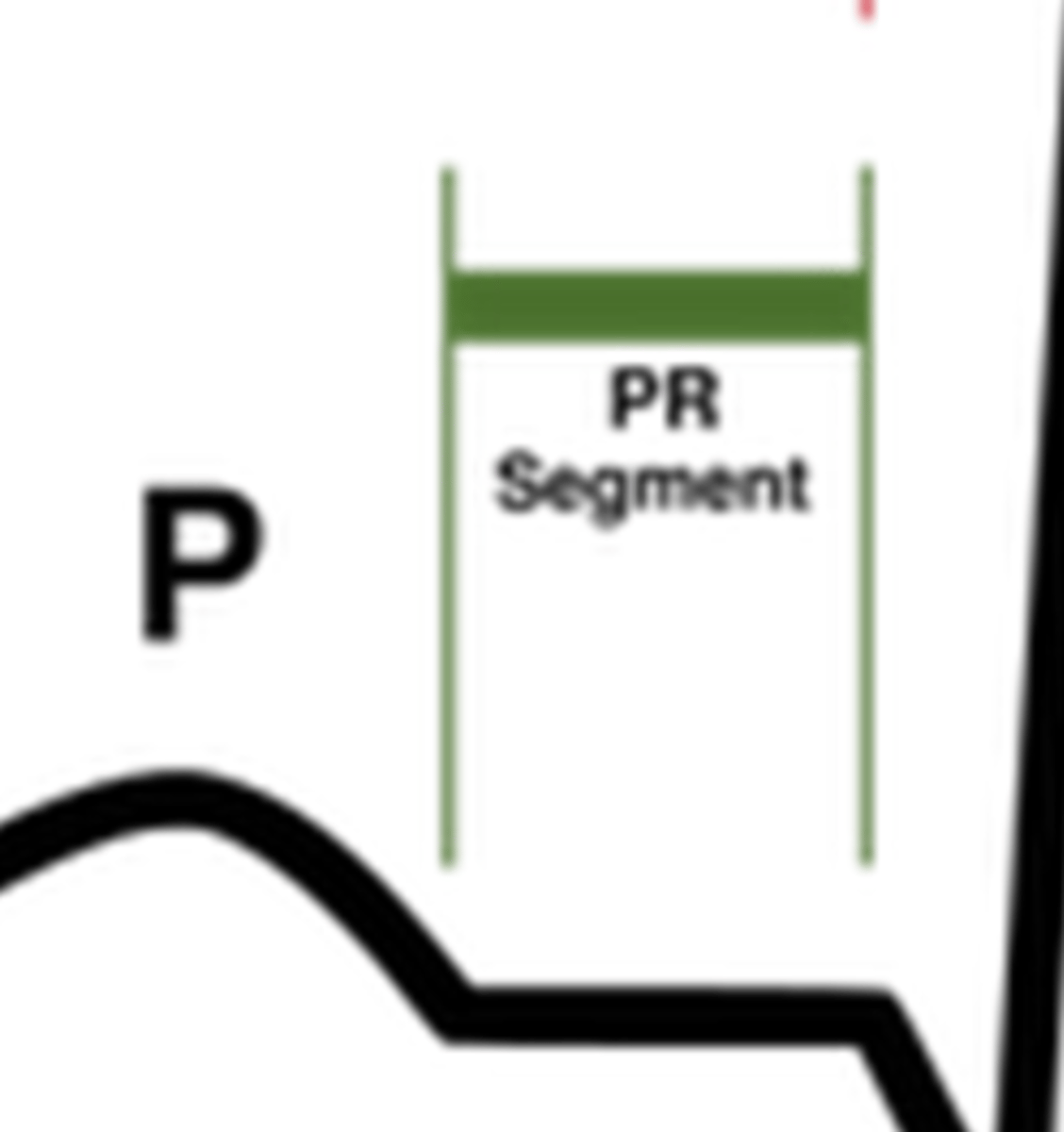
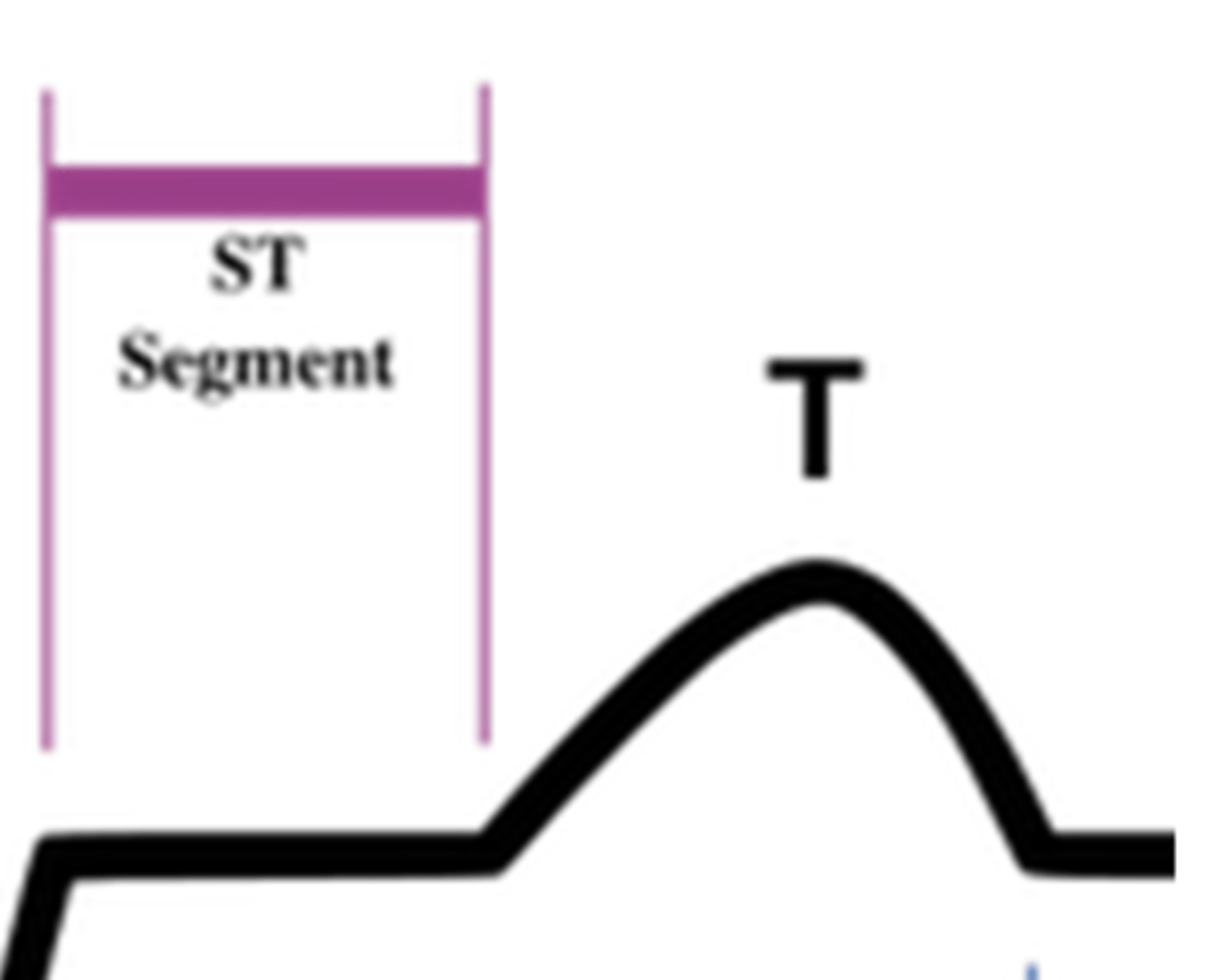
What does the ST segment represent?
plateau phase of the fast AP (between ventricular depolarization and repolarization)
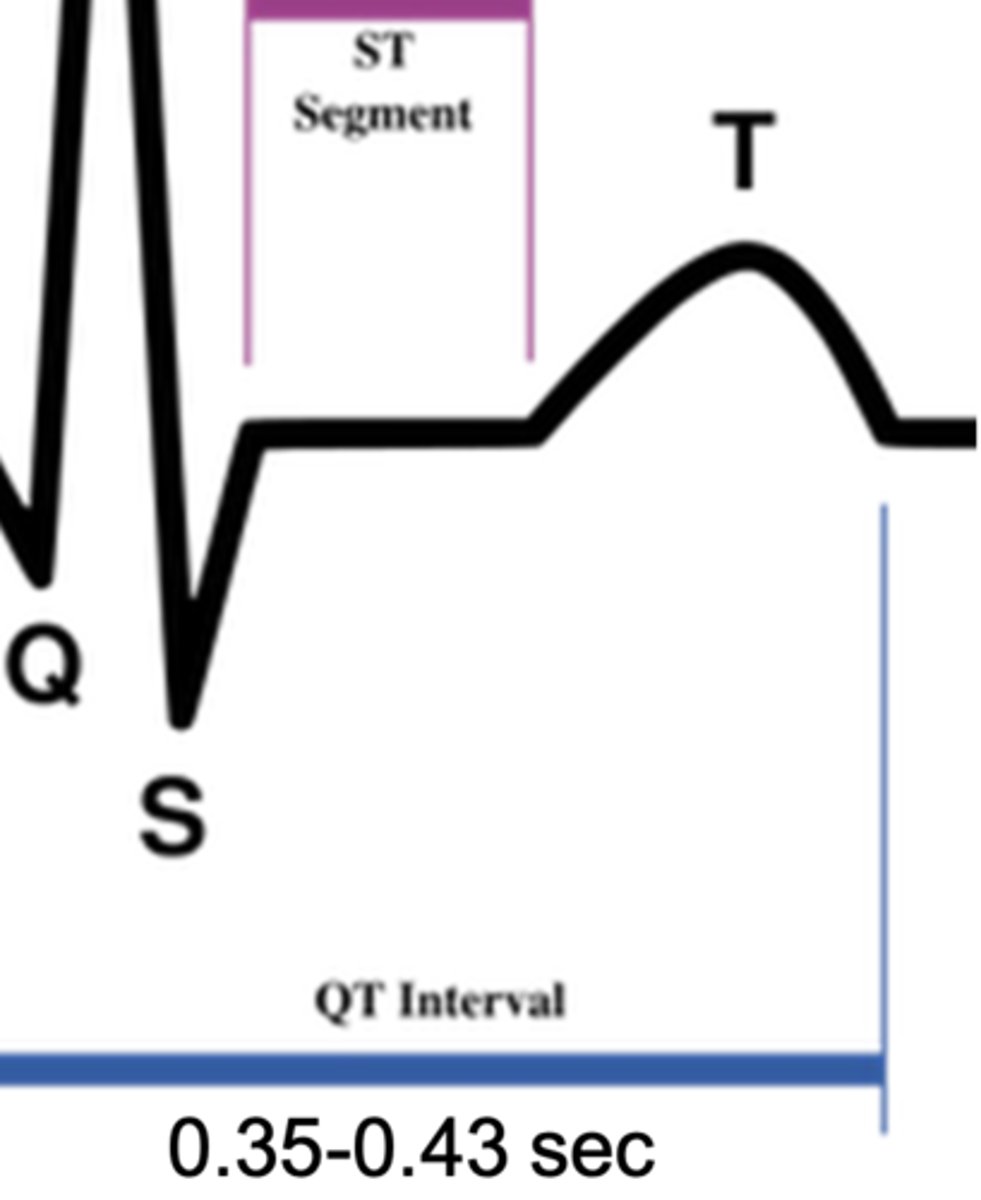
What does the QT interval represent?
the total duration of ventricular depolarization and repolarization
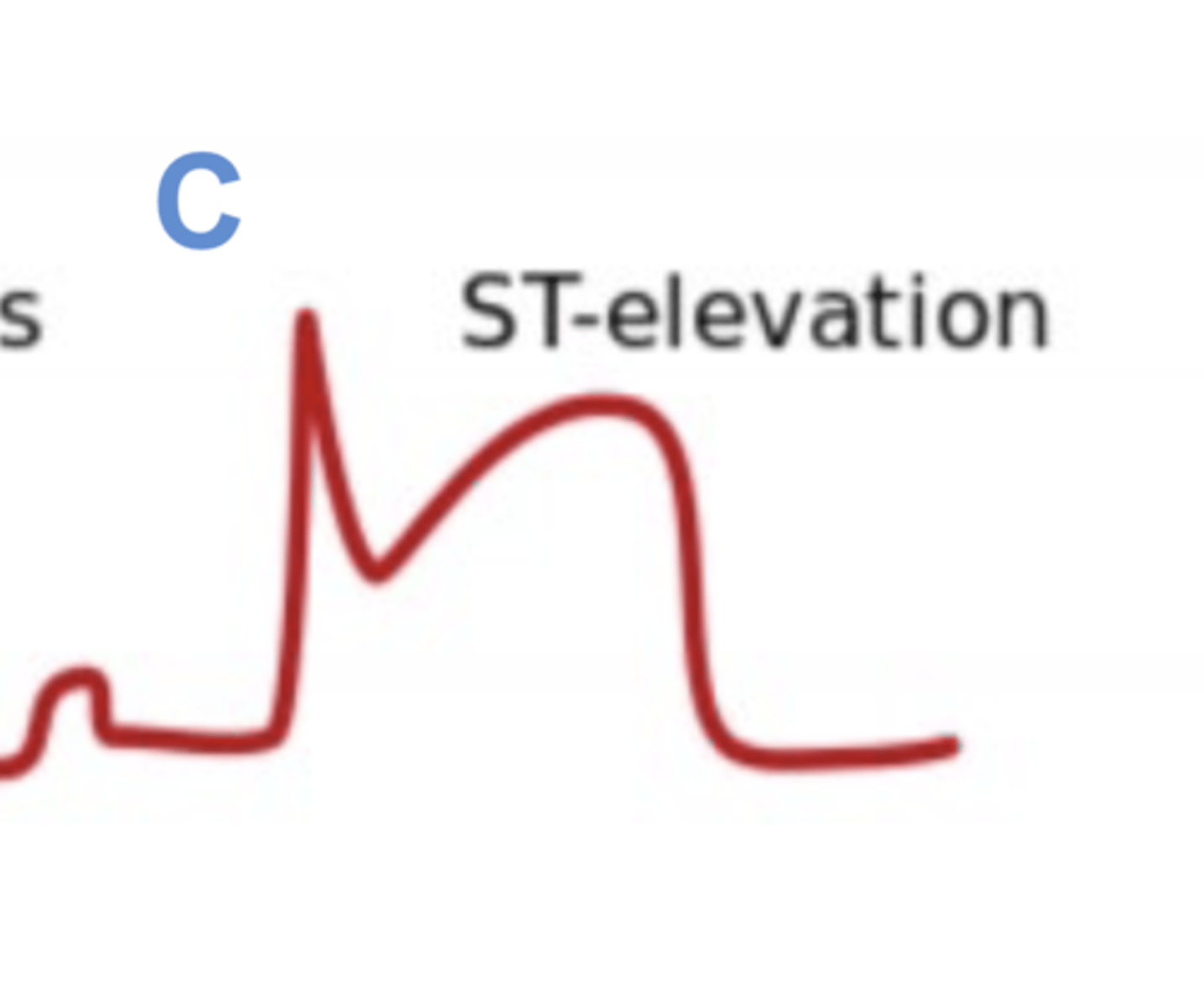
ST Elevation
STEMI (transmural infarct)
T Wave Inversion
ischemia or necrosis
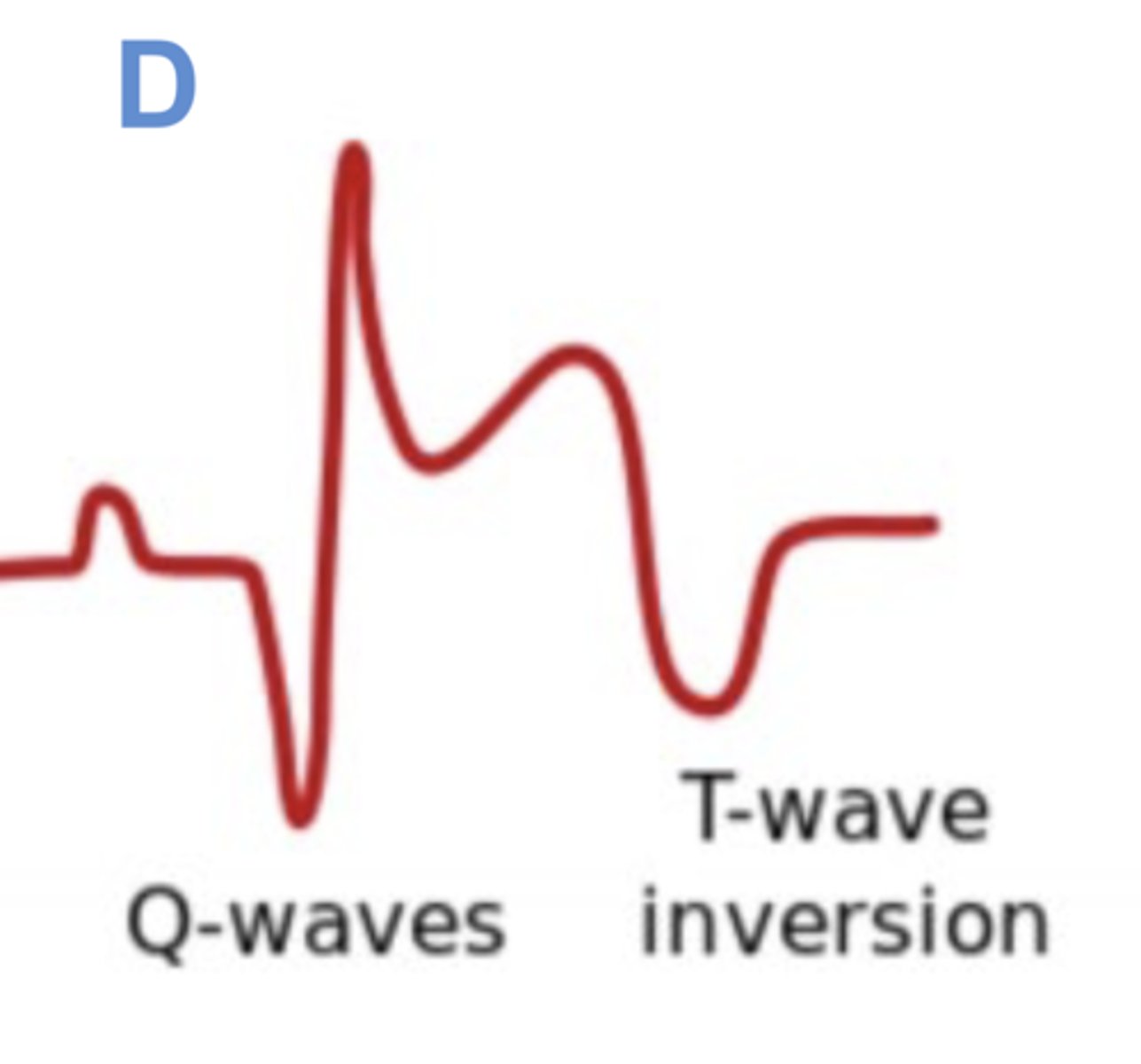
Pathologic Q Wave
old infarct/fibrosis

How do non-DHPs and β-blockers impact ECG readings?
prolong PR interval due to AV nodal delay