World History-Advanced Placement:Modern_(U7,U8,U9)
1/392
Earn XP
Description and Tags
WHAP Vocabulary Terms 1900-Present Unit(7,8,9) Made for: L.E. Elkins High School Exam date: March 5th 2024
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
393 Terms
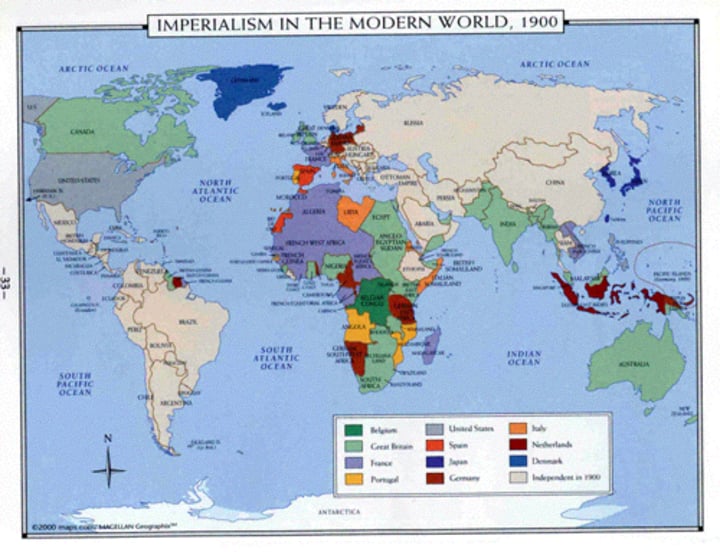
Imperialism
The act of extending the rule or authority over foreign countries - A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.

Sino-Japanese War
Japan's imperialistic war against China to gain control of natural resources and markets for their goods. It ended with the Treaty of Portsmouth which granted Japan Chinese port city trading rights, control of Manchuria, the annexation of the island of Sakhalin, and Korea became its protectorate.
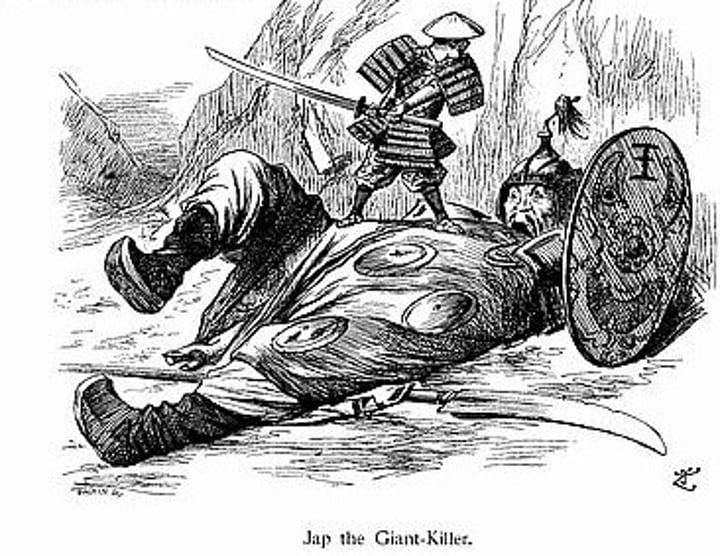

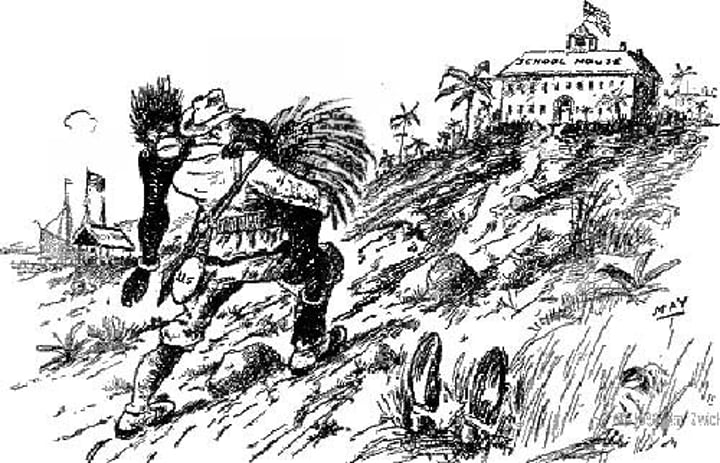
White Man's Burden
Based off of a poem by Rudyard Kipling, the idea of the "duty" to on Europeans to "help" civilize "savages" or primitive people as they were incapable of self-government

Nation
a people group who share a common culture, language, as well as often religion and same geographic region
Nationalism
idea of devotion to one's country - believing its interests are superior to others
British East India Company
A British joint stock company that controlled most of India during the period of imperialism. This company controlled the political, social, and economic life in India for more than 200 years.

Dutch East India Company
A chartered company established in 1602, when the States General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out trade activities in Asia.
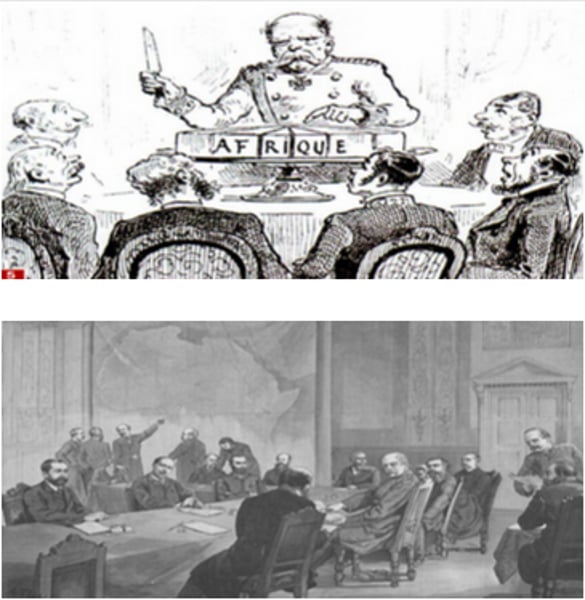
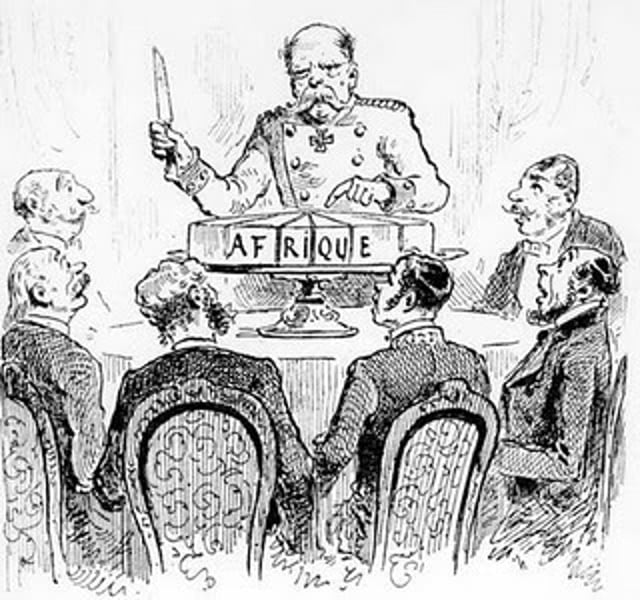
Otto Van Bismarck
Chancelor of Germany who called the Berlin Conference to prevent conflict between European nations.

Scramble for Africa
"Rush" to claim lands in Africa

Berlin Conference
A meeting from 1884-1885 at which representatives of European nations agreed on rules colonization of Africa

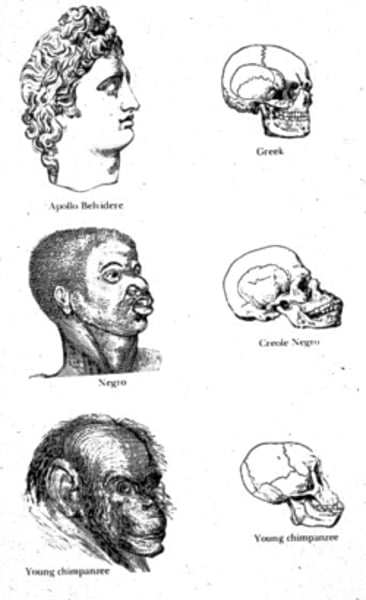
Racism
prejudice or discrimination based on the belief that one's own race is superior
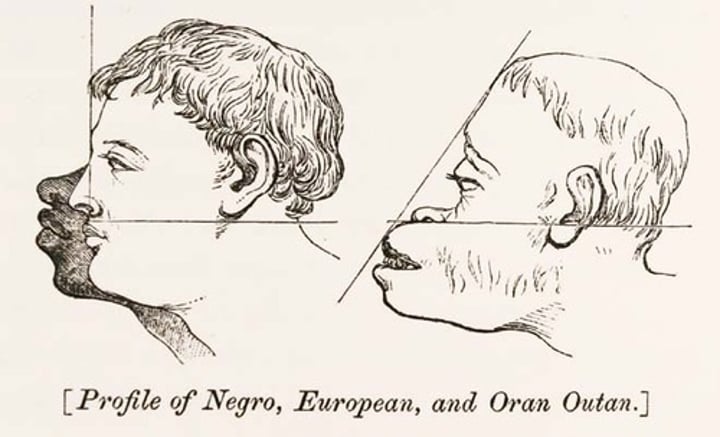
Phrenology
Psuedoscience that believed the study of the size and shape of the skull was indicative of mental faculties, intelligence and character.
Colonies of Great Britain
India, Egypt, Sudan, South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, Canada
Colonies of France
West Africa (including Algeria) and Southeast Asia (including Vietnam & Laos)
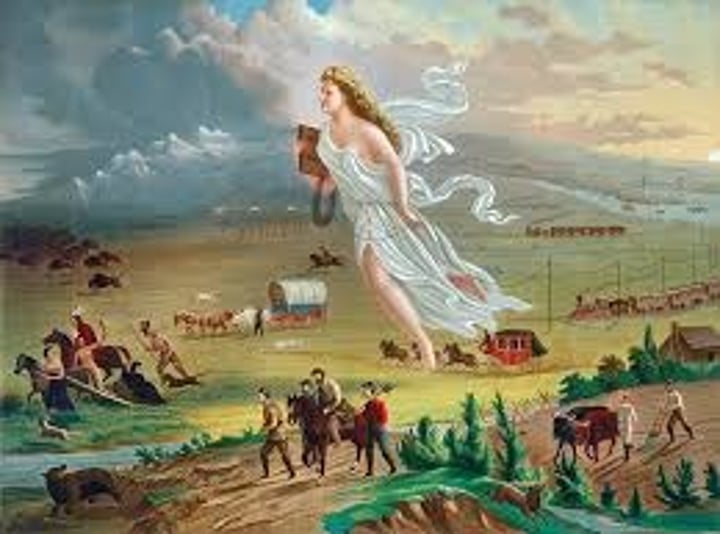
Manifest Desiny
the belief that defended American expansion to the Pacific Ocean saying that it was necessary and destined.

German Unification (1871)
Otto von Bismark used 3 wars beginning in 1864 to unite the various German populations
Protectorate Status
Allowing local and native-born officials to maintain their power in exchange for certain economic or military concessions such as access to raw resources.
Diplomacy
The practice of conducting negotiations between countries
Anglo-Zulu War
War between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom. Notable for several particularly bloody battles, as well as for being a landmark in the timeline of colonialism in the region. The war ended the Zulu nation's independence.
Indian Rebellion of 1857
Sepoys (Indian soldiers) rebelled when learning of rumors that the end of ammunition cartridges were greased using either pork or cow fat, led to an uprising by the soldiers, effect was direct control from the British government rather than the British East India Company

Cattle Killing Movement
Movement in South Africa led by a Xhosa prophetess who believed if they killed their livestock that their ancestors would return to drive out the European settlers. Unfortunately, the Xhosa lost to the British and then suffered from massive starvation.
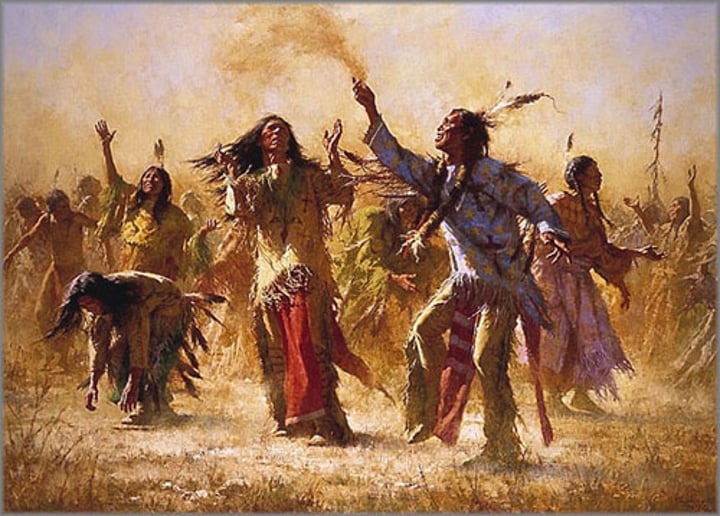
Ghost Dance Movement
The last effort of Native Americans to resist US domination and drive whites from their ancestral lands, came through as a religious movement.

Sokoto Caliphate
Islamic empire founded in 1809 and centered in northern Nigeria
Corvee laborers
Unpaid labor (as toward constructing roads) due to a government or labor exacted in lieu of taxes by public authorities especially for highway construction or repair.

Settler Colony
A form of colonization where families move into a region and an imperial political power oversees the immigration of these settlers. (New Zealand was an example of this)
Boer Wars
a conflict, lasting from 1899 to 1902, in which the Dutch and the British fought for control of territory in South Africa. British pushed Afrikaners (Dutch decedents) inland and Africans from their lands.
King Leopold II
King of Belgium who became the brutal and oppressive ruler over the Congo Free State. Owned the colony personally and had a ruthless system of economic exploitation over the Congolese for harvesting rubber

Spheres of Influence
Areas in which countries have some political and economic control but do not govern directly (ex. Europe and U.S. in China)

Taiping Rebellion
a mid-19th century rebellion against the Qing Dynasty in China, led by Hong Xiuquan over the corruption of the Qing and starvation of peasants. With French & British intervention, Qing prevailed.
Boxer Rebellion
1899 rebellion in Beijing, China started by a secret society of Chinese who opposed the "foreign devils". The rebellion was ended by British troops.
Dutch East Indies
A group of islands in South East Asia (modern Indonesia) claimed by the Dutch during Imperialism.
Penal Colony
a colony to which convicts are sent as an alternative to prison (Australia was an example of this)
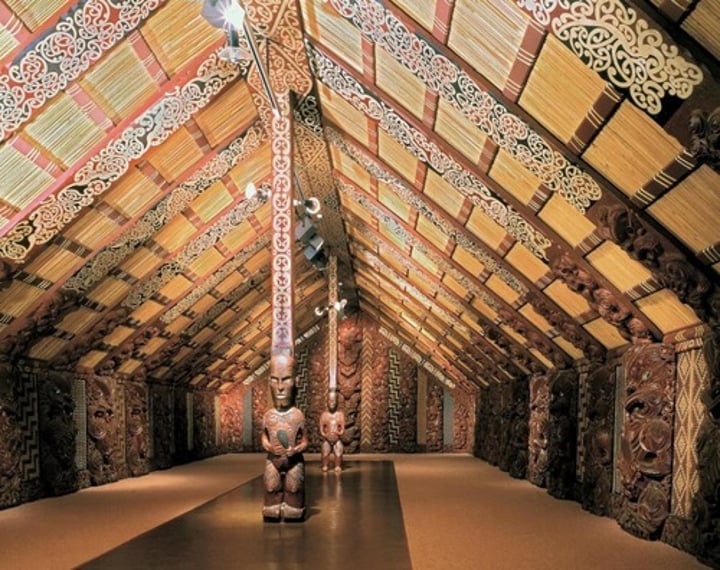
Maori
New Zealand indigenous culture established around 800 CE

Tupac Amaru II
Member of Inca aristocracy who led a rebellion against Spanish authorities in Peru in 1780-1781. He was captured and executed with his wife and other members of his family.

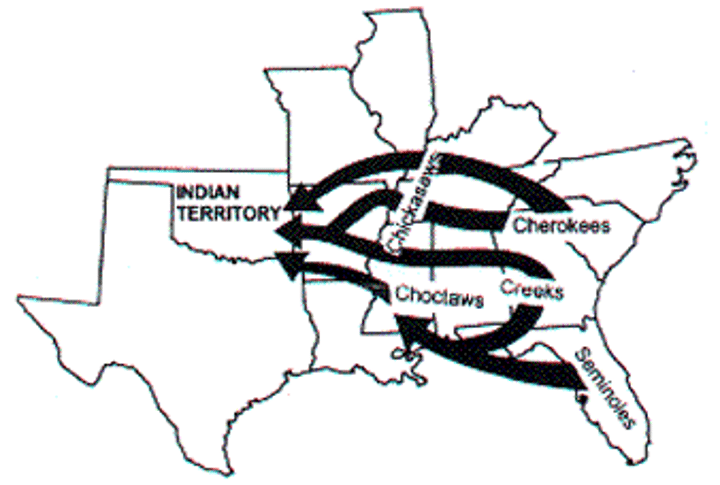
Indian Removal Act
Passed in 1830, authorized Andrew Jackson to negotiate land-exchange treaties with tribes living east of the Mississippi. The treaties enacted under this act's provisions paved the way for the reluctant—and often forcible—emigration of tens of thousands of American Indians to the West.
Mahdist Revolt
Rebellion of Sudanic peoples against the British. Sudanese use guerilla tactics and mass followings to fight, while the British pin them against each other. Over run by British-Egyptian forces in 1885.
Railroads
Networks of iron or steel rails on which steam locomotives pulled long trains at high speeds. The first were built in England in the 1830s. Spread throughout the world during this era.
Cecil Rhodes
British entrepreneur and politician involved in the expansion of the British Empire from South Africa into Central Africa. Desired to create a railroad connecting Cape Town to Cairo.

Steamships
Invention that allowed for merchants to advance up rivers to points that sailboats could not reach because of inconvenient twists, turns, or winds.

Telegraph
A device for rapid, long-distance transmission of information over an electric wire. It was introduced in England and North America in the 1830s and 1840s.

Cash Crops
crops, such as tobacco, sugar, and cotton, raised in large quantities in order to be sold for profit

Guano
Bird droppings used as fertilizer; a major trade item of Peru & Chile in the late nineteenth century
Rubber
Natively found in the Amazon and Central Africa - used for tires on automobiles and bicycles during this era.
Palm Oil
A West African tropical product often used to make soap and as a lubricant in machines during the Industrial Revolution

De Beers Mining Company
Owned by British Cecil Rhodes, this company controlled up to 90% of the world's rough diamonds.

Monocultures
the cultivation of a single crop in a given area - lack of plant diversity often happened in developing countries where cash crops were grown

Economic Imperialism
Control of a country's economy by the businesses and economic interests of another nation

Opium Wars
Wars between Britain and the Qing Empire (mind 1800s), caused by the Qing government's refusal to let Britain import Opium. China lost and Britain and most other European powers were able to develop a strong trade presence throughout China against their wishes.

Treaty of Nanjing
"Unequal treaty" that marked the end of the Opium War in which China had to accept British terms for peace

Banana Republics
Politically unstable states in Latin American that were friendly to the U.S.; given these name as a term for their exported tropical products.
Indentured Servants
Labor system where another would pay a migrant their passage, and in exchange, the laborer would serve that person for a set length of time (usually seven years) and then would be free.
emigrate
To leave one country or region and settle in another
migrant
Person who moves from one region or country to another, often for economic opportunity
Diaspora
A dispersion of people from their homeland
Ethnic Enclave
A place with a high concentration of an ethnic group that is distinct from those in the surrounding area

Great Famine
A terrible famine in 1315-1322 that hit much of Europe after a period of climate change, most notably that impacted the Irish due to potato blight.

acquiring territories using military control, Warfare, diplomacy, establishing settler colonies. expanding nearby land holdings, economic imperialism.
State power shifted between 1750-1900. Some states with existing colonies. What processes were used to gain power?
Turkification
Flashcard: "Turkification" refers to the policy of promoting Turkish culture, language, and identity in the Ottoman Empire and later in the Republic of Turkey. It aimed to assimilate non-Turkish communities into the dominant Turkish culture.
Flashcard: Bolshevik
Radical socialist group led by Vladimir Lenin that seized power in the 1917 Russian Revolution. They aimed to establish a communist state and implemented policies like land redistribution and nationalization of industry. The Bolsheviks later became the Communist Party of the Soviet Union.
Communists
Advocates for a classless society where resources are shared equally. Believes in collective ownership of means of production and distribution.
Flashcard: Young Turks
Group of reformist Ottoman intellectuals who sought to modernize the empire in the early 20th century. Advocated for constitutional government, secularism, and equality. Led the Young Turk Revolution in 1908, establishing a constitutional monarchy. Played a significant role in shaping the Turkish Republic.
Flashcard: Mexican Revolution
Armed conflict in Mexico from 1910 to 1920, characterized by social, political, and economic upheaval. It resulted in the overthrow of the long-standing dictatorship of Porfirio Díaz, and the establishment of a more democratic government. The revolution aimed to address issues of land, labor, and social inequality, and led to significant political and cultural changes in Mexico.
Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI)
PRI: Political party in Mexico that held power for over 70 years (1929-2000). Known for its authoritarian rule and ability to maintain political stability. Implemented modernization policies and promoted economic development. Lost power in 2000, but remains influential in Mexican politics.
Sun Yat-sen
Leader of the Chinese revolution in 1911. Founded the Republic of China and served as its first president. Advocated for modernization, democracy, and nationalism. Played a crucial role in overthrowing the Qing dynasty. Known as the "Father of Modern China."
Kemal Ataturk
Revolutionary leader of Turkey in the early 20th century. Implemented sweeping reforms to modernize the country and break away from traditional Islamic practices. Established a secular government, introduced Western laws and education, and promoted gender equality. Known as the founder of modern Turkey.
Porfirio Diaz
Flashcard: Porfirio Diaz
Ruled Mexico from 1876-1911
Implemented policies of modernization and industrialization
Promoted foreign investment and economic growth
Centralized power and limited political freedoms
Led to growing social inequality and widespread unrest
Overthrown in the Mexican Revolution of 1910
Francisco Madero
Flashcard: Francisco Madero
Role: Mexican politician and revolutionary leader
Significance: Led the Mexican Revolution against Porfirio Díaz's dictatorship
Accomplishments: Elected President in 1911, implemented land reforms and labor laws
Legacy: Considered a key figure in Mexico's transition to democracy and social justice
Impact: Inspired future generations of Mexican leaders and political movements
Francisco “Pancho” Villa
Flashcard: Francisco "Pancho" Villa
Mexican revolutionary leader
Fought against government forces during Mexican Revolution
Known for his guerrilla tactics and fierce determination
Led the famous raid on Columbus, New Mexico in 1916
Considered a folk hero in Mexico for his efforts in the revolution
Emiliano Zapata
Flashcard: Emiliano Zapata
Leader of the Mexican Revolution
Championed agrarian reform and land redistribution
Fought for the rights of peasants and indigenous communities
Founded the Liberation Army of the South
Demanded "Tierra y Libertad" (Land and Liberty) for the people
The Great War
Flashcard: Term: The Great War Definition: A global conflict that took place from 1914 to 1918, involving major world powers. It was primarily fought in Europe and resulted in millions of casualties. The war was triggered by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary and led to significant political, social, and economic changes worldwide.
Gavrilo Princip
Flashcard: Gavrilo Princip Member of the Black Hand, Serbian nationalist group. Assassinated Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in 1914, sparking WWI.
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Assassination sparked WWI, heir to Austro-Hungarian throne, killed in Sarajevo by Gavrilo Princip on June 28, 1914, led to a chain reaction of events.
Triple Entente
Alliance formed in 1907 between France, Russia, and Britain. Aimed to counter the threat of the Triple Alliance.
Triple Alliance
Triple Alliance: A military agreement formed in 1882 between Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy. It aimed to maintain peace and provide mutual support in case of attack. However, Italy later switched sides during World War I, weakening the alliance's effectiveness.
Central Powers
Flashcard: Central Powers
Alliance formed during World War I
Led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire
Opposed the Allied Powers (France, Britain, Russia)
Fought for territorial gains and power in Europe
Eventually defeated in 1918, leading to the end of the war.
Black Hand (Serbia)
Flashcard: A secret society formed in Serbia in 1911, known as "Black Hand." They aimed to unite all Serbs into a single nation and were involved in the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which triggered World War I.
Militarism
Flashcard: A belief in the strong influence and importance of the military in a country's affairs, often leading to an increase in military spending and the glorification of war.
Self-determination
Flashcard: Self-determination is the right of a group to freely choose their political status and determine their own economic, social, and cultural development.
Conscription
Forced enlistment of civilians into military service, typically during times of war or national emergency.
Stalemate
Stalemate: A situation in which neither side can make progress or gain an advantage, resulting in a deadlock or standstill. It often occurs in conflicts, games, or negotiations when neither party can achieve a decisive victory.
Propaganda
A method of spreading biased information to manipulate public opinion and shape beliefs. Often used in advertising, politics, and war to influence attitudes and behaviors.
Reparations
Reparations refer to the compensation or payment made by a country or group to individuals or communities who have been harmed or suffered losses as a result of past injustices, such as slavery, colonization, or human rights abuses. The concept of reparations aims to address historical wrongs and provide redress for the lasting impacts of these injustices. The specific form and extent of reparations can vary depending on the context and the nature of the harm inflicted.
Lusitania
The Lusitania was a British ocean liner that was famously sunk by a German submarine during World War I on May 7, 1915. The sinking of the Lusitania played a significant role in the eventual entry of the United States into the war. It resulted in the loss of over 1,100 lives, including 128 Americans. The incident raised international outrage and contributed to the anti-German sentiment at the time.
Zimmerman Telegram
The Zimmerman Telegram was a secret diplomatic communication sent in 1917 by Germany to Mexico during World War I. It proposed a military alliance between Germany and Mexico, with the promise of helping Mexico regain lost territories from the United States. The telegram was intercepted and decoded by British intelligence, which then shared it with the United States. This revelation played a significant role in the United States' decision to enter the war against Germany.
Total war
Total war is a military strategy that involves the complete mobilization of a nation's resources and population towards the war effort. It emerged during World War I and was characterized by the involvement of civilians in the war, the targeting of civilian infrastructure, and the use of propaganda to rally support for the war. It often leads to significant social, economic, and political changes in the countries involved.
ANZAC
ANZAC stands for Australian and New Zealand Army Corps. It refers to the combined forces of Australia and New Zealand that fought together during World War I. The ANZACs are particularly remembered for their bravery and sacrifice during the Gallipoli Campaign in 1915. ANZAC Day is observed on April 25th each year to honor the soldiers who served and died in all wars, conflicts, and peacekeeping operations.
Gallipoli Campaign (battle)
The Gallipoli Campaign was a World War I battle that took place from April 1915 to January 1916. It was a joint British and French attempt to capture the Ottoman Empire's capital, Constantinople (now Istanbul), by securing control of the Dardanelles Strait. The campaign ultimately failed, resulting in heavy casualties on both sides. The battle is known for its fierce fighting, harsh conditions, and strategic mistakes. It had a significant impact on the war and the subsequent formation of modern Turkey.
Paris Peace Conference
The Paris Peace Conference was a meeting held in 1919 after World War I to negotiate peace treaties. It resulted in the Treaty of Versailles, which imposed harsh terms on Germany and led to significant political and territorial changes in Europe.
Unknown
Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson was the 28th President of the United States, serving from 1913 to 1921. He is known for his leadership during World War I and his efforts to establish the League of Nations. Wilson's presidency also saw the passage of significant domestic reforms, including the Federal Reserve Act and the 19th Amendment, which granted women the right to vote.
David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George was a prominent British politician who served as the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. He played a crucial role in leading Britain during World War I and was known for his progressive policies, including the introduction of social welfare reforms. Lloyd George was a key figure in the negotiations that led to the Treaty of Versailles and the establishment of the League of Nations. He was also instrumental in the passage of the People's Budget of 1909, which introduced taxes on the wealthy to fund social programs. Overall, Lloyd George made significant contributions to British politics and left a lasting impact on the country's history.
Georges Clemenceau
Georges Clemenceau was a French statesman who served as the Prime Minister of France during World War I. He was known for his strong leadership and determination in leading France to victory. Clemenceau played a crucial role in negotiating the Treaty of Versailles, which ended the war. He was also a key figure in the Paris Peace Conference and advocated for harsh terms against Germany. Clemenceau's leadership during the war earned him the nickname "The Tiger."
Vittorio Orlando
Vittorio Orlando was an Italian statesman and diplomat who served as the Prime Minister of Italy during World War I. He played a significant role in the negotiations of the Treaty of Versailles, representing Italy's interests.
Fourteen Points
The Fourteen Points was a statement by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson in 1918 outlining his vision for a post-World War I world. It included principles such as open diplomacy, freedom of the seas, self-determination for nations, and the establishment of a League of Nations. The Fourteen Points aimed to promote peace and prevent future conflicts.
.League of Nations
The League of Nations was an international organization founded in 1920 after World War I. Its main goal was to maintain peace and prevent future conflicts. However, it faced challenges and ultimately failed to prevent World War II.
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed in 1919 that officially ended World War I. It was negotiated and signed by the "Big Four" countries: the United States, Great Britain, France, and Italy. The treaty imposed harsh terms on Germany, including territorial losses, disarmament, and reparations. It also established the League of Nations, an international organization aimed at preventing future conflicts. The Treaty of Versailles is often criticized for its role in contributing to the rise of Adolf Hitler and World War II.
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic was the democratic government established in Germany after World War I, from 1919 to 1933. It was named after the city of Weimar, where the new constitution was drafted. The Weimar Republic faced numerous challenges, including economic instability, political extremism, and social unrest. Despite its efforts to establish a stable democracy, it ultimately collapsed with the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in 1933.
Trench warfare
Trench warfare was a military strategy used during World War I, characterized by soldiers digging deep trenches for protection. It involved a stalemate where opposing forces would engage in intense fighting from their respective trenches. This strategy aimed to provide cover from enemy fire and create a defensive position. Trenches were often connected by a network of communication trenches. This type of warfare resulted in high casualties and a prolonged conflict. It was a defining feature of World War I and had a significant impact on the tactics and strategies used in subsequent wars.
U-boat
A U-boat, short for Unterseeboot, was a type of submarine used by the German Navy during World War I and World War II. These submarines played a significant role in naval warfare, particularly in the Battle of the Atlantic. U-boats were known for their stealth and ability to launch surprise attacks on enemy ships. They were equipped with torpedoes and often targeted merchant vessels, causing significant damage to Allied supply lines. The U-boat campaign was a major factor in both world wars and had a significant impact on the outcome of the conflicts.
Deficit spending
Deficit spending refers to a situation where a government spends more money than it receives in revenue during a specific period. This results in a budget deficit, which is typically financed through borrowing or issuing government bonds. Deficit spending can be used as a fiscal policy tool to stimulate economic growth, but it can also lead to increased national debt if not managed properly.