3 Lec 13 (Exam 3): Oral Manifestations of Systemic Diseases
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
K,A,D,E
of vitamins A, B, C, D, E and K, which ones are fat soluble?
B,C
of vitamins A, B, C, D, E and K, which ones are water soluble?
thiamine
what is the other name for vitamin B1?
niacin
what is the other name for vitamin B3?
retinol
what is the other name for vitamin A?
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
deficiency in this vitamin is associated with pellagra, mouth inflammation (glossitis, angular stomatitis, cheilitis) and the 3 Ds:
•Dermatitis
•Diarrhea
•Dementia
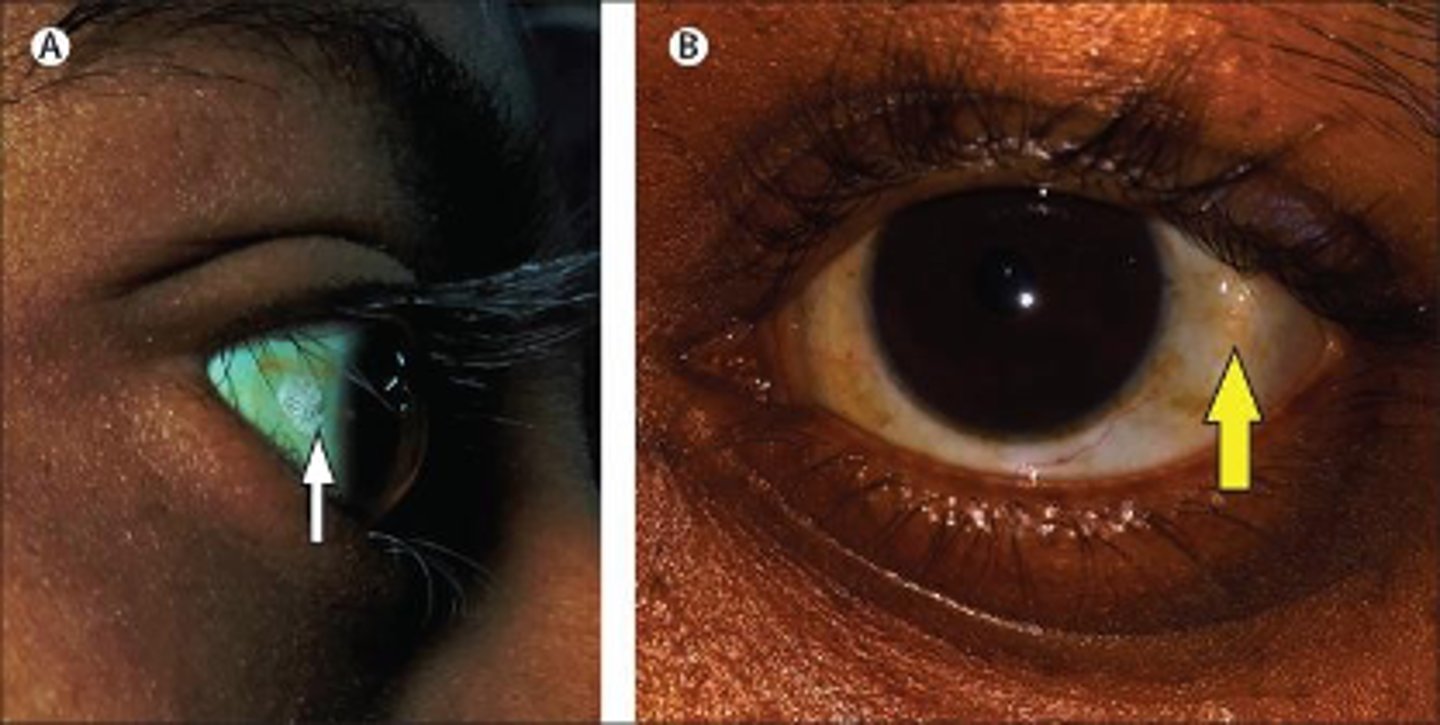
Vitamin A (Retinol)
deficiency in this vitamin is associated with night blindness, xerophthalmia (dry eyes) and Bitot spots:
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
deficiency in this vitamin is associated with Beriberi, anorexia, irritability, and a decrease in short-term memory:
•Poor dietary intake due to lack of food
•Disproportionate reliance on highly processed
staple crops
•High-heat or long-duration cooking
what is the usual cause of a Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) deficiency?
Vitamin B12
the main functions of this vitamin include:
•DNA synthesis
•Methylation
•Mitochondrial metabolism
Deficiency is largely caused by gastric abnormalities/disorders that disrupt absorption:
GI abnormalities/diseases that impair absorption
what is the usual cause of a Vitamin B12 deficiency?
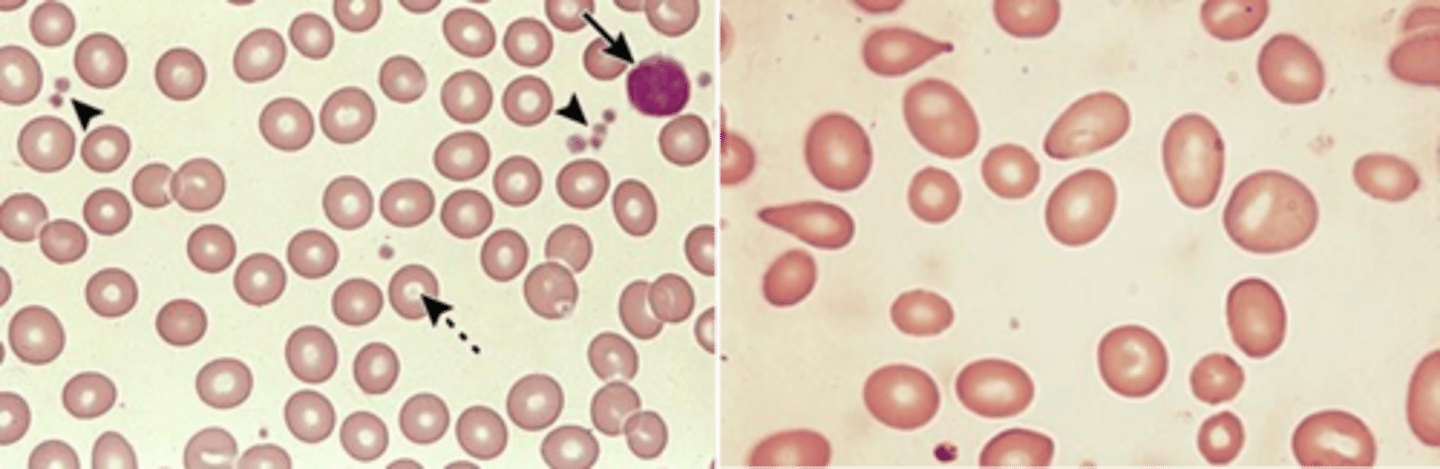
Vitamin B12
macro-ovaloctye changes in RBCs is associated with a deficiency in what vitamin?
Vitamin B12
Hypersegmentation of a neutrophil and abnormally large erythroid precursor cells are associated with a deficiency in what vitamin?
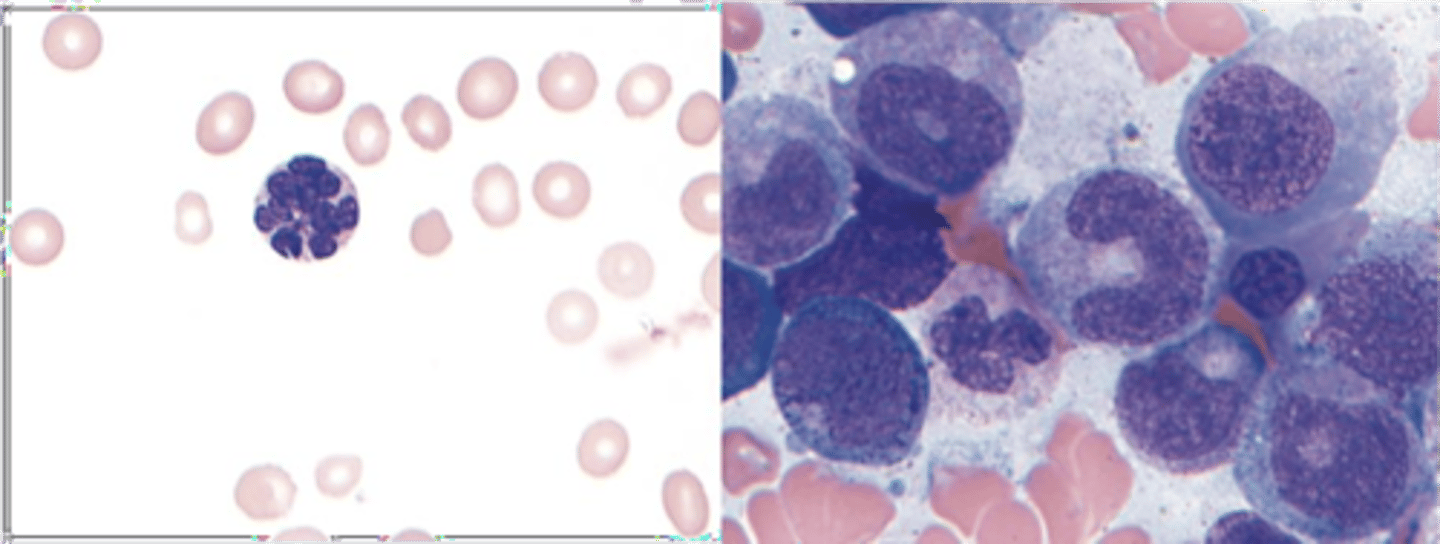
Vitamin B12
consequences of a deficiency in this vitamin can result in:
-megaloblastic anaemia or macrocytic anemia (due to impaired DNA synthesis)
-impaired sensory and peripheral nerve function
-increased melanin production
-fatigue
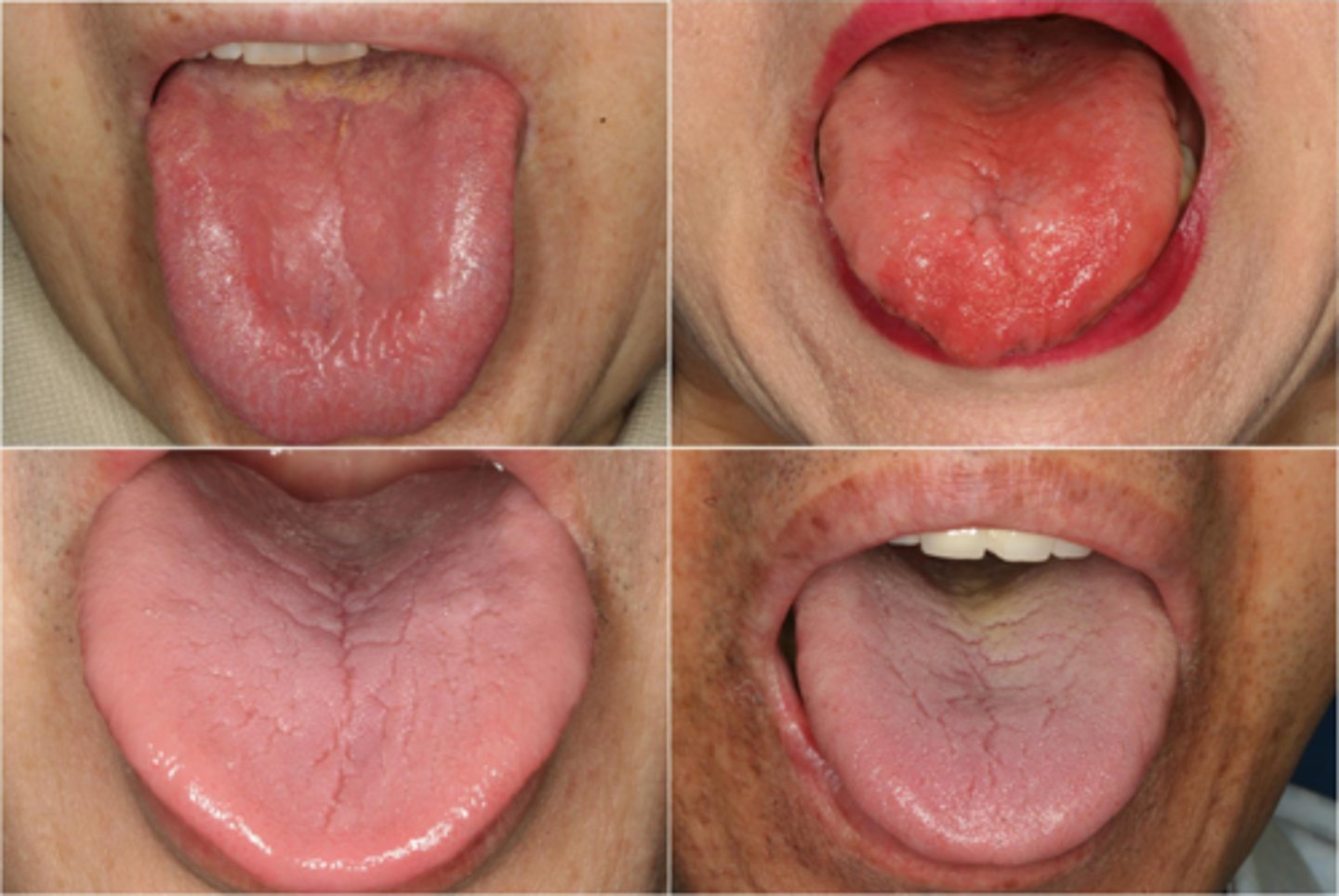
Vitamin B12
The following are oral manifestations of a deficiency in what vitamin?
•Glossodynia
•erythema and depapillation
of the tongue
•dry mouth
•angular cheilitis
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
deficiency in this vitamin is associated with Scurvy and impaired collagen synthesis
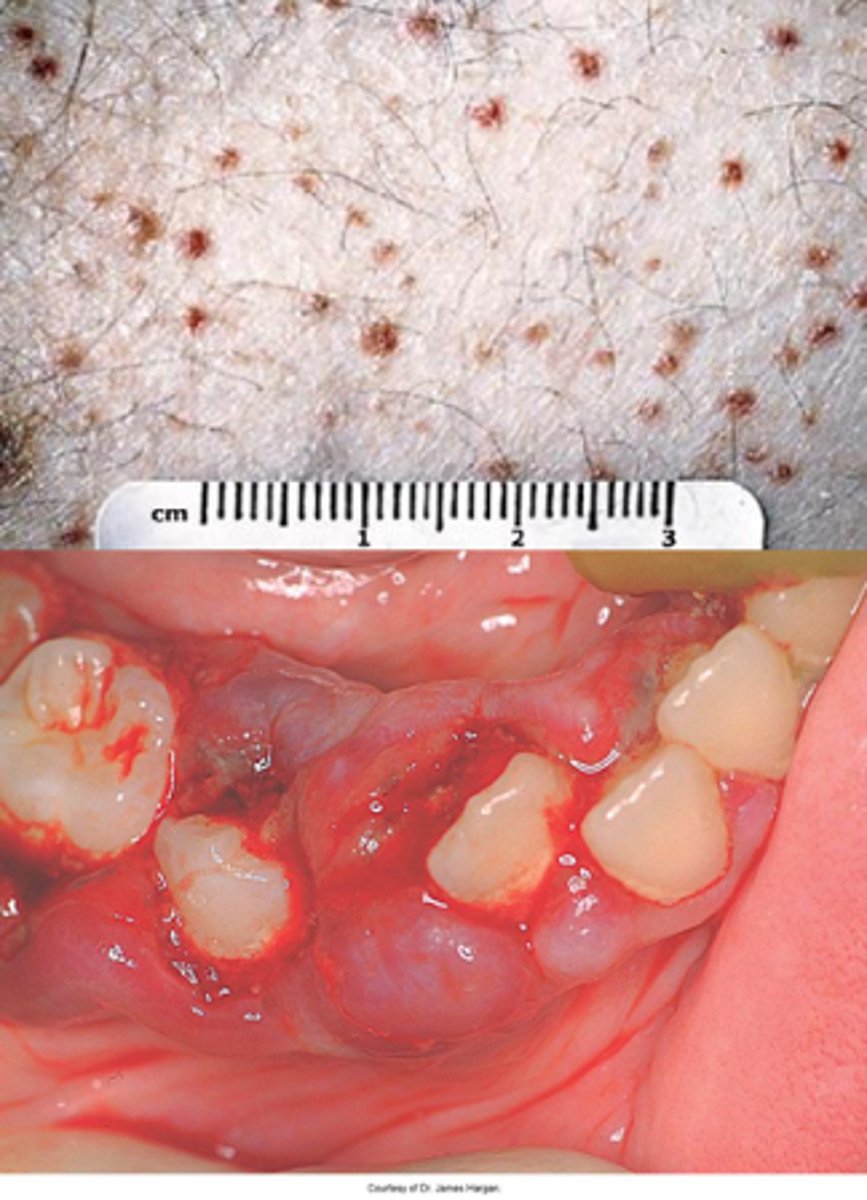
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
The following are oral manifestations of a deficiency in what vitamin?
-Petechiae
•Generalized gingival swelling
•Hemorrhage (petechiae, ecchymosis)
•Tooth mobility
•Ulceration
•Increased periodontal infection
•Delayed wound healing
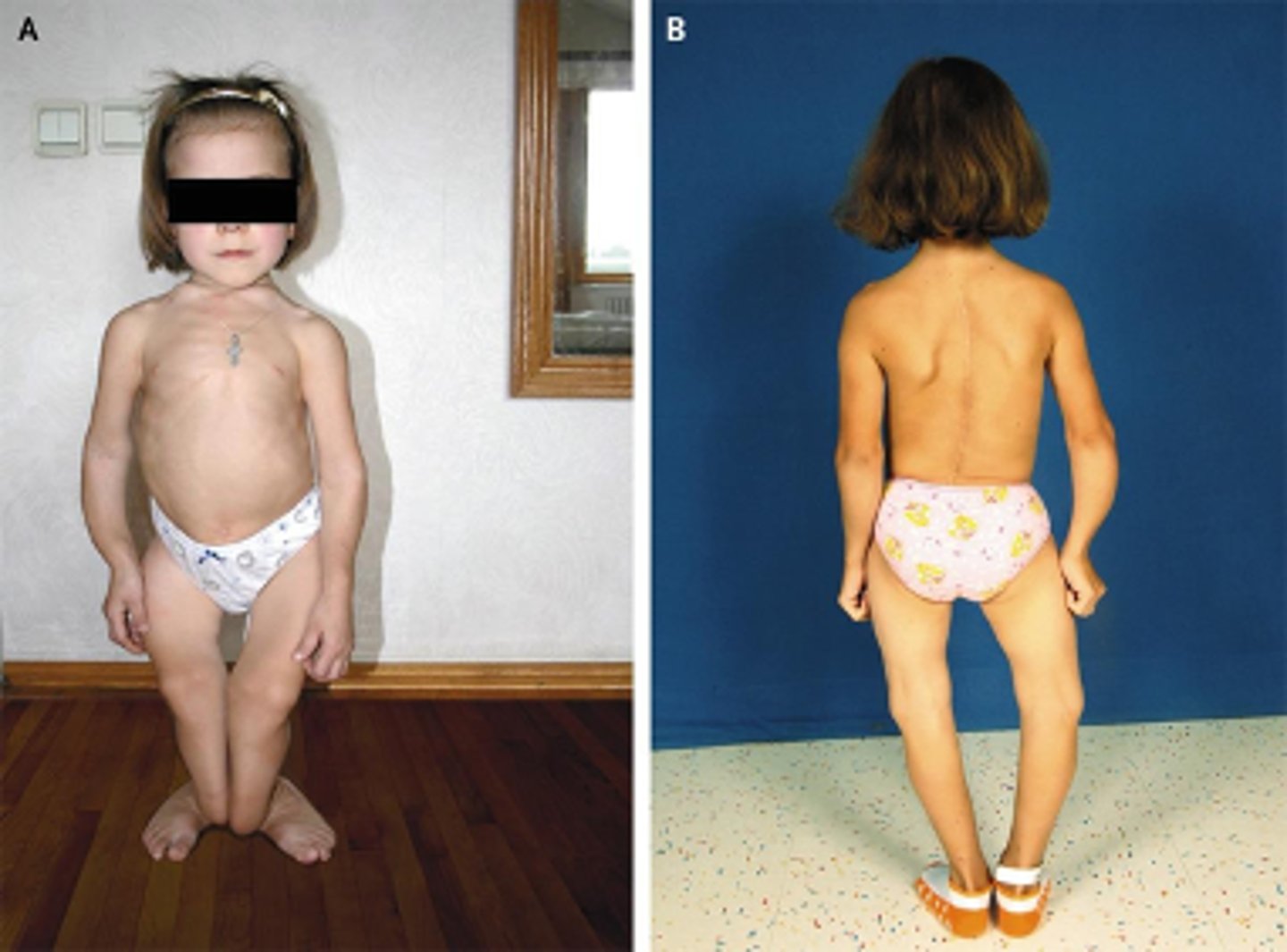
Vitamin D
this vitamin and its metabolites are hormones and hormone precursors rather than vitamins, aids in calcium absorption in the body:
Vitamin D
deficiency in this vitamin is associated with Rickets in infants, leading to:
•Growth impairment
•Irritability
•Significant bowing of bones
•Hypomineralization of teeth
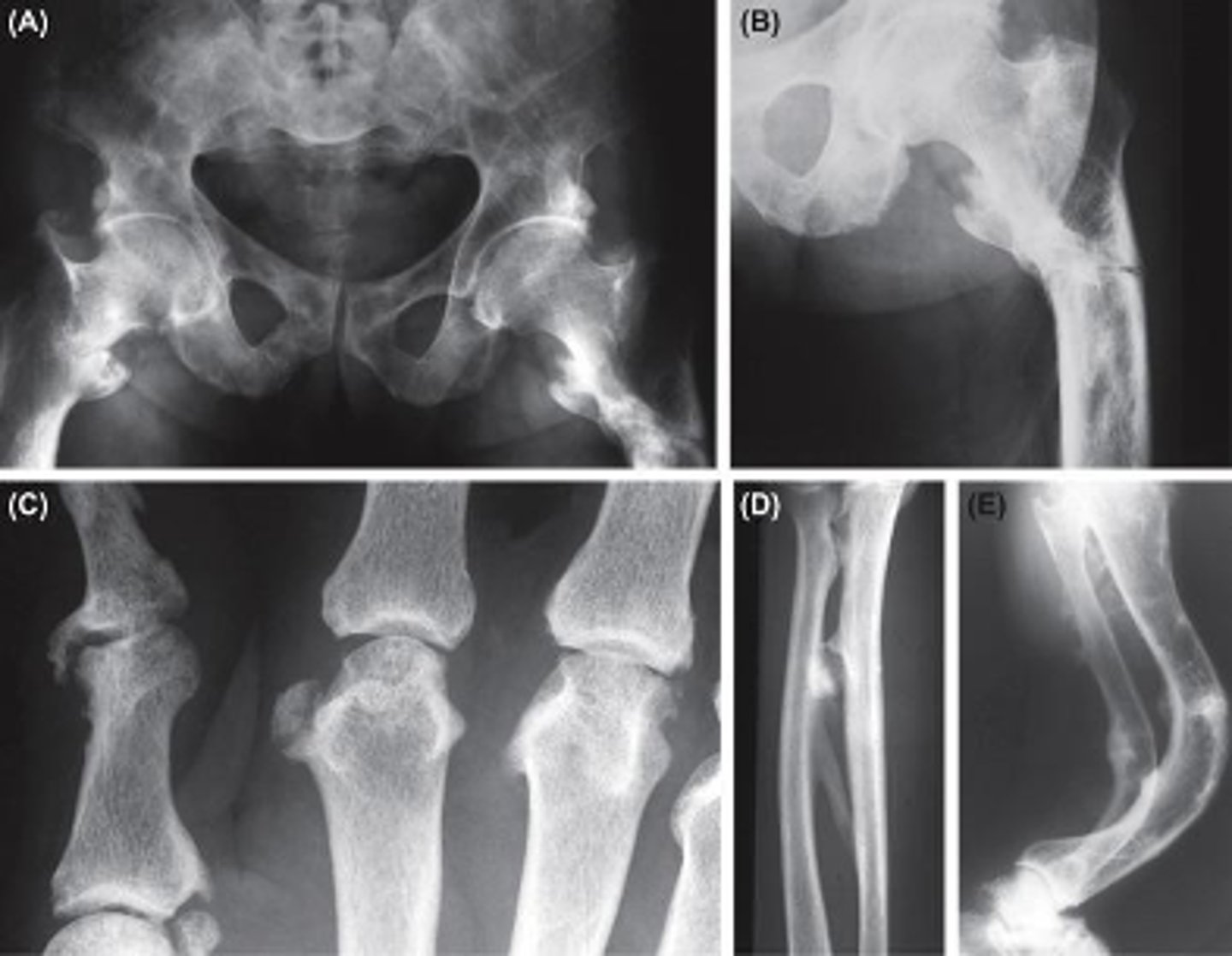
Vitamin D
deficiency in this vitamin is associated with Osteomalacia in adults, leading to:
•Diffuse skeletal pain
•Susceptible to fracture
Vitamin D
The following are oral manifestations of a deficiency in what vitamin?
•Severe early childhood caries
•Periodontal disease
•Enamel chronological hypoplasia
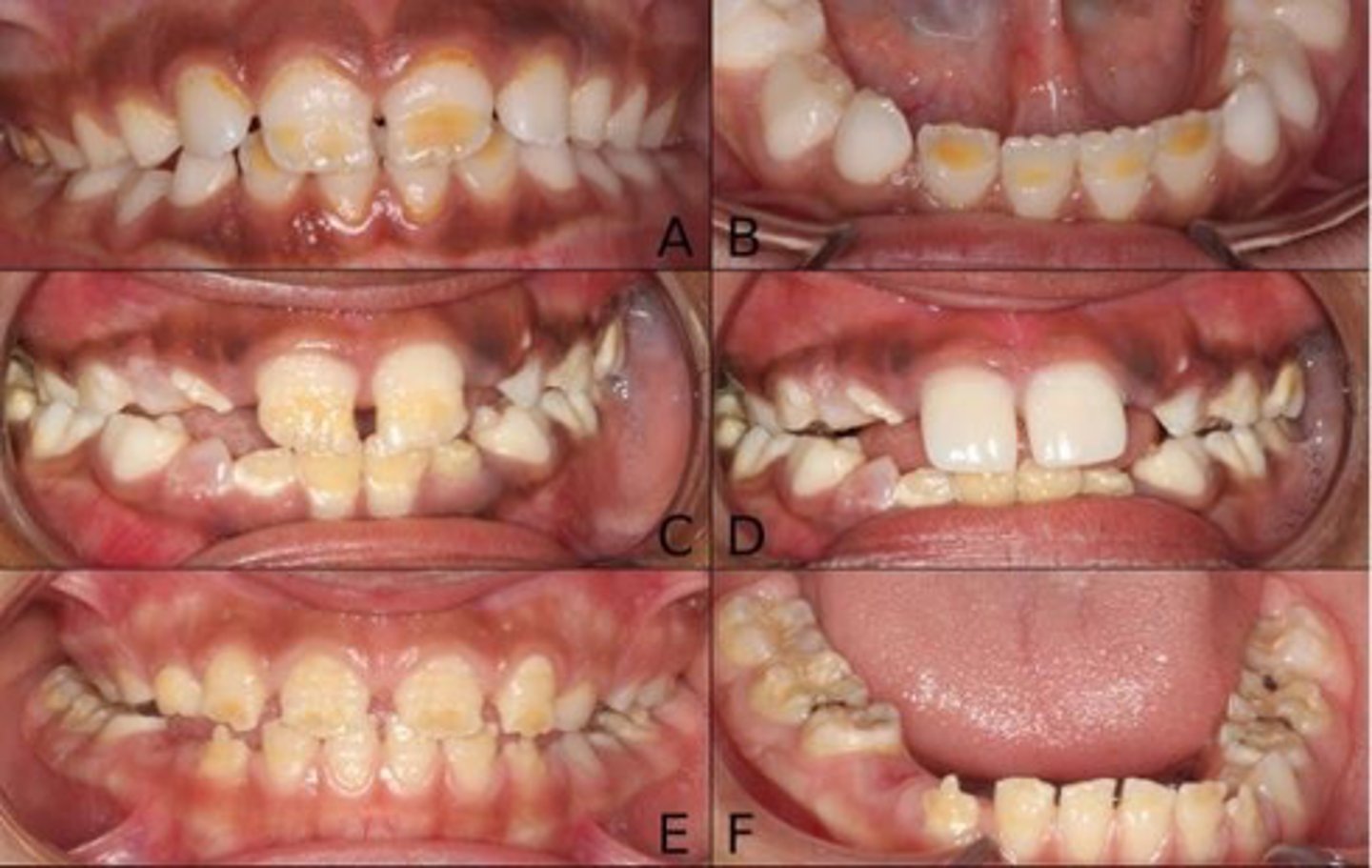
Vitamin K
the main functions of this vitamin include:
•Coagulation
•necessary for activation of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X
•Activation of protein C and protein S (inhibiting excess generation of thrombin )
•bone formation (osteocalcin)
Coronary vascularcalcification
Acromegaly
An excess secretion of growth hormone
(GH) will cause what disorder?
Anterior pituitary adenoma
What is the most common cause of acromegaly?
Acromegaly
Clinical features of this disorder include:
•Coarse facial features
•Hypertrophy of soft palate tissues
•Mandibular prognathism
•Anterior open bite (Apertognathia)
•Diastema formation
•Macroglossia
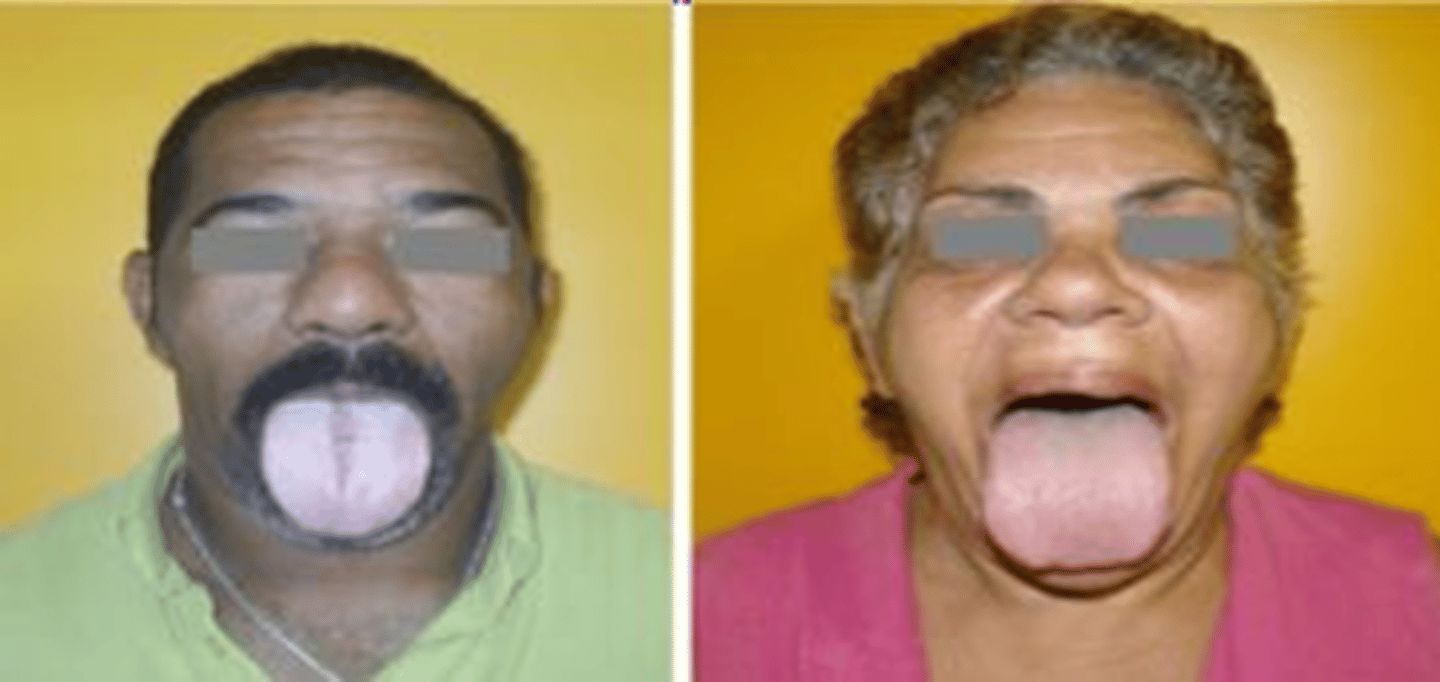
Hypothyroidism
ID the pathology:
-signs/symptoms include: dry skin facial edema, hoarseness, enlargement of tongue
-can be caused by iodine excess or deficiency
Oral symptoms:
•Macroglossia
•Dysgeusia
•Poor periodontal health
•Burning mouth syndrome
•Dry mouth
•Effect on bone health
Hyperthyroidism
ID the pathology:
Classic symptoms
•heat intolerance
•Tremor
•Palpitations
•Anxiety
•weight loss despite a normal or increased
appetite
•Increased frequency of bowel movements
•shortness of breath
Graves disease
Most common cause of hyperthyroidism:
Graves disease
•Most common cause of hyperthyroidism
•Occurs at all ages but especially in women of reproductive age.
•Results from autoantibodies targeting TSHR
•Diffuse thyroid enlargement
hyperparathyroidism
Stones, bones, groans, with psychiatric overtones are associated with:
•Facial asymmetry/swelling
•Bone expansion
•Malocclusion
•Brown tumors (5%)
•Loss of lamina dura
•Pain/neuropathy
•Delayed eruption
•Hypoplastic enamel
•Root resorption
•Ground glass trabeculation pattern
•Thinning of the mandibular cortex
Orofacial manifestations of hyperparathyroidism:
Hypoparathyroidism
Clinical Features of this pathology:
•Pitting enamel hypoplasia if during tooth development
•Metabolic alkalosis, tetany
•Chvostek sign: upper lip twitches when facial nerve tapped below zygomatic process
diabetes mellitus
Oral complications of this disease includes:
•Periodontal disease
•Infections
•-Oral candidiasis
•-Mucormycosis
•Xerostomia and hyposalivation
•Tastes disturbance and BMS
•Delayed wound healing
diabetes mellitus
The most common risk factor for mucormycosis is:
Sickle cell anemia
•Hair-on-end radiographic feature is associated with:
Sickle cell anemia
ID the pathology:
•Hair-on-end radiographic feature
•BM hyperplasia; enlarged marrow spaces
•Widened bone trabeculations (stepladder configuration)
•Thickening of lamina dura
•Thinning of inferior border of mandible
•Pulpal necrosis, osteomyelitis
•Peripheral neuropathy
•Delayed eruption, hypoplasia
Thalassemia
ID the pathology:
•Disorder of hemoglobin synthesis
•A form of hemolytic anemia
•Reduced synthesis of alpha/beta
globin chains
•Prominent in the Mediterranean, Africa, India, Southeast Asia
•Red blood cells are microcytic and hypochromic
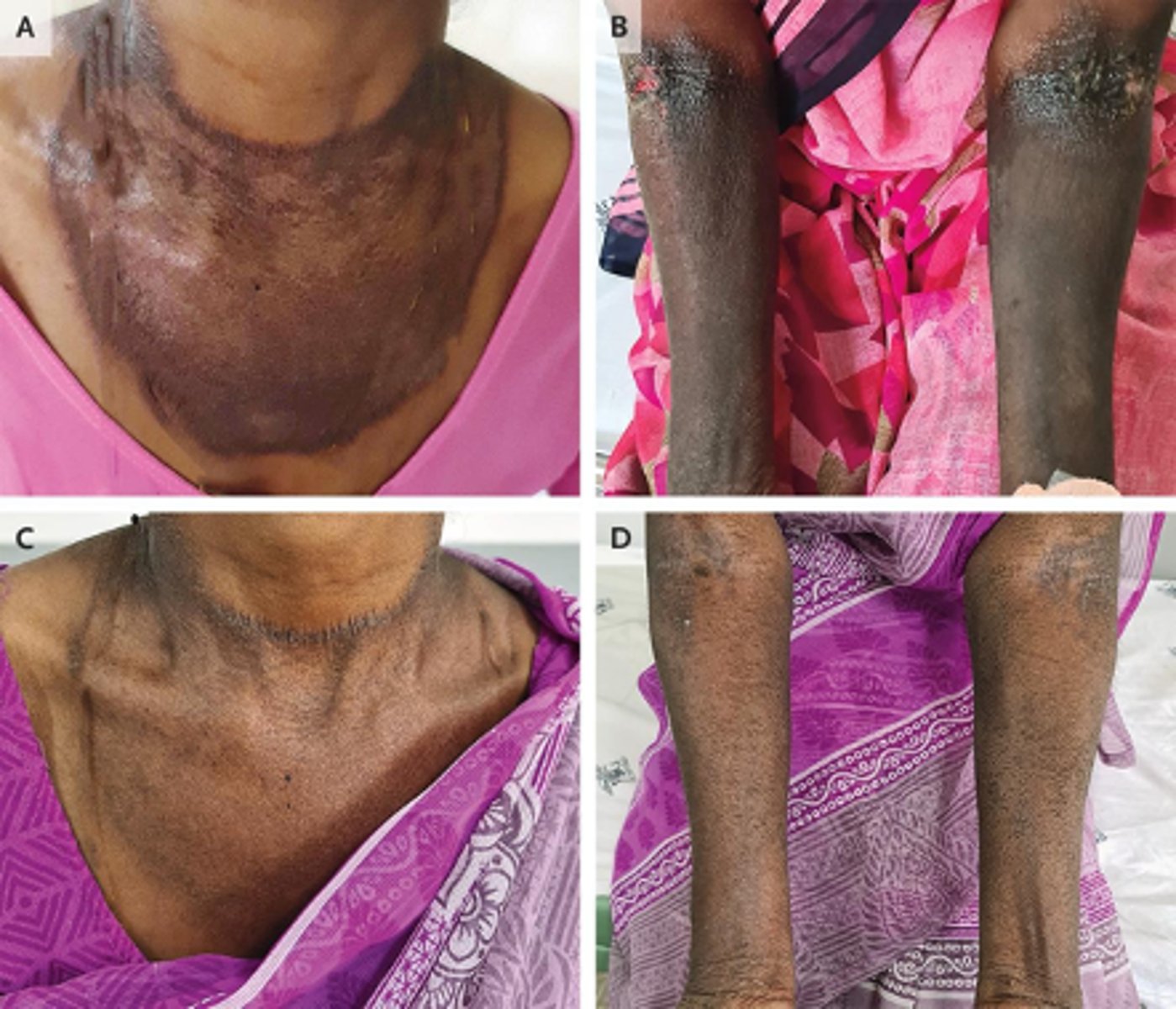
𝜷−Thalassemia
ID the pathology:
•Hepatosplenomegaly
•Bone abnormalities
•Osteopenia
•Pathological fractures
•Skin pigmentation
•Cardiomyopathy
•Liver fibrosis
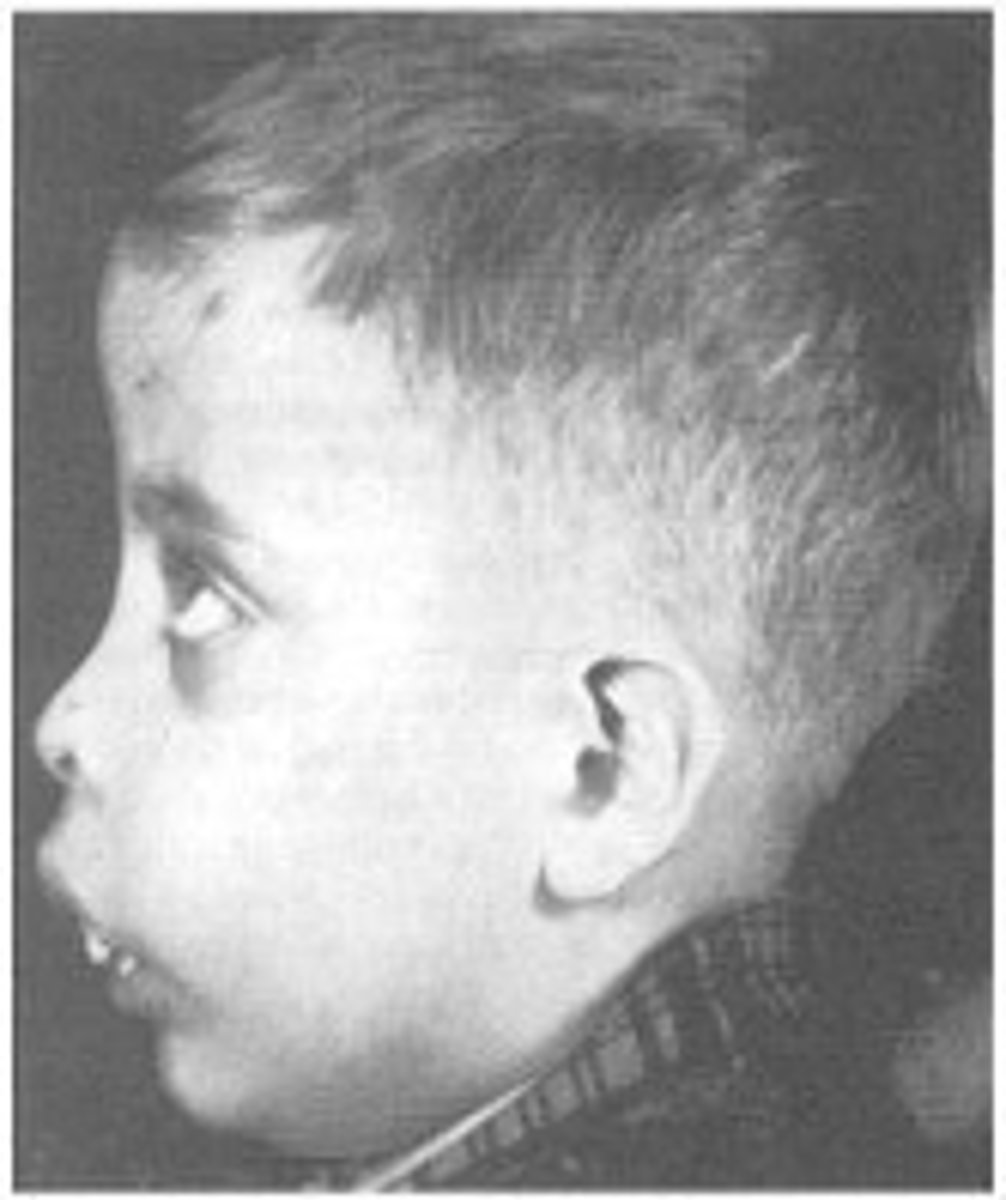
Endocrine failure
Orofacial features:
-enlargement of upper jaw, (chipmunk face)
-migration. and spacing of upper anterior teeth
increase dental decay
-delayed dental development
Amyloidosis
ID the pathology:
•Condition causes deposition of extracellular proteinaceous material
•Amyloid- Beta pleated sheet configuration
•Occur in a specific organ or occur systemically
•Organ-Limited
Amyloidosis
ID the pathology:

Crohn disease
•Inflammatory condition primarily affecting distal small intestine and proximal colon (can be seen anywhere in the GI tract)
Crohn disease
ID the pathology:
•Orofacial granulomatosis
•Aphthous-like ulcerations
•Cobblestone appearance of mucosa
•Mucosal tags and soft tissue swellings resembling epulis fissuratum
•Linear ulcers in buccal vestibule