07.3C U7P2 (PART C) Central Nervous System (NO Protection)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
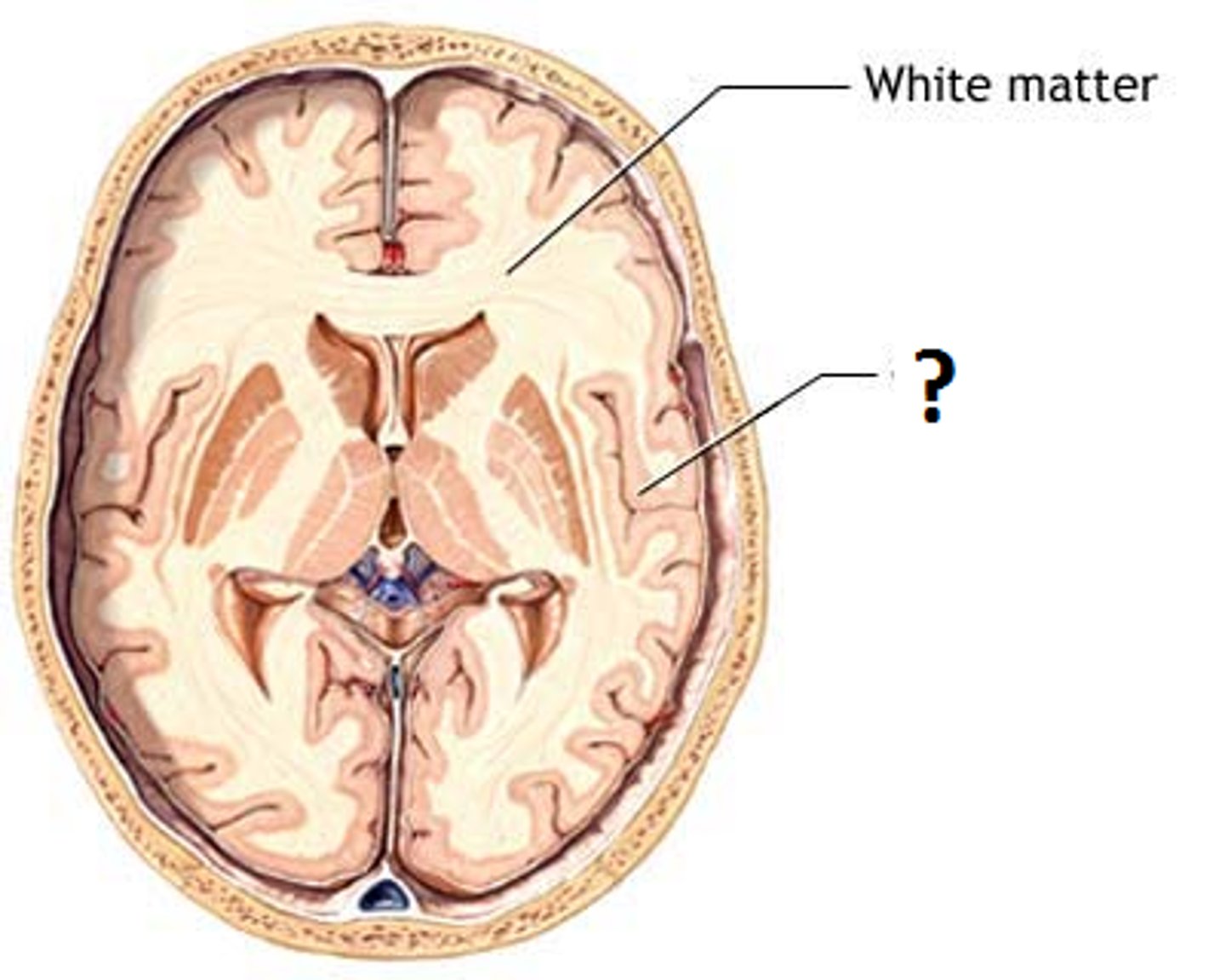
White matter
Myelinated nerve fibers (axons) found within brain and spinal cord that create pathways for the transmission of nerve impulses to and from the cortex
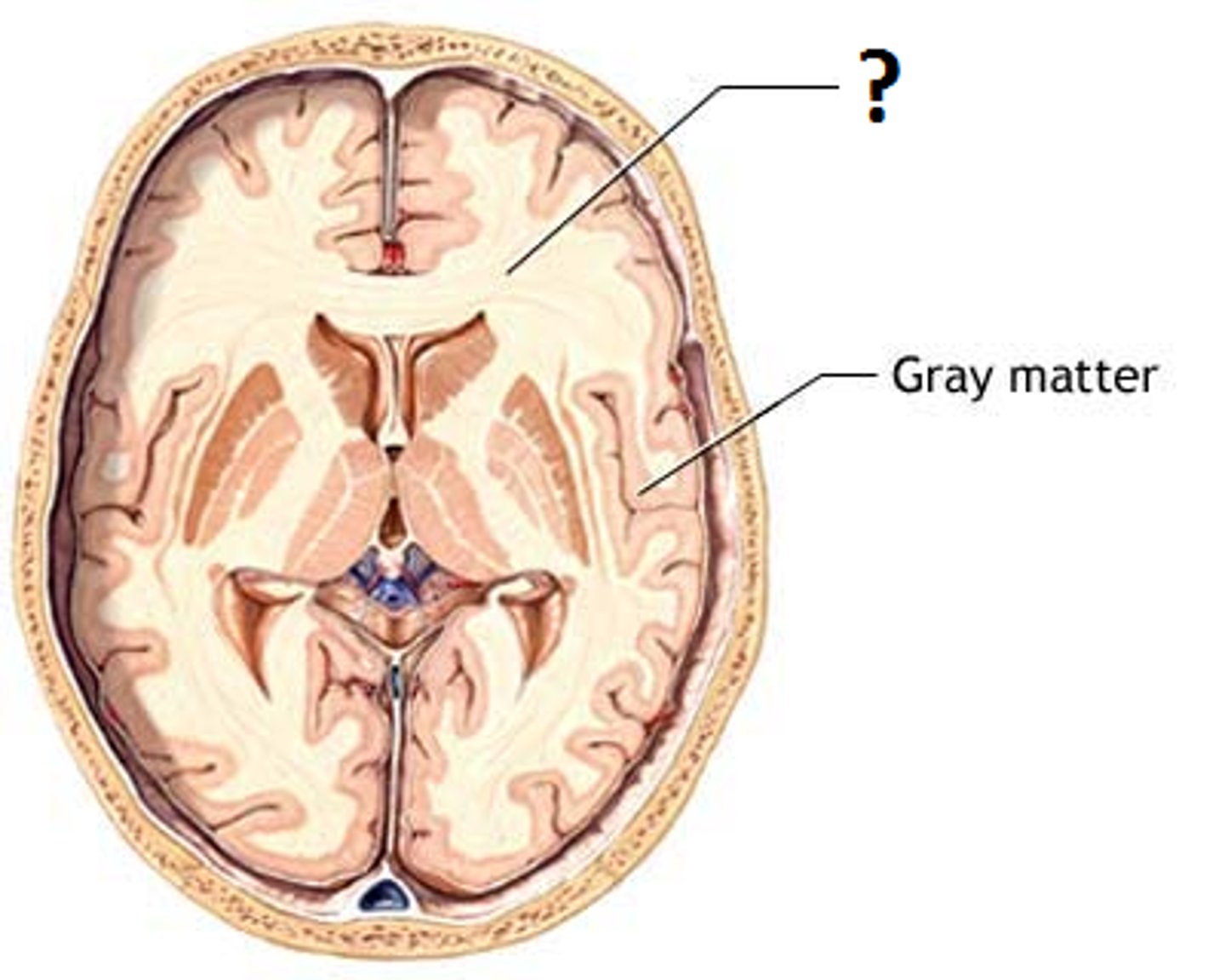
Gray matter
Nerve cell bodies and unmyelinated nerve fibers covering the outside (cortex) and patches inside (nuclei) of the brain
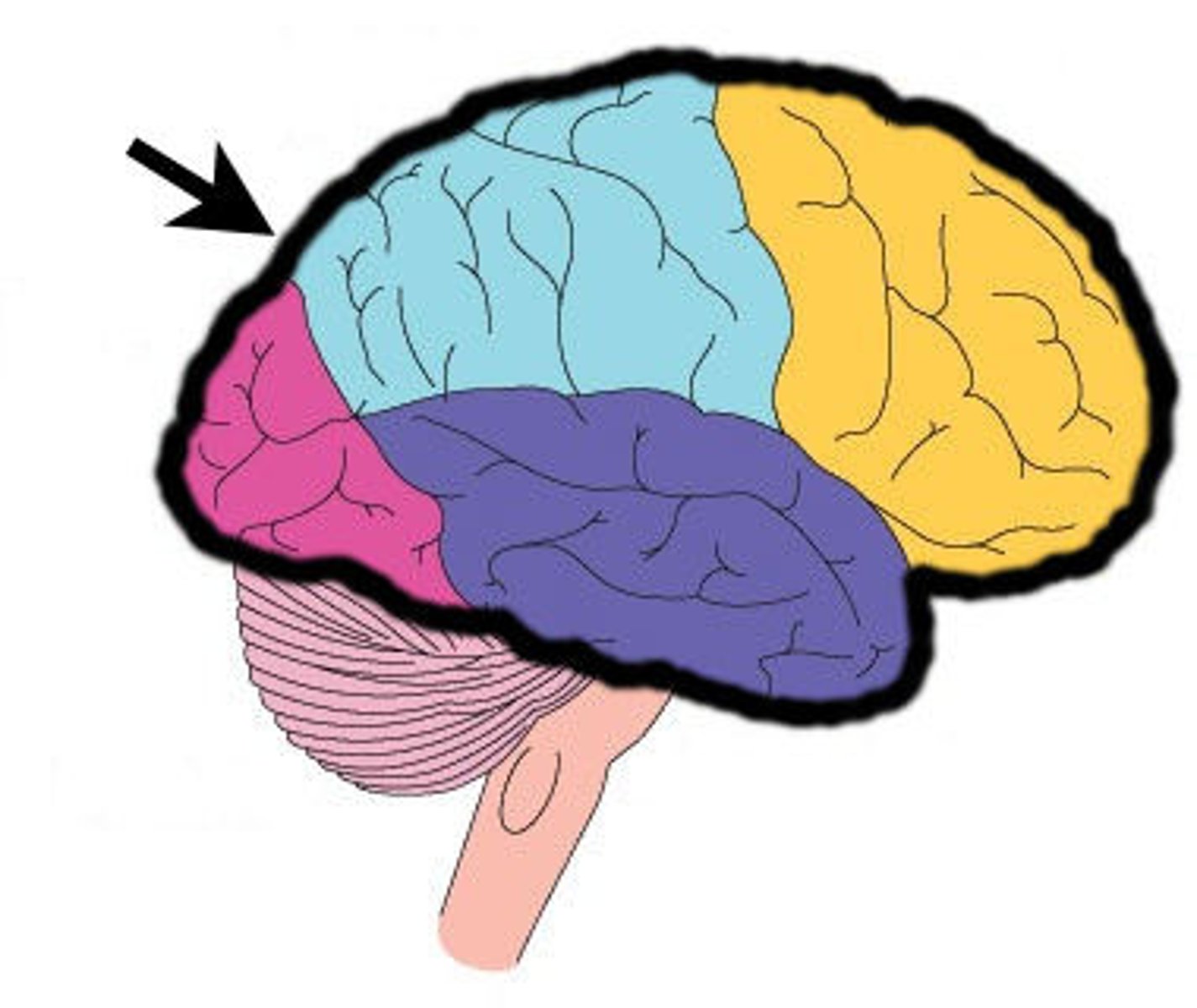
Cerebral cortex
The outermost portion of the cerebrum; composed of gray matter approx. 2-3 mm thick; receives sensory input and sends instructions to the muscles and glands for control of bodily movement and activity
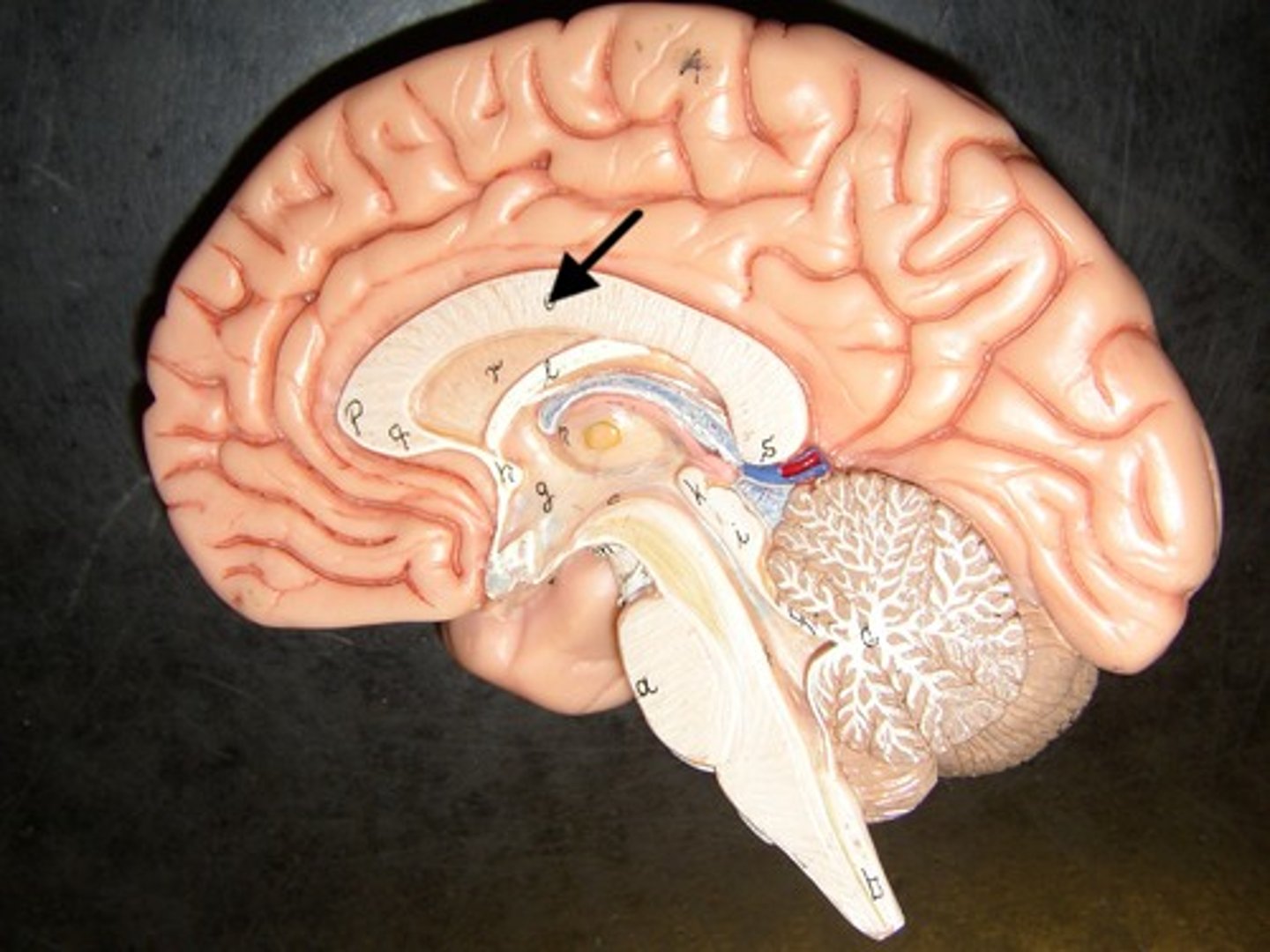
Corpus callosum
The largest and densest bundle of white matter fibers within the cerebrum; forms the roof of the lateral ventricles and connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres
Cerebrum (Description)
The largest portion of the brain that is divided into left and right hemispheres; involved in thought judgment, memory, and discrimination
Cerebrum (Lobes)
This region of the brain is made of the:
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Temporal lobe
Frontal lobe (Location)
Located at the front of the skull
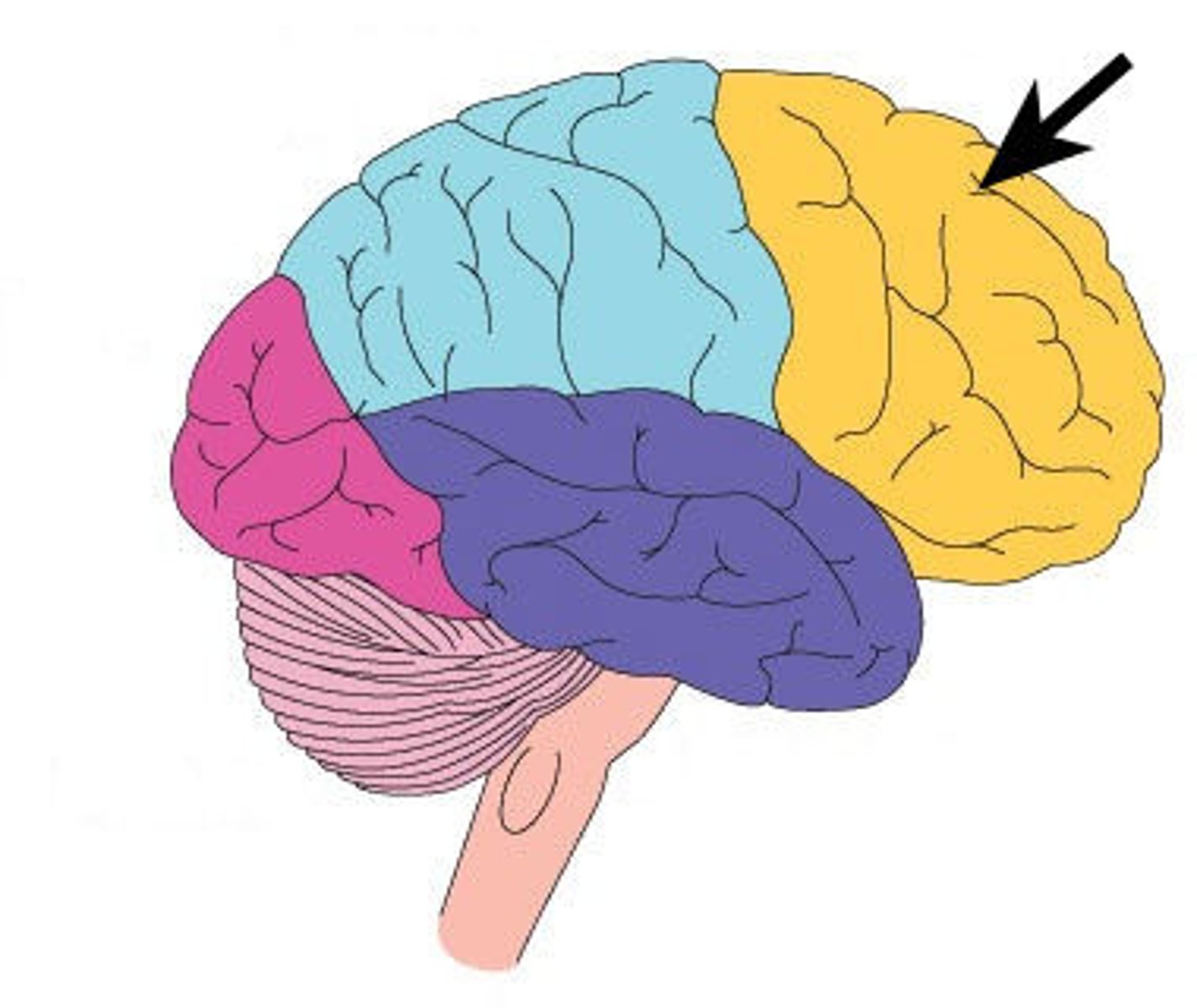
Frontal lobe (Function)
A lobe of the brain that is responsible for decision-making, problem solving, planning, cognition and memory
Parietal lobe (Location)
Located in the middle portion of each cerebral hemisphere just posterior to the central sulcus
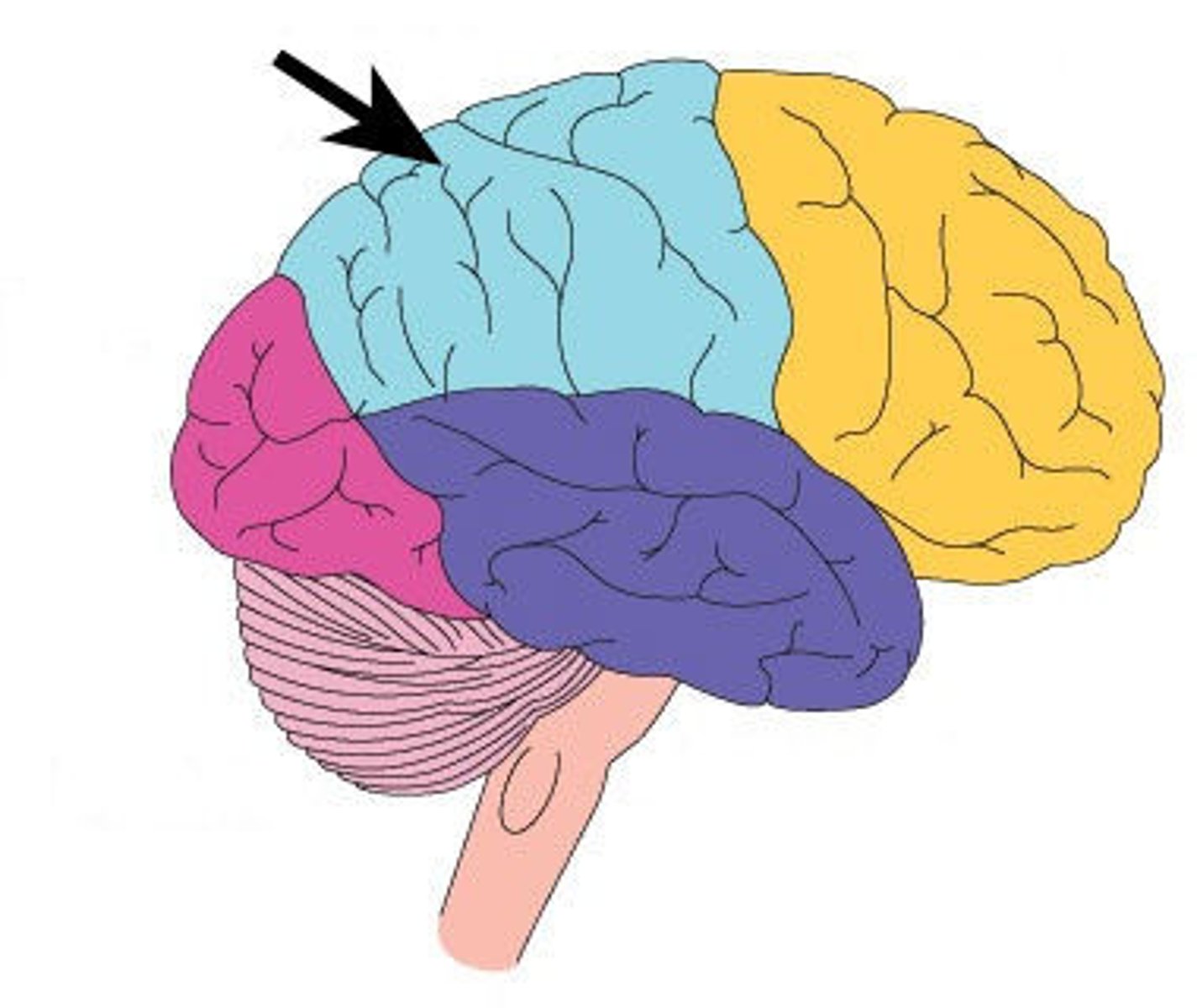
Parietal lobe (Function)
This lobe is associated with the perception of temperature, touch, pressure, vibration, pain, and taste & is involved in writing and some aspects of reading
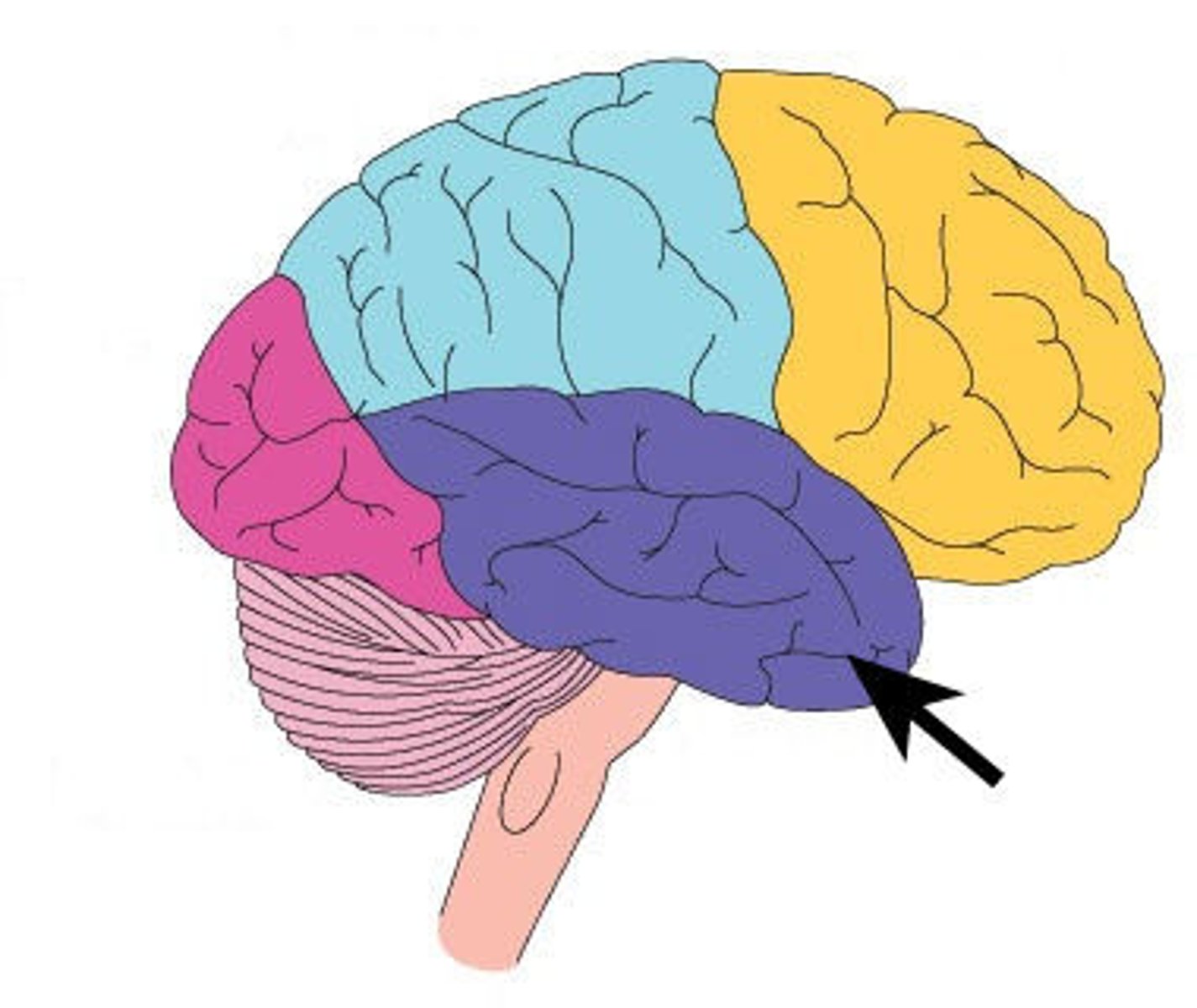
Occipital lobe (Location)
Located in the most posterior region of the brain; involved in processing visual stimuli
Occipital lobe (Function)
Lobe of the brain responsible for vision and integrating visual processing (color, shape, distance)
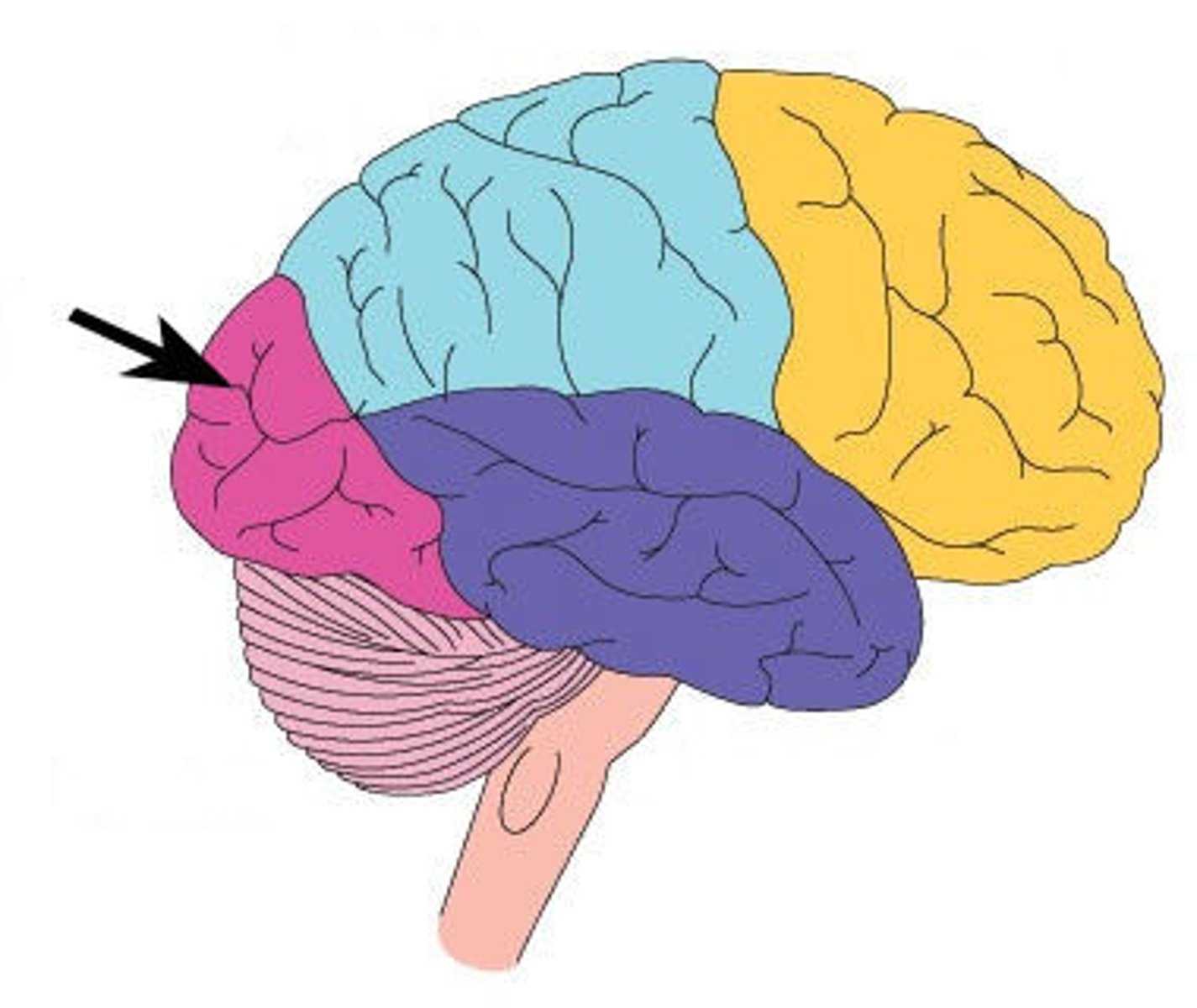
Temporal lobe (Location)
Location of this lobe is anterior to the occipital lobe and on the side of the brain closest to the ears
Temporal lobe (Function)
Functions of this lobe include conscious perceptions of auditory and olfactory stimuli as well as dominance for language
Primary Visual Area (Function)
Receives input from the optic tract via the optic about shape, color, and movement of visual stimuli; radiations extending from the thalamus
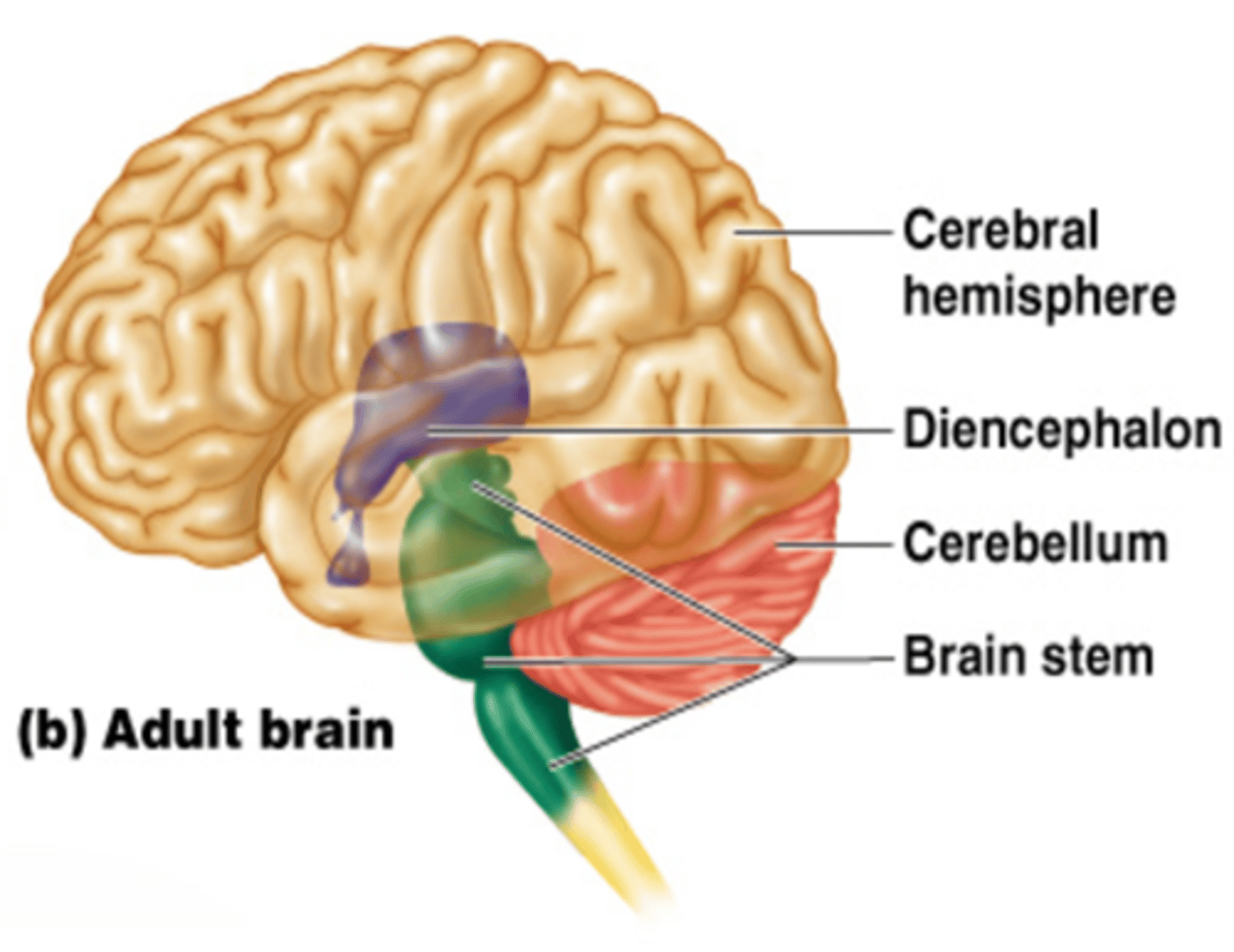
Diencephalon (Structures)
A brain region that surrounds the midline 3rd ventricle and consists of the:
- Epithalamus
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary Gland
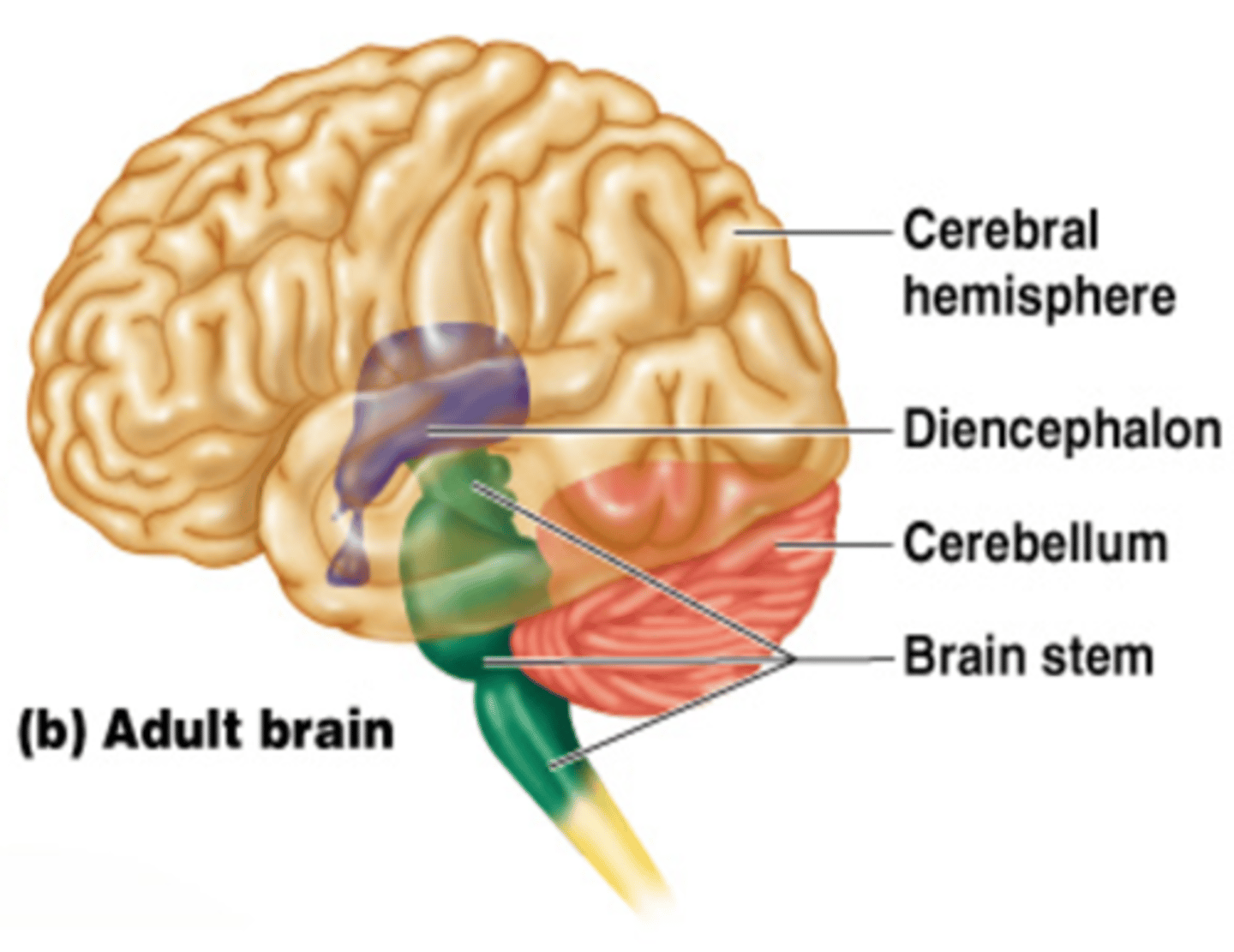
Diencephalon (Function)
A region of the brain that sits on top of the brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres; acts as a relay center for sensory information, controls both autonomic and endocrine functions, and works with limbic system
Epithalamus
Part of the diencephalon that forms the roof of the 3rd ventricle and is made up of cells that secrete CSF
Thalamus
Tract of nerves that surrounds the third ventricle; serves as a relay station to and from the cerebral cortex
Hypothalamus
Helps maintain homeostasis as it controls regulation of temperature, appetite, sex drive & sleep patterns, HR, BP, regulation of the endocrine system, especially the release of hormons from the anterior and posterior pituitary
Pituitary gland (hypophysis)
The master endocrine gland connected by a stalk to the hypothalamus
Pineal gland
An endocrine structure that makes up the epithalamus; secretes the hormone melatonin that aids in the regulation of day-night cycles and reproductive functions
Pons
Part of the brainstem that control respiration
Amygdala
Coordinates the actions of the autonomic & endocrine systems & is concerned with fear and memory
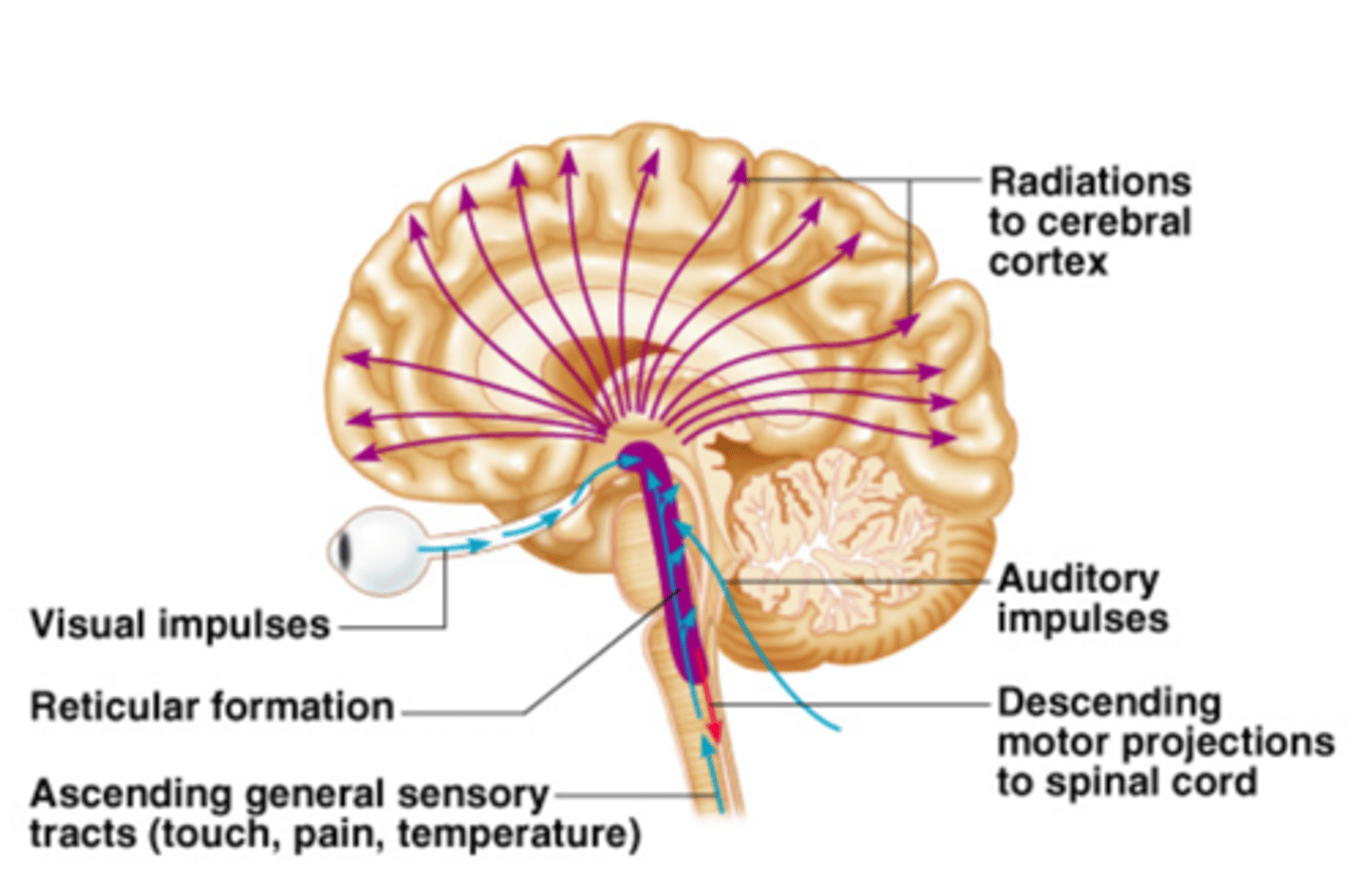
Reticular formation
An area in the central core of the brainstem that helps to control day/night cycles
Quadrigeminna
A structure in the midbrain that is composed of four rounded protuberances contained in the tectum (quadrigeminal plate)
Cerebral peduncles
A structure that is made up of large ropelike bundles anterior to the cerebral aqueduct composed of axons that are a direct extension of the fibers of the internal capsule & extend from the cerebral cortex to spinal cord
Medulla oblongata
Control many of the autonomic functions like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and vomiting
Cerebellum
Referred to as the "little brain"; attaches posteriorly to the brainstem and occupies the posterior cranial fossa
Ventricles
Four fluid filled cavities deep in brain
Choroid plexus
Produces cerebral spinal fluid
Limbic system
Emotional aspects of behavior (aggression, submission, and sexual behavior); memory, learning and general emotional responses
Brainstem
This region of the brain is made up of the:
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Medulla oblongata
Cerebral aqueduct
Connects 3rd and 4th ventricle