What is Economics? Chapter 1 (copy)
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is Economics?
the study of how people allocate their limited resources to satisfy their unlimited wants (economic problem).
it is a study of scarcity and choice
Economic Problem
people are faced with limited resources and unlimited wants
consists of choice and scarcity
Scarcity
Anything that has a price is relatively scarce (economic good)
Problem of choice
Making choices when confronted by scarcity involves a trade-off
Three basic economic questions
Production
What to produce?
How to produce?
production technique (labour or capital
Distribution
For whom to produce?
Price mechanism
Why is Economics a Social Science?
Uses scientific methods to investigate and analyse human behaviour.
Types of Resources (3) / factors of production
Natural Resources
supplied from the natural environment
Human Resources
the quality or quantity of the labour force
labour (physical & mental) and enterprise (coordination & management)
Capital
man-made resources which assists the production of goods & services
can be referred to as an investment
Microeconomics
deals with the economic problem from an individual (smaller) perspective
studies how markets and prices work to allocate resources between all the competing industries in the economy
Macroeconomics
deals with the economic problem from society’s POV (large)
concerned with the performance of the whole economy
production, price levels, employment
Social Science
studies the behaviour of people and the choices they make in response to the economic problem
scientific method is used to identify the principles that govern economic behaviour
Ceteris Paribus
‘all other things constant’ - independent variables are kept constant in the hypothesis and observation
Used to isolate the cause and effect of each seperate variable
Economic Model
a simplified representation of economic reality showing the relationship between certain economic variables.
describes what is happening ib an economy, simulate what has happened and forcast what might happen
Rational Self-Interest
people make rational decisions following a logical process in order to compare the benefit and costs.
used by economists to explain human (behaviour) purchasing
Positive economics
can be proven true or false, or tested objectively
“what is…”
can be used to build theories & models which can be put into practice
Normative economics
are subjective statements, opinion rather than facts
“Should…”
Involves a value judgment
Relative Scarcity
resources re limited relative to society’s unlimited wants
Once we satisfy a want there will always be another to take its place
Can be proven true or false
Free Good
not considered scare as it doesn’t have a price
we do not need to make a choice and can consume an unlimited amount (air)
Opportunity Cost and Trade-offs
Every decision involves a choice between one course of action and another, a trade off
the value of the best alternative foregone
represents the real or economic cost of a decision
it is not always financial
Marginal analysis
compares the additional benefits derived from an activity with the extra cost incurred
it makes sense to allocate resources as long as the marginal benefits exceed the marginal costs.
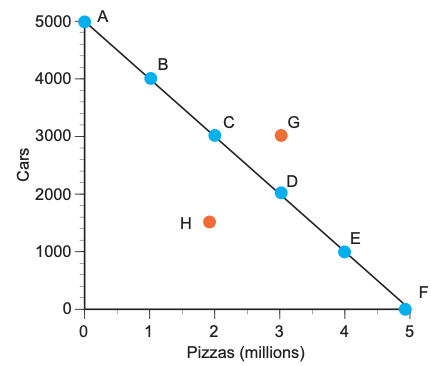
Production Possibility Frontier
Shows all the combinations of goods and services that can be produced by an economy given the available resources and the level of technology
PPF assumptions
resources are fixed
technology is fixed
the economy produces just 2 products
What the PPF shows
When we graph a PPF it shows the maximum and ideal output given the fixed resources and technology
Point H is attainable but inefficient
Point G is unattainable as we don’t have enough resources
the basic economic problem, scarcity and choice
Economic Growth
refers to an increase in the capacity of an economy to produce goods and services
result of an increase in the quantity of resources or an improvement of their quality
investment increases economic growth
consumption only lasts short periods of time
Economic Systems
how a county’s resources are allocated to deal with the economic problem
Must answer the three economic questions
For whom
What
How
determine the allocation of resources and distribution of income
Capitalist/free enterprise economy
Free market
All resources are owned privately, decisions made by the owners in their self-interest
Planned or Command economy
Resources are owned by the state and decisions are made by planning authorities
Most of the time are communist communities
government spends OTHERS money - no care
Mixed Economy
Most economies are mixed, combining elements of both
The government still has important role in providing goods and services
scarcity does not mean
shortage
natural resources
“gifts of nature” water, air
Human resources
quantity and quality of the labour force
types of human resources
Labour
Physical or mental effort applied in the production of a good/service
Enterprise
the coordination and management of production by an entrepreneur.
Ideas/social skills needed to create good/services
Capital resources
man-made resources which assists human resources in the production of goods/services.
social overhead capital
basic infrastructure of the economy. transport, communications
investment “engine of economic growth”
creation of new capital goods
principle of decreasing marginal benefit
as you consume more of something the extra or additional benefit you get declines
net benefits
total benefits and total costs
optimal number
where the net benefits are largest
keep allocating resources until we maximise the net benefits
Why is the PPF sloped downwards
trade-off, to produce more of one good production must decrease for another good
scarcity
what does a straight line PPF mean
constant oppurtunity cost
movement along the curve of PPF
opportunity cost of changing production
law of increasing opportunity cost
As more of one good is produced opportunity cost increases since resources are not equally productive at producing both goods
economic growth will cause PPF to
shift right
lower rate of economic growth
where more resources are voted to producing consumption goods
frontier only moves a short distance right
market economy
both government and private sector determine allocation of resources
consumer is considered sovereign
spending determines what is produced
shortages and surpluses are rare, prices will always adjust to ‘clear the markey’
most efficient because prices reflect relative scarcity