Acids and bases
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Defintion of a bronsted lowry base
proton acceptor
Definition of a bronsted lowry acid
proton donor
How can H2O act like an acid and a base
It can accept a proton to form a hydronium ion, and donate a proton to become a hydroxide ion
What type of acid is ethanoic acid (2 words)
weak monobasic
What type of acid is sulfuric acid
Strong dibasic acid
What does “p” mean in chemistry generally
-log of the quantity
Calculating pH for strong acids
The acids fully dissociate, meaning [acid] = n[H+] where n is the number of hydrogens that the acid can donate
pH = ?
-log[H+]
General form for Ka (acid dissociation constant) and units
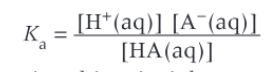
What is pKa relationship to Ka
pKa = -logKa
How do Ka and pKa vary depending on the strength of the acid
As acid strength increases, Ka increases and pKa decreases
Expression for Ka of a weak acid (without approximations)
E
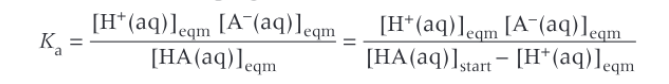
Expression for Ka for a weak acid with approximations

Approximations for calculation pH of a weak acid
That the concentration of hydrogen ions are equal to the concentration of anions (there are some H+ from the water)
We assume the concentration of the acid at equilibrium is equal to the concentration of the acid at the start, as not a lot dissociates
Kw expression and value at 298K
10^-14
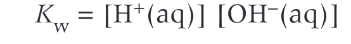
How to calculate pH of a strong base
Kw/[OH-] = [H+] and n[OH-]→[base]
What is a buffer system
Reduces the effect of acids and bases on the system
What components make up a buffer solution
HA and A-
Ways to prepare buffer solutions
Using a salt and acid or partial neutralisation (excess of weak acid with a strong base)
What happens when H+ is added to a buffer solution
H+ ions react with conjugate base, the equilibrium shifts toward the acid which reduces the H+ ions
What happens when OH- is added to a buffer solution
OH- + H+ → H20, so equilibrium shifts toward the H+ + A- as HA dissociates
When [HA] = [A-]
pH = pKa
What is the healthy pH of blood, and the bounds in which pH is safe
7.4, 7.35-7.45
What is the buffer system in the blood
Carbonic acid
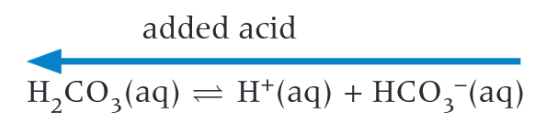
How to use a pH meter
You must calibrate the pH meter by dipping in a solution of known concentration of acid/alkali and a neutral solution, depending if we are using an excess of acid/alkali
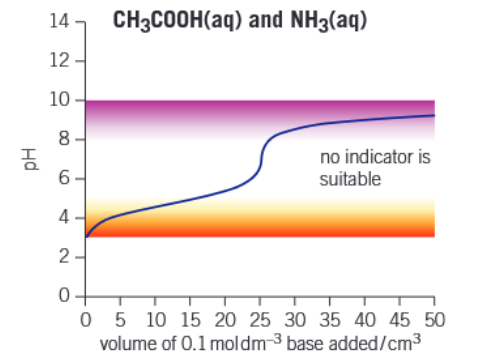
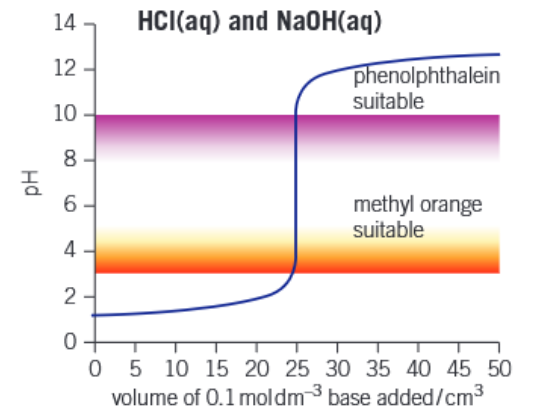
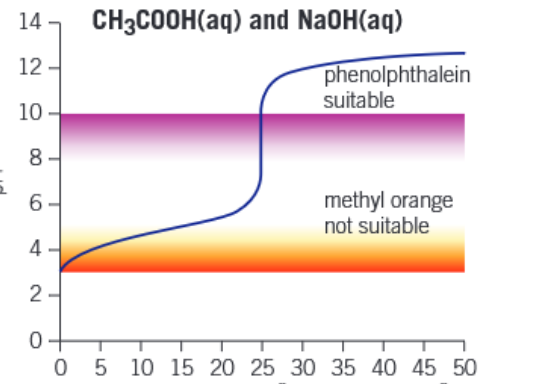
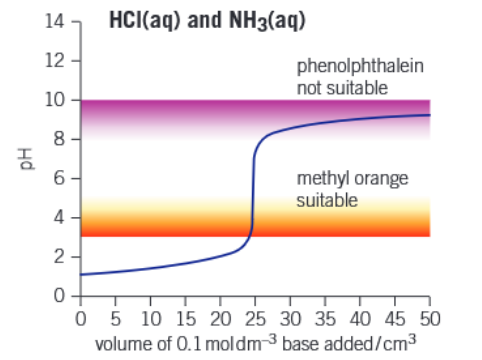
What is the equivalence point of a titration
The centre of the vertical section of a pH curve, which is wherethe volume of one solution exactly reacts with the volume of the other solution
The colour of an end point to a titration
A colour inbetween the colour of the the conjugate base and weak acid
An indicator is a weak acid, which way is the equilibrium shifted toward when in excess of acid
To the left
At the end point, pKa =
pH
Over what range to indicators change colourq
2 pH
To choose a suitable indicator, what must the pH where it changes colour relate to in the titration
Should encompass the range where the vertical section of a titration is
Graph of strong acid - strong base titration
Graph of weak acid - strong base titration
Graph of strong acid - weak base titration
Graph of weak acid - weak base titration