Psych 135: Synesthesia
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
multisensory
natural objects and events are usually _.
sensory modalities
specialized processing systems are dedicated to different _.
vision
sensory modality labelled as color brown
audition
sensory modality labelled as color light blue
somatosensation
sensory modality labelled as color yellow
“what” and “where” information
system information flow that divides into two streams
intraparietal sulcus (IP) and superior temporal polysensory area (STP)
multisensory processing occurs relatively late in the _ and _ .
Fodor
said that cognition is a collection of independent information processing subsystems, often called “modules”
modules
collection of independent information processing subsystems
modular processing
theory of cognitive processing in which different functions such as vision, hearing and memory are implemented in separate and independent processing modules
new sensory functions or modalities, completely independent sensory subsystems
_ can be created by adding new subsystems as and when they are required. On the other hand, _ can pose problems
time-sensitive processing
there is an issue about how _ can be coordinated across independent subsystems (ex. our visual perception of lip movements is synchronized with auditory perception of individual speech sounds)
independent subsystems
_ cannot take advantage of correlated information in different sensory modalities, such as when we both see and hear someone speaking.
vision, audition and somatosensation
they orient our attention to external events
object identification
all sensory systems supply information that can be used to identify objects, ultimately accessing the same stored representations
localization
the apparent location of a sensory event in one modality can be influenced by information in other modalities. both vision and audition have high-resolution processes for computing the location of objects and events
body motion visual and vestibular responses
contribute to estimates of body motion
flavor information from olfaction, gustation and other senses
combined to mediate perception of food edibility and flavor.
earlier
research demonstrates that information is shared across sensory modalities _ in processing than previously thought.
modularity
is a key principle in modern computer hardware and software system design, and offers the same advantages as it does for neural systems
measuring reaction times
orienting to novel or unpredictable stimuli is often studied by _ to their appearance.
Diederich and Colonius
measured simple RTs to the presentation of stimuli in three different modalities in separate experimental sessions (unimodal stimulation)
signal detection theory (SDT)
offers tools that are used to distinguish between decision and sensory influences on cueing because it provides separate measures of perceptual detectability (d) and decision criterion (bias beta).
cross-modal cueing
occurs when a cue stimulus presented in one sensory modality facilitates the detection or discrimination of a target stimulus presented in a different sensory modality
parallel activation & coactivation
two explanation for enhanced performance using multimodal stimuli
parallel activation
a bi- or trimodal stimulus generates activity in two or three modality-specific processing modules in parallel.
coactivation
modality-specific responses to multimodal stimuli come together at polysensory brain areas. the combined response is stronger and more reliable than responses generated by unimodal stimuli, so RTs and detectability are both better.
sound and vision (lip movements)
spoken words can be identified from a combination of _.
McGurk Effect
a perceptual interaction between vision and hearing in which visual observation of a speaker’s lips alters perception of speech sounds. speech sound actually heard by a listener is altered by observation of the speaker’s lip movements.
sound and touch
manipulating sound made as the hands are rubbed together can alter perception of skin texture
smell and color
when liquid is colored red, strawberry smell of a liquid appears stronger.
sound and light
auditory noise presented with light tends to be perceived as louder than noise presented alone
light and touch
tactile discrimination thresholds are lower during visual observation
3 rules of the effect of a multimodal stimulus on a cell’s response
spatial coincidence, temporal coincidence, inverse effectiveness
spatial coincidence
neuron sensitive to both visual and auditory stimuli may have receptive fields in both modalities; visual stimuli must fall in a specific region of space, and auditory stimuli must emanate for a restricted range of directions.
area of overlap
multisensory response enhancement only occurs when the respective stimuli fall inside the _.
temporal coincidence
response enhancement only occurs when stimuli in different modalities arrive at about the same time.
inverse effectiveness
if a neuron responds very strongly to a unimodal stimulus, its response changes relatively little when another stimulus is added. But if the unimodal response is weak, there are stronger interactions with other stimuli.
multisensory convergence zones
multimodal processing occurs in the high-level _ in the brain.
superior colliculus
nucleus receives projections from multiple modalities, as well as the cortex, and is thought to be involved in multimodal orienting
superadditive response
a response to a combined stimulus which is greater than the sum of the responses to each stimulus presented separately
primary sensory cortex
receives projections both from auditory cortex and from STP. top-down feedback.
secondary association cortex
several regions from this cortex are involved in multimodal processing. multimodal processing occurs in both major cortical processing.
synesthesia
an intriguing multisensory phenomenon in which stimulation in one sensory modality causes a sensory experience in another modality
colored hearing
most commonly associated with speech sounds
sensory union
common type of synesthesia. involves ordered sequences such as numbers, letters or days being perceived as sequences of colors.
area v4/v8
region normally activated by color.
unimodal cortical areas
the most plausible account of synesthesia is that it involves direct neural connections between _.
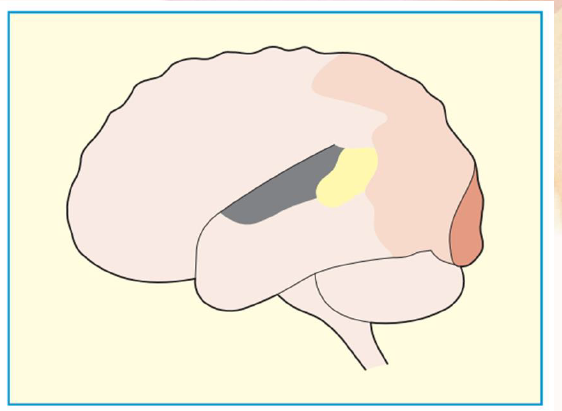
human striate visual cortex
dark brown area
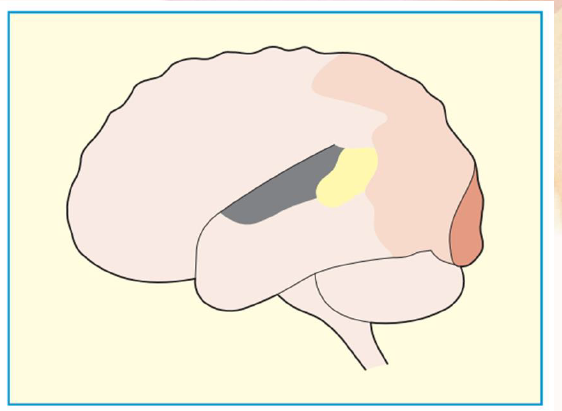
extrastriate visual cortex
light tan area
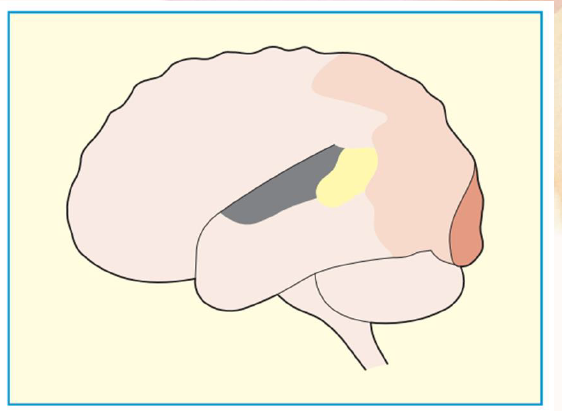
auditory cortex
dark gray area
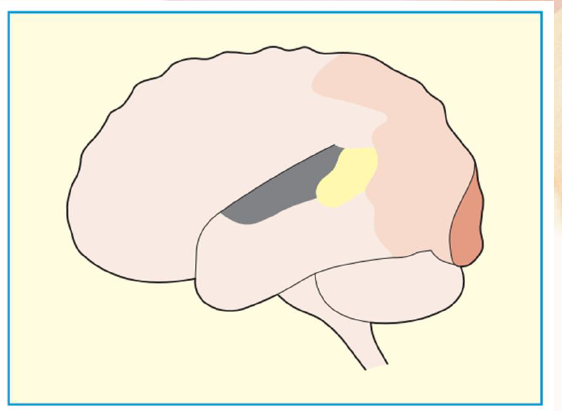
Wernicke’s speech area
yellow area
creative
people with synesthesia are more _, and therefore more able to generate novel and adaptive ideas which promote survival and reproduction. this idea is contradicted by studies that find no conclusive evidence for differences in creativity between synesthetic and control subjects.
synesthetic, control
In Yaro and Ward’s experiment, _ subjects consistently recalled words more than _ subjects.
A & E
letters that are colored red
I,M,N
letters that are colored white
D
letters colored yellow